Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Chemio Act 3
Chemio Act 3
Uploaded by
Tamura Kouji0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
1 views3 pagesCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pdf or txt
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
1 views3 pagesChemio Act 3
Chemio Act 3
Uploaded by
Tamura KoujiCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pdf or txt
You are on page 1of 3
Properties of Most Organic and Inorganic Compounds
Properties Organic Inorganic
Flammable (yes/no) Yes Yes
Melting point (low/high) Low High
Boiling point (low/high) Low High
Solubility in water (yes/no) Yes Yes
Solubility in nonpolar liquids (yes/no) Yes No
Types of bonding (covalent/ionic) Covalent Ionic
Reaction occur between (molecules/ions) Molecules Ions
Atoms per molecule (many/few) Few Many
Structure (complex/simpler) Complex Simpler
Electrolyte (yes/no) Yes Yes
CHEMIO ACT 3
Name: Tamura Kouji T
Section: P 21
I. Complete the table below about Organic and Inorganic Compounds
II. Complete the table about different types of organic compounds.
GROUPS OF ORGANIC Definition 3 EXAMPLES (NAMES &
COMPOUNDS CHEMICAL STRUCTURE)
Alkane any of the series of methane - CH4
saturated hydrocarbons ethane - CH3CH3
including methane, ethane, butane - CH3CH2CH2CH3
propane, and higher
members.
Alkene any of the series of ethene - CH2=CH2
unsaturated hydrocarbons propene - CH2=CHCH3
containing a double bond, butene - CH2=CHCH2CH3
including ethylene and
propylene.
Alkyne any of the series of Propyne - C3H4
unsaturated hydrocarbons Butyne - C4H6
containing a triple bond, Hexyne - C6H10
including acetylene.
Aromatic Hydrocarbon are cyclic, planar compounds aniline - C6H5–NH2
that resemble benzene in benzoic acid - C6H5–COOH
electronic configuration and bromobenzene - C6H5–Br
chemical behavior.
Alcohol any organic compound Ethanol - C2H5OH
whose molecule contains propanol - CH3CH2CH2OH
one or more hydroxyl groups butanol - CH3CH2CH2C
attached to a carbon atom. H2OH
Aldehyde an organic compound Methanal - HCHO
containing the group —CHO, Ethan - CH2CHO
formed by the oxidation of Propanal - C2H5CHO
alcohols. Typical aldehydes
include methanal
(formaldehyde) and ethanal
(acetaldehyde).
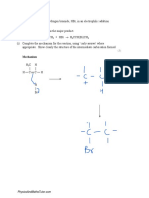
Ketone an organic compound Propanone - CH3−O∣∣C−CH3
containing a carbonyl group acetophenone - C8H8O
=C=O bonded to two benzophenone - C13H10O
hydrocarbon groups, made
by oxidizing secondary
alcohols. The simplest such
compound is acetone.
Carboxylic acid an organic acid containing a caproic acid - CH3(CH2)4CO2H
carboxyl group. The simplest enanthic acid CH3(CH2)5CO2H
examples are methanoic (or caprylic acidCH3(CH2)6CO2H
formic) acid and ethanoic (or
acetic) acid.
Ether pleasant-smelling colorless
volatile liquid that is highly Methoxy CH3O–
flammable. It is used as an Ethoxy CH3CH2O
anesthetic and as a solvent Isopropoxy (CH3)2CHO
or intermediate in industrial
processes.
Ester an organic compound made methyl acetate-CH3COOCH3
by replacing the hydrogen of ethyl acetate-CH3COOCH2CH3
an acid by an alkyl or other ethyl
organic group. Many propionate-CH3CH2COOCH2C
naturally occurring fats and H3
essential oils are esters of
fatty acids.
Amine an organic compound made Methylamine - CH3NH2
by replacing the hydrogen of Aniline - C6H5NH2
an acid by an alkyl or other trimethylamine - C3H9N
organic group. Many
naturally occurring fats and
essential oils are esters of
fatty acids.
Amide an organic compound Formamide HCONH2
containing the group Polyamide
—C(O)NH2, related to
ammonia by replacing a
hydrogen atom by an acyl
group.
You might also like
- Data Tables For Alien Gene AnalysisDocument3 pagesData Tables For Alien Gene Analysisapi-382372564100% (3)
- Schaum's Easy Outline of Organic Chemistry, Second EditionFrom EverandSchaum's Easy Outline of Organic Chemistry, Second EditionRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2)
- Hydrocarbon IUPAC Revision PDFDocument17 pagesHydrocarbon IUPAC Revision PDFpatel_monilNo ratings yet
- Charge To Mass Ratio For An Electron PASCODocument5 pagesCharge To Mass Ratio For An Electron PASCOAkash PatelNo ratings yet
- 04 Organic ChemistryDocument17 pages04 Organic ChemistrysandeepNo ratings yet
- Carbon CompoundDocument16 pagesCarbon CompoundAidah AmirNo ratings yet
- IGCSE Chemistry Notes-Organic ChemistryDocument7 pagesIGCSE Chemistry Notes-Organic ChemistryFasih AhmadNo ratings yet
- ) Iupac (International Union of Pure and Applied Chemistry) - Is Used To Name OrganicDocument11 pages) Iupac (International Union of Pure and Applied Chemistry) - Is Used To Name OrganicPkrajen PillaiNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Organic ChemistryDocument12 pagesIntroduction To Organic ChemistryPaul Nathaniel GwapoNo ratings yet
- Topic 3 Carbonyl CompoundDocument25 pagesTopic 3 Carbonyl CompoundacatcomelNo ratings yet
- Ch4 PDFDocument129 pagesCh4 PDFNerdalert NNo ratings yet
- CHAPTER 9 HydrocarbonsDocument2 pagesCHAPTER 9 HydrocarbonsJaishree RamNo ratings yet
- General Science Unit 3 Note 2016Document26 pagesGeneral Science Unit 3 Note 2016Tedla AlemayehuNo ratings yet
- EthersDocument11 pagesEthersbomzanaakritiNo ratings yet
- Organic Chemistry NotesDocument9 pagesOrganic Chemistry NotesBuana SandilaNo ratings yet
- Aldehydes & Ketones: (Alkanals & Alkanones)Document41 pagesAldehydes & Ketones: (Alkanals & Alkanones)Hunain NadeemNo ratings yet
- 3D Chemistry Concepts & Questions 2023-24 2.0Document63 pages3D Chemistry Concepts & Questions 2023-24 2.0Anushka ChauhanNo ratings yet
- Organic Chemistry Review: For Medical BiochemistryDocument19 pagesOrganic Chemistry Review: For Medical BiochemistryMike GNo ratings yet
- Organic Chemistry 1Document110 pagesOrganic Chemistry 1Mahmoud RslanNo ratings yet
- Aldehydes Ketones: Structural TheoryDocument75 pagesAldehydes Ketones: Structural TheoryNasif Abdur RazzaqueNo ratings yet
- Organic Copound Module - 6 Pages 208Document208 pagesOrganic Copound Module - 6 Pages 208brightcoachingacademyindiaNo ratings yet
- Alcohols Phenols and EthersDocument26 pagesAlcohols Phenols and EthersGuestNo ratings yet
- c23 - Alcohols and Carboxylic AcidsDocument7 pagesc23 - Alcohols and Carboxylic AcidsgarethongshNo ratings yet
- 1: Understanding Carbon Compounds I (Textbook: Chapter 2 Page 33-92)Document35 pages1: Understanding Carbon Compounds I (Textbook: Chapter 2 Page 33-92)Haslimi Bin HassanNo ratings yet
- Organic Chemistry MasterDocument128 pagesOrganic Chemistry MasterLeigh DensingNo ratings yet
- Biochem Lab Feb10Document3 pagesBiochem Lab Feb10ac manguladNo ratings yet
- Organic Chemistry CurrentDocument48 pagesOrganic Chemistry CurrentBierzo JomarNo ratings yet
- Chapter - 03 Prop Fisicas y NomenclaturaDocument115 pagesChapter - 03 Prop Fisicas y NomenclaturaIsa WitzNo ratings yet
- 4.carbon and Its CompoundsDocument8 pages4.carbon and Its CompoundsBhai JaanNo ratings yet
- Ch24 Lecture21 112204Document77 pagesCh24 Lecture21 112204Che PeñalesNo ratings yet
- Lesson 2 Organic Chemistry FundamentalsDocument17 pagesLesson 2 Organic Chemistry Fundamentalsaloysius limNo ratings yet
- C10 Organic ChemistryDocument36 pagesC10 Organic ChemistryAlice NgaNo ratings yet
- Pioneer Junior College Higher 2 Chemistry (9647) Organic Chemistry Carbonyl Compounds (Tutor's Copy)Document22 pagesPioneer Junior College Higher 2 Chemistry (9647) Organic Chemistry Carbonyl Compounds (Tutor's Copy)Timothy HandokoNo ratings yet
- Carbon CompoundDocument48 pagesCarbon CompoundIlakiya Sharvinee KumarNo ratings yet
- Nomenclature of Organic Compounds-3Document32 pagesNomenclature of Organic Compounds-3Muhammad ArhamNo ratings yet
- Organic Chemistry Summary by EljackDocument6 pagesOrganic Chemistry Summary by EljackMohammed EljackNo ratings yet
- SPM Chemistry Form 5 NotesDocument16 pagesSPM Chemistry Form 5 NotesHongYu Hui100% (4)
- Try To Answer: IsopropylbenzeneDocument33 pagesTry To Answer: IsopropylbenzeneRoxanne Sioco100% (1)
- O R C H O R C R: Carbonyl Compounds (Aldehydes and Ketones)Document10 pagesO R C H O R C R: Carbonyl Compounds (Aldehydes and Ketones)Fakin AsholNo ratings yet
- Science g9 q2 w6 ModDocument8 pagesScience g9 q2 w6 ModRhia Mae AjocNo ratings yet
- Learner q2 Week 67 Gen - ChemDocument82 pagesLearner q2 Week 67 Gen - ChemrikrikNo ratings yet
- AlcoholDocument21 pagesAlcohollinda.wairepoNo ratings yet
- Organic Chemistry - Lecture 2: Review Alkanes, Alkenes, Alkynes Hydrocarbon NomenclatureDocument29 pagesOrganic Chemistry - Lecture 2: Review Alkanes, Alkenes, Alkynes Hydrocarbon NomenclatureEmma AssaadNo ratings yet
- Chapter 25 - Organic Chemistry Notes: Catenation Is The Process of An Element Bonding To Itself To Make A Chain or RingDocument4 pagesChapter 25 - Organic Chemistry Notes: Catenation Is The Process of An Element Bonding To Itself To Make A Chain or RingMelanieNo ratings yet
- ORGANIC CHEMISTRY - Tr. BDocument47 pagesORGANIC CHEMISTRY - Tr. BChishala IsaacNo ratings yet
- Aldehydes and KetonesDocument75 pagesAldehydes and KetonesSayantan MukherjeeNo ratings yet
- Laboratory Manual For Practical Exercises Properties of Organic CompoundsDocument18 pagesLaboratory Manual For Practical Exercises Properties of Organic CompoundsSaraNo ratings yet
- Nota Kimia Carbon Compoun Form 5Document16 pagesNota Kimia Carbon Compoun Form 5akusabrina2012No ratings yet
- Carbon and Its CompoundsDocument5 pagesCarbon and Its CompoundsAmanPatelNo ratings yet
- Loaded1-Prof - DO.Moronkola-CHE-176-2023-Course Content1Document58 pagesLoaded1-Prof - DO.Moronkola-CHE-176-2023-Course Content1taiwodamola789No ratings yet
- Selina Sol Concise Chem Class 10 CH 12Document6 pagesSelina Sol Concise Chem Class 10 CH 12Soureesh MukherjeeNo ratings yet
- 4.6 Organic Chemistry 2Document30 pages4.6 Organic Chemistry 2PeterNo ratings yet
- Star Coaching Centre Aligarh: (Organic Chemistry and Polymers)Document20 pagesStar Coaching Centre Aligarh: (Organic Chemistry and Polymers)hacker GodNo ratings yet
- 4.6 Organic Chemistry 2Document30 pages4.6 Organic Chemistry 2Lenah MoiNo ratings yet
- 5 Hydrocarbon Derivatives 2Document28 pages5 Hydrocarbon Derivatives 2Marivic TayabanNo ratings yet
- Organic Chemistry: Unique Natures of Carbon AtomDocument13 pagesOrganic Chemistry: Unique Natures of Carbon AtomSANDEEP SINGHNo ratings yet
- CHEM 332 Carbonyl Cpds Keto and AldsDocument16 pagesCHEM 332 Carbonyl Cpds Keto and Aldsoyamo markNo ratings yet
- Chapter 15 Intro To OrganicDocument8 pagesChapter 15 Intro To OrganicLisa DentonNo ratings yet
- Practice Makes Perfect in Chemistry: Organic Chemistry with AnswersFrom EverandPractice Makes Perfect in Chemistry: Organic Chemistry with AnswersNo ratings yet
- Practice Makes Perfect in Chemistry: Organic ChemistryFrom EverandPractice Makes Perfect in Chemistry: Organic ChemistryRating: 3 out of 5 stars3/5 (1)
- Practice Makes Perfect in Chemistry: Acids, Bases, and Salts with AnswersFrom EverandPractice Makes Perfect in Chemistry: Acids, Bases, and Salts with AnswersNo ratings yet
- Production of Car Seat Cushion Using Palm OilDocument25 pagesProduction of Car Seat Cushion Using Palm OilSeiswaran PandeinNo ratings yet
- MatlabDocument6 pagesMatlabDaniel García100% (1)
- Surface Vehicle Recommended Practice: 400 Commonwealth Drive, Warrendale, PA 15096-0001Document20 pagesSurface Vehicle Recommended Practice: 400 Commonwealth Drive, Warrendale, PA 15096-0001Leonardo Gonçalves GomideNo ratings yet
- Alkaloids: DR N AhmedDocument23 pagesAlkaloids: DR N AhmedMohammad SamirNo ratings yet
- Peter GoldbergDocument98 pagesPeter Goldbergapi-3743459100% (1)
- Sikadur - 52: Low Viscosity Injection ResinDocument3 pagesSikadur - 52: Low Viscosity Injection ResinSunny RohillaNo ratings yet
- MM Aqua Technologies LTD.: TubedekDocument47 pagesMM Aqua Technologies LTD.: TubedekSourabh Manuja100% (1)
- TB072A Evaluation of A.C. in Liquid Phase Appl. (Preparation of Isotherms)Document7 pagesTB072A Evaluation of A.C. in Liquid Phase Appl. (Preparation of Isotherms)mhuurNo ratings yet
- F HG I KJ: NEET (UG) 2020 Exam PaperDocument23 pagesF HG I KJ: NEET (UG) 2020 Exam PaperN KNo ratings yet
- Ammonia Probe: Model ISENH318101 or ISENH318103: Safety InformationDocument14 pagesAmmonia Probe: Model ISENH318101 or ISENH318103: Safety InformationwaskitaNo ratings yet
- EDO-PPP-ME-GNR-INT-XXX-013-107-108-Rev-A-AMMONIA STORAGE TANK DESIGN PDFDocument33 pagesEDO-PPP-ME-GNR-INT-XXX-013-107-108-Rev-A-AMMONIA STORAGE TANK DESIGN PDFErol DAĞ100% (1)
- Centrifugation in The Pharmaceutical IndustryDocument12 pagesCentrifugation in The Pharmaceutical Industrymamun_ruNo ratings yet
- Synthesis of Modified Silane Acrylic Resins and Their Physical Properties As Weather-Resistant CoatingsDocument14 pagesSynthesis of Modified Silane Acrylic Resins and Their Physical Properties As Weather-Resistant CoatingszainNo ratings yet
- ECJ Dossier 2020 SustainabilityDocument49 pagesECJ Dossier 2020 SustainabilityJose LopezNo ratings yet
- Phase Diagram WS Long 1Document2 pagesPhase Diagram WS Long 1Jonar MarieNo ratings yet
- Chesterton 891Document2 pagesChesterton 891aiindustriyahoocoidNo ratings yet
- VizagSteel MgmtTRAINEEDocument28 pagesVizagSteel MgmtTRAINEERaghu88% (16)
- Dimensional Tolerance & Physical Defects of Refractory Bricks-350T TLC-N...Document5 pagesDimensional Tolerance & Physical Defects of Refractory Bricks-350T TLC-N...Bholanath BeraNo ratings yet
- Coordination Compound & MatallurgyDocument118 pagesCoordination Compound & MatallurgyMD MoonNo ratings yet
- Advances in Bio MimeTicsDocument532 pagesAdvances in Bio MimeTicsJosé RamírezNo ratings yet
- Note 4 Approving Welding Procedure - Test To Qualify ProceduresDocument27 pagesNote 4 Approving Welding Procedure - Test To Qualify ProceduresMohamad Yusuf HelmiNo ratings yet
- Usw Alloy Designation AND Description Issued Data Sheet: Revision No. ADocument1 pageUsw Alloy Designation AND Description Issued Data Sheet: Revision No. AbrunizzaNo ratings yet
- Catalytic Beds Protection: Procatalyse Catalysts & AdsorbentsDocument1 pageCatalytic Beds Protection: Procatalyse Catalysts & Adsorbentsmohsen ranjbarNo ratings yet
- Alkenes 2 QP AnsDocument11 pagesAlkenes 2 QP AnshhheeeNo ratings yet
- Fundamental Operations in Compunding, PPTDocument32 pagesFundamental Operations in Compunding, PPTdoctorneha6691% (22)
- FAO Coconut Water ProcessingDocument46 pagesFAO Coconut Water Processingivyrana0% (1)
- Fire Detection and Alarm SystemDocument41 pagesFire Detection and Alarm SystemMohamad Arif Ali100% (1)
- Fatigue: TorsionalDocument9 pagesFatigue: TorsionalShankar RamanNo ratings yet