Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Language and Its Organisation
Language and Its Organisation
Uploaded by
PadmaDevCopyright:
Available Formats
You might also like
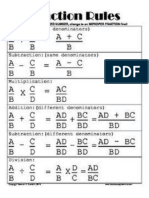
- Fraction RulesDocument1 pageFraction RulesPadmaDev100% (1)
- Hc2e TG Level2Document184 pagesHc2e TG Level2ceracal100% (3)
- Grammatical Structure of The English LanguageDocument15 pagesGrammatical Structure of The English LanguageАнна Сокол100% (1)
- English Grammar For DummiesDocument2 pagesEnglish Grammar For Dummiesqazi1975100% (1)
- Basic Com. Information Sheet.1.1-1 Part of SpeechDocument5 pagesBasic Com. Information Sheet.1.1-1 Part of SpeechJhoerey D VillegasNo ratings yet
- What Does It Mean To Know A WordDocument5 pagesWhat Does It Mean To Know A WordAlthea Mae GelacioNo ratings yet
- IELTS GRAMMAR (From Basic To Types)Document18 pagesIELTS GRAMMAR (From Basic To Types)Builoan1986No ratings yet
- Unit - 1 BeDocument115 pagesUnit - 1 Bevicky PatelNo ratings yet
- Someone, Everybody, Etc.) Is A Word That Takes The Place of A NounDocument2 pagesSomeone, Everybody, Etc.) Is A Word That Takes The Place of A NounCt Fairuz HananiNo ratings yet
- Purposive Communication.Document8 pagesPurposive Communication.Kyla Ramos Diamsay100% (1)
- Textbook 2Document91 pagesTextbook 2Anh PhanNo ratings yet
- Part I. Essentials of GrammarDocument4 pagesPart I. Essentials of GrammarIX-B angkatan 21No ratings yet
- Grammar For PPSCDocument22 pagesGrammar For PPSCAlina NoreenNo ratings yet
- Parts of SpeechDocument6 pagesParts of SpeechsteinrizkyNo ratings yet
- The 9 Parts of SpeechDocument3 pagesThe 9 Parts of SpeechDana Sofia GrapaNo ratings yet
- The Noun and Its Grammatical CategoriesDocument2 pagesThe Noun and Its Grammatical CategoriesAzat ArnaNo ratings yet
- Parts of SpeechDocument9 pagesParts of SpeechJose BrabanteNo ratings yet
- A. Noun: Proper Nouns Are The Names of Individual People, Places, Titles, Calendar Times, EtcDocument44 pagesA. Noun: Proper Nouns Are The Names of Individual People, Places, Titles, Calendar Times, EtcAnonymous 1cCIhqNo ratings yet
- Grammar DefinitionsDocument11 pagesGrammar DefinitionsMaría VielmanNo ratings yet
- English Apsa PPT Group 4Document53 pagesEnglish Apsa PPT Group 4acrtannNo ratings yet
- ESP-UNIT-5Document8 pagesESP-UNIT-5Setia WanNo ratings yet
- Grammar Erisa Newati SihombingDocument38 pagesGrammar Erisa Newati SihombingLesbra SandyNo ratings yet
- What Is Noun?Document4 pagesWhat Is Noun?Christian GarciaNo ratings yet
- Syntax: The Relationship Between Morphology and SyntaxDocument13 pagesSyntax: The Relationship Between Morphology and SyntaxKiana Marie BlancoNo ratings yet
- GrammarDocument21 pagesGrammaralbertosgfNo ratings yet
- Makalah GrammarDocument10 pagesMakalah GrammarMonalisa AritonangNo ratings yet
- English Assignment 1Document9 pagesEnglish Assignment 1ha khanNo ratings yet
- Types of PronounsDocument11 pagesTypes of PronounsReynaldo Aluyen Guinoden Jr.No ratings yet
- 9 Parts of SpeechDocument4 pages9 Parts of SpeechFACHRIANI -2020-BLOK 3100% (1)
- The Simple Sentence: Parts of Speech Sentence AnalysisDocument7 pagesThe Simple Sentence: Parts of Speech Sentence AnalysismiriamacunaNo ratings yet
- Parts of SpeechDocument19 pagesParts of Speechzafar iqbalNo ratings yet
- Pronoun: Everything, Some, Any, No, My, His, Etc. Mine, Hers, Etc.)Document10 pagesPronoun: Everything, Some, Any, No, My, His, Etc. Mine, Hers, Etc.)Diana KimNo ratings yet
- Primary Grammar Glossary For ParentsDocument6 pagesPrimary Grammar Glossary For ParentsJack EdieNo ratings yet
- The Verb Is Perhaps The Most Important Part of The SentenceDocument2 pagesThe Verb Is Perhaps The Most Important Part of The SentencemahyoolNo ratings yet
- English Pertemuan 1Document15 pagesEnglish Pertemuan 1Aurel ArafanyNo ratings yet
- The 9 Parts of SpeechDocument6 pagesThe 9 Parts of SpeechLeonardo ColjaNo ratings yet
- DocumentoDocument9 pagesDocumentoMatias Solis MelendresNo ratings yet
- Unit2 LexisDocument5 pagesUnit2 LexisEnier Antonio Guerrero VergelNo ratings yet
- Raysha's SyntaxDocument5 pagesRaysha's SyntaxM. Fauzi ArrasyidNo ratings yet
- Unit 1. Wha T Ar E Wor Ds ?: - Identify Words - Word ClassesDocument5 pagesUnit 1. Wha T Ar E Wor Ds ?: - Identify Words - Word ClassesDiana MarisolNo ratings yet
- 00 - Parts of SpeechDocument13 pages00 - Parts of Speechiam_maria1997No ratings yet
- Parts of SpeechDocument19 pagesParts of Speechleona dao100% (3)
- Parts of SpeechDocument11 pagesParts of SpeechAyesha AsifNo ratings yet
- The Verb Phrase: Unit 1Document20 pagesThe Verb Phrase: Unit 1Valeria Sofia MachicoteNo ratings yet
- Cheat Sheet Grammar HTTP WWW - DummiesDocument4 pagesCheat Sheet Grammar HTTP WWW - DummiesXisco Capllonch AlcoverNo ratings yet
- PARTS OF SPEECH UpdatedDocument12 pagesPARTS OF SPEECH UpdatedMCC Gilgit-BaltistanNo ratings yet
- Grammar Elfrida BakaraDocument34 pagesGrammar Elfrida BakaraLesbra SandyNo ratings yet
- The Eight Parts of SpeechDocument2 pagesThe Eight Parts of SpeechTin ListancoNo ratings yet
- Notes Part of SpeechDocument11 pagesNotes Part of SpeechNurin Adleena AdamulhaszaNo ratings yet
- Grammar - Grade 7Document1 pageGrammar - Grade 7Saira FaisalNo ratings yet
- Glossary of Linguistic Terms: What Is A Noun?Document8 pagesGlossary of Linguistic Terms: What Is A Noun?Widya sari ismailNo ratings yet
- Word Classes: Functions: S, P, SA Etc. Realizations: NP, VPDocument5 pagesWord Classes: Functions: S, P, SA Etc. Realizations: NP, VPAlexandra VersluijsNo ratings yet
- Reach Dream: Makalah Eight Parts of SpeechDocument9 pagesReach Dream: Makalah Eight Parts of SpeechMelfi Namora nasutionNo ratings yet
- Grammar Friska SipayungDocument36 pagesGrammar Friska SipayungLesbra SandyNo ratings yet
- Part of SpeechDocument23 pagesPart of SpeechTimilehin GbengaNo ratings yet
- Basic Grammar and StructureDocument3 pagesBasic Grammar and StructureYeni LampungNo ratings yet
- SSS 1Document34 pagesSSS 1ALALADE VICTORNo ratings yet
- Biru Hijau Imut Ceria Tugas Presentasi Kelompok - 20240317 - 230007 - 0000Document24 pagesBiru Hijau Imut Ceria Tugas Presentasi Kelompok - 20240317 - 230007 - 0000saputsaput251No ratings yet
- Basic EnglishDocument4 pagesBasic EnglishwuhemosesNo ratings yet
- A Review of Grammar and SentencesDocument29 pagesA Review of Grammar and SentencesDonavan Tadia CabantacNo ratings yet
- Advanced English Grammar with ExercisesFrom EverandAdvanced English Grammar with ExercisesRating: 2 out of 5 stars2/5 (1)
- Mourning_DoveDocument52 pagesMourning_DovePadmaDevNo ratings yet
- ADOBE Suite agreement TERMSDocument1 pageADOBE Suite agreement TERMSPadmaDevNo ratings yet
- Articles-Cheat-SheetDocument4 pagesArticles-Cheat-SheetPadmaDevNo ratings yet
- British vs EU LanguageDocument4 pagesBritish vs EU LanguagePadmaDevNo ratings yet
- THE CONDITION OF THE AGREEMENT LANguageDocument2 pagesTHE CONDITION OF THE AGREEMENT LANguagePadmaDevNo ratings yet
- Nail Varnish, Colours & Art - Nails - Maybelline UKDocument1 pageNail Varnish, Colours & Art - Nails - Maybelline UKPadmaDevNo ratings yet
- Watchers and DoersDocument3 pagesWatchers and DoersPadmaDev0% (1)
- Problem SolvingDocument7 pagesProblem SolvingPadmaDevNo ratings yet
- Linq To SQL Cheat SheetDocument1 pageLinq To SQL Cheat SheetPadmaDevNo ratings yet
- SQL Cheat SheetDocument1 pageSQL Cheat SheetPadmaDevNo ratings yet
- Irregular VerbsDocument1 pageIrregular VerbsPadmaDevNo ratings yet
- Data WranglingDocument1 pageData WranglingPadmaDevNo ratings yet
- Solar System Cheat SheetDocument1 pageSolar System Cheat SheetPadmaDevNo ratings yet
- Since or For? Fill in Since or ForDocument2 pagesSince or For? Fill in Since or ForFLORES GUARACHI PABLO GABRIELNo ratings yet
- Business Quiz LetterDocument8 pagesBusiness Quiz LetterCookie Pookie BallerShopNo ratings yet
- How To Teach English Abroad Like A ProDocument55 pagesHow To Teach English Abroad Like A ProangtenNo ratings yet
- English Consonant Letters and Their SoundsDocument2 pagesEnglish Consonant Letters and Their SoundsThiru PathiNo ratings yet
- 2a Lesson 7Document3 pages2a Lesson 7林巍洋No ratings yet
- A Man Called Pearse Desmond RyanDocument146 pagesA Man Called Pearse Desmond RyanSol Desireet Santander MendozaNo ratings yet
- On Egypt & Other CountriesDocument174 pagesOn Egypt & Other Countriessmk11No ratings yet
- Portfolio-ARW1 180089 0Document2 pagesPortfolio-ARW1 180089 0FioNo ratings yet
- 2018-01-10 Thomas-Wilhelm CV From AprDocument5 pages2018-01-10 Thomas-Wilhelm CV From Aprapi-390703726No ratings yet
- Mid Test Paper (19-04-2021)Document2 pagesMid Test Paper (19-04-2021)Darma ManurungNo ratings yet
- FX6 - FX7 - FX8 - FX9 - FX10 - FX11 - FX12Document14 pagesFX6 - FX7 - FX8 - FX9 - FX10 - FX11 - FX12Yuvraj BappiNo ratings yet
- ICSK Counselling L2Document12 pagesICSK Counselling L2redred121No ratings yet
- ExpresiiDocument8 pagesExpresiiSorana DobreanuNo ratings yet
- English Grammer For SSCDocument24 pagesEnglish Grammer For SSCAnkit Sharma71% (7)
- Libro de InglesDocument77 pagesLibro de InglesSteve PsJNo ratings yet
- Summative Assessment For The Term2 Characteristic of Tasks For Summative Assessment For The 4 TermDocument14 pagesSummative Assessment For The Term2 Characteristic of Tasks For Summative Assessment For The 4 TermaizokoshaNo ratings yet
- Pathway To English SMA XIDocument10 pagesPathway To English SMA XI06Alyyusyawal Widardi67% (3)
- Mix TenseDocument5 pagesMix TenseДавид КлушинNo ratings yet
- Emailing Lyla B DasDocument378 pagesEmailing Lyla B DasNotes50% (2)
- Soal-Soal Cerdas Cermat Bahasa Inggris Smp... Oleh: SalahuddinDocument14 pagesSoal-Soal Cerdas Cermat Bahasa Inggris Smp... Oleh: SalahuddinSusanto ThomasNo ratings yet
- "Trees" by Joyce KilmerDocument2 pages"Trees" by Joyce KilmerJochelleNo ratings yet
- Data Migration To HadoopDocument26 pagesData Migration To Hadoopkrishna100% (2)
- Grade 5 Big Summative 2 (Gulshan Anar)Document2 pagesGrade 5 Big Summative 2 (Gulshan Anar)Xalida HasanovaNo ratings yet
- Selenium AutomationDocument58 pagesSelenium AutomationJiji Abhilash100% (1)
- English: Third Quarter-Module 1 Composing An Argumentative EssayDocument13 pagesEnglish: Third Quarter-Module 1 Composing An Argumentative EssayVinMoroCipriano100% (1)
- Tense PDFDocument32 pagesTense PDFMoga JagdishNo ratings yet
- Language Assessment: Education in 2500 Words LengthDocument2 pagesLanguage Assessment: Education in 2500 Words Lengthwayan suastikaNo ratings yet
- The Teacher-Student Communication Pattern: A Need To Follow?Document7 pagesThe Teacher-Student Communication Pattern: A Need To Follow?Alexandra RenteaNo ratings yet
- The Magic Cafe Forums - Final Curtain Book by BorodinDocument21 pagesThe Magic Cafe Forums - Final Curtain Book by BorodinHendri AlamNo ratings yet
Language and Its Organisation
Language and Its Organisation
Uploaded by
PadmaDevCopyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Language and Its Organisation
Language and Its Organisation
Uploaded by
PadmaDevCopyright:
Available Formats
LANGUAGE AND ITS ORGANISATION
Every language in it origin has a certain way it is used and this and is polished and made into
a form of communication gets organised into a certain structure
Whether you’re engaging in everyday speech or writing the perfect paper, you need to be
familiar with the various parts of English grammar.
This helps to effectively get your meaning across and make yourself a proper member of the
society .
Knowing how to correctly use nouns, verbs, adjectives, pronouns, prepositions, and
punctuation as well as how to properly structure a sentence can make or break a good grade
or a professional presentation.
Parts of speech in English grammar
Every time you write or speak, you use nouns, verbs, prepositions, conjunctions, and other
parts of the English language. Knowing how to use these parts of speech can help you speak
more eloquently, write more clearly, and feel more confident when communicating with
others.
Noun: names a person, place, thing, idea (Lulu, jail, cantaloupe, loyalty, and so on)
Pronoun: takes the place of a noun (he, who, I, what, and so on)
Verb: expresses action or being (scrambled, was, should win, and so on)
Adjective: describes a noun or pronoun (messy, strange, alien, and so on)
Adverb: describes a verb, adjective, or other adverb (willingly, woefully, very, and so
on)
Preposition: relates a noun or a pronoun to another word in the sentence (by, for,
from, and so on)
Conjunction: ties two words or groups of words together (and, after, although, and
so on)
Interjection: expresses strong emotion (yikes! wow! ouch! and so on)
Parts of a sentence
After you get a good grip on the different parts of speech, it’s time to put them all together to
form the proper sentence. The right words and punctuation in the right order can make all the
difference in good communication. Keep in mind that you need a minimum number of parts
to make a complete sentence: subject/predicate/endmark.
Verb (also called the predicate): expresses the action or state of being
Subject: the person or thing being talked about
Complement: a word or group of words that completes the meaning of the subject-
verb pair
Types of complements: direct and indirect objects, subject complement, objective
complement
Pronoun tips for proper English grammar
The Beatles sang of “I, Me, Mine,” but understanding pronouns takes a little practice.
Pronouns can be objective or subjective, and can show possession. You, me, him, her, them,
us . . . everyone can speak and write more clearly by understanding pronouns.
Pronouns that may be used only as subjects or subject complements: I, he, she,
we, they, who, whoever.
Pronouns that may be used only as objects or objective complements: me, him,
her, us, them, whom, whomever.
Common pronouns that may be used as either subjects or objects: you, it,
everyone, anyone, no one, someone, mine, ours, yours, theirs, either, neither, each,
everybody, anybody, nobody, somebody, everything, anything, nothing, something,
any, none, some, which, what, that.
Pronouns that show possession: my, mine, your, yours, his, her, hers, its, our, ours,
their, theirs, whose.
You might also like
- Fraction RulesDocument1 pageFraction RulesPadmaDev100% (1)
- Hc2e TG Level2Document184 pagesHc2e TG Level2ceracal100% (3)
- Grammatical Structure of The English LanguageDocument15 pagesGrammatical Structure of The English LanguageАнна Сокол100% (1)
- English Grammar For DummiesDocument2 pagesEnglish Grammar For Dummiesqazi1975100% (1)
- Basic Com. Information Sheet.1.1-1 Part of SpeechDocument5 pagesBasic Com. Information Sheet.1.1-1 Part of SpeechJhoerey D VillegasNo ratings yet
- What Does It Mean To Know A WordDocument5 pagesWhat Does It Mean To Know A WordAlthea Mae GelacioNo ratings yet
- IELTS GRAMMAR (From Basic To Types)Document18 pagesIELTS GRAMMAR (From Basic To Types)Builoan1986No ratings yet
- Unit - 1 BeDocument115 pagesUnit - 1 Bevicky PatelNo ratings yet
- Someone, Everybody, Etc.) Is A Word That Takes The Place of A NounDocument2 pagesSomeone, Everybody, Etc.) Is A Word That Takes The Place of A NounCt Fairuz HananiNo ratings yet
- Purposive Communication.Document8 pagesPurposive Communication.Kyla Ramos Diamsay100% (1)
- Textbook 2Document91 pagesTextbook 2Anh PhanNo ratings yet
- Part I. Essentials of GrammarDocument4 pagesPart I. Essentials of GrammarIX-B angkatan 21No ratings yet
- Grammar For PPSCDocument22 pagesGrammar For PPSCAlina NoreenNo ratings yet
- Parts of SpeechDocument6 pagesParts of SpeechsteinrizkyNo ratings yet
- The 9 Parts of SpeechDocument3 pagesThe 9 Parts of SpeechDana Sofia GrapaNo ratings yet
- The Noun and Its Grammatical CategoriesDocument2 pagesThe Noun and Its Grammatical CategoriesAzat ArnaNo ratings yet
- Parts of SpeechDocument9 pagesParts of SpeechJose BrabanteNo ratings yet
- A. Noun: Proper Nouns Are The Names of Individual People, Places, Titles, Calendar Times, EtcDocument44 pagesA. Noun: Proper Nouns Are The Names of Individual People, Places, Titles, Calendar Times, EtcAnonymous 1cCIhqNo ratings yet
- Grammar DefinitionsDocument11 pagesGrammar DefinitionsMaría VielmanNo ratings yet
- English Apsa PPT Group 4Document53 pagesEnglish Apsa PPT Group 4acrtannNo ratings yet
- ESP-UNIT-5Document8 pagesESP-UNIT-5Setia WanNo ratings yet
- Grammar Erisa Newati SihombingDocument38 pagesGrammar Erisa Newati SihombingLesbra SandyNo ratings yet
- What Is Noun?Document4 pagesWhat Is Noun?Christian GarciaNo ratings yet
- Syntax: The Relationship Between Morphology and SyntaxDocument13 pagesSyntax: The Relationship Between Morphology and SyntaxKiana Marie BlancoNo ratings yet
- GrammarDocument21 pagesGrammaralbertosgfNo ratings yet
- Makalah GrammarDocument10 pagesMakalah GrammarMonalisa AritonangNo ratings yet
- English Assignment 1Document9 pagesEnglish Assignment 1ha khanNo ratings yet
- Types of PronounsDocument11 pagesTypes of PronounsReynaldo Aluyen Guinoden Jr.No ratings yet
- 9 Parts of SpeechDocument4 pages9 Parts of SpeechFACHRIANI -2020-BLOK 3100% (1)
- The Simple Sentence: Parts of Speech Sentence AnalysisDocument7 pagesThe Simple Sentence: Parts of Speech Sentence AnalysismiriamacunaNo ratings yet
- Parts of SpeechDocument19 pagesParts of Speechzafar iqbalNo ratings yet
- Pronoun: Everything, Some, Any, No, My, His, Etc. Mine, Hers, Etc.)Document10 pagesPronoun: Everything, Some, Any, No, My, His, Etc. Mine, Hers, Etc.)Diana KimNo ratings yet
- Primary Grammar Glossary For ParentsDocument6 pagesPrimary Grammar Glossary For ParentsJack EdieNo ratings yet
- The Verb Is Perhaps The Most Important Part of The SentenceDocument2 pagesThe Verb Is Perhaps The Most Important Part of The SentencemahyoolNo ratings yet
- English Pertemuan 1Document15 pagesEnglish Pertemuan 1Aurel ArafanyNo ratings yet
- The 9 Parts of SpeechDocument6 pagesThe 9 Parts of SpeechLeonardo ColjaNo ratings yet
- DocumentoDocument9 pagesDocumentoMatias Solis MelendresNo ratings yet
- Unit2 LexisDocument5 pagesUnit2 LexisEnier Antonio Guerrero VergelNo ratings yet
- Raysha's SyntaxDocument5 pagesRaysha's SyntaxM. Fauzi ArrasyidNo ratings yet
- Unit 1. Wha T Ar E Wor Ds ?: - Identify Words - Word ClassesDocument5 pagesUnit 1. Wha T Ar E Wor Ds ?: - Identify Words - Word ClassesDiana MarisolNo ratings yet
- 00 - Parts of SpeechDocument13 pages00 - Parts of Speechiam_maria1997No ratings yet
- Parts of SpeechDocument19 pagesParts of Speechleona dao100% (3)
- Parts of SpeechDocument11 pagesParts of SpeechAyesha AsifNo ratings yet
- The Verb Phrase: Unit 1Document20 pagesThe Verb Phrase: Unit 1Valeria Sofia MachicoteNo ratings yet
- Cheat Sheet Grammar HTTP WWW - DummiesDocument4 pagesCheat Sheet Grammar HTTP WWW - DummiesXisco Capllonch AlcoverNo ratings yet
- PARTS OF SPEECH UpdatedDocument12 pagesPARTS OF SPEECH UpdatedMCC Gilgit-BaltistanNo ratings yet
- Grammar Elfrida BakaraDocument34 pagesGrammar Elfrida BakaraLesbra SandyNo ratings yet
- The Eight Parts of SpeechDocument2 pagesThe Eight Parts of SpeechTin ListancoNo ratings yet
- Notes Part of SpeechDocument11 pagesNotes Part of SpeechNurin Adleena AdamulhaszaNo ratings yet
- Grammar - Grade 7Document1 pageGrammar - Grade 7Saira FaisalNo ratings yet
- Glossary of Linguistic Terms: What Is A Noun?Document8 pagesGlossary of Linguistic Terms: What Is A Noun?Widya sari ismailNo ratings yet
- Word Classes: Functions: S, P, SA Etc. Realizations: NP, VPDocument5 pagesWord Classes: Functions: S, P, SA Etc. Realizations: NP, VPAlexandra VersluijsNo ratings yet
- Reach Dream: Makalah Eight Parts of SpeechDocument9 pagesReach Dream: Makalah Eight Parts of SpeechMelfi Namora nasutionNo ratings yet
- Grammar Friska SipayungDocument36 pagesGrammar Friska SipayungLesbra SandyNo ratings yet
- Part of SpeechDocument23 pagesPart of SpeechTimilehin GbengaNo ratings yet
- Basic Grammar and StructureDocument3 pagesBasic Grammar and StructureYeni LampungNo ratings yet
- SSS 1Document34 pagesSSS 1ALALADE VICTORNo ratings yet
- Biru Hijau Imut Ceria Tugas Presentasi Kelompok - 20240317 - 230007 - 0000Document24 pagesBiru Hijau Imut Ceria Tugas Presentasi Kelompok - 20240317 - 230007 - 0000saputsaput251No ratings yet
- Basic EnglishDocument4 pagesBasic EnglishwuhemosesNo ratings yet
- A Review of Grammar and SentencesDocument29 pagesA Review of Grammar and SentencesDonavan Tadia CabantacNo ratings yet
- Advanced English Grammar with ExercisesFrom EverandAdvanced English Grammar with ExercisesRating: 2 out of 5 stars2/5 (1)
- Mourning_DoveDocument52 pagesMourning_DovePadmaDevNo ratings yet
- ADOBE Suite agreement TERMSDocument1 pageADOBE Suite agreement TERMSPadmaDevNo ratings yet
- Articles-Cheat-SheetDocument4 pagesArticles-Cheat-SheetPadmaDevNo ratings yet
- British vs EU LanguageDocument4 pagesBritish vs EU LanguagePadmaDevNo ratings yet
- THE CONDITION OF THE AGREEMENT LANguageDocument2 pagesTHE CONDITION OF THE AGREEMENT LANguagePadmaDevNo ratings yet
- Nail Varnish, Colours & Art - Nails - Maybelline UKDocument1 pageNail Varnish, Colours & Art - Nails - Maybelline UKPadmaDevNo ratings yet
- Watchers and DoersDocument3 pagesWatchers and DoersPadmaDev0% (1)
- Problem SolvingDocument7 pagesProblem SolvingPadmaDevNo ratings yet
- Linq To SQL Cheat SheetDocument1 pageLinq To SQL Cheat SheetPadmaDevNo ratings yet
- SQL Cheat SheetDocument1 pageSQL Cheat SheetPadmaDevNo ratings yet
- Irregular VerbsDocument1 pageIrregular VerbsPadmaDevNo ratings yet
- Data WranglingDocument1 pageData WranglingPadmaDevNo ratings yet
- Solar System Cheat SheetDocument1 pageSolar System Cheat SheetPadmaDevNo ratings yet
- Since or For? Fill in Since or ForDocument2 pagesSince or For? Fill in Since or ForFLORES GUARACHI PABLO GABRIELNo ratings yet
- Business Quiz LetterDocument8 pagesBusiness Quiz LetterCookie Pookie BallerShopNo ratings yet
- How To Teach English Abroad Like A ProDocument55 pagesHow To Teach English Abroad Like A ProangtenNo ratings yet
- English Consonant Letters and Their SoundsDocument2 pagesEnglish Consonant Letters and Their SoundsThiru PathiNo ratings yet
- 2a Lesson 7Document3 pages2a Lesson 7林巍洋No ratings yet
- A Man Called Pearse Desmond RyanDocument146 pagesA Man Called Pearse Desmond RyanSol Desireet Santander MendozaNo ratings yet
- On Egypt & Other CountriesDocument174 pagesOn Egypt & Other Countriessmk11No ratings yet
- Portfolio-ARW1 180089 0Document2 pagesPortfolio-ARW1 180089 0FioNo ratings yet
- 2018-01-10 Thomas-Wilhelm CV From AprDocument5 pages2018-01-10 Thomas-Wilhelm CV From Aprapi-390703726No ratings yet
- Mid Test Paper (19-04-2021)Document2 pagesMid Test Paper (19-04-2021)Darma ManurungNo ratings yet
- FX6 - FX7 - FX8 - FX9 - FX10 - FX11 - FX12Document14 pagesFX6 - FX7 - FX8 - FX9 - FX10 - FX11 - FX12Yuvraj BappiNo ratings yet
- ICSK Counselling L2Document12 pagesICSK Counselling L2redred121No ratings yet
- ExpresiiDocument8 pagesExpresiiSorana DobreanuNo ratings yet
- English Grammer For SSCDocument24 pagesEnglish Grammer For SSCAnkit Sharma71% (7)
- Libro de InglesDocument77 pagesLibro de InglesSteve PsJNo ratings yet
- Summative Assessment For The Term2 Characteristic of Tasks For Summative Assessment For The 4 TermDocument14 pagesSummative Assessment For The Term2 Characteristic of Tasks For Summative Assessment For The 4 TermaizokoshaNo ratings yet
- Pathway To English SMA XIDocument10 pagesPathway To English SMA XI06Alyyusyawal Widardi67% (3)
- Mix TenseDocument5 pagesMix TenseДавид КлушинNo ratings yet
- Emailing Lyla B DasDocument378 pagesEmailing Lyla B DasNotes50% (2)
- Soal-Soal Cerdas Cermat Bahasa Inggris Smp... Oleh: SalahuddinDocument14 pagesSoal-Soal Cerdas Cermat Bahasa Inggris Smp... Oleh: SalahuddinSusanto ThomasNo ratings yet
- "Trees" by Joyce KilmerDocument2 pages"Trees" by Joyce KilmerJochelleNo ratings yet
- Data Migration To HadoopDocument26 pagesData Migration To Hadoopkrishna100% (2)
- Grade 5 Big Summative 2 (Gulshan Anar)Document2 pagesGrade 5 Big Summative 2 (Gulshan Anar)Xalida HasanovaNo ratings yet
- Selenium AutomationDocument58 pagesSelenium AutomationJiji Abhilash100% (1)
- English: Third Quarter-Module 1 Composing An Argumentative EssayDocument13 pagesEnglish: Third Quarter-Module 1 Composing An Argumentative EssayVinMoroCipriano100% (1)
- Tense PDFDocument32 pagesTense PDFMoga JagdishNo ratings yet
- Language Assessment: Education in 2500 Words LengthDocument2 pagesLanguage Assessment: Education in 2500 Words Lengthwayan suastikaNo ratings yet
- The Teacher-Student Communication Pattern: A Need To Follow?Document7 pagesThe Teacher-Student Communication Pattern: A Need To Follow?Alexandra RenteaNo ratings yet
- The Magic Cafe Forums - Final Curtain Book by BorodinDocument21 pagesThe Magic Cafe Forums - Final Curtain Book by BorodinHendri AlamNo ratings yet