Professional Documents
Culture Documents
1.1.8-1.1.11 Muscular system
1.1.8-1.1.11 Muscular system
Uploaded by
stormzstormz40 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
1 views1 pageCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as docx, pdf, or txt
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
1 views1 page1.1.8-1.1.11 Muscular system
1.1.8-1.1.11 Muscular system
Uploaded by
stormzstormz4Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as docx, pdf, or txt
You are on page 1of 1
Muscular system
1.1.7 What are the 3 types of muscle groups?
1. Voluntary muscles – Under your control
2. Involuntary muscles – Not under your control. Controlled by the involuntary nervous
system
3. Cardiac muscle – Only found in the wall of the heart. We cannot control the
contractions
GCSE bitesize
1.1.8 What are the 12 muscles important to the GCSE examination?
1. Deltoid - shoulder muscles (abducts the upper arm from body)
2. Pectoralis major – chest muscles (adducts the arm at the shoulder)
3. Latissimus dorsi - lower back muscle (rotates upper arm at the shoulders)
4. Biceps - top of arm muscles (flexion of arm at the elbow)
5. Triceps - underneath of arm muscles (extension of arm at the elbow)
6. External obliques – to the side of the abdomen (pull the chest downwards; flex and
rotate the spinal column)
7. Gluteals - buttocks (extension of the upper leg)
8. Hip flexors – connect the leg to the pelvis and abdomen (flexion at the hip)
9. Quadriceps - front of leg muscles (extension of the leg at the knee)
10. Hamstrings - back of leg muscles (flexion of the leg at the knee)
11. Gastrocnemius - calf muscles (plantar-flexion of the foot)
12. Tibialis anterior – runs don the shin (pulls the toes towards the shin)
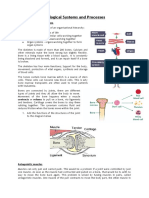
1.1.9 What are antagonistic pairs?
Some muscles work in pairs. When one muscle contracts (agonist), the other relaxes
(antagonist).
Where does this occur?
1. Biceps and triceps
2. Quadriceps and hamstrings YouTube
3. Gastrocnemius and tibialis
4. Hip flexor and gluteus maximus
1.1.10 What are the two types of muscle fibre?
1. Type I - Slow twitch – suited to low intensity work e.g. marathon running as they can be
used for a long period without fatiguing.
2. Type IIa - Fast twitch – used in anaerobic work; can be improved through endurance
training to increase their resistance to fatigue.
3. Type IIx – Fast twitch – used in anaerobic work and can generate much greater force
than other fibre types, but fatigue quickly.
1.1.11 How does the skeletal and muscular systems work together?
The main function is to create movement but also keep you stable, protect you and give you
good posture. By working together they also create levers in the body.
Fulcrum – the point around which the lever rotates
Articulation – the state of having a joint; being a joint
Articulate – act as a joint
You might also like
- CostAccounting 2016 VanderbeckDocument396 pagesCostAccounting 2016 VanderbeckAngel Kitty Labor88% (32)
- MODULE 12 Gross Anatomy of The Muscular SystemDocument3 pagesMODULE 12 Gross Anatomy of The Muscular SystemPrincess Faniega SugatonNo ratings yet
- Tuning Guide Peug. 206 2.0L HDI EDC15C2 90cv - 120HP by J-SkyDocument6 pagesTuning Guide Peug. 206 2.0L HDI EDC15C2 90cv - 120HP by J-Skyzo68No ratings yet
- PE 2 Human Movements Until FinalsDocument32 pagesPE 2 Human Movements Until FinalsFreda Mari100% (1)
- Lab 7 The Muscular SystemDocument14 pagesLab 7 The Muscular Systemcindy tranNo ratings yet
- Name. Zainulabidin Roll No. DPT02201029 Assignment. Kinesiology Submitted To. Dr. Ayesha NoureenDocument13 pagesName. Zainulabidin Roll No. DPT02201029 Assignment. Kinesiology Submitted To. Dr. Ayesha Noureenzain jutt100% (2)
- Hand Out For PE32 Midterm ExamDocument4 pagesHand Out For PE32 Midterm Examakaneyuzu123No ratings yet
- Anatomy ASS Two FinishedDocument8 pagesAnatomy ASS Two Finishedhakimabrahim77No ratings yet
- Elective Phe Theory: Unit 2Document17 pagesElective Phe Theory: Unit 2Stephanie LaureynsNo ratings yet
- Muscular SystemDocument27 pagesMuscular Systemapi-531520430No ratings yet
- WEEK 7 LAB EXERCISE - Muscular SystemDocument11 pagesWEEK 7 LAB EXERCISE - Muscular SystemMARY KATE L. CEBALLOSNo ratings yet
- Group 2 PeDocument9 pagesGroup 2 PeDanielle FacturaNo ratings yet
- Physical EducationDocument6 pagesPhysical EducationLiquerish HeathenNo ratings yet
- Personal Trainer-E-BookDocument4 pagesPersonal Trainer-E-BooksampradanaNo ratings yet
- Pe 1 Module 3Document25 pagesPe 1 Module 3Dimple BolotaoloNo ratings yet
- MUSCLESDocument6 pagesMUSCLESTishonna DouglasNo ratings yet
- Module III - Lesson 1 Fitness ConceptDocument4 pagesModule III - Lesson 1 Fitness ConceptPancho RJNo ratings yet
- Coverage For PE1Document7 pagesCoverage For PE1Jeprain ArduoNo ratings yet
- MusclesDocument89 pagesMusclesSelena ReyesNo ratings yet
- Bones and MusclesDocument8 pagesBones and MusclesMarc Justine Gamiao GoNo ratings yet
- Stretching: Muscle Strength For SpeedDocument4 pagesStretching: Muscle Strength For SpeedGerardClarkeNo ratings yet
- Muscle Produce MovementDocument10 pagesMuscle Produce Movementtine84394No ratings yet
- Unit IV Aerobic ExerciseDocument25 pagesUnit IV Aerobic ExerciseMERAZOLE PACA-ANASNo ratings yet
- Chest Muscles Functions: Flexion AdductionDocument4 pagesChest Muscles Functions: Flexion Adductionxilina BacasnotNo ratings yet
- Muscles WorkbookDocument35 pagesMuscles WorkbookProdosh ChatterjeeNo ratings yet
- Muscles - Workbook PDFDocument71 pagesMuscles - Workbook PDFakash100% (1)
- Viva QuestionsDocument10 pagesViva QuestionsAbhijeet ParateNo ratings yet
- Muscle TissueDocument5 pagesMuscle TissueRoby DerejeNo ratings yet
- Health Education ClassDocument8 pagesHealth Education ClassAlicia ValverdeNo ratings yet
- The Incredible Muscular SystemDocument13 pagesThe Incredible Muscular Systemchrisdaviscng100% (1)
- The Muscular SystemDocument12 pagesThe Muscular SystemMarielle Grace PadilloNo ratings yet
- Human AnatomyDocument4 pagesHuman Anatomyapi-553373137No ratings yet
- The Incredible Muscular SystemDocument13 pagesThe Incredible Muscular SystemchrisdaviscngNo ratings yet
- Unit 1 Presentation WeeblyDocument85 pagesUnit 1 Presentation Weeblyapi-276945651No ratings yet
- Circuit Training-1Document7 pagesCircuit Training-1acamillexxiNo ratings yet
- Anatomi - Olah Raga 1st MeetingDocument79 pagesAnatomi - Olah Raga 1st MeetingR DarmawanNo ratings yet
- Muscular 1Document67 pagesMuscular 1Cherub ChuaNo ratings yet
- Did You Get It (Chapter 6)Document2 pagesDid You Get It (Chapter 6)Chris CaoagdanNo ratings yet
- JSS2 Basic Science Lesson Note PDFDocument40 pagesJSS2 Basic Science Lesson Note PDFJuddy ScienceNo ratings yet
- Obf Handout For Core StabilityDocument2 pagesObf Handout For Core Stabilityapi-292367499No ratings yet
- Muscular FitnessDocument44 pagesMuscular FitnessJack Messaros100% (1)
- Chapter 8 BiomechanicsDocument7 pagesChapter 8 BiomechanicsSakshamNo ratings yet
- The Science of Human Movement ModuleDocument5 pagesThe Science of Human Movement ModuleJerome SagunNo ratings yet
- UNIT I Movement EnhancementDocument7 pagesUNIT I Movement EnhancementKervin Rey Guevarra JacksonNo ratings yet
- Written Report Group 1 HSHSHSHSJSJDNXNXBDocument23 pagesWritten Report Group 1 HSHSHSHSJSJDNXNXBNoronisa PendalidayNo ratings yet
- Ed 1Document6 pagesEd 1Dalupire, Jhonryl A.No ratings yet
- Muscular System2Document43 pagesMuscular System2LeocadiaNo ratings yet
- Muscles of LegsDocument8 pagesMuscles of LegsGeorge OstNo ratings yet
- Muscle Ligaments & TendonsDocument5 pagesMuscle Ligaments & TendonsMahnoor JawadNo ratings yet
- T1 Condicion Fisica 4º EsoDocument6 pagesT1 Condicion Fisica 4º EsoMartín Benítez del HoyoNo ratings yet
- Biological Systems and Processes BookletDocument31 pagesBiological Systems and Processes Bookletapi-422428700100% (1)
- Lesson 2 PEDocument3 pagesLesson 2 PEAthena SyierNo ratings yet
- Document 6Document10 pagesDocument 6shivalee.abirajNo ratings yet
- ANAPHYSIODocument2 pagesANAPHYSIOEli AyaseNo ratings yet
- Practical 2 - Muscular system (student)Document13 pagesPractical 2 - Muscular system (student)zoha aslamNo ratings yet
- Reintroduction of Core TrainingDocument3 pagesReintroduction of Core TrainingAjay MacadangdangNo ratings yet
- Muscles of The Human Body PDFDocument13 pagesMuscles of The Human Body PDFPalma, Arrabela M.No ratings yet
- Muscular System - Lesson 19Document17 pagesMuscular System - Lesson 19Gamer0092No ratings yet
- Muscle Fun FactsDocument18 pagesMuscle Fun FactsrimeoznekNo ratings yet
- 9-1 PE Revision GuideDocument27 pages9-1 PE Revision GuideChrisNo ratings yet
- Healthy Hips Handbook: Exercises for Treating and Preventing Common Hip Joint InjuriesFrom EverandHealthy Hips Handbook: Exercises for Treating and Preventing Common Hip Joint InjuriesNo ratings yet
- Tut Sheet7Document2 pagesTut Sheet7Ekta SharmaNo ratings yet
- Anesthetic Consideration in Thyroid SurgeryDocument36 pagesAnesthetic Consideration in Thyroid Surgerymaulina13No ratings yet
- Akira - GA - Intro-To-Coding-Html-CssDocument46 pagesAkira - GA - Intro-To-Coding-Html-CssVinoth JayaprakasamNo ratings yet
- Native Son Essay TopicsDocument7 pagesNative Son Essay TopicsafabioemwNo ratings yet
- Iklan Transtv - Ani, Adel, Vinda - Kelas ADocument9 pagesIklan Transtv - Ani, Adel, Vinda - Kelas ANur JamilaNo ratings yet
- MTCNA Lab Guide INTRA 1st Edition - Id.en PDFDocument87 pagesMTCNA Lab Guide INTRA 1st Edition - Id.en PDFreyandyNo ratings yet
- Free CV Template 31Document1 pageFree CV Template 31Aaron WilsonNo ratings yet
- Uji Chi SquareDocument5 pagesUji Chi Squareeldiya yuliSNo ratings yet
- Biomedx Workshop AgendaDocument6 pagesBiomedx Workshop AgendabiomedxNo ratings yet
- Indu Lagna - For Waelth and FinanceDocument7 pagesIndu Lagna - For Waelth and Financeybbvvprasada raoNo ratings yet
- Gl04 FM Tam 019 FsefDocument4 pagesGl04 FM Tam 019 FsefManish TiwariNo ratings yet
- Remarks:: Republic of The Philippines City of General SantosDocument1 pageRemarks:: Republic of The Philippines City of General SantosThe MatrixNo ratings yet
- Statement of PurposeDocument3 pagesStatement of PurposeehsanNo ratings yet
- Housekeeping Management Practices and Standards of Selected Hotels and Restaurants of Ilocos Sur, PhilippinesDocument8 pagesHousekeeping Management Practices and Standards of Selected Hotels and Restaurants of Ilocos Sur, PhilippinesMehwish FatimaNo ratings yet
- 6068TF250 Engine Performance CurveDocument2 pages6068TF250 Engine Performance CurveJulioNo ratings yet
- OceanofPDF - Com Strictly Research - Terry TowersDocument284 pagesOceanofPDF - Com Strictly Research - Terry TowersKenny SimNo ratings yet
- Anti-Friction Bearings FundamentalsDocument21 pagesAnti-Friction Bearings FundamentalssubrataNo ratings yet
- Wa0004.Document15 pagesWa0004.Sudhir RoyNo ratings yet
- Montessori ObservationsDocument7 pagesMontessori Observationsapi-439426688No ratings yet
- About BITS CmdletsDocument3 pagesAbout BITS CmdletsvashsauNo ratings yet
- Suntrust VeronaDocument12 pagesSuntrust Veronalyanca majanNo ratings yet
- List of TradeMark Forms & Therein PDFDocument17 pagesList of TradeMark Forms & Therein PDFShreeneetRathiNo ratings yet
- Paul CooksDocument4 pagesPaul CooksMicNo ratings yet
- (LN) Orc Eroica - Volume 01 (YP)Document282 pages(LN) Orc Eroica - Volume 01 (YP)FBINo ratings yet
- Partnership in Class Questions 2015Document3 pagesPartnership in Class Questions 2015Nella KingNo ratings yet
- Pentaho CE Vs EE ComparisonDocument4 pagesPentaho CE Vs EE Comparisonbangipool100% (1)
- City Center Unifier Deployment PDFDocument35 pagesCity Center Unifier Deployment PDFSachin PatilNo ratings yet
- Support/downloads or Scan Above QR Code For Detailed Policy WordingDocument10 pagesSupport/downloads or Scan Above QR Code For Detailed Policy Wordingraj VenkateshNo ratings yet