Professional Documents
Culture Documents
83c53c91-1ce9-4c54-bf6a-3330a5f5355f_202307160651228037 (1)
83c53c91-1ce9-4c54-bf6a-3330a5f5355f_202307160651228037 (1)
Uploaded by
rqnzggCopyright:
Available Formats
You might also like
- Hurst's Notes On The Origin and Evolution of Our Garden RosesDocument18 pagesHurst's Notes On The Origin and Evolution of Our Garden RosesAdrian Joel ColombetNo ratings yet
- Lions Mane Ultimate Guide 00Document1 pageLions Mane Ultimate Guide 00János JuhászNo ratings yet
- Atomic Energy Education Society: Handout Class Ix Biology - 6 TISSUES (Module 1)Document6 pagesAtomic Energy Education Society: Handout Class Ix Biology - 6 TISSUES (Module 1)Bhawan malhiNo ratings yet
- Plant Tissues: Class: 7 Board: ICSE Year: 2021-2022Document31 pagesPlant Tissues: Class: 7 Board: ICSE Year: 2021-2022shalu malani100% (1)
- Ix Biology 6 1, PPTDocument35 pagesIx Biology 6 1, PPTShruti TiwariNo ratings yet
- Vnd.openxmlformats Officedocument.presentationml.presentation&Rendition=1Document44 pagesVnd.openxmlformats Officedocument.presentationml.presentation&Rendition=1cricket19710No ratings yet
- Plant Tissue - Study NotesDocument11 pagesPlant Tissue - Study NotesrockyajeetNo ratings yet
- Plant Tissue SystemDocument123 pagesPlant Tissue SystemAnkit Bansal100% (1)
- Plant Tissue - Study NotesDocument10 pagesPlant Tissue - Study Notesjjoshin10No ratings yet
- Plant Cell Type and Its FunctionDocument36 pagesPlant Cell Type and Its Functionlamberto revecheNo ratings yet
- Storage - Emulated - 0 - Whatsapp - Media - WhatsApp Documents - NOTES CLASS 9 TISSUESDocument14 pagesStorage - Emulated - 0 - Whatsapp - Media - WhatsApp Documents - NOTES CLASS 9 TISSUESdubeymaya153No ratings yet
- BIOL223-Lab 10Document60 pagesBIOL223-Lab 10chicken friesNo ratings yet
- Tissues NotesDocument9 pagesTissues NotesPrathiba AugustineNo ratings yet
- Class 9 Plant Tissues Notes - 1, 2022-23Document4 pagesClass 9 Plant Tissues Notes - 1, 2022-23collins thomasNo ratings yet
- TissuesDocument6 pagesTissuessrianshNo ratings yet
- Notes of CH Tissues Class 9Document20 pagesNotes of CH Tissues Class 9PrabhaNo ratings yet
- Tissue 9 PDFDocument5 pagesTissue 9 PDFNilesh NagarNo ratings yet
- Sa Nka LP: Sankalp EducationDocument3 pagesSa Nka LP: Sankalp Educationshalini priyaNo ratings yet
- Tissues - YTDocument94 pagesTissues - YTRaima Sharma100% (3)
- TISSUESDocument9 pagesTISSUEStyrtNo ratings yet
- TISSUES (Prashant Kirad)Document9 pagesTISSUES (Prashant Kirad)abhijotsinghas83No ratings yet
- Asgn 5974128103Document7 pagesAsgn 5974128103rappycatNo ratings yet
- 9tissuesppt 150802072720 Lva1 App6892Document29 pages9tissuesppt 150802072720 Lva1 App6892Vipul GuptaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 6Document49 pagesChapter 6Jidnyasa DambhareNo ratings yet
- Tissues Class Ix NotesDocument19 pagesTissues Class Ix Notesjrheisenberg5No ratings yet
- Notes Plant TissuesDocument7 pagesNotes Plant TissuesHariprasanthNo ratings yet
- MF009 2B Plant Cells Tissues James L2Document12 pagesMF009 2B Plant Cells Tissues James L2Horng Ke GoNo ratings yet
- TissuesDocument13 pagesTissuesAdil Khan100% (1)
- CH 6 Tissues 1Document49 pagesCH 6 Tissues 1srinikamuriki2010No ratings yet
- Biology:: ObjectiveDocument6 pagesBiology:: Objectivesreehaasini kandregulaNo ratings yet
- Chapter-6 Tissues-Full NotesDocument12 pagesChapter-6 Tissues-Full NotesAdithya VinodNo ratings yet
- Plant & Animal TissueDocument39 pagesPlant & Animal TissuePrincess Erbie Austria100% (1)
- BiologyDocument5 pagesBiologysakthilogi123No ratings yet
- Chapter TissuesDocument10 pagesChapter TissuesAarti JainNo ratings yet
- TissueDocument14 pagesTissueBarkha Agrawal100% (1)
- Bio - CH 2 TissuesDocument92 pagesBio - CH 2 TissuesPagli MonkeyNo ratings yet
- Tissues NotesDocument12 pagesTissues NotesNandakeshava KaustubhNo ratings yet
- Tissues 9thDocument15 pagesTissues 9thANKIT RAJNo ratings yet
- (Lecture - 3) Tissue OrganisationDocument38 pages(Lecture - 3) Tissue OrganisationN. W. FlannelNo ratings yet
- Life Sciences Term 2 Content Workshopplant Tissues, Plant OrgansDocument29 pagesLife Sciences Term 2 Content Workshopplant Tissues, Plant Organsonthabiseng mathNo ratings yet
- 2023-01-12-0.08742459605466757Document25 pages2023-01-12-0.08742459605466757loiptoip14No ratings yet
- Miedy Corazon Tabang Sta. Monica High School PhilippinesDocument68 pagesMiedy Corazon Tabang Sta. Monica High School PhilippinesArman Austria100% (1)
- Biology Ls 6Document14 pagesBiology Ls 6KhatrasNo ratings yet
- Tissues - Comprehensive NotesDocument4 pagesTissues - Comprehensive NotesRatheesh HrishikeshNo ratings yet
- TISSUES - Class Notes - SprintDocument40 pagesTISSUES - Class Notes - SprintMr Vinod yadavNo ratings yet
- TissueDocument47 pagesTissuemasuma.bvbvnird21No ratings yet
- L-2 Tissues - 210822Document22 pagesL-2 Tissues - 210822hridaanNo ratings yet
- Edu246 Botany 2Document8 pagesEdu246 Botany 2ANNE MARGUERITE BARETENo ratings yet
- 7.plant TissueDocument3 pages7.plant TissueRAVINDRA PRASADNo ratings yet
- Permanent TissueDocument3 pagesPermanent TissueTECH CORNERNo ratings yet
- Laboratory Activity 5 A Peep at The Simple Plant Tissue: Its Parenchyma, Collenchyma, and SclerenchymaDocument5 pagesLaboratory Activity 5 A Peep at The Simple Plant Tissue: Its Parenchyma, Collenchyma, and SclerenchymaAnnie Lourrie CasabuenaNo ratings yet
- Activity Sheet 1 in General Biology - 02Document4 pagesActivity Sheet 1 in General Biology - 02Julianne Maxine FloresNo ratings yet
- Plant Tissue and Anatomy NotesDocument15 pagesPlant Tissue and Anatomy Noteskhan kashif100% (1)
- TissuesDocument35 pagesTissuesAbhi LiteNo ratings yet
- 9th Biology Chapter Tissue Study NotesDocument6 pages9th Biology Chapter Tissue Study NotesNiharika Nagrath Verma50% (2)
- Tissues Part - 1Document4 pagesTissues Part - 1Monika Mehan100% (2)
- Plant TissueDocument15 pagesPlant TissueTaahirahNo ratings yet
- A Group of Closely Associated Cells That Perform Related Functions and Are Similar in StructureDocument25 pagesA Group of Closely Associated Cells That Perform Related Functions and Are Similar in StructureMichael Pradhan100% (2)
- L2-Tissues-3Simple Permanent Tissues-20.7.21Document20 pagesL2-Tissues-3Simple Permanent Tissues-20.7.21mvsubtitles276No ratings yet
- Simple Permanent TissueDocument9 pagesSimple Permanent Tissueking100% (1)
- Living TissuesDocument18 pagesLiving Tissuesdissanayakeinduwara2008No ratings yet
- Pembuatan Pembersih Lantai Sni 06-1842-1995Document7 pagesPembuatan Pembersih Lantai Sni 06-1842-1995Febrianto DimazNo ratings yet
- Crop Identification and NamesDocument4 pagesCrop Identification and NamesehsanranaNo ratings yet
- Sunflower Sutra Allen Ginsberg: BerkeleyDocument4 pagesSunflower Sutra Allen Ginsberg: BerkeleyAgustín Loaiza SarazaNo ratings yet
- Biology and Cultivation of Black Ear Mushroom - Auricularia SPPDocument4 pagesBiology and Cultivation of Black Ear Mushroom - Auricularia SPPFareed NaufalNo ratings yet
- 2015 - An Ethnobotanical Study of Medicinal Plants of Chungtia VillageDocument13 pages2015 - An Ethnobotanical Study of Medicinal Plants of Chungtia VillageNur FitriantoNo ratings yet
- LESSON 3 - Botany As A ScienceDocument4 pagesLESSON 3 - Botany As A ScienceReuth Thessalonica Dela VictoriaNo ratings yet
- Dent Et Al 2021Document24 pagesDent Et Al 2021Demet BiltekinNo ratings yet
- الاشجار الخشبيهDocument20 pagesالاشجار الخشبيهDriss El BouamraniNo ratings yet
- The Growth and Development in Plants: BiologyDocument27 pagesThe Growth and Development in Plants: BiologyRoland KristoferNo ratings yet
- Bio341 Sum10 Hemp Jute PPDocument21 pagesBio341 Sum10 Hemp Jute PPChristine FransNo ratings yet
- CpSci 101 - MODULE 1 - Lesson 5 and 6 Translocation and AssimilationDocument4 pagesCpSci 101 - MODULE 1 - Lesson 5 and 6 Translocation and AssimilationRegan Roldan RolaNo ratings yet
- Test Papers For Grade 5Document5 pagesTest Papers For Grade 5chandaloka100% (2)
- Brahmastra Test SeriesDocument51 pagesBrahmastra Test SeriesAhkil NandaNo ratings yet
- Arthly Fruit BearingDocument14 pagesArthly Fruit BearingleijuliaNo ratings yet
- To Study The Transverse Section of Clove BudsDocument3 pagesTo Study The Transverse Section of Clove Budspooja arya100% (1)
- Fpu 102Document58 pagesFpu 102Clariss MortejoNo ratings yet
- Pakistan Journal of Botany (Author Guidelines)Document4 pagesPakistan Journal of Botany (Author Guidelines)m.hammad22tNo ratings yet
- Reproduction in Flowering Plants PrintDocument10 pagesReproduction in Flowering Plants PrintSarada KasyapNo ratings yet
- Sexual and Asexual Reproduction of PlantsDocument8 pagesSexual and Asexual Reproduction of Plantskangaro ossyNo ratings yet
- Activity Sheets - First QuarterDocument11 pagesActivity Sheets - First QuarterJohn Alvin YanezNo ratings yet
- wk7-8 - Distinguish How Spore-Bearing and Cone-Bearing Plants ReproduceDocument28 pageswk7-8 - Distinguish How Spore-Bearing and Cone-Bearing Plants ReproduceErnita Corpuz Raymundo100% (2)
- Traditional Food Plants of Baiga TribalDocument4 pagesTraditional Food Plants of Baiga TribalJitesh Kumar MaharanaNo ratings yet
- 5 Ukba Bonsai Handbook Developing Your BonsaiDocument16 pages5 Ukba Bonsai Handbook Developing Your Bonsaiapi-493330869No ratings yet
- Inventario 2020Document10 pagesInventario 2020Sara EliizbethNo ratings yet
- cATALOGFLAVOURS-111945 2Document10 pagescATALOGFLAVOURS-111945 2Alberto Da SilvaNo ratings yet
- Worksheet. 5. Sexual Reproduction in PlantDocument4 pagesWorksheet. 5. Sexual Reproduction in PlantLeonita SwandjajaNo ratings yet
- Nota Biologi (Byrophyta)Document33 pagesNota Biologi (Byrophyta)Muhammad FadhilNo ratings yet
- Cluster Fig Tree: Glimpses of NAL S Flora & FaunaDocument1 pageCluster Fig Tree: Glimpses of NAL S Flora & Faunachoo59No ratings yet
83c53c91-1ce9-4c54-bf6a-3330a5f5355f_202307160651228037 (1)
83c53c91-1ce9-4c54-bf6a-3330a5f5355f_202307160651228037 (1)
Uploaded by
rqnzggCopyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
83c53c91-1ce9-4c54-bf6a-3330a5f5355f_202307160651228037 (1)
83c53c91-1ce9-4c54-bf6a-3330a5f5355f_202307160651228037 (1)
Uploaded by
rqnzggCopyright:
Available Formats
UDGAM SCHOOL FOR CHILDREN
Science [2023-24]
Ch-6: Tissues (Notes)
Name: _____________________ Std. IX / Sec.: _____ Roll No.: _____ Date: _____
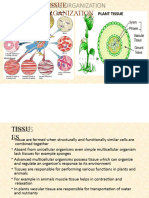
TISSUE: A group of cells that are similar in structure and/or work together to achieve a function is
defined as a tissue.
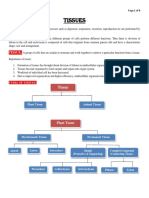
Types of Tissues:
Meristematic tissue: Tissues that are capable of division and are responsible for the
growth of the plants are termed as meristematic tissues.
Permanent tissue: The tissues that have lost the capability to divide and attain permanent
shape, size and perform a certain function are termed as permanent tissues.
FEATURE MERISTEMATIC PERMANENT
Living/dead Cells are living Cells may be living or non-living
Ability of cell Able to divide throughout plant Do not have power of cell division
division life
Arrangement of Compactly arranged May be loosely or compactly arranged
cells
Inter cellular Absent Often present
space
Cell wall Thin, formed of cellulose only May be thin in some tissues but thick in
others
Shape & size Small, spherical, round, oval, Large, they are of different shapes
rectangular, polygonal according to the type of permanent
tissue.
Vacuole Absent/small Large central vacuole is usually present
Cytoplasm Cells are filled with cytoplasm Cytoplasm forms a thin layer between
cell wall and vacuole or may be absent
Nucleus Large and central Small, lies in the peripheral cytoplasm
Location Growing tip of stems and roots, Cortex of roots, below epidermis in
base of node, internode, leaf, stems, hard covering of seeds, nuts, root,
beneath the bark of the tree, stem, leaf of higher plants
vascular bundle
Function Elongation of root and stem, Supporting and conducting tissues,
increase in the length of the protection of internal tissues against
branches, increase in the mechanical injury, prevents desiccation
diameter and girth of the plant of plant.
TYPES OF APICAL INTERCALARY LATERAL
MERISTEMATIC
TISSUE
FUNCTION Elongation Elongation of Increase in the
of root & nodes & thickness of
stem internodes stem & root
Std : 9 / Science / Ch- 6/ notes 2023-24. Page 1 of 9
LOCATION Tips of root Near the node Sides of stem
& stem & root
TYPES OF PERMANENT TISSUES:
SIMPLE PERMANENT COMPLEX PERMANENT
They consist of only one type of cells They consist of more than one type of cells
Cells are similar in structure and perform Different types of cells perform different function
similar function
3 simple tissues- parenchyma, collenchyma, 2 permanent tissues- xylem, phloem
sclerenchyma
Present in soft parts of the plant, between Root, stem, veins of leaves
different tissues, base of leaves and branches,
hard parts of the plant
Packing tissues, storage of food, Transportation of water, minerals and food
photosynthesis, provides buoyancy, flexibility,
mechanical support
SIMPLE PERMANENT TISSUES:
FEATURE PARENCHYMA COLLENCHYMA SCLERENCHYMA
Arrangement Loosely arranged Closely arranged Tightly packed
of cells
Intercellular Large spaces Small spaces Absent
spaces
Shape Oval, polygonal, round Elongated Long, narrow
Cell wall Thin Thick Very thick, hard
Cell wall No thickening, made up Thickened at the corners Cell wall is thickened due
thickening of cellulose due to deposition of to deposition of lignin
pectin
Nucleus Present Present Absent
Living/dead Living tissue Living tissue Dead tissue
Vacuole Single, large Single, large Absent
Cytoplasm Dense Peripheral Absent
Location Soft parts of plant, Base of leaves and Stem, veins of leaves, hard
between different branches covering of seeds, nuts
tissues
Function Packing tissue, storage Flexibility and Mechanical support
of food, buoyancy, mechanical support
photosynthesis
1. Chlorenchyma- Parenchyma that contains chlorophyll and performs photosynthesis.
2. Aerenchyma- Parenchyma that has large air cavities to give buoyancy to the aquatic plants
to help them float.
COMPLEX PERMANENT TISSUES:
XYLEM PHLOEM
Std : 9 / Science / Ch- 6/ notes 2023-24. Page 2 of 9
Transports water and minerals in the plants Transports food in the plants from the leaves to
from the roots to the stem and leaves all the other parts of the plant
Made up of 3 dead components- trachieds, Made up of 3 living components- sieve
vessels, xylem fibres and 1 living component- elements, companion cells, phloem parenchyma
xylem parenchyma and 1 dead component- phloem fibres
Transportation of water and minerals takes Transportation of food takes place from leaves
place only in upward direction through xylem to all directions through phloem
XYLEM COMPONENTS FUNCTIONS
Xylem vessels and tracheids transport water and minerals vertically in the plants
Xylem fibres provide mechanical support
Xylem parenchyma stores food and helps in sideways conduction of
water
PHLOEM COMPONENTS FUNCTIONS
Sieve elements Helps in translocation of food in the plants
(sieve cells, sieve tubes)
Companion cells Helps the sieve tubes to carry out their function
Phloem fibres. Provides mechanical strength to the plant body
Phloem parenchyma Store food materials
BBQ (Page 61)
Ans 2.
Tissues perform multiple functions in the body of multicellular organisms like providing
protection and mechanical strength and facilitating division of labour in the body. Since tissues
carry out only a particular function, they do it very efficiently.
E.g., In humans, muscle cells contract and relax to cause movement. In plants, vascular tissues
(xylem and phloem) conduct water and minerals, food from one part of the plant to another.
BBQ (Page 65)
Ans 3.
The sclerenchyma which is a permanent tissue makes up the husk of coconut.
End Exercise (Page 70)
Ans 5.
a. They allow exchange of gases (CO2 &O2) with the atmosphere.
b. Evaporation of water from the leaf surface occurs through the stomata. It helps in the process
of transpiration.
Ans 13.
a. Cells of the epidermis are water resistant, thus they prevent excess loss of water.
b. It is a protective tissue which protects the plant body against mechanical injury.
c. It allows exchange of gases through stomata.
d. Protection of the underlying cells and tissues.
e. Absorption of water and minerals through epidermis of the root and root hairs.
Ans 14.
Cork cells are dead and compactly arranged without intercellular spaces. They also have a
chemical called ‘suberin’ in their walls that make them impervious to gases and water.
a. Thus they provide strong mechanical strength to plants.
b. It protects the underlying tissues from excess loss of water and adverse external
environment, pathogens/infections.
Additional Question-
Std : 9 / Science / Ch- 6/ notes 2023-24. Page 3 of 9
The aerial parts of the plants have a waxy coating in their epidermis. What is it made up of?
Give its functions.
Ans. It is made up of cutin.
a. It protects the plant from dehydration, mechanical injury and attack of parasites.
b. It prevents wetting of leaves.
c. It prevents loss of water through transpiration.
ANIMAL TISSUES
EPITHELIAL TISSUE AND ITS TYPES
TYPE STRUCTURE LOCATION FUNCTION FIGURE
Simple Extremely thin, Inner lining of 1. Protects the
squamous flat, irregular mouth cavity, underlying parts from
oesophagus, mechanical injury,
blood vessels germs, drying up etc.
and alveoli of 2. Helps in diffusion
lungs of gases and
materials
Stratified Many layers of Skin To prevent wear and
squamous irregularly tear
shaped cells
Cuboidal Cube shaped Lining of kidney 1. Provides
cells, large, tubules, ducts of mechanical support
spherical and salivary glands 2. Helps in secretion
central nuclei and absorption of
substances
Columnar(Pillar Tall pillar like Lines most 1. Absorption of
like) cells, elongated organs of the nutrients through
cells, large, digestive tract intestinal linings.
spherical and including the 2. Secretion of
nuclei at the stomach, small substances.
base of the cell intestine and
large intestine,
uterus
Ciliated Elongated cells, Inner lining of The lashing
columnar large, spherical nasal cavity, movement of cilia
and nuclei at oviduct or helps to move the
the base of the fallopian tube substances in a
cell, tiny hair direction.
like structure
called cilia on
the outer
surface
Std : 9 / Science / Ch- 6/ notes 2023-24. Page 4 of 9
Glandular Some epithelial Forms the The gland cells
tissues fold covering of all secrete several
inward and their major glands substances
cells change like salivary
shape and glands (saliva),
function and sweat glands
form glands (sweat), testes
which are and ovaries
clusters of cells (hormones),
that are digestive glands
specialized to (enzymes)
secrete
substances
Std : 9 / Science / Ch- 6/ notes 2023-24. Page 5 of 9
Connective Tissues
Characteristics Blood Bone (rigid, non-flexible tissue) Tendon Ligament
Matrix Fluid matrix (Plasma- contains Tough, hard matrix of calcium Soft matrix Soft gel like matrix
proteins, salts & hormones) phosphate
Fibres(in matrix) No fibres Collagen Collagen Collagen
Cells Red Blood Corpuscles(Erythrocytes) Osteoblast, Osteocytes Tenocytes Fibrocytes
White Blood Corpuscle (Leukocytes)
Platelets (Thrombocytes)
Location Blood vessels- arteries, veins, Forms the internal skeleton Attach muscle to Attach bone to
capillaries bone bone
Function It transports gases, digested food, 1. It forms the framework that Helps to move the Helps in musculo-
hormones and waste materials to supports the body. bone skeletal
different parts of the body. 2. It anchors the muscles and movements
R.B.C. - supply of O2 to tissues supports the main organs of the
which bounds to hemoglobin. body.
W.B.C.- kill microbes by producing 3. Bones like skull and rib cage
antibodies protect internal organs from injury.
Platelets- help in clotting of blood
Image
Connective Tissues
Std : 9 / Science / Ch- 6/ notes 2023-24. Page 6 of 9
Characteristics Cartilage (not as hard & rigid as Areolar Adipose
bone, flexible tissue)
Matrix Firm and strong, matrix of proteins Gelatinous matrix Jelly like matrix
and sugars
Fibres(in matrix) Collagen, elastin Collagen, elastin Few fibres (collagen)
Cells Chondrocytes Plasma cells, fibroblast, Adipocytes (large, oval, contain fat)
macrophage, mast cells
Location Ear pinna, nose tip, nasal septum, Between skin and muscles, around Below the skin, between internal
epiglottis, rings of trachea, ends of blood vessels and nerves and in organs, in bone marrow
long bones at the joints bone marrow
Function 1. It works like a cushion in the 1. It fills the space inside the organs. 1. It is a fat storing tissue, so it
joints and prevents rubbing of provides energy during starvation or
2. Supports internal organs
bones against each other. physical exertion.
3. Helps in repair of tissues
2. It provides flexibility to body 2. Provides insulation (prevents the
parts and prevents damage from 4. Kills the bacteria and viruses that body from becoming cold)
mechanical injury. enter the body
Image
Std : 9 / Science / Ch- 6/ notes 2023-24. Page 7 of 9
MUSCULAR TISSUE AND THEIR TYPES
CHARACTERISTICS STRIATED/ UNSTRIATED/ CARDIAC
SKELETAL SMOOTH
Shape Long, cylindrical, Long, spindle shaped, Short, cylindrical,
unbranched fibres tapering ends branched fibres
No. of Nuclei Multinucleate Uninucleate Uninucleate
Position Of Nuclei Peripheral Central Central
Appearance Under Alternate dark and No transverse bands Fine criss-cross
Microscope light transverse striations
bands
Type Of Control Voluntary, get Involuntary Involuntary
fatigued very soon
Location Hands and legs, Walls of stomach, intestine, Walls of heart
face, neck, tongue, iris of eye, bronchi of lungs,
diaphragm ureters, urinary bladder
Function Voluntary Peristaltic movement in the Rhythmic contraction
movements of body, wall of alimentary canal and and relaxation of the
responsible for help to push the food down, heart muscles help to
locomotion, tongue Produce fast contractions pump blood and
movement. and help to remove distribute it to the
contents of organs like different parts of the
ureters, urinary bladder, body.
uterus etc.
Figure
Muscles contain special proteins called contractile proteins (actin, myosin) which contract and
relax to cause movement.
NERVOUS TISSUE (REFER FIG. 6.12, Pg. 69 FROM TEXTBOOK)
The cells of this tissue are called nerve cells/neurons. The brain, spinal cord and nerves are all
composed of the nervous tissue.
The cell body or cyton, is the spherical part of the neuron that contains the nucleus and
cytoplasm. Dendrons are short hair like extensions arising from the cyton. Dendrons further
branch into thin dendrites and carry nerve impulses to the cyton. Axon is a large branch that
arises from the cyton of a nerve cell. It carries nerve impulse from the cyton and passes on
further.
Function- It controls the body’s movements, sends and carries signals to and from the different
parts of the body to the brain and spinal cord and plays an important role in controlling bodily
functions.
BBQ (Page 69)
Std : 9 / Science / Ch- 6/ notes 2023-24. Page 8 of 9
Ans 1.
Muscular tissue and Nervous tissue are jointly responsible for the movement in our body.
End Exercise (Page 70)
Ans 10.
(a) Tissue that forms the inner lining of our mouth – The epithelial tissue, Squamous epithelium.
(b) Tissue that connects muscle to bone in humans – Tendon
(c) Tissue that transports food in plants – Phloem
(d) Tissue that stores fat in our body – Adipose tissue
(e) Connective tissue with a fluid matrix – Blood, it is a fluid connective tissue
(f) Tissue present in the brain – Nervous tissue
Std : 9 / Science / Ch- 6/ notes 2023-24. Page 9 of 9
You might also like
- Hurst's Notes On The Origin and Evolution of Our Garden RosesDocument18 pagesHurst's Notes On The Origin and Evolution of Our Garden RosesAdrian Joel ColombetNo ratings yet
- Lions Mane Ultimate Guide 00Document1 pageLions Mane Ultimate Guide 00János JuhászNo ratings yet
- Atomic Energy Education Society: Handout Class Ix Biology - 6 TISSUES (Module 1)Document6 pagesAtomic Energy Education Society: Handout Class Ix Biology - 6 TISSUES (Module 1)Bhawan malhiNo ratings yet
- Plant Tissues: Class: 7 Board: ICSE Year: 2021-2022Document31 pagesPlant Tissues: Class: 7 Board: ICSE Year: 2021-2022shalu malani100% (1)
- Ix Biology 6 1, PPTDocument35 pagesIx Biology 6 1, PPTShruti TiwariNo ratings yet
- Vnd.openxmlformats Officedocument.presentationml.presentation&Rendition=1Document44 pagesVnd.openxmlformats Officedocument.presentationml.presentation&Rendition=1cricket19710No ratings yet
- Plant Tissue - Study NotesDocument11 pagesPlant Tissue - Study NotesrockyajeetNo ratings yet
- Plant Tissue SystemDocument123 pagesPlant Tissue SystemAnkit Bansal100% (1)
- Plant Tissue - Study NotesDocument10 pagesPlant Tissue - Study Notesjjoshin10No ratings yet
- Plant Cell Type and Its FunctionDocument36 pagesPlant Cell Type and Its Functionlamberto revecheNo ratings yet
- Storage - Emulated - 0 - Whatsapp - Media - WhatsApp Documents - NOTES CLASS 9 TISSUESDocument14 pagesStorage - Emulated - 0 - Whatsapp - Media - WhatsApp Documents - NOTES CLASS 9 TISSUESdubeymaya153No ratings yet
- BIOL223-Lab 10Document60 pagesBIOL223-Lab 10chicken friesNo ratings yet
- Tissues NotesDocument9 pagesTissues NotesPrathiba AugustineNo ratings yet
- Class 9 Plant Tissues Notes - 1, 2022-23Document4 pagesClass 9 Plant Tissues Notes - 1, 2022-23collins thomasNo ratings yet
- TissuesDocument6 pagesTissuessrianshNo ratings yet
- Notes of CH Tissues Class 9Document20 pagesNotes of CH Tissues Class 9PrabhaNo ratings yet
- Tissue 9 PDFDocument5 pagesTissue 9 PDFNilesh NagarNo ratings yet
- Sa Nka LP: Sankalp EducationDocument3 pagesSa Nka LP: Sankalp Educationshalini priyaNo ratings yet
- Tissues - YTDocument94 pagesTissues - YTRaima Sharma100% (3)
- TISSUESDocument9 pagesTISSUEStyrtNo ratings yet
- TISSUES (Prashant Kirad)Document9 pagesTISSUES (Prashant Kirad)abhijotsinghas83No ratings yet
- Asgn 5974128103Document7 pagesAsgn 5974128103rappycatNo ratings yet
- 9tissuesppt 150802072720 Lva1 App6892Document29 pages9tissuesppt 150802072720 Lva1 App6892Vipul GuptaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 6Document49 pagesChapter 6Jidnyasa DambhareNo ratings yet
- Tissues Class Ix NotesDocument19 pagesTissues Class Ix Notesjrheisenberg5No ratings yet
- Notes Plant TissuesDocument7 pagesNotes Plant TissuesHariprasanthNo ratings yet
- MF009 2B Plant Cells Tissues James L2Document12 pagesMF009 2B Plant Cells Tissues James L2Horng Ke GoNo ratings yet
- TissuesDocument13 pagesTissuesAdil Khan100% (1)
- CH 6 Tissues 1Document49 pagesCH 6 Tissues 1srinikamuriki2010No ratings yet
- Biology:: ObjectiveDocument6 pagesBiology:: Objectivesreehaasini kandregulaNo ratings yet
- Chapter-6 Tissues-Full NotesDocument12 pagesChapter-6 Tissues-Full NotesAdithya VinodNo ratings yet
- Plant & Animal TissueDocument39 pagesPlant & Animal TissuePrincess Erbie Austria100% (1)
- BiologyDocument5 pagesBiologysakthilogi123No ratings yet
- Chapter TissuesDocument10 pagesChapter TissuesAarti JainNo ratings yet
- TissueDocument14 pagesTissueBarkha Agrawal100% (1)
- Bio - CH 2 TissuesDocument92 pagesBio - CH 2 TissuesPagli MonkeyNo ratings yet
- Tissues NotesDocument12 pagesTissues NotesNandakeshava KaustubhNo ratings yet
- Tissues 9thDocument15 pagesTissues 9thANKIT RAJNo ratings yet
- (Lecture - 3) Tissue OrganisationDocument38 pages(Lecture - 3) Tissue OrganisationN. W. FlannelNo ratings yet
- Life Sciences Term 2 Content Workshopplant Tissues, Plant OrgansDocument29 pagesLife Sciences Term 2 Content Workshopplant Tissues, Plant Organsonthabiseng mathNo ratings yet
- 2023-01-12-0.08742459605466757Document25 pages2023-01-12-0.08742459605466757loiptoip14No ratings yet
- Miedy Corazon Tabang Sta. Monica High School PhilippinesDocument68 pagesMiedy Corazon Tabang Sta. Monica High School PhilippinesArman Austria100% (1)
- Biology Ls 6Document14 pagesBiology Ls 6KhatrasNo ratings yet
- Tissues - Comprehensive NotesDocument4 pagesTissues - Comprehensive NotesRatheesh HrishikeshNo ratings yet
- TISSUES - Class Notes - SprintDocument40 pagesTISSUES - Class Notes - SprintMr Vinod yadavNo ratings yet
- TissueDocument47 pagesTissuemasuma.bvbvnird21No ratings yet
- L-2 Tissues - 210822Document22 pagesL-2 Tissues - 210822hridaanNo ratings yet
- Edu246 Botany 2Document8 pagesEdu246 Botany 2ANNE MARGUERITE BARETENo ratings yet
- 7.plant TissueDocument3 pages7.plant TissueRAVINDRA PRASADNo ratings yet
- Permanent TissueDocument3 pagesPermanent TissueTECH CORNERNo ratings yet
- Laboratory Activity 5 A Peep at The Simple Plant Tissue: Its Parenchyma, Collenchyma, and SclerenchymaDocument5 pagesLaboratory Activity 5 A Peep at The Simple Plant Tissue: Its Parenchyma, Collenchyma, and SclerenchymaAnnie Lourrie CasabuenaNo ratings yet
- Activity Sheet 1 in General Biology - 02Document4 pagesActivity Sheet 1 in General Biology - 02Julianne Maxine FloresNo ratings yet
- Plant Tissue and Anatomy NotesDocument15 pagesPlant Tissue and Anatomy Noteskhan kashif100% (1)
- TissuesDocument35 pagesTissuesAbhi LiteNo ratings yet
- 9th Biology Chapter Tissue Study NotesDocument6 pages9th Biology Chapter Tissue Study NotesNiharika Nagrath Verma50% (2)
- Tissues Part - 1Document4 pagesTissues Part - 1Monika Mehan100% (2)
- Plant TissueDocument15 pagesPlant TissueTaahirahNo ratings yet
- A Group of Closely Associated Cells That Perform Related Functions and Are Similar in StructureDocument25 pagesA Group of Closely Associated Cells That Perform Related Functions and Are Similar in StructureMichael Pradhan100% (2)
- L2-Tissues-3Simple Permanent Tissues-20.7.21Document20 pagesL2-Tissues-3Simple Permanent Tissues-20.7.21mvsubtitles276No ratings yet
- Simple Permanent TissueDocument9 pagesSimple Permanent Tissueking100% (1)
- Living TissuesDocument18 pagesLiving Tissuesdissanayakeinduwara2008No ratings yet
- Pembuatan Pembersih Lantai Sni 06-1842-1995Document7 pagesPembuatan Pembersih Lantai Sni 06-1842-1995Febrianto DimazNo ratings yet
- Crop Identification and NamesDocument4 pagesCrop Identification and NamesehsanranaNo ratings yet
- Sunflower Sutra Allen Ginsberg: BerkeleyDocument4 pagesSunflower Sutra Allen Ginsberg: BerkeleyAgustín Loaiza SarazaNo ratings yet
- Biology and Cultivation of Black Ear Mushroom - Auricularia SPPDocument4 pagesBiology and Cultivation of Black Ear Mushroom - Auricularia SPPFareed NaufalNo ratings yet
- 2015 - An Ethnobotanical Study of Medicinal Plants of Chungtia VillageDocument13 pages2015 - An Ethnobotanical Study of Medicinal Plants of Chungtia VillageNur FitriantoNo ratings yet
- LESSON 3 - Botany As A ScienceDocument4 pagesLESSON 3 - Botany As A ScienceReuth Thessalonica Dela VictoriaNo ratings yet
- Dent Et Al 2021Document24 pagesDent Et Al 2021Demet BiltekinNo ratings yet
- الاشجار الخشبيهDocument20 pagesالاشجار الخشبيهDriss El BouamraniNo ratings yet
- The Growth and Development in Plants: BiologyDocument27 pagesThe Growth and Development in Plants: BiologyRoland KristoferNo ratings yet
- Bio341 Sum10 Hemp Jute PPDocument21 pagesBio341 Sum10 Hemp Jute PPChristine FransNo ratings yet
- CpSci 101 - MODULE 1 - Lesson 5 and 6 Translocation and AssimilationDocument4 pagesCpSci 101 - MODULE 1 - Lesson 5 and 6 Translocation and AssimilationRegan Roldan RolaNo ratings yet
- Test Papers For Grade 5Document5 pagesTest Papers For Grade 5chandaloka100% (2)
- Brahmastra Test SeriesDocument51 pagesBrahmastra Test SeriesAhkil NandaNo ratings yet
- Arthly Fruit BearingDocument14 pagesArthly Fruit BearingleijuliaNo ratings yet
- To Study The Transverse Section of Clove BudsDocument3 pagesTo Study The Transverse Section of Clove Budspooja arya100% (1)
- Fpu 102Document58 pagesFpu 102Clariss MortejoNo ratings yet
- Pakistan Journal of Botany (Author Guidelines)Document4 pagesPakistan Journal of Botany (Author Guidelines)m.hammad22tNo ratings yet
- Reproduction in Flowering Plants PrintDocument10 pagesReproduction in Flowering Plants PrintSarada KasyapNo ratings yet
- Sexual and Asexual Reproduction of PlantsDocument8 pagesSexual and Asexual Reproduction of Plantskangaro ossyNo ratings yet
- Activity Sheets - First QuarterDocument11 pagesActivity Sheets - First QuarterJohn Alvin YanezNo ratings yet
- wk7-8 - Distinguish How Spore-Bearing and Cone-Bearing Plants ReproduceDocument28 pageswk7-8 - Distinguish How Spore-Bearing and Cone-Bearing Plants ReproduceErnita Corpuz Raymundo100% (2)
- Traditional Food Plants of Baiga TribalDocument4 pagesTraditional Food Plants of Baiga TribalJitesh Kumar MaharanaNo ratings yet
- 5 Ukba Bonsai Handbook Developing Your BonsaiDocument16 pages5 Ukba Bonsai Handbook Developing Your Bonsaiapi-493330869No ratings yet
- Inventario 2020Document10 pagesInventario 2020Sara EliizbethNo ratings yet
- cATALOGFLAVOURS-111945 2Document10 pagescATALOGFLAVOURS-111945 2Alberto Da SilvaNo ratings yet
- Worksheet. 5. Sexual Reproduction in PlantDocument4 pagesWorksheet. 5. Sexual Reproduction in PlantLeonita SwandjajaNo ratings yet
- Nota Biologi (Byrophyta)Document33 pagesNota Biologi (Byrophyta)Muhammad FadhilNo ratings yet
- Cluster Fig Tree: Glimpses of NAL S Flora & FaunaDocument1 pageCluster Fig Tree: Glimpses of NAL S Flora & Faunachoo59No ratings yet