Professional Documents
Culture Documents
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
2 views2 Renal Tubular Function
2 Renal Tubular Function
Uploaded by
Its FlorenceMap for renal tubular function
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You might also like
- AUBF Case StudyDocument35 pagesAUBF Case StudyAlecs Elinor Amoguis100% (3)
- Classification of DiureticDocument3 pagesClassification of DiureticJanice Malafu De GuiaNo ratings yet
- Teste de Linguas UfpaDocument57 pagesTeste de Linguas Ufpanatale_carvalho100% (1)
- 1b, Amurao, Richmond A., SGD 1-Renal 1Document2 pages1b, Amurao, Richmond A., SGD 1-Renal 1Dr. RemedyNo ratings yet
- Anatomy 1Document1 pageAnatomy 1Jenna LynnNo ratings yet
- ANPH Wk14 - Urinary SystemDocument10 pagesANPH Wk14 - Urinary SystemSin I GangNo ratings yet
- Anatomy of Excretory System, NephronDocument10 pagesAnatomy of Excretory System, NephronPaulína PalčinskáNo ratings yet
- Anatomy of Excretory System, NephronDocument10 pagesAnatomy of Excretory System, Nephronlulu.borsikovaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 25 - Urinary System - Class OutlineDocument22 pagesChapter 25 - Urinary System - Class Outlinestupidisg00gleofcourseNo ratings yet
- Lecture 21Document23 pagesLecture 21sara shloulNo ratings yet
- Excretion 1Document7 pagesExcretion 1swinky.dsNo ratings yet
- L8-Urine Conc.Document15 pagesL8-Urine Conc.Bryn MasvaureNo ratings yet
- 1 Renal FunctionDocument5 pages1 Renal FunctionChristopher BucuNo ratings yet
- From The Capillaries Into The Capsule ThroughDocument3 pagesFrom The Capillaries Into The Capsule ThroughRashid DayaoNo ratings yet
- Urinary Lab OnlineDocument25 pagesUrinary Lab OnlineretterateNo ratings yet
- AUBFDocument8 pagesAUBFIssha CasañasNo ratings yet
- L5 - 6 - Renal Reabsorbation and SecretationDocument21 pagesL5 - 6 - Renal Reabsorbation and SecretationBryn MasvaureNo ratings yet
- Excretory Products and Its EliminationDocument2 pagesExcretory Products and Its Eliminationmariamfernandes6No ratings yet
- Uia 09 PHYSIOLOGY OF THE KIDNEYDocument5 pagesUia 09 PHYSIOLOGY OF THE KIDNEYIbrahim QariNo ratings yet
- Applied Renal PhysiologyDocument18 pagesApplied Renal PhysiologyDamián ContrerasNo ratings yet
- Urinary SysDocument3 pagesUrinary SysMario Antonio CarpioNo ratings yet
- Topic 2 Aubf Renal Function PDFDocument5 pagesTopic 2 Aubf Renal Function PDFBanana QNo ratings yet
- Excretory Products N Their Elimination NotesDocument4 pagesExcretory Products N Their Elimination Notescoolakshat3664No ratings yet
- Urinary SystemDocument7 pagesUrinary SystemFjhvbhhNo ratings yet
- Topic Outline: PlasmaDocument3 pagesTopic Outline: PlasmaChristian AlacarNo ratings yet
- Cell Membrane Homeostasis Because It Controls What EntersDocument9 pagesCell Membrane Homeostasis Because It Controls What Enterseli bermiNo ratings yet
- Urinary SystemDocument6 pagesUrinary Systemshane.surigaoNo ratings yet
- ANAT 1053 Unit 6 Urinary System Prof Slides Fall 2021Document58 pagesANAT 1053 Unit 6 Urinary System Prof Slides Fall 2021abextekNo ratings yet
- Absorption & Transocation of Water &?? Dissolved Minerals in Plant SystemDocument3 pagesAbsorption & Transocation of Water &?? Dissolved Minerals in Plant SystemNUR'AIN BINTI AZHAR / UPMNo ratings yet
- REN Revision LectureDocument43 pagesREN Revision Lecturegyamfi.rolandNo ratings yet
- Osmoregulation AP MineDocument28 pagesOsmoregulation AP MineMaureen GabrielleNo ratings yet
- Renal Physiology Handout 2 Slides Per Page PDFDocument37 pagesRenal Physiology Handout 2 Slides Per Page PDFmike hunt100% (1)
- Osmotic Regulation and ExcretionDocument46 pagesOsmotic Regulation and ExcretionKhent SyNo ratings yet
- 25.6 Tubular Reabsorption - Anatomy and Physiology 2e - OpenStaxDocument12 pages25.6 Tubular Reabsorption - Anatomy and Physiology 2e - OpenStaxMarlene AngwaforNo ratings yet
- Anatomy of The Urinary System Pre LabDocument15 pagesAnatomy of The Urinary System Pre LabbobbyNo ratings yet
- Renal AnatomyDocument13 pagesRenal AnatomyApril Lady Faith P. PaundogNo ratings yet
- Renal Physiology GDocument42 pagesRenal Physiology Gayekani561No ratings yet
- Reabsorption & SecreDocument1 pageReabsorption & SecreMowlidAbdirahman Ali madaaleNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3 ReveiwerDocument8 pagesChapter 3 ReveiwerrizzamaegomezoctavianoNo ratings yet
- Urinary SystemDocument10 pagesUrinary SystemAly HannahNo ratings yet
- Chapter 18: Urinary System and Fluid Balance: TH RDDocument3 pagesChapter 18: Urinary System and Fluid Balance: TH RDPrecious Faith RodriguezNo ratings yet
- 4th Shift - HistoDocument24 pages4th Shift - HistoVeronica MagpocNo ratings yet
- FS1 R KR7 OMu 7 VZFPL B13 XDocument4 pagesFS1 R KR7 OMu 7 VZFPL B13 Xaadeshthite476No ratings yet
- Renal Function AubfDocument11 pagesRenal Function AubfHANNA CASANDRA GARCIANo ratings yet
- Reviewer Bio q2Document5 pagesReviewer Bio q2Aviel BuenoNo ratings yet
- Renal Physiology PDFDocument12 pagesRenal Physiology PDFLolitaNo ratings yet
- Manejo Tubular de SolutosDocument4 pagesManejo Tubular de SolutosAnghelussNo ratings yet
- Renal Anatomy and Physiology - Notes - GnvEriDocument3 pagesRenal Anatomy and Physiology - Notes - GnvEriEricka GenoveNo ratings yet
- Electrolyte and Fluid Losses in Diarrhoeal Illness2023Document49 pagesElectrolyte and Fluid Losses in Diarrhoeal Illness2023Sibabalwe DlovasheNo ratings yet
- Peperoism: PhotosynthesisDocument6 pagesPeperoism: PhotosynthesisanneNo ratings yet
- Urinary SystemDocument9 pagesUrinary SystemPrincess OrsinoNo ratings yet
- Cell TransportDocument7 pagesCell Transportako parin itoNo ratings yet
- Renal Medulla: BloodDocument4 pagesRenal Medulla: BloodLindsay GabrielNo ratings yet
- AUBF - Lec Chapter 3 4 5 COMPLETE - Transes 1Document18 pagesAUBF - Lec Chapter 3 4 5 COMPLETE - Transes 1Princess Eve OlowanNo ratings yet
- The KidneyDocument1 pageThe KidneyMushu MunuNo ratings yet
- (Week 16) Urinary SystemDocument3 pages(Week 16) Urinary SystemDiana Leen Dela CruzNo ratings yet
- Renal System 6 1Document30 pagesRenal System 6 1gaurav singhNo ratings yet
- Basic Dialysis Theory SweenyDocument28 pagesBasic Dialysis Theory SweenyAmmar YasserNo ratings yet
- Urine Formation: Yousaf Khan Renal Dialysis LecturerDocument30 pagesUrine Formation: Yousaf Khan Renal Dialysis LecturerSalman KhanNo ratings yet
- Ncert Explanation Deep With ExamplesDocument10 pagesNcert Explanation Deep With ExamplesasterclixNo ratings yet
- Nefrotik Sindrom: A Three-Layer StructureDocument5 pagesNefrotik Sindrom: A Three-Layer StructurepradaniNo ratings yet
- Sakhanokho 2018Document6 pagesSakhanokho 2018AlexNo ratings yet
- Targeted Disruption of The GlucocorticoidDocument15 pagesTargeted Disruption of The GlucocorticoidSyifa SariNo ratings yet
- Essentials of Pharmacology For Health Professions 7th Edition Woodrow Test BankDocument25 pagesEssentials of Pharmacology For Health Professions 7th Edition Woodrow Test BankNormanDanielsyftz100% (54)
- BKK Hospital Medical CertificateDocument12 pagesBKK Hospital Medical CertificateWinThant KhineNo ratings yet
- Fibre ExtractionDocument40 pagesFibre ExtractionUzoma EmekaNo ratings yet
- Chapter-2 Taxonomic AidsDocument12 pagesChapter-2 Taxonomic AidsNandini Classes,City Light ,Surat. Cell (9429090525No ratings yet
- Agrobacterium Protocols - Volume 2. 2-Humana Press (2014)Document395 pagesAgrobacterium Protocols - Volume 2. 2-Humana Press (2014)Maritza Matteo100% (1)
- Human Development and Growth Notes For Mids (2nd Semester)Document4 pagesHuman Development and Growth Notes For Mids (2nd Semester)Ambreen TahirNo ratings yet
- Lipids NotesDocument5 pagesLipids NotesnofacejackNo ratings yet
- Microplastics in The OceanDocument98 pagesMicroplastics in The OceanDevika Hemalatha DeviNo ratings yet
- PREBOARD Gen Ed 1Document16 pagesPREBOARD Gen Ed 1Janice Mayola Alcorin100% (1)
- Pentraxin-3 in Chronic Heart Failure: The CORONA and GISSI-HF TrialsDocument8 pagesPentraxin-3 in Chronic Heart Failure: The CORONA and GISSI-HF TrialscamiloNo ratings yet
- The World's Flora and FaunaDocument8 pagesThe World's Flora and Faunakleberviteri120No ratings yet
- Gram-Negative Bacteria - Wikipedia, The Free EncyclopediaDocument8 pagesGram-Negative Bacteria - Wikipedia, The Free EncyclopediaNadiya AfifahNo ratings yet
- (PROJECT) RHINO - Rhinoceros Facts For Kids - StudyDocument15 pages(PROJECT) RHINO - Rhinoceros Facts For Kids - StudyIan FlackNo ratings yet
- Life Science Class X V2Document159 pagesLife Science Class X V2Surya Narayan DasNo ratings yet
- NG ModulesDocument47 pagesNG Moduleshybri8No ratings yet
- Earth and Life Science: Quarter 2 - Module 21: Evolving Concept of Life Based On Emerging Pieces of EvidenceDocument235 pagesEarth and Life Science: Quarter 2 - Module 21: Evolving Concept of Life Based On Emerging Pieces of EvidenceArenz CudalNo ratings yet
- Typo-Morphological Approach To Transforming An Urban FabricDocument5 pagesTypo-Morphological Approach To Transforming An Urban FabricSatrio Suryana PrasetyaNo ratings yet
- ESS - Topic 3.2Document30 pagesESS - Topic 3.2Pol Ayra FuenteNo ratings yet
- Reparation, Characterization, and Optimization of Microemulsion For Topical Delivery of ItraconazoleDocument10 pagesReparation, Characterization, and Optimization of Microemulsion For Topical Delivery of ItraconazoleVeni UNNo ratings yet
- PBL MCDDocument15 pagesPBL MCDMustafaNo ratings yet
- The Flowers of Ilex GuayusaDocument7 pagesThe Flowers of Ilex GuayusaGabriela Barriga CoronelNo ratings yet
- Unit 11 National Parks Practice Grade 10Document18 pagesUnit 11 National Parks Practice Grade 10An AnNo ratings yet
- The Impact of Shock Wave Therapy at VariDocument9 pagesThe Impact of Shock Wave Therapy at VariArifSurtonoNo ratings yet
- Apps - Xxns Adp Commission Payroll VDocument9 pagesApps - Xxns Adp Commission Payroll VKishan KaranamNo ratings yet
- The Implications of Vitamin D Status During Pregnancy On Mother and Her Developing ChildDocument11 pagesThe Implications of Vitamin D Status During Pregnancy On Mother and Her Developing ChildindahNo ratings yet
- Nouradini PDFDocument15 pagesNouradini PDFDavi AhmadNo ratings yet
2 Renal Tubular Function
2 Renal Tubular Function
Uploaded by
Its Florence0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
2 views1 pageMap for renal tubular function
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentMap for renal tubular function
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pdf or txt
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
2 views1 page2 Renal Tubular Function
2 Renal Tubular Function
Uploaded by
Its FlorenceMap for renal tubular function
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pdf or txt
You are on page 1of 1
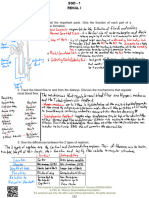
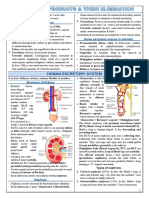
-Na+ and Cl- efflux from thick ascending limb makes interstitium Hypotonic/osmolar - less strong than
hyperosmolar Isotonic/osmolar - equally as strong as
so water drawn out of descending limb - inside of tube more conc. > Hypertonic/osmolar - more strong than
-More Na+ and Cl- diffuse out of thin ascending limb and in thick
ascending limb which makes remaining fluid hypoosmolar Two types of nephron:
- Cortical (majority) - glomeruli in outer cortex, short loop of Henle
- Juxtamedullary - long loop of Henle
Nephron tubule lined with epithelial cells which
separates filtrate in the lumen from interstitial
space
Ht secretion and bicarbonate reabsorption in the proximal tubule
Renal tubular
Threshold usually 7-13 mmo1/L
function
r
Reabsorption and secretion
Fluid that leaves is isotonic ←
Columnar epithelial cells
Nephron function:
At
- Reabsorption of solutes e.g. glucose
- Some substances secreted into it e.g. waste
- Regulation of urine vol. ~ double body weight
Glucose and amino acid reabsorption in proximal tubule
Thin descending and ascending loop of
Henle
→ Generating conc. gradient
You might also like
- AUBF Case StudyDocument35 pagesAUBF Case StudyAlecs Elinor Amoguis100% (3)
- Classification of DiureticDocument3 pagesClassification of DiureticJanice Malafu De GuiaNo ratings yet
- Teste de Linguas UfpaDocument57 pagesTeste de Linguas Ufpanatale_carvalho100% (1)
- 1b, Amurao, Richmond A., SGD 1-Renal 1Document2 pages1b, Amurao, Richmond A., SGD 1-Renal 1Dr. RemedyNo ratings yet
- Anatomy 1Document1 pageAnatomy 1Jenna LynnNo ratings yet
- ANPH Wk14 - Urinary SystemDocument10 pagesANPH Wk14 - Urinary SystemSin I GangNo ratings yet
- Anatomy of Excretory System, NephronDocument10 pagesAnatomy of Excretory System, NephronPaulína PalčinskáNo ratings yet
- Anatomy of Excretory System, NephronDocument10 pagesAnatomy of Excretory System, Nephronlulu.borsikovaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 25 - Urinary System - Class OutlineDocument22 pagesChapter 25 - Urinary System - Class Outlinestupidisg00gleofcourseNo ratings yet
- Lecture 21Document23 pagesLecture 21sara shloulNo ratings yet
- Excretion 1Document7 pagesExcretion 1swinky.dsNo ratings yet
- L8-Urine Conc.Document15 pagesL8-Urine Conc.Bryn MasvaureNo ratings yet
- 1 Renal FunctionDocument5 pages1 Renal FunctionChristopher BucuNo ratings yet
- From The Capillaries Into The Capsule ThroughDocument3 pagesFrom The Capillaries Into The Capsule ThroughRashid DayaoNo ratings yet
- Urinary Lab OnlineDocument25 pagesUrinary Lab OnlineretterateNo ratings yet
- AUBFDocument8 pagesAUBFIssha CasañasNo ratings yet
- L5 - 6 - Renal Reabsorbation and SecretationDocument21 pagesL5 - 6 - Renal Reabsorbation and SecretationBryn MasvaureNo ratings yet
- Excretory Products and Its EliminationDocument2 pagesExcretory Products and Its Eliminationmariamfernandes6No ratings yet
- Uia 09 PHYSIOLOGY OF THE KIDNEYDocument5 pagesUia 09 PHYSIOLOGY OF THE KIDNEYIbrahim QariNo ratings yet
- Applied Renal PhysiologyDocument18 pagesApplied Renal PhysiologyDamián ContrerasNo ratings yet
- Urinary SysDocument3 pagesUrinary SysMario Antonio CarpioNo ratings yet
- Topic 2 Aubf Renal Function PDFDocument5 pagesTopic 2 Aubf Renal Function PDFBanana QNo ratings yet
- Excretory Products N Their Elimination NotesDocument4 pagesExcretory Products N Their Elimination Notescoolakshat3664No ratings yet
- Urinary SystemDocument7 pagesUrinary SystemFjhvbhhNo ratings yet
- Topic Outline: PlasmaDocument3 pagesTopic Outline: PlasmaChristian AlacarNo ratings yet
- Cell Membrane Homeostasis Because It Controls What EntersDocument9 pagesCell Membrane Homeostasis Because It Controls What Enterseli bermiNo ratings yet
- Urinary SystemDocument6 pagesUrinary Systemshane.surigaoNo ratings yet
- ANAT 1053 Unit 6 Urinary System Prof Slides Fall 2021Document58 pagesANAT 1053 Unit 6 Urinary System Prof Slides Fall 2021abextekNo ratings yet
- Absorption & Transocation of Water &?? Dissolved Minerals in Plant SystemDocument3 pagesAbsorption & Transocation of Water &?? Dissolved Minerals in Plant SystemNUR'AIN BINTI AZHAR / UPMNo ratings yet
- REN Revision LectureDocument43 pagesREN Revision Lecturegyamfi.rolandNo ratings yet
- Osmoregulation AP MineDocument28 pagesOsmoregulation AP MineMaureen GabrielleNo ratings yet
- Renal Physiology Handout 2 Slides Per Page PDFDocument37 pagesRenal Physiology Handout 2 Slides Per Page PDFmike hunt100% (1)
- Osmotic Regulation and ExcretionDocument46 pagesOsmotic Regulation and ExcretionKhent SyNo ratings yet
- 25.6 Tubular Reabsorption - Anatomy and Physiology 2e - OpenStaxDocument12 pages25.6 Tubular Reabsorption - Anatomy and Physiology 2e - OpenStaxMarlene AngwaforNo ratings yet
- Anatomy of The Urinary System Pre LabDocument15 pagesAnatomy of The Urinary System Pre LabbobbyNo ratings yet
- Renal AnatomyDocument13 pagesRenal AnatomyApril Lady Faith P. PaundogNo ratings yet
- Renal Physiology GDocument42 pagesRenal Physiology Gayekani561No ratings yet
- Reabsorption & SecreDocument1 pageReabsorption & SecreMowlidAbdirahman Ali madaaleNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3 ReveiwerDocument8 pagesChapter 3 ReveiwerrizzamaegomezoctavianoNo ratings yet
- Urinary SystemDocument10 pagesUrinary SystemAly HannahNo ratings yet
- Chapter 18: Urinary System and Fluid Balance: TH RDDocument3 pagesChapter 18: Urinary System and Fluid Balance: TH RDPrecious Faith RodriguezNo ratings yet
- 4th Shift - HistoDocument24 pages4th Shift - HistoVeronica MagpocNo ratings yet
- FS1 R KR7 OMu 7 VZFPL B13 XDocument4 pagesFS1 R KR7 OMu 7 VZFPL B13 Xaadeshthite476No ratings yet
- Renal Function AubfDocument11 pagesRenal Function AubfHANNA CASANDRA GARCIANo ratings yet
- Reviewer Bio q2Document5 pagesReviewer Bio q2Aviel BuenoNo ratings yet
- Renal Physiology PDFDocument12 pagesRenal Physiology PDFLolitaNo ratings yet
- Manejo Tubular de SolutosDocument4 pagesManejo Tubular de SolutosAnghelussNo ratings yet
- Renal Anatomy and Physiology - Notes - GnvEriDocument3 pagesRenal Anatomy and Physiology - Notes - GnvEriEricka GenoveNo ratings yet
- Electrolyte and Fluid Losses in Diarrhoeal Illness2023Document49 pagesElectrolyte and Fluid Losses in Diarrhoeal Illness2023Sibabalwe DlovasheNo ratings yet
- Peperoism: PhotosynthesisDocument6 pagesPeperoism: PhotosynthesisanneNo ratings yet
- Urinary SystemDocument9 pagesUrinary SystemPrincess OrsinoNo ratings yet
- Cell TransportDocument7 pagesCell Transportako parin itoNo ratings yet
- Renal Medulla: BloodDocument4 pagesRenal Medulla: BloodLindsay GabrielNo ratings yet
- AUBF - Lec Chapter 3 4 5 COMPLETE - Transes 1Document18 pagesAUBF - Lec Chapter 3 4 5 COMPLETE - Transes 1Princess Eve OlowanNo ratings yet
- The KidneyDocument1 pageThe KidneyMushu MunuNo ratings yet
- (Week 16) Urinary SystemDocument3 pages(Week 16) Urinary SystemDiana Leen Dela CruzNo ratings yet
- Renal System 6 1Document30 pagesRenal System 6 1gaurav singhNo ratings yet
- Basic Dialysis Theory SweenyDocument28 pagesBasic Dialysis Theory SweenyAmmar YasserNo ratings yet
- Urine Formation: Yousaf Khan Renal Dialysis LecturerDocument30 pagesUrine Formation: Yousaf Khan Renal Dialysis LecturerSalman KhanNo ratings yet
- Ncert Explanation Deep With ExamplesDocument10 pagesNcert Explanation Deep With ExamplesasterclixNo ratings yet
- Nefrotik Sindrom: A Three-Layer StructureDocument5 pagesNefrotik Sindrom: A Three-Layer StructurepradaniNo ratings yet
- Sakhanokho 2018Document6 pagesSakhanokho 2018AlexNo ratings yet
- Targeted Disruption of The GlucocorticoidDocument15 pagesTargeted Disruption of The GlucocorticoidSyifa SariNo ratings yet
- Essentials of Pharmacology For Health Professions 7th Edition Woodrow Test BankDocument25 pagesEssentials of Pharmacology For Health Professions 7th Edition Woodrow Test BankNormanDanielsyftz100% (54)
- BKK Hospital Medical CertificateDocument12 pagesBKK Hospital Medical CertificateWinThant KhineNo ratings yet
- Fibre ExtractionDocument40 pagesFibre ExtractionUzoma EmekaNo ratings yet
- Chapter-2 Taxonomic AidsDocument12 pagesChapter-2 Taxonomic AidsNandini Classes,City Light ,Surat. Cell (9429090525No ratings yet
- Agrobacterium Protocols - Volume 2. 2-Humana Press (2014)Document395 pagesAgrobacterium Protocols - Volume 2. 2-Humana Press (2014)Maritza Matteo100% (1)
- Human Development and Growth Notes For Mids (2nd Semester)Document4 pagesHuman Development and Growth Notes For Mids (2nd Semester)Ambreen TahirNo ratings yet
- Lipids NotesDocument5 pagesLipids NotesnofacejackNo ratings yet
- Microplastics in The OceanDocument98 pagesMicroplastics in The OceanDevika Hemalatha DeviNo ratings yet
- PREBOARD Gen Ed 1Document16 pagesPREBOARD Gen Ed 1Janice Mayola Alcorin100% (1)
- Pentraxin-3 in Chronic Heart Failure: The CORONA and GISSI-HF TrialsDocument8 pagesPentraxin-3 in Chronic Heart Failure: The CORONA and GISSI-HF TrialscamiloNo ratings yet
- The World's Flora and FaunaDocument8 pagesThe World's Flora and Faunakleberviteri120No ratings yet
- Gram-Negative Bacteria - Wikipedia, The Free EncyclopediaDocument8 pagesGram-Negative Bacteria - Wikipedia, The Free EncyclopediaNadiya AfifahNo ratings yet
- (PROJECT) RHINO - Rhinoceros Facts For Kids - StudyDocument15 pages(PROJECT) RHINO - Rhinoceros Facts For Kids - StudyIan FlackNo ratings yet
- Life Science Class X V2Document159 pagesLife Science Class X V2Surya Narayan DasNo ratings yet
- NG ModulesDocument47 pagesNG Moduleshybri8No ratings yet
- Earth and Life Science: Quarter 2 - Module 21: Evolving Concept of Life Based On Emerging Pieces of EvidenceDocument235 pagesEarth and Life Science: Quarter 2 - Module 21: Evolving Concept of Life Based On Emerging Pieces of EvidenceArenz CudalNo ratings yet
- Typo-Morphological Approach To Transforming An Urban FabricDocument5 pagesTypo-Morphological Approach To Transforming An Urban FabricSatrio Suryana PrasetyaNo ratings yet
- ESS - Topic 3.2Document30 pagesESS - Topic 3.2Pol Ayra FuenteNo ratings yet
- Reparation, Characterization, and Optimization of Microemulsion For Topical Delivery of ItraconazoleDocument10 pagesReparation, Characterization, and Optimization of Microemulsion For Topical Delivery of ItraconazoleVeni UNNo ratings yet
- PBL MCDDocument15 pagesPBL MCDMustafaNo ratings yet
- The Flowers of Ilex GuayusaDocument7 pagesThe Flowers of Ilex GuayusaGabriela Barriga CoronelNo ratings yet
- Unit 11 National Parks Practice Grade 10Document18 pagesUnit 11 National Parks Practice Grade 10An AnNo ratings yet
- The Impact of Shock Wave Therapy at VariDocument9 pagesThe Impact of Shock Wave Therapy at VariArifSurtonoNo ratings yet
- Apps - Xxns Adp Commission Payroll VDocument9 pagesApps - Xxns Adp Commission Payroll VKishan KaranamNo ratings yet
- The Implications of Vitamin D Status During Pregnancy On Mother and Her Developing ChildDocument11 pagesThe Implications of Vitamin D Status During Pregnancy On Mother and Her Developing ChildindahNo ratings yet
- Nouradini PDFDocument15 pagesNouradini PDFDavi AhmadNo ratings yet