Professional Documents
Culture Documents
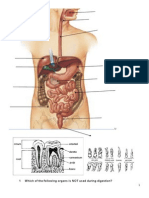
digestive-quizee
digestive-quizee
Uploaded by
Mary Grace MacawileCopyright:
Available Formats
You might also like
- Human Digestive System WorksheetDocument3 pagesHuman Digestive System WorksheetSana Shakeel100% (9)
- Exilis Ultra 360 Brochure Body 4k6feUgOVtqiPnODocument2 pagesExilis Ultra 360 Brochure Body 4k6feUgOVtqiPnOJohn LuNo ratings yet
- Human Digestive System WorksheetDocument3 pagesHuman Digestive System WorksheetEvgeni Genev60% (5)
- Human Digestive System WorksheetDocument3 pagesHuman Digestive System WorksheetSumi Vj100% (2)
- Quiz BankDocument722 pagesQuiz BankMouniraNo ratings yet
- DigestiveDocument2 pagesDigestiveR NovNo ratings yet
- Healthy Pancreas, Healthy You. Part 1: Structure, Function, and Disorders of the PancreasFrom EverandHealthy Pancreas, Healthy You. Part 1: Structure, Function, and Disorders of the PancreasRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (4)
- Practice Test 1 Answer Key AP BioDocument16 pagesPractice Test 1 Answer Key AP Biotessarox161No ratings yet
- Digestive System Multiple Choice QuizDocument11 pagesDigestive System Multiple Choice QuizJerilee SoCute Watts100% (1)
- CH 04 ClickerDocument35 pagesCH 04 ClickerClyde CapapasNo ratings yet
- CH 03 ClickerDocument35 pagesCH 03 ClickerMr ReasonNo ratings yet
- Lymphatic SystemDocument35 pagesLymphatic SystemImmanuel Capurcos Duabe JavilagNo ratings yet
- Where Does Digestion Begin?: Questions and AnswersDocument10 pagesWhere Does Digestion Begin?: Questions and AnswersJosefitaNo ratings yet
- Nutrition and You Core Concepts For Good Health MyPlate Edition 1st Edition Blake Test Bank 1Document11 pagesNutrition and You Core Concepts For Good Health MyPlate Edition 1st Edition Blake Test Bank 1randy100% (64)
- 1 Which of The Following Organs Is NOT Used During Digestion?Document4 pages1 Which of The Following Organs Is NOT Used During Digestion?aby251188No ratings yet
- 7 Human Nutrition Topic Booklet 1 CIE IGCSE BiologyDocument15 pages7 Human Nutrition Topic Booklet 1 CIE IGCSE Biologyaasthasardana9No ratings yet
- Solution.: Multiple Choice QuestionsDocument11 pagesSolution.: Multiple Choice QuestionsSiddhi KankaleNo ratings yet
- Digestive SystemDocument2 pagesDigestive SystemArina Khusna100% (1)
- IGCSE Digestion - Print - QuizizzDocument5 pagesIGCSE Digestion - Print - Quizizzjv peridoNo ratings yet
- Neet Digestion systemMCQDocument58 pagesNeet Digestion systemMCQiGadgetProNo ratings yet
- MCQs of AHN Unit-1 GIT 31 Disorders CompleteDocument36 pagesMCQs of AHN Unit-1 GIT 31 Disorders Completeloferk44No ratings yet
- B g8 Digestive SystemDocument3 pagesB g8 Digestive SystemnoorlailyNo ratings yet
- Blood QuizbeeDocument35 pagesBlood QuizbeeBianca TejadaNo ratings yet
- CH 03 Clicker QuestionsDocument53 pagesCH 03 Clicker QuestionsCharmane Sherisse DumlaoNo ratings yet
- Human Digestive System WorksheetDocument3 pagesHuman Digestive System WorksheetMoath AlsaidNo ratings yet
- Unit 5: Digestive System Test BankDocument8 pagesUnit 5: Digestive System Test Bankjv peridoNo ratings yet
- Digestion & Absorption MCQs PDFDocument73 pagesDigestion & Absorption MCQs PDFJatin SinglaNo ratings yet
- Dairy Judging Questions: (Updated 5/2005)Document23 pagesDairy Judging Questions: (Updated 5/2005)Rizwan AliNo ratings yet
- Digestive System TestDocument4 pagesDigestive System Testbakhtawariqra24No ratings yet
- Digestion 2 MCQDocument6 pagesDigestion 2 MCQgopod60% (5)
- Quiz Gastrointestinal Part 1 of 2Document117 pagesQuiz Gastrointestinal Part 1 of 2MedShare100% (11)
- Science 8 Summative Exam Q4Document4 pagesScience 8 Summative Exam Q4Kelvin Jason ArellanoNo ratings yet
- Untitled (Flyer) (Flyer)Document10 pagesUntitled (Flyer) (Flyer)Angelica Joy SevillaNo ratings yet
- 05 Clicker QuestionsDocument34 pages05 Clicker QuestionsLucas VaughnNo ratings yet
- Class 7 KV Paper Chap 2Document4 pagesClass 7 KV Paper Chap 2Saurabh Kumar jhaNo ratings yet
- DIGESTIONDocument4 pagesDIGESTIONjsz2013bangtanNo ratings yet
- Instant Download PDF Comprehensive Radiographic Pathology 6th Edition Eisenberg Test Bank Full ChapterDocument48 pagesInstant Download PDF Comprehensive Radiographic Pathology 6th Edition Eisenberg Test Bank Full Chapterzyadajagvir100% (5)
- Full download Comprehensive Radiographic Pathology 6th Edition Eisenberg Test Bank all chapter 2024 pdfDocument44 pagesFull download Comprehensive Radiographic Pathology 6th Edition Eisenberg Test Bank all chapter 2024 pdfsapnaialsene100% (9)
- Nutrition For Life 3rd Edition Thompson Test BankDocument15 pagesNutrition For Life 3rd Edition Thompson Test BankLuisMurraypreiz100% (17)
- Human Nutrition CorrectedDocument17 pagesHuman Nutrition Correcteddhritiramduny12No ratings yet
- Human Biology 12Th Edition Mader Test Bank Full Chapter PDFDocument44 pagesHuman Biology 12Th Edition Mader Test Bank Full Chapter PDFninhdermotc1u100% (11)
- Human Biology 12th Edition Mader Test BankDocument34 pagesHuman Biology 12th Edition Mader Test Banklaeliacaixpoyf100% (39)
- DigestionpracticetestDocument41 pagesDigestionpracticetestRennik McCaigNo ratings yet
- Class 10 Icse BioDocument14 pagesClass 10 Icse BioSpidey GamerNo ratings yet
- Digestion 1 MCQDocument11 pagesDigestion 1 MCQgopodNo ratings yet
- Key PT NutritionDocument3 pagesKey PT Nutritionchoudharyasif9999No ratings yet
- NCERT Exemplar Class 7 Science Solutions Chapter 2 Nutrition in AnimalsDocument18 pagesNCERT Exemplar Class 7 Science Solutions Chapter 2 Nutrition in AnimalsSiva PrasadNo ratings yet
- Human Nutrition Question BankDocument11 pagesHuman Nutrition Question BankA RahmanNo ratings yet
- Chapter - 16 - Digestion - and - Absorption Ncert SolutionDocument10 pagesChapter - 16 - Digestion - and - Absorption Ncert SolutionGuru KhanNo ratings yet
- 821695101193222-LS NutritioninanimalsanswerkeyliworksheetDocument3 pages821695101193222-LS NutritioninanimalsanswerkeyliworksheetSiddhi AgrawalNo ratings yet
- DateDocument10 pagesDatenavneetkpatil8409No ratings yet
- Digestion and Absorption: Fact/Definition Type QuestionsDocument9 pagesDigestion and Absorption: Fact/Definition Type QuestionsNayan BhardwazNo ratings yet
- Ls 2nutritioninanimalsworksheetl1Document3 pagesLs 2nutritioninanimalsworksheetl1Siddhi AgrawalNo ratings yet
- DIGSTIVE-SYSEM Q4 WK1 Sci8Document26 pagesDIGSTIVE-SYSEM Q4 WK1 Sci8Jasmine kNo ratings yet
- Gitmcqs 2 NdyearDocument46 pagesGitmcqs 2 NdyearAmbika dawadiNo ratings yet
- Digestive System Exam IIDocument13 pagesDigestive System Exam IIhugomiso100% (3)
- Nutrition in AnimalsDocument6 pagesNutrition in AnimalsSarika AhujaNo ratings yet
- Xii Cluny Zoo DPT 4-01-2023Document2 pagesXii Cluny Zoo DPT 4-01-2023pinnaacleclasses salemNo ratings yet
- Vii Form Nutrition in Animals (WS 2)Document7 pagesVii Form Nutrition in Animals (WS 2)Vanya bajajNo ratings yet
- Plant and Animal Cell OperationDocument8 pagesPlant and Animal Cell Operationapi-325015040No ratings yet
- Yield and Nutrient Content of Tomato As Influenced by The Application of Vermicompost and Chemical FertilizersDocument8 pagesYield and Nutrient Content of Tomato As Influenced by The Application of Vermicompost and Chemical FertilizersJingky MarzanPurisima Lumauig SallicopNo ratings yet
- Agustin V CADocument8 pagesAgustin V CAAnonymous pxhKxbMNo ratings yet
- Lec 1 Introduction To The Course and History of PharmacyDocument4 pagesLec 1 Introduction To The Course and History of PharmacyahusainNo ratings yet
- (Biology Form 4) Stage in MeiosisDocument6 pages(Biology Form 4) Stage in MeiosisFuzieanna BakhtiarNo ratings yet
- Wheaters Basic Pathology A Text Atlas and Review of Histopathology 5th Edition Young Test BankDocument5 pagesWheaters Basic Pathology A Text Atlas and Review of Histopathology 5th Edition Young Test BankNicoleRoweanbtc100% (15)
- XI - UNIT-10 Training and Doping in SportsDocument58 pagesXI - UNIT-10 Training and Doping in Sportspriya2kalyanNo ratings yet
- MicroorganismsDocument24 pagesMicroorganismsprameeta100% (3)
- Parts of The Body: Grade IIIDocument15 pagesParts of The Body: Grade IIIRose Angel ManaogNo ratings yet
- Class9 NSO 2017 SetB - SolutionsDocument15 pagesClass9 NSO 2017 SetB - SolutionsAmbica JainNo ratings yet
- D-1-10 Horticultural Oils.198104904Document3 pagesD-1-10 Horticultural Oils.198104904ReilpeterNo ratings yet
- ES228 S13 Lecture2 Biopolymers ViscoelasticityDocument47 pagesES228 S13 Lecture2 Biopolymers ViscoelasticityFei PuNo ratings yet
- Ts of Ethanolic Leaf Extract of Justicia Carnea On The Kidney Function Parameters in Alloxan-Induced Diabetic Albino Wistar RatsDocument39 pagesTs of Ethanolic Leaf Extract of Justicia Carnea On The Kidney Function Parameters in Alloxan-Induced Diabetic Albino Wistar RatsNwigwe Promise ChukwuebukaNo ratings yet
- (PDF) bài tập về từ đồng nghĩaDocument98 pages(PDF) bài tập về từ đồng nghĩaminhducvn2004No ratings yet
- A Detailed Lesson Plan in Science in Grade IVDocument5 pagesA Detailed Lesson Plan in Science in Grade IVmary grace sendrejasNo ratings yet
- Paediatric Drugs, 2020-Drug Treatment of Progressive Myoclonus Epilepsy - MISMAR20-MM-S-AK-039Document16 pagesPaediatric Drugs, 2020-Drug Treatment of Progressive Myoclonus Epilepsy - MISMAR20-MM-S-AK-039veerraju tvNo ratings yet
- 1099 - Somatic Hybridization and CybridizationDocument33 pages1099 - Somatic Hybridization and CybridizationkeroNo ratings yet
- Phenolic Profile and Antioxidant ActivitDocument7 pagesPhenolic Profile and Antioxidant ActivithocineNo ratings yet
- Plant Reproduction BookletDocument10 pagesPlant Reproduction BookletfarahNo ratings yet
- Order Pictorial KeyDocument8 pagesOrder Pictorial KeyNova Tri Kusuma DewiNo ratings yet
- QIAamp DNA Mini and Blood Mini HandbookDocument72 pagesQIAamp DNA Mini and Blood Mini HandbookMaribel GatitoNo ratings yet
- Genetics Practice ProbsDocument4 pagesGenetics Practice Probsajaysharma19686191No ratings yet
- Que Es Un Individuo Concreto. Mario BungeDocument9 pagesQue Es Un Individuo Concreto. Mario BungeManuel Antonio Requena ArriolaNo ratings yet
- Combinatorics 2 Solutions UHSMCDocument5 pagesCombinatorics 2 Solutions UHSMCWalker KroubalkianNo ratings yet
- Comparative Assessment of Salivary Level of Cortisol Anxiety and Depression in Patients With Oral Conditions A Case Control StudyDocument6 pagesComparative Assessment of Salivary Level of Cortisol Anxiety and Depression in Patients With Oral Conditions A Case Control StudyAthenaeum Scientific PublishersNo ratings yet
- Neural Networks: Chapter 20, Section 5Document21 pagesNeural Networks: Chapter 20, Section 5api-19801502No ratings yet
- Culturable Heterotrophic Bacteria Associated With A Laboratory Culture of Botryococcus Braunii, A Colonial Oil-Producing Green Alga From Paoay Lake, Ilocos NorteDocument39 pagesCulturable Heterotrophic Bacteria Associated With A Laboratory Culture of Botryococcus Braunii, A Colonial Oil-Producing Green Alga From Paoay Lake, Ilocos NorteGela16No ratings yet
- Origin of LanguangeDocument94 pagesOrigin of LanguangeDarkk Sunn0% (1)
digestive-quizee
digestive-quizee
Uploaded by
Mary Grace MacawileCopyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
digestive-quizee
digestive-quizee
Uploaded by
Mary Grace MacawileCopyright:
Available Formats
Chapter 14
The Digestive
System
Clicker Questions
© 2015 Pearson Education, Inc.
Which organ creates bile?
a) skin
b) pancreas
c) gallbladder
d) liver
© 2015 Pearson Education, Inc.
Which organ creates bile?
a) skin
b) pancreas
c) gallbladder
d) liver
© 2015 Pearson Education, Inc.
Which condition is the result of the release of
bile salts and bile pigments from the liver and
into the bloodstream?
a) hepatitis
b) jaundice
c) cirrhosis
d) gallstones
© 2015 Pearson Education, Inc.
Which condition is the result of the release of
bile salts and bile pigments from the liver and
into the bloodstream?
a) hepatitis
b) jaundice
c) cirrhosis
d) gallstones
© 2015 Pearson Education, Inc.
Local collections of the lymphatic system that
are found in the submucosa of the small
intestine are known as
a) duodenal papillae
b) plicae circulares
c) haustra
d) Peyer’s patches
© 2015 Pearson Education, Inc.
Local collections of the lymphatic system that
are found in the submucosa of the small
intestine are known as
a) duodenal papillae
b) plicae circulares
c) haustra
d) Peyer’s patches
© 2015 Pearson Education, Inc.
The number of teeth in a full set of baby teeth
is
a) 16.
b) 20.
c) 30.
d) 32.
© 2015 Pearson Education, Inc.
The number of teeth in a full set of baby teeth
is
a) 16.
b) 20.
c) 30.
d) 32.
© 2015 Pearson Education, Inc.
This bicarbonate-rich (alkaline) juice begins
starch digestion in the mouth.
a) amylase
b) peptidase
c) lipase
d) secretin
© 2015 Pearson Education, Inc.
This bicarbonate-rich (alkaline) juice begins
starch digestion in the mouth.
a) amylase
b) peptidase
c) lipase
d) secretin
© 2015 Pearson Education, Inc.
The major absorptive section of the alimentary
canal is the
a) liver.
b) large intestine.
c) stomach.
d) small intestine.
© 2015 Pearson Education, Inc.
The major absorptive section of the alimentary
canal is the
a) liver.
b) large intestine.
c) stomach.
d) small intestine.
© 2015 Pearson Education, Inc.
This circular muscle is between the stomach
and the small intestine.
a) lesser omentum
b) ileocecal valve
c) cardiac sphincter
d) pyloric sphincter
© 2015 Pearson Education, Inc.
This circular muscle is between the stomach
and the small intestine.
a) lesser omentum
b) ileocecal valve
c) cardiac sphincter
d) pyloric sphincter
© 2015 Pearson Education, Inc.
This protein-digesting enzyme works primarily
on milk protein and makes it look lumpy, like
cottage cheese.
a) gastrin
b) amylase
c) secretin
d) rennin
© 2015 Pearson Education, Inc.
This protein-digesting enzyme works primarily
on milk protein and makes it look lumpy, like
cottage cheese.
a) gastrin
b) amylase
c) secretin
d) rennin
© 2015 Pearson Education, Inc.
Essential amino acids are
a) amino acids needed to make proteins.
b) amino acids our body makes.
c) amino acids our body cannot make and that we
must consume in our diet.
d) all 20 amino acids in our body.
© 2015 Pearson Education, Inc.
Essential amino acids are
a) amino acids needed to make proteins.
b) amino acids our body makes.
c) amino acids our body cannot make and that
we must consume in our diet.
d) all 20 amino acids in our body.
© 2015 Pearson Education, Inc.
Which is the terminal portion of the small
intestine?
a) pyloric sphincter
b) ileum
c) cecum
d) ileocecal valve
© 2015 Pearson Education, Inc.
Which is the terminal portion of the small
intestine?
a) pyloric sphincter
b) ileum
c) cecum
d) ileocecal valve
© 2015 Pearson Education, Inc.
Digestion of proteins begins in the
a) large intestine.
b) mouth.
c) small intestine.
d) stomach.
© 2015 Pearson Education, Inc.
Digestion of proteins begins in the
a) large intestine.
b) mouth.
c) small intestine.
d) stomach.
© 2015 Pearson Education, Inc.
This substance is needed for absorption of
vitamin B12 from the small intestine.
a) pepsinogen
b) intrinsic factor
c) chyme
d) gastric juice
© 2015 Pearson Education, Inc.
This substance is needed for absorption of
vitamin B12 from the small intestine.
a) pepsinogen
b) intrinsic factor
c) chyme
d) gastric juice
© 2015 Pearson Education, Inc.
Which layer of the alimentary canal surrounds
the lumen?
a) mucosa
b) muscularis externa
c) serosa
d) submucosa
© 2015 Pearson Education, Inc.
Which layer of the alimentary canal surrounds
the lumen?
a) mucosa
b) muscularis externa
c) serosa
d) submucosa
© 2015 Pearson Education, Inc.
Which organ contributes to the chemical
breakdown of ALL food types?
a) liver
b) pancreas
c) stomach
d) salivary glands
© 2015 Pearson Education, Inc.
Which organ contributes to the chemical
breakdown of ALL food types?
a) liver
b) pancreas
c) stomach
d) salivary glands
© 2015 Pearson Education, Inc.
Which anatomical structure prevents the
backflow of acid into the esophagus?
a) pyloric sphincter
b) cardioesophageal sphincter
c) ileocecal valve
d) external anal aphincter
© 2015 Pearson Education, Inc.
Which anatomical structure prevents the
backflow of acid into the esophagus?
a) pyloric sphincter
b) cardioesophageal sphincter
c) ileocecal valve
d) external anal aphincter
© 2015 Pearson Education, Inc.
This extension of the peritoneum covers the
abdominal organs and contains fat and
lymphoid follicles.
a) submucosa
b) muscularis externa
c) lesser omentum
d) greater omentum
© 2015 Pearson Education, Inc.
This extension of the peritoneum covers the
abdominal organs and contains fat and
lymphoid follicles.
a) submucosa
b) muscularis externa
c) lesser omentum
d) greater omentum
© 2015 Pearson Education, Inc.
This is a structural abnormality in which the
superior part of the stomach protrudes
slightly above the diaphragm.
a) esophagitis
b) gastritis
c) hiatal hernia
d) emesis
© 2015 Pearson Education, Inc.
This is a structural abnormality in which the
superior part of the stomach protrudes
slightly above the diaphragm.
a) esophagitis
b) gastritis
c) hiatal hernia
d) emesis
© 2015 Pearson Education, Inc.
You might also like
- Human Digestive System WorksheetDocument3 pagesHuman Digestive System WorksheetSana Shakeel100% (9)
- Exilis Ultra 360 Brochure Body 4k6feUgOVtqiPnODocument2 pagesExilis Ultra 360 Brochure Body 4k6feUgOVtqiPnOJohn LuNo ratings yet
- Human Digestive System WorksheetDocument3 pagesHuman Digestive System WorksheetEvgeni Genev60% (5)
- Human Digestive System WorksheetDocument3 pagesHuman Digestive System WorksheetSumi Vj100% (2)
- Quiz BankDocument722 pagesQuiz BankMouniraNo ratings yet
- DigestiveDocument2 pagesDigestiveR NovNo ratings yet
- Healthy Pancreas, Healthy You. Part 1: Structure, Function, and Disorders of the PancreasFrom EverandHealthy Pancreas, Healthy You. Part 1: Structure, Function, and Disorders of the PancreasRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (4)
- Practice Test 1 Answer Key AP BioDocument16 pagesPractice Test 1 Answer Key AP Biotessarox161No ratings yet
- Digestive System Multiple Choice QuizDocument11 pagesDigestive System Multiple Choice QuizJerilee SoCute Watts100% (1)
- CH 04 ClickerDocument35 pagesCH 04 ClickerClyde CapapasNo ratings yet
- CH 03 ClickerDocument35 pagesCH 03 ClickerMr ReasonNo ratings yet
- Lymphatic SystemDocument35 pagesLymphatic SystemImmanuel Capurcos Duabe JavilagNo ratings yet
- Where Does Digestion Begin?: Questions and AnswersDocument10 pagesWhere Does Digestion Begin?: Questions and AnswersJosefitaNo ratings yet
- Nutrition and You Core Concepts For Good Health MyPlate Edition 1st Edition Blake Test Bank 1Document11 pagesNutrition and You Core Concepts For Good Health MyPlate Edition 1st Edition Blake Test Bank 1randy100% (64)
- 1 Which of The Following Organs Is NOT Used During Digestion?Document4 pages1 Which of The Following Organs Is NOT Used During Digestion?aby251188No ratings yet
- 7 Human Nutrition Topic Booklet 1 CIE IGCSE BiologyDocument15 pages7 Human Nutrition Topic Booklet 1 CIE IGCSE Biologyaasthasardana9No ratings yet
- Solution.: Multiple Choice QuestionsDocument11 pagesSolution.: Multiple Choice QuestionsSiddhi KankaleNo ratings yet
- Digestive SystemDocument2 pagesDigestive SystemArina Khusna100% (1)
- IGCSE Digestion - Print - QuizizzDocument5 pagesIGCSE Digestion - Print - Quizizzjv peridoNo ratings yet
- Neet Digestion systemMCQDocument58 pagesNeet Digestion systemMCQiGadgetProNo ratings yet
- MCQs of AHN Unit-1 GIT 31 Disorders CompleteDocument36 pagesMCQs of AHN Unit-1 GIT 31 Disorders Completeloferk44No ratings yet
- B g8 Digestive SystemDocument3 pagesB g8 Digestive SystemnoorlailyNo ratings yet
- Blood QuizbeeDocument35 pagesBlood QuizbeeBianca TejadaNo ratings yet
- CH 03 Clicker QuestionsDocument53 pagesCH 03 Clicker QuestionsCharmane Sherisse DumlaoNo ratings yet
- Human Digestive System WorksheetDocument3 pagesHuman Digestive System WorksheetMoath AlsaidNo ratings yet
- Unit 5: Digestive System Test BankDocument8 pagesUnit 5: Digestive System Test Bankjv peridoNo ratings yet
- Digestion & Absorption MCQs PDFDocument73 pagesDigestion & Absorption MCQs PDFJatin SinglaNo ratings yet
- Dairy Judging Questions: (Updated 5/2005)Document23 pagesDairy Judging Questions: (Updated 5/2005)Rizwan AliNo ratings yet
- Digestive System TestDocument4 pagesDigestive System Testbakhtawariqra24No ratings yet
- Digestion 2 MCQDocument6 pagesDigestion 2 MCQgopod60% (5)
- Quiz Gastrointestinal Part 1 of 2Document117 pagesQuiz Gastrointestinal Part 1 of 2MedShare100% (11)
- Science 8 Summative Exam Q4Document4 pagesScience 8 Summative Exam Q4Kelvin Jason ArellanoNo ratings yet
- Untitled (Flyer) (Flyer)Document10 pagesUntitled (Flyer) (Flyer)Angelica Joy SevillaNo ratings yet
- 05 Clicker QuestionsDocument34 pages05 Clicker QuestionsLucas VaughnNo ratings yet
- Class 7 KV Paper Chap 2Document4 pagesClass 7 KV Paper Chap 2Saurabh Kumar jhaNo ratings yet
- DIGESTIONDocument4 pagesDIGESTIONjsz2013bangtanNo ratings yet
- Instant Download PDF Comprehensive Radiographic Pathology 6th Edition Eisenberg Test Bank Full ChapterDocument48 pagesInstant Download PDF Comprehensive Radiographic Pathology 6th Edition Eisenberg Test Bank Full Chapterzyadajagvir100% (5)
- Full download Comprehensive Radiographic Pathology 6th Edition Eisenberg Test Bank all chapter 2024 pdfDocument44 pagesFull download Comprehensive Radiographic Pathology 6th Edition Eisenberg Test Bank all chapter 2024 pdfsapnaialsene100% (9)
- Nutrition For Life 3rd Edition Thompson Test BankDocument15 pagesNutrition For Life 3rd Edition Thompson Test BankLuisMurraypreiz100% (17)
- Human Nutrition CorrectedDocument17 pagesHuman Nutrition Correcteddhritiramduny12No ratings yet
- Human Biology 12Th Edition Mader Test Bank Full Chapter PDFDocument44 pagesHuman Biology 12Th Edition Mader Test Bank Full Chapter PDFninhdermotc1u100% (11)
- Human Biology 12th Edition Mader Test BankDocument34 pagesHuman Biology 12th Edition Mader Test Banklaeliacaixpoyf100% (39)
- DigestionpracticetestDocument41 pagesDigestionpracticetestRennik McCaigNo ratings yet
- Class 10 Icse BioDocument14 pagesClass 10 Icse BioSpidey GamerNo ratings yet
- Digestion 1 MCQDocument11 pagesDigestion 1 MCQgopodNo ratings yet
- Key PT NutritionDocument3 pagesKey PT Nutritionchoudharyasif9999No ratings yet
- NCERT Exemplar Class 7 Science Solutions Chapter 2 Nutrition in AnimalsDocument18 pagesNCERT Exemplar Class 7 Science Solutions Chapter 2 Nutrition in AnimalsSiva PrasadNo ratings yet
- Human Nutrition Question BankDocument11 pagesHuman Nutrition Question BankA RahmanNo ratings yet
- Chapter - 16 - Digestion - and - Absorption Ncert SolutionDocument10 pagesChapter - 16 - Digestion - and - Absorption Ncert SolutionGuru KhanNo ratings yet
- 821695101193222-LS NutritioninanimalsanswerkeyliworksheetDocument3 pages821695101193222-LS NutritioninanimalsanswerkeyliworksheetSiddhi AgrawalNo ratings yet
- DateDocument10 pagesDatenavneetkpatil8409No ratings yet
- Digestion and Absorption: Fact/Definition Type QuestionsDocument9 pagesDigestion and Absorption: Fact/Definition Type QuestionsNayan BhardwazNo ratings yet
- Ls 2nutritioninanimalsworksheetl1Document3 pagesLs 2nutritioninanimalsworksheetl1Siddhi AgrawalNo ratings yet
- DIGSTIVE-SYSEM Q4 WK1 Sci8Document26 pagesDIGSTIVE-SYSEM Q4 WK1 Sci8Jasmine kNo ratings yet
- Gitmcqs 2 NdyearDocument46 pagesGitmcqs 2 NdyearAmbika dawadiNo ratings yet
- Digestive System Exam IIDocument13 pagesDigestive System Exam IIhugomiso100% (3)
- Nutrition in AnimalsDocument6 pagesNutrition in AnimalsSarika AhujaNo ratings yet
- Xii Cluny Zoo DPT 4-01-2023Document2 pagesXii Cluny Zoo DPT 4-01-2023pinnaacleclasses salemNo ratings yet
- Vii Form Nutrition in Animals (WS 2)Document7 pagesVii Form Nutrition in Animals (WS 2)Vanya bajajNo ratings yet
- Plant and Animal Cell OperationDocument8 pagesPlant and Animal Cell Operationapi-325015040No ratings yet
- Yield and Nutrient Content of Tomato As Influenced by The Application of Vermicompost and Chemical FertilizersDocument8 pagesYield and Nutrient Content of Tomato As Influenced by The Application of Vermicompost and Chemical FertilizersJingky MarzanPurisima Lumauig SallicopNo ratings yet
- Agustin V CADocument8 pagesAgustin V CAAnonymous pxhKxbMNo ratings yet
- Lec 1 Introduction To The Course and History of PharmacyDocument4 pagesLec 1 Introduction To The Course and History of PharmacyahusainNo ratings yet
- (Biology Form 4) Stage in MeiosisDocument6 pages(Biology Form 4) Stage in MeiosisFuzieanna BakhtiarNo ratings yet
- Wheaters Basic Pathology A Text Atlas and Review of Histopathology 5th Edition Young Test BankDocument5 pagesWheaters Basic Pathology A Text Atlas and Review of Histopathology 5th Edition Young Test BankNicoleRoweanbtc100% (15)
- XI - UNIT-10 Training and Doping in SportsDocument58 pagesXI - UNIT-10 Training and Doping in Sportspriya2kalyanNo ratings yet
- MicroorganismsDocument24 pagesMicroorganismsprameeta100% (3)
- Parts of The Body: Grade IIIDocument15 pagesParts of The Body: Grade IIIRose Angel ManaogNo ratings yet
- Class9 NSO 2017 SetB - SolutionsDocument15 pagesClass9 NSO 2017 SetB - SolutionsAmbica JainNo ratings yet
- D-1-10 Horticultural Oils.198104904Document3 pagesD-1-10 Horticultural Oils.198104904ReilpeterNo ratings yet
- ES228 S13 Lecture2 Biopolymers ViscoelasticityDocument47 pagesES228 S13 Lecture2 Biopolymers ViscoelasticityFei PuNo ratings yet
- Ts of Ethanolic Leaf Extract of Justicia Carnea On The Kidney Function Parameters in Alloxan-Induced Diabetic Albino Wistar RatsDocument39 pagesTs of Ethanolic Leaf Extract of Justicia Carnea On The Kidney Function Parameters in Alloxan-Induced Diabetic Albino Wistar RatsNwigwe Promise ChukwuebukaNo ratings yet
- (PDF) bài tập về từ đồng nghĩaDocument98 pages(PDF) bài tập về từ đồng nghĩaminhducvn2004No ratings yet
- A Detailed Lesson Plan in Science in Grade IVDocument5 pagesA Detailed Lesson Plan in Science in Grade IVmary grace sendrejasNo ratings yet
- Paediatric Drugs, 2020-Drug Treatment of Progressive Myoclonus Epilepsy - MISMAR20-MM-S-AK-039Document16 pagesPaediatric Drugs, 2020-Drug Treatment of Progressive Myoclonus Epilepsy - MISMAR20-MM-S-AK-039veerraju tvNo ratings yet
- 1099 - Somatic Hybridization and CybridizationDocument33 pages1099 - Somatic Hybridization and CybridizationkeroNo ratings yet
- Phenolic Profile and Antioxidant ActivitDocument7 pagesPhenolic Profile and Antioxidant ActivithocineNo ratings yet
- Plant Reproduction BookletDocument10 pagesPlant Reproduction BookletfarahNo ratings yet
- Order Pictorial KeyDocument8 pagesOrder Pictorial KeyNova Tri Kusuma DewiNo ratings yet
- QIAamp DNA Mini and Blood Mini HandbookDocument72 pagesQIAamp DNA Mini and Blood Mini HandbookMaribel GatitoNo ratings yet
- Genetics Practice ProbsDocument4 pagesGenetics Practice Probsajaysharma19686191No ratings yet
- Que Es Un Individuo Concreto. Mario BungeDocument9 pagesQue Es Un Individuo Concreto. Mario BungeManuel Antonio Requena ArriolaNo ratings yet
- Combinatorics 2 Solutions UHSMCDocument5 pagesCombinatorics 2 Solutions UHSMCWalker KroubalkianNo ratings yet
- Comparative Assessment of Salivary Level of Cortisol Anxiety and Depression in Patients With Oral Conditions A Case Control StudyDocument6 pagesComparative Assessment of Salivary Level of Cortisol Anxiety and Depression in Patients With Oral Conditions A Case Control StudyAthenaeum Scientific PublishersNo ratings yet
- Neural Networks: Chapter 20, Section 5Document21 pagesNeural Networks: Chapter 20, Section 5api-19801502No ratings yet
- Culturable Heterotrophic Bacteria Associated With A Laboratory Culture of Botryococcus Braunii, A Colonial Oil-Producing Green Alga From Paoay Lake, Ilocos NorteDocument39 pagesCulturable Heterotrophic Bacteria Associated With A Laboratory Culture of Botryococcus Braunii, A Colonial Oil-Producing Green Alga From Paoay Lake, Ilocos NorteGela16No ratings yet
- Origin of LanguangeDocument94 pagesOrigin of LanguangeDarkk Sunn0% (1)