Professional Documents
Culture Documents
M&O Samenvatting
M&O Samenvatting
Uploaded by
Honey ChangOriginal Description:
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
M&O Samenvatting
M&O Samenvatting
Uploaded by
Honey ChangCopyright:
Available Formats
Lecture 1 value chain: Breaks the org up in parts (cost and value factor). More focus on externalmarket&consumers.
operations management: the physical production of goods or services (line processes) efficiency: use minimal resources raw materials, money and labor to produce the desired volume of output effectivity: degree to which the organization achieves stated goal Vraag 1 Mock supply chain management: managing the sequence of suppliers and purchasers, covering all stages of processing from obtaining raw materials to distributing finished goods to final consumers. competitive strategy: Product leadership (R&D, highschool employees, diferentation), Cost leadership (operational excellence), Customer intimacy productivity: organizations output of products and services divided by its inputs Lecture 2 competitive advantage as a wedge between willingness to pay and costs. 3 steps: 1. using activities to analyze costs (determine cost drivers), 2. analyse relative willingness to pay ( quality & design) 3. strategic options and choices Costs & willingness to pay strategic planning: breaking down processes, relative costs position, relative willingness to pay Lecture 3 corporate culture: The set of key values, beliefs, understandings, and norms that members of an organization share. 1 adaptive cultures : visible behaviour (change & risks). Expressed value (value people and change processes) Unadaptive cultures: visible behaviour ( politically. Bureaucratically, no change) Expressed value ( own benefit, reduce risk) types of cultures. Needs of environment zie blaadje!
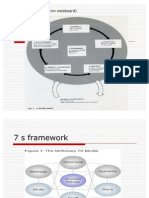
Lecture 4 7-s model Purpose vraag 2 Mock Hard ( Easier to define, managementdirectly influence) : Strategy (the plan devised to maintain and build competitive advantage over the competition.), Structure (the way the organization is structured and who reports to whom.), Systems (the daily activities and procedures that staff members engage in to get the job done.) Soft (Difficult to describe, less tangible, more influenced by culture): Style (the style of leadership adopted.), Staff the employees and their general capabilities., Skills (the actual skills and competencies of the employees working for the company)., Shared values (core values of the company that are evidenced in the corporate culture and the general work ethic.) Lecture 5 communication is essential for effective management and managers use communication to persuade and influence others Purpose directed (attention to vision, values, employee behavior), stragetic conversation (open comm. Listening and feedback), methods (richchannles, personal networks, non-verbal ecommunication) 1 concept of channel richness, Vraag 3 Mock dialogue: reveal feelings, build common ground, shared meaning, long-term discussion: state positions, build oppositions, short-term complex and difficult situationdecentralize( expensive, high quality, innovation), simple situationcentralize Lecture 6 Mintzberg understand function of organization. 5 structures Simple structure(shop), machine bureaucracy(airline), professional org(university), division org(government sector), ad-hocracy(R&d company) 5 coordination meganism direct supervision, mutual adjustment, standaridzation of work, skills, outpur 6 key parts stragetic appex (top management), middle-line (middle management), operating core ( operation processes), technostructure ( design systems), support staff, ideology (norms, values) design parameters individual positions, superstructure, planning, decision-making system, decentralization situational factors age, technical systems, environment, power
Lecture 7 Vraag 6 Mock Possible criteria for decision making: utilirian approach, individualism apporach, moral rights approach, justice approach, disruptive approach Total corporate social responsibility: economic responsibility(profitable), legal resp(obey the law)., ethical resp(do whats right), discretionary resp (contribute to community). Sustainable Development: Economic Development that generates wealth, Meets the needs of current generation, Saving the environment for future generations Managers are weaving sustainability into strategic decisions Lecture 9 4 tools for putting stratgey into action: leadership (motivation), Human resources (training), Information and control systems (budget allocations), Structural design ( organization chart) 3 types of control: feed forward (input, inspect raw materials), concurrent control(ongoing activities, adaptive culture), feedback control ( organizations output, survey customers). Balanced scorecard = comprehensive management control system that balances traditional financial measures with measures of customer service, internal business processes, and the organizations capacity for learning and growth Lecture 10 Stragetic HRM structure: Find right people, manage talent, maintain effective workplace. Innovations in HRM: part-time employees, technology in support systems. Attracting effective workforce: HR planning, recruiting resource, select candidate, welcome employee Improve quality of people ! Lecture 11 3 stages achieving behavioral change: unfreezing, changing, refreezing 8-step model: urgency, coalition, clear vision, communicate, empower, celebrate, consolidate, support 4 reasons for resistance: self-interest, lack of understanding, uncertainty, different assesment& goals
5 colors of thinking: yellow (`use power to achieve solutions), blue ( rational process focussed on the best outcome), red ( proper use of HRM tools), green ( creating learning situations), white ( let energy flow free) Lecture 12 PARADIGM:A set of assumptions, concepts, values, and practices that constitutes a way of viewing reality for the community that shares them (symbols, stories, rituals, control, power, org structre) Confusius approach to social harmony and defined moral obligations between individuals and social systems. formalized into political and religious system Rheinland model european model coordination by shared values, government involvment, collectivism Anglosaxion American model coordinated by rules, minimum government involvment, individual goals
Project Cost leadership means for Linganet that is offer language programs as cheap as possible. The organization aggressively seeks efficient webhosts and pursues cost reduction. A low cost position means that Linganet can undercut its competitors prices and still offer comparable quality and earn some profit Linganet is has a simple structure and contains the following situational factors: - Young - Small - Simple - Dynamic The company is leaded by only one person, Roos Steevels, and makes this company an entrepreneurial firm. She is the boss and has only some employees who are outsourced. The age and size of the company are young and small, therefore is doesnt have a formalization kind of behavior. However this could be an advantage since the industry where Linganet is operation, requires a quick decision making leadership style. Linganet is a young company that's tightly controlled by the owner, R. Steevels. Entrepreneurial organizations or sole proprietorships are the most common types of organization. However, a particularly strong leader may be able to sustain an entrepreneurial organization as it grows, and when large companies face hostile conditions, they can revert to this structure to keep strict control from the top.
You might also like
- MGT510 ShortNotes TQM Letures 1 To 22Document19 pagesMGT510 ShortNotes TQM Letures 1 To 22Mohammad Anas75% (4)
- VF Brands - Case Write Up - Group8Document6 pagesVF Brands - Case Write Up - Group8maheshNo ratings yet
- 0A SMETA Guide To Pre-Audit InformationDocument6 pages0A SMETA Guide To Pre-Audit InformationladislaoNo ratings yet
- l4 03 Measuring Purchasing PerformanceDocument150 pagesl4 03 Measuring Purchasing PerformanceMahendra Kumar Soni100% (3)
- Organizational Theory Design and Change SummaryDocument38 pagesOrganizational Theory Design and Change Summarycaarlijnnn100% (3)
- Operations Management Study GuideDocument8 pagesOperations Management Study GuidemariavcromeroNo ratings yet
- Organizational Analysis Model Template PDFDocument4 pagesOrganizational Analysis Model Template PDFmhardi cubacubNo ratings yet
- Procurement PolicyDocument58 pagesProcurement PolicyBejace NyachhyonNo ratings yet
- Vinod - OD - Notes PDFDocument16 pagesVinod - OD - Notes PDFnannawarevinod1No ratings yet
- MANA 341 - Midterm NotesDocument41 pagesMANA 341 - Midterm NotesNassrine ZahabiNo ratings yet
- Organization and Information SystemsDocument58 pagesOrganization and Information SystemsHerlan NurachmanNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1: Organizations and Organizational EffectivenessDocument3 pagesChapter 1: Organizations and Organizational EffectivenessLol LolNo ratings yet
- Introduction To OBDocument31 pagesIntroduction To OBRohit SharmaNo ratings yet
- Theories of Management Part 2Document8 pagesTheories of Management Part 2Mudodzwa LuvhaNo ratings yet
- Summary of All Modules - b102Document6 pagesSummary of All Modules - b102Sean Michael SpiresNo ratings yet
- Change ModelDocument35 pagesChange ModelAslam HussainNo ratings yet
- Management Theory and PracticeDocument24 pagesManagement Theory and Practiceprvigneshkumar100% (1)
- Session - 1 Significance of Organization Structure and DesignDocument26 pagesSession - 1 Significance of Organization Structure and DesignBhargavNo ratings yet
- International Marketing of MC DonaldsDocument23 pagesInternational Marketing of MC Donaldsranson dantisNo ratings yet
- BBA Syllabus - 7,8Document10 pagesBBA Syllabus - 7,8anon_934723673No ratings yet
- Chapter 4 Resources and ProccesesDocument4 pagesChapter 4 Resources and Proccesesvrmfvwt9vdNo ratings yet
- MBA SyllabusDocument152 pagesMBA Syllabusdattuk77No ratings yet
- Organizational BehaviorDocument64 pagesOrganizational Behaviorniamoetz2100% (1)
- 15655842191802159808Document66 pages15655842191802159808Sathya KamarajNo ratings yet
- Organizations and Organization Theory: Chapter OneDocument4 pagesOrganizations and Organization Theory: Chapter Onedramane007No ratings yet
- Chap 01Document32 pagesChap 01Alvis MenezesNo ratings yet
- The Impact of Operations Management On Organizational CultureDocument10 pagesThe Impact of Operations Management On Organizational CultureMuhammad Ben Mahfouz Al-ZubairiNo ratings yet
- Viva EditedDocument10 pagesViva EditedAshley Wood100% (1)
- mgmt106 Textbook SummaryDocument51 pagesmgmt106 Textbook SummaryJoyceNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1 SummaryDocument8 pagesChapter 1 Summarythaonnguyenn02No ratings yet
- Business Contingency Plan: Prepared By: Function: Human ResourcesDocument19 pagesBusiness Contingency Plan: Prepared By: Function: Human ResourcesmebequayNo ratings yet
- Challenges Facing HRM ZOOMDocument10 pagesChallenges Facing HRM ZOOMahmed attiaNo ratings yet
- ORGBEVDocument15 pagesORGBEVJethro TeriaNo ratings yet
- East Africa University: Faculty: Social ScienceDocument6 pagesEast Africa University: Faculty: Social ScienceAbdullahiNo ratings yet
- MS 56Document9 pagesMS 56Rajni KumariNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2Document4 pagesChapter 2Khalid AlkoohejiNo ratings yet
- Chapters 1-2-3Document9 pagesChapters 1-2-3Jim ThiveosNo ratings yet
- Why Organizational Culture MattersDocument27 pagesWhy Organizational Culture MattersFazal QambraniNo ratings yet
- Bormgt SummarizeDocument5 pagesBormgt SummarizeKylie BatitisNo ratings yet
- Q1 Explain Organizational Behavior and Why It Is ImportantDocument26 pagesQ1 Explain Organizational Behavior and Why It Is ImportantUbed ShaikhNo ratings yet
- OB NotesDocument93 pagesOB NotesSwastik Jamadar100% (1)
- Building An HR Strategy: (Chap 7: HR Value Proposition) Supreet Kaur Saurabh PandeyDocument16 pagesBuilding An HR Strategy: (Chap 7: HR Value Proposition) Supreet Kaur Saurabh PandeyyrperdanaNo ratings yet
- 1od IntroductionDocument24 pages1od IntroductionSampada GuptaNo ratings yet
- CharacteristicsDocument10 pagesCharacteristicsAmuliya VSNo ratings yet
- Assignment1 PDFDocument4 pagesAssignment1 PDFSunil S ShettyNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1: What Is Organization Behavior?: The Importance of Interpersonal SkillsDocument5 pagesChapter 1: What Is Organization Behavior?: The Importance of Interpersonal SkillsPhạm Châu Thuý KiềuNo ratings yet
- Pom 1 PDFDocument22 pagesPom 1 PDFRamnath PeethambaranNo ratings yet
- The Learning OrganizationDocument40 pagesThe Learning OrganizationSovraj G. BaruahNo ratings yet
- C M S College of Engineering, Namakkal - 637 003 Department of Management Studies BA9265 Organizational Theory, Design and Development Unit - IDocument21 pagesC M S College of Engineering, Namakkal - 637 003 Department of Management Studies BA9265 Organizational Theory, Design and Development Unit - IsudhaaNo ratings yet
- Role of Work Ethics in Organizational EffectivenessDocument2 pagesRole of Work Ethics in Organizational EffectivenessRajdeep PaulNo ratings yet
- HRM Unit 1 NotesDocument5 pagesHRM Unit 1 Notesnishant mehtaNo ratings yet
- Management: Lecture OverviewDocument32 pagesManagement: Lecture Overviewkajojo joyNo ratings yet
- Exact Syllabus Sem 1 NoyorikaDocument13 pagesExact Syllabus Sem 1 NoyorikaNoyorika PrasadNo ratings yet
- What Is The Behavioural Science Approach To ManagementDocument4 pagesWhat Is The Behavioural Science Approach To ManagementPahulpreet SinghNo ratings yet
- Organizational Theory and DesignDocument5 pagesOrganizational Theory and DesignBenchaminJacobNo ratings yet
- Organization Theory: Organization Theory: Organization Theory: Organization TheoryDocument23 pagesOrganization Theory: Organization Theory: Organization Theory: Organization TheoryvelusnNo ratings yet
- Em 673 Assignment 2Document17 pagesEm 673 Assignment 2api-652656444No ratings yet
- Management Mid Copy 2Document17 pagesManagement Mid Copy 2Shamma AlshamsiNo ratings yet
- Unit 1Document68 pagesUnit 1Kowsalya ArunachalamNo ratings yet
- Business Orgnaisation - Page 288Document304 pagesBusiness Orgnaisation - Page 288Rohit KhannaNo ratings yet
- ORGS - Chapter 1Document4 pagesORGS - Chapter 1hemanthsoni16No ratings yet
- The Collegial Leadership Model: Six Basic Elements for Agile Organisational DevelopmentFrom EverandThe Collegial Leadership Model: Six Basic Elements for Agile Organisational DevelopmentNo ratings yet
- 001 2018 4 Study-GuideDocument154 pages001 2018 4 Study-GuideDINEO PRUDENCE NONGNo ratings yet
- Final Resume Format - v5Document1 pageFinal Resume Format - v5Sarthak MakkarNo ratings yet
- Supply Chain Strategy and Performance MeasuresDocument28 pagesSupply Chain Strategy and Performance MeasuresSHIVANSHUNo ratings yet
- Internship at Forward SportsDocument9 pagesInternship at Forward SportsMuzamil MushtaqNo ratings yet
- Evolution of Supply Chain ManagementDocument1 pageEvolution of Supply Chain ManagementAkshay Mungase100% (1)
- The Eight Essential Supply Chain Management Processes2004Document10 pagesThe Eight Essential Supply Chain Management Processes2004SERGIO BARRIOS TORRESNo ratings yet
- Strategic Supply Chain & Logistics Management MGMT 3017: Welcome ToDocument59 pagesStrategic Supply Chain & Logistics Management MGMT 3017: Welcome ToWonderkid YHHNo ratings yet
- New Product Development, CadburyDocument15 pagesNew Product Development, CadburyUnscrewing_buks100% (9)
- Makerere University: Nansana Municipal CouncilDocument41 pagesMakerere University: Nansana Municipal CouncilddhgdhgNo ratings yet
- Oracle Warehouse Management: Oracle Value Chain Execution SolutionDocument4 pagesOracle Warehouse Management: Oracle Value Chain Execution SolutionkfccNo ratings yet
- APICS Magazine JanFEB12Document52 pagesAPICS Magazine JanFEB12royreid99No ratings yet
- Logistics and Supply Chain Management Unit-3Document24 pagesLogistics and Supply Chain Management Unit-3AkhiNo ratings yet
- M.B.A (CBCS Pattern) (For The Affiliated College Students Admitted During The Academic Year 20012-13&onwards) ExaminationsDocument11 pagesM.B.A (CBCS Pattern) (For The Affiliated College Students Admitted During The Academic Year 20012-13&onwards) ExaminationsRamkumarNo ratings yet
- Digital Marketing Strategies For Value Co Creation Models and Approaches For Online Brand Communities Wilson Ozuem Full ChapterDocument68 pagesDigital Marketing Strategies For Value Co Creation Models and Approaches For Online Brand Communities Wilson Ozuem Full Chapterannie.coombs631100% (19)
- Live Order Tracking SystemDocument5 pagesLive Order Tracking SystemEsha GuptaNo ratings yet
- Batch 2 SCM Assignment PresentationDocument14 pagesBatch 2 SCM Assignment Presentation18M108 - ARAVINTH ENo ratings yet
- Cbmec Midterm LessonsDocument7 pagesCbmec Midterm LessonsMyunimintNo ratings yet
- EFQM Excellence Model Guide 2010Document45 pagesEFQM Excellence Model Guide 2010Dmr PandaNo ratings yet
- Supply Chain Tutorial4Document3 pagesSupply Chain Tutorial4高玉山67% (9)
- Industrial Marketing ManagementDocument11 pagesIndustrial Marketing ManagementSoheil JuushiruoNo ratings yet
- OPER8020-3 Instructional Plan F22 (Rev)Document1 pageOPER8020-3 Instructional Plan F22 (Rev)vishvajitsinh BhatiNo ratings yet
- Project Profile On Plastic ProductsDocument7 pagesProject Profile On Plastic ProductsOm SharmaNo ratings yet
- Connecting ERP and Supply Chain Management StrategiesDocument12 pagesConnecting ERP and Supply Chain Management StrategiessahilkaushikNo ratings yet
- UNICEF Procedure On Sustainable ProcurementDocument4 pagesUNICEF Procedure On Sustainable ProcurementberkNo ratings yet
- TSC-CaseStudy - AppliedMaterials Supply Chain PDFDocument2 pagesTSC-CaseStudy - AppliedMaterials Supply Chain PDFPandu PanduNo ratings yet
- ERP II - Next-Generation Extended Enterprise ResourDocument7 pagesERP II - Next-Generation Extended Enterprise ResourjackNo ratings yet