Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Lesson 02_Inverse_Functions_Inverse_Triginometric_Functions-1-1 (1)
Lesson 02_Inverse_Functions_Inverse_Triginometric_Functions-1-1 (1)
Uploaded by
nahid.sarker.241Copyright:
Available Formats
You might also like
- MATH2023 Multivariable Calculus Chapter 6 Vector Calculus L2/L3 (Fall 2019)Document40 pagesMATH2023 Multivariable Calculus Chapter 6 Vector Calculus L2/L3 (Fall 2019)物理系小薯No ratings yet
- Mappings and FunctionsDocument4 pagesMappings and FunctionsAlvan MmaduwubaNo ratings yet
- Lesson 03_Exponential and Logarithmic Function-1-1Document6 pagesLesson 03_Exponential and Logarithmic Function-1-1nahid.sarker.241No ratings yet
- BeamDocument18 pagesBeamfantahun ayalnehNo ratings yet
- Beam 2Document19 pagesBeam 2fantahun ayalnehNo ratings yet
- Inverse FunctionsDocument14 pagesInverse FunctionsFano ThomasNo ratings yet
- MATH2023 Multivariable Calculus Chapter 3 Partial Derivatives L2/L3 (Fall 2019)Document36 pagesMATH2023 Multivariable Calculus Chapter 3 Partial Derivatives L2/L3 (Fall 2019)物理系小薯No ratings yet
- INVERSE FUNCTIONDocument8 pagesINVERSE FUNCTIONjohnlloydrocasNo ratings yet
- Diff. Calc. Module 7 Trigonometric & Inverse FunctionsDocument10 pagesDiff. Calc. Module 7 Trigonometric & Inverse FunctionsFernandez DanielNo ratings yet
- UNIT 4.1: DifferentialsDocument5 pagesUNIT 4.1: DifferentialsMarc ImperialNo ratings yet
- Robotics Course: LR02.3:: 3 Dimensional Homogenous TransformationDocument17 pagesRobotics Course: LR02.3:: 3 Dimensional Homogenous TransformationThiha Ye ThwayNo ratings yet
- FALLSEM2023-24 BMAT201L TH VL2023240102089 2023-07-25 Reference-Material-IDocument60 pagesFALLSEM2023-24 BMAT201L TH VL2023240102089 2023-07-25 Reference-Material-IComical comicNo ratings yet
- University of Limpopo: MemorandumDocument6 pagesUniversity of Limpopo: MemorandumNtokozo MasemulaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2 Mat455Document36 pagesChapter 2 Mat455Ajaq 98No ratings yet
- BOHOL MATHSHS GENMATH Q1 PLP3DAY3 v.01Document4 pagesBOHOL MATHSHS GENMATH Q1 PLP3DAY3 v.01Angelica CamaraoNo ratings yet
- HSVZJX DDocument10 pagesHSVZJX DCes SyNo ratings yet
- Module General Mathematics 3Document8 pagesModule General Mathematics 3sherilyn palacayNo ratings yet
- Unit-2 Vector CalculusDocument86 pagesUnit-2 Vector CalculusRitesh MukhNo ratings yet
- Coursework 5 - Module 4 - Calculus 2Document5 pagesCoursework 5 - Module 4 - Calculus 2Trina ArmeaNo ratings yet
- Complex Analytic FunctionsDocument60 pagesComplex Analytic FunctionsKiran YadavNo ratings yet
- Unit-Iii Two Dimensional Scalar Variable ProblemsDocument29 pagesUnit-Iii Two Dimensional Scalar Variable ProblemsFun timeNo ratings yet
- Gradient Of A Function هّلادلا رادحنإDocument11 pagesGradient Of A Function هّلادلا رادحنإGafeer FableNo ratings yet
- Handout 1 Gen MathDocument3 pagesHandout 1 Gen MathOliric NabcihNo ratings yet
- Log Graphs (Linear Reduction) : Type 1 X Is in The Power Type 2 - X Is in The BaseDocument5 pagesLog Graphs (Linear Reduction) : Type 1 X Is in The Power Type 2 - X Is in The BaseZantaye ThomasNo ratings yet
- 1 Notations and Reviews: 1.1 Spectral Theory of Bounded Self Adjoint OperatorsDocument5 pages1 Notations and Reviews: 1.1 Spectral Theory of Bounded Self Adjoint Operatorscw538No ratings yet
- CH3 Vector CalculusDocument39 pagesCH3 Vector CalculusAfie Fahry AdzmiNo ratings yet
- Lecture 1Document9 pagesLecture 1owronrawan74No ratings yet
- MA1511 2021S1 Chapter 4 Vector FieldsDocument22 pagesMA1511 2021S1 Chapter 4 Vector FieldsJustin NgNo ratings yet
- Lesson 05 - Directional DerivativesDocument12 pagesLesson 05 - Directional Derivativesrakibnabil800No ratings yet
- 5 Fea CadDocument12 pages5 Fea CadMohamed AbdelazizNo ratings yet
- Genmathweek 3Document7 pagesGenmathweek 3Ricky LumantaNo ratings yet
- Intro Metric FinalDocument51 pagesIntro Metric FinalBrendo CostaNo ratings yet
- L2 Vector AdditionDocument5 pagesL2 Vector AdditionAvneetK SainiNo ratings yet
- 2023 Problem Set 5P PDFDocument4 pages2023 Problem Set 5P PDF物理系小薯No ratings yet
- MA1511 Chapter 4Document18 pagesMA1511 Chapter 4Kang Le LimNo ratings yet
- Study Material Xii (Maths) 041 2023-24Document85 pagesStudy Material Xii (Maths) 041 2023-24AimbotNo ratings yet
- Piecewise, Continuous, Even and Odd FxnsDocument24 pagesPiecewise, Continuous, Even and Odd FxnsJohannah ManokoNo ratings yet
- 01 - Fundamental Mathematics For ElasticityDocument10 pages01 - Fundamental Mathematics For ElasticityEngr. John Mark Payawal, MSCENo ratings yet
- Lesson 5 - Inverse FunctionDocument24 pagesLesson 5 - Inverse Functionfranzortenero.schoolworkNo ratings yet
- 3.0 Introduction of Derivative: DX Dy DX DFDocument40 pages3.0 Introduction of Derivative: DX Dy DX DFGoh Siak PengNo ratings yet
- SLG 7.1.1 Functions That Have Inverses 1Document8 pagesSLG 7.1.1 Functions That Have Inverses 1Faye AbianNo ratings yet
- Worksheet 2Document2 pagesWorksheet 2Yordanos MekonnenNo ratings yet
- Conservative Vector FieldDocument17 pagesConservative Vector Fielddurga03No ratings yet
- Math Lec. 1Document8 pagesMath Lec. 1owronrawan74No ratings yet
- PHYS 101 - General Physics I Midterm Exam 1 Solutions: Duration: 90 Minutes Saturday, 09 November 2019 10:00Document3 pagesPHYS 101 - General Physics I Midterm Exam 1 Solutions: Duration: 90 Minutes Saturday, 09 November 2019 10:00Mohammed AL-sharafiNo ratings yet
- Pre-Calculus STEM Q2 L5Document11 pagesPre-Calculus STEM Q2 L5Maxine ReyesNo ratings yet
- Vector Calculus I 2Document52 pagesVector Calculus I 2Ayush SawNo ratings yet
- Lecture 2 - NasDocument37 pagesLecture 2 - Nasnourhandardeer3No ratings yet
- MAT Lecture2Document47 pagesMAT Lecture2Deniz Egemen YılmazNo ratings yet
- MPPT8 The Definite Integral and ApplicationsDocument44 pagesMPPT8 The Definite Integral and ApplicationsStandardNo ratings yet
- Lecture 10 03 12 2022Document8 pagesLecture 10 03 12 2022owronrawan74No ratings yet
- Elasticity T01-2Document9 pagesElasticity T01-2Giannis MamalakisNo ratings yet
- Mathematics (Algebra, Geometry, Trigonometry)Document3 pagesMathematics (Algebra, Geometry, Trigonometry)Java Katrina, BautistaNo ratings yet
- Bend TestDocument7 pagesBend TestAman NigamNo ratings yet
- Lnote - IIIDocument7 pagesLnote - IIIUpdirahman MohamoudNo ratings yet
- Vector Calculus - GATE Study Material in PDFDocument10 pagesVector Calculus - GATE Study Material in PDFSupriya Santre100% (1)
- Vector Calculus GATE Study Material in PDF 1Document10 pagesVector Calculus GATE Study Material in PDF 1nazeeraNo ratings yet
- XkjijjnnDocument11 pagesXkjijjnnmohit bhardwajNo ratings yet
- Lecture 1 02 10 2022Document8 pagesLecture 1 02 10 2022owronrawan74No ratings yet
- Notes GraphDocument9 pagesNotes GraphFurkan memonNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2 - Discrete-Mathematics-Set-Operations-Discrete-Mathematics-Basic-Structures-SetsDocument76 pagesChapter 2 - Discrete-Mathematics-Set-Operations-Discrete-Mathematics-Basic-Structures-SetsbusatifcNo ratings yet
- Terminologies and Special Types of GraphsDocument5 pagesTerminologies and Special Types of GraphsSean CatapangNo ratings yet
- 1.1 Functions and Continuity QsDocument4 pages1.1 Functions and Continuity QsSri Devi NagarjunaNo ratings yet
- Homework 3Document6 pagesHomework 3Leo ChungNo ratings yet
- M3 Adv. AlgebraDocument4 pagesM3 Adv. AlgebraAngel Von Heart PandesNo ratings yet
- Multiple Choice Questions: Cbse Class 12 Maths MCQ'S & Case StudyDocument7 pagesMultiple Choice Questions: Cbse Class 12 Maths MCQ'S & Case StudyDhayananthNo ratings yet
- HW Checkpoint #5 (Relations and Functions)Document2 pagesHW Checkpoint #5 (Relations and Functions)Menna ArafaNo ratings yet
- Types of FunctionsDocument6 pagesTypes of FunctionsMartin AlonsoNo ratings yet
- Week 8 HomeworkDocument3 pagesWeek 8 HomeworkmoppommtyNo ratings yet
- Function ModuleDocument52 pagesFunction ModulepifodaNo ratings yet
- The Mathematics of GraphsDocument6 pagesThe Mathematics of GraphsJebbrys LargoNo ratings yet
- Class 11 - Maths - Relations and FunctionsDocument19 pagesClass 11 - Maths - Relations and FunctionsAaminNo ratings yet
- A Linverse Nuit Incolore Nuit Incolore - A LinverseDocument3 pagesA Linverse Nuit Incolore Nuit Incolore - A LinverseelearningcorrectionsNo ratings yet
- Terminologies in Graph Theory: Md. Saidur RahmanDocument35 pagesTerminologies in Graph Theory: Md. Saidur RahmanAvi ShekNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2 SolutionsDocument20 pagesChapter 2 SolutionsS.packialakshmiNo ratings yet
- 0026 - Neutrosophic Chromatic NumberDocument68 pages0026 - Neutrosophic Chromatic NumberHenry GarrettNo ratings yet
- Full Solution Manual For Discrete Mathematics With Graph Theory 3 E 3Rd Edition Edgar G Goodaire Michael M Parmenter PDF Docx Full Chapter ChapterDocument36 pagesFull Solution Manual For Discrete Mathematics With Graph Theory 3 E 3Rd Edition Edgar G Goodaire Michael M Parmenter PDF Docx Full Chapter Chaptersquireenmabbyzc7meu100% (24)
- SMT5201Document70 pagesSMT5201Piku MajhiNo ratings yet
- Venn Diagram: Set OperationsDocument6 pagesVenn Diagram: Set OperationsAkim ApallaNo ratings yet
- GB Sir Calculs PrbomDocument607 pagesGB Sir Calculs PrbomAnish VijayNo ratings yet
- Topology 1 KSOU TextbookDocument186 pagesTopology 1 KSOU Textbookindujois021118No ratings yet
- Math in NetworksDocument22 pagesMath in NetworksHannah RasumanNo ratings yet
- Chapter 8Document31 pagesChapter 8Nguyễn Minh HoàngNo ratings yet
- Xii MathsDocument118 pagesXii Mathsmisterrandom006No ratings yet
- Drawing Inverse Function Graphs:: Key Features of The GraphDocument3 pagesDrawing Inverse Function Graphs:: Key Features of The GraphShraddha NayakNo ratings yet
- Eulerian Graph and DigraphDocument9 pagesEulerian Graph and DigraphCantika ValensiaNo ratings yet
- Finding Domain and Range of A Function G8Document27 pagesFinding Domain and Range of A Function G8kennethvilla07No ratings yet
- PlanarGraph (2022 - 02 - 01 16 - 13 - 34 UTC)Document26 pagesPlanarGraph (2022 - 02 - 01 16 - 13 - 34 UTC)ValentinaNo ratings yet
Lesson 02_Inverse_Functions_Inverse_Triginometric_Functions-1-1 (1)
Lesson 02_Inverse_Functions_Inverse_Triginometric_Functions-1-1 (1)
Uploaded by
nahid.sarker.241Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Lesson 02_Inverse_Functions_Inverse_Triginometric_Functions-1-1 (1)
Lesson 02_Inverse_Functions_Inverse_Triginometric_Functions-1-1 (1)
Uploaded by
nahid.sarker.241Copyright:
Available Formats
Inverse Functions, Inverse Trigonometric Functions
Ref. Textbook: Calculus (10th ed.) by Anton, Bivens and Davis
❑ Inverse Functions
If the functions 𝑓(𝑥) and 𝑔(𝑥) satisfy the two conditions
𝑔(𝑓(𝑥)) = 𝑥 for every 𝑥 in the domain of 𝑓
𝑓(𝑔(𝑥)) = 𝑥 for every 𝑥 in the domain of 𝑔
then 𝒇 is an inverse of 𝒈 and 𝒈 is an inverse of 𝒇
or 𝒇 and 𝒈 are inverse functions to each other. 𝒇(𝒙) = 𝒙𝟑 + 𝟏
Example. 𝑓 𝑥 = 𝑥 3 + 1 is the inverse of
3
𝑔 𝑥 = 𝑥 − 1 as
3 3
𝑓 𝑔 𝑥 = 𝑓 𝑥 − 1 = ( 𝑥 − 1)3 +1 = 𝑥
3
𝑔 𝑓 𝑥 = 𝑔 𝑥3 + 1 = 𝑥3 + 1 − 1 = 𝑥
We can write,
3
𝑓 −1 𝑥 = 𝑔 𝑥 = 𝑥 − 1
𝑔−1 𝑥 = 𝑓 𝑥 = 𝑥 3 + 1 𝟑
𝒈(𝒙) = 𝒙−𝟏
The graphs of 𝑦 = 𝑓(𝑥) and 𝑦 = 𝑔 𝑥 are
reflections of each other about the line 𝑦 = 𝑥.
Lesson 02: Inverse Functions and Inverse
2/7/2023 1
Trigonometric functions
Inverse Functions, Inverse Trigonometric Functions
Ref. Textbook: Calculus (10th ed.) by Anton, Bivens and Davis
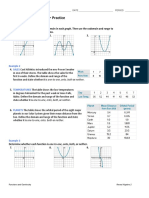
Example. For 𝑓(𝑥) = 3𝑥 − 2 with 𝑥 as the independent variable, find 𝑓 −1 (𝑥) and state the
domain and range of 𝑓 −1 (𝑥). Also, graph both 𝑓 𝑥 and 𝑓 −1 (𝑥) in the same coordinate
system.
2 𝑦 2 +2
Solution. We assume that 𝑦 = 𝑓 𝑥 = 3 𝑥 −3 ⇒ 𝑦2 = 3𝑥 − 2 ⇒ 𝑥 = 3
𝑥2 + 2
∴ 𝑓 −1 𝑥 = 𝑥2 + 2
3 𝑦=
3
2
Here, Dom 𝑓 = ,∞ and Range 𝑓 = [0, ∞)
3
Therefore, 𝒚 = 𝟑𝒙 − 𝟐
2
Dom 𝑓 −1 = 0, ∞ and Range 𝑓 −1 = ,∞
3
Lesson 02: Inverse Functions and Inverse
2/7/2023 2
Trigonometric functions
Inverse Functions, Inverse Trigonometric Functions
Ref. Textbook: Calculus (10th ed.) by Anton, Bivens and Davis
𝑥
Example. (a) The inverse of 𝑓(𝑥) = 2𝑥 is 𝑓 −1 𝑥 = 2
(b) The inverse of 𝑓 𝑥 = 𝑥 3 is 𝑓 −1 𝑥 = 𝑥 1/3
𝑥
(a) 𝑦 = 2𝑥 and 𝑦 = 2 are mirror image of (b) 𝑦 = 𝑥 3 and 𝑦 = 𝑥 1/3 are mirror image
each other with respect to the line 𝑦 = 𝑥. of each other with respect to the line 𝑦 =
𝑥.
Lesson 02: Inverse Functions and Inverse
2/7/2023 3
Trigonometric functions
Inverse Functions, Inverse Trigonometric Functions
Ref. Textbook: Calculus (10th ed.) by Anton, Bivens and Davis
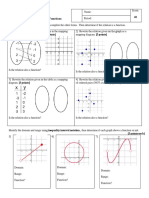
Theorem (The Horizontal Line Test) A function has an inverse function if and only if its graph is cut
at most once by any horizontal line.
Example. 𝑓 𝑥 = 𝑥 2 has no inverse but 𝑓 𝑥 = 𝑥 3 does.
➢ A horizontal line cuts the graph of 𝑦 = 𝑥 2 more ➢ Any horizontal line cuts the graph of 𝑦 = 𝑥 3 at
than once, so 𝑓 𝑥 = 𝑥 2 is not invertible. most once, so 𝑓 𝑥 = 𝑥 3 is invertible.
Lesson 02: Inverse Functions and Inverse
2/7/2023 4
Trigonometric functions
Inverse Functions, Inverse Trigonometric Functions
Ref. Textbook: Calculus (10th ed.) by Anton, Bivens and Davis
❑ Restricting Domains for Invertibility
Example. Restricted functions 𝑓 𝑥 = 𝑥 2 , 𝑥 ≥ 0 and g 𝑥 = 𝑥 2 , 𝑥 ≤ 0 pass the horizontal line
test, hence these functions are invertible.
Their inverse functions are 𝑓 −1 𝑥 = 𝑥 and 𝑔−1 𝑥 = − 𝑥.
Lesson 02: Inverse Functions and Inverse
2/7/2023 5
Trigonometric functions
Inverse Functions, Inverse Trigonometric Functions
Ref. Textbook: Calculus (10th ed.) by Anton, Bivens and Davis
❑Inverse Trigonometric Functions (sin−1 𝑥, cos −1 𝑥, tan−1 𝑥, sec −1 𝑥)
Lesson 02: Inverse Functions and Inverse
2/7/2023 6
Trigonometric functions
Inverse Functions, Inverse Trigonometric Functions
Ref. Textbook: Calculus (10th ed.) by Anton, Bivens and Davis
❑Exercise Set 0.4
Lesson 02: Inverse Functions and Inverse
2/7/2023 7
Trigonometric functions
You might also like
- MATH2023 Multivariable Calculus Chapter 6 Vector Calculus L2/L3 (Fall 2019)Document40 pagesMATH2023 Multivariable Calculus Chapter 6 Vector Calculus L2/L3 (Fall 2019)物理系小薯No ratings yet
- Mappings and FunctionsDocument4 pagesMappings and FunctionsAlvan MmaduwubaNo ratings yet
- Lesson 03_Exponential and Logarithmic Function-1-1Document6 pagesLesson 03_Exponential and Logarithmic Function-1-1nahid.sarker.241No ratings yet
- BeamDocument18 pagesBeamfantahun ayalnehNo ratings yet
- Beam 2Document19 pagesBeam 2fantahun ayalnehNo ratings yet
- Inverse FunctionsDocument14 pagesInverse FunctionsFano ThomasNo ratings yet
- MATH2023 Multivariable Calculus Chapter 3 Partial Derivatives L2/L3 (Fall 2019)Document36 pagesMATH2023 Multivariable Calculus Chapter 3 Partial Derivatives L2/L3 (Fall 2019)物理系小薯No ratings yet
- INVERSE FUNCTIONDocument8 pagesINVERSE FUNCTIONjohnlloydrocasNo ratings yet
- Diff. Calc. Module 7 Trigonometric & Inverse FunctionsDocument10 pagesDiff. Calc. Module 7 Trigonometric & Inverse FunctionsFernandez DanielNo ratings yet
- UNIT 4.1: DifferentialsDocument5 pagesUNIT 4.1: DifferentialsMarc ImperialNo ratings yet
- Robotics Course: LR02.3:: 3 Dimensional Homogenous TransformationDocument17 pagesRobotics Course: LR02.3:: 3 Dimensional Homogenous TransformationThiha Ye ThwayNo ratings yet
- FALLSEM2023-24 BMAT201L TH VL2023240102089 2023-07-25 Reference-Material-IDocument60 pagesFALLSEM2023-24 BMAT201L TH VL2023240102089 2023-07-25 Reference-Material-IComical comicNo ratings yet
- University of Limpopo: MemorandumDocument6 pagesUniversity of Limpopo: MemorandumNtokozo MasemulaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2 Mat455Document36 pagesChapter 2 Mat455Ajaq 98No ratings yet
- BOHOL MATHSHS GENMATH Q1 PLP3DAY3 v.01Document4 pagesBOHOL MATHSHS GENMATH Q1 PLP3DAY3 v.01Angelica CamaraoNo ratings yet
- HSVZJX DDocument10 pagesHSVZJX DCes SyNo ratings yet
- Module General Mathematics 3Document8 pagesModule General Mathematics 3sherilyn palacayNo ratings yet
- Unit-2 Vector CalculusDocument86 pagesUnit-2 Vector CalculusRitesh MukhNo ratings yet
- Coursework 5 - Module 4 - Calculus 2Document5 pagesCoursework 5 - Module 4 - Calculus 2Trina ArmeaNo ratings yet
- Complex Analytic FunctionsDocument60 pagesComplex Analytic FunctionsKiran YadavNo ratings yet
- Unit-Iii Two Dimensional Scalar Variable ProblemsDocument29 pagesUnit-Iii Two Dimensional Scalar Variable ProblemsFun timeNo ratings yet
- Gradient Of A Function هّلادلا رادحنإDocument11 pagesGradient Of A Function هّلادلا رادحنإGafeer FableNo ratings yet
- Handout 1 Gen MathDocument3 pagesHandout 1 Gen MathOliric NabcihNo ratings yet
- Log Graphs (Linear Reduction) : Type 1 X Is in The Power Type 2 - X Is in The BaseDocument5 pagesLog Graphs (Linear Reduction) : Type 1 X Is in The Power Type 2 - X Is in The BaseZantaye ThomasNo ratings yet
- 1 Notations and Reviews: 1.1 Spectral Theory of Bounded Self Adjoint OperatorsDocument5 pages1 Notations and Reviews: 1.1 Spectral Theory of Bounded Self Adjoint Operatorscw538No ratings yet
- CH3 Vector CalculusDocument39 pagesCH3 Vector CalculusAfie Fahry AdzmiNo ratings yet
- Lecture 1Document9 pagesLecture 1owronrawan74No ratings yet
- MA1511 2021S1 Chapter 4 Vector FieldsDocument22 pagesMA1511 2021S1 Chapter 4 Vector FieldsJustin NgNo ratings yet
- Lesson 05 - Directional DerivativesDocument12 pagesLesson 05 - Directional Derivativesrakibnabil800No ratings yet
- 5 Fea CadDocument12 pages5 Fea CadMohamed AbdelazizNo ratings yet
- Genmathweek 3Document7 pagesGenmathweek 3Ricky LumantaNo ratings yet
- Intro Metric FinalDocument51 pagesIntro Metric FinalBrendo CostaNo ratings yet
- L2 Vector AdditionDocument5 pagesL2 Vector AdditionAvneetK SainiNo ratings yet
- 2023 Problem Set 5P PDFDocument4 pages2023 Problem Set 5P PDF物理系小薯No ratings yet
- MA1511 Chapter 4Document18 pagesMA1511 Chapter 4Kang Le LimNo ratings yet
- Study Material Xii (Maths) 041 2023-24Document85 pagesStudy Material Xii (Maths) 041 2023-24AimbotNo ratings yet
- Piecewise, Continuous, Even and Odd FxnsDocument24 pagesPiecewise, Continuous, Even and Odd FxnsJohannah ManokoNo ratings yet
- 01 - Fundamental Mathematics For ElasticityDocument10 pages01 - Fundamental Mathematics For ElasticityEngr. John Mark Payawal, MSCENo ratings yet
- Lesson 5 - Inverse FunctionDocument24 pagesLesson 5 - Inverse Functionfranzortenero.schoolworkNo ratings yet
- 3.0 Introduction of Derivative: DX Dy DX DFDocument40 pages3.0 Introduction of Derivative: DX Dy DX DFGoh Siak PengNo ratings yet
- SLG 7.1.1 Functions That Have Inverses 1Document8 pagesSLG 7.1.1 Functions That Have Inverses 1Faye AbianNo ratings yet
- Worksheet 2Document2 pagesWorksheet 2Yordanos MekonnenNo ratings yet
- Conservative Vector FieldDocument17 pagesConservative Vector Fielddurga03No ratings yet
- Math Lec. 1Document8 pagesMath Lec. 1owronrawan74No ratings yet
- PHYS 101 - General Physics I Midterm Exam 1 Solutions: Duration: 90 Minutes Saturday, 09 November 2019 10:00Document3 pagesPHYS 101 - General Physics I Midterm Exam 1 Solutions: Duration: 90 Minutes Saturday, 09 November 2019 10:00Mohammed AL-sharafiNo ratings yet
- Pre-Calculus STEM Q2 L5Document11 pagesPre-Calculus STEM Q2 L5Maxine ReyesNo ratings yet
- Vector Calculus I 2Document52 pagesVector Calculus I 2Ayush SawNo ratings yet
- Lecture 2 - NasDocument37 pagesLecture 2 - Nasnourhandardeer3No ratings yet
- MAT Lecture2Document47 pagesMAT Lecture2Deniz Egemen YılmazNo ratings yet
- MPPT8 The Definite Integral and ApplicationsDocument44 pagesMPPT8 The Definite Integral and ApplicationsStandardNo ratings yet
- Lecture 10 03 12 2022Document8 pagesLecture 10 03 12 2022owronrawan74No ratings yet
- Elasticity T01-2Document9 pagesElasticity T01-2Giannis MamalakisNo ratings yet
- Mathematics (Algebra, Geometry, Trigonometry)Document3 pagesMathematics (Algebra, Geometry, Trigonometry)Java Katrina, BautistaNo ratings yet
- Bend TestDocument7 pagesBend TestAman NigamNo ratings yet
- Lnote - IIIDocument7 pagesLnote - IIIUpdirahman MohamoudNo ratings yet
- Vector Calculus - GATE Study Material in PDFDocument10 pagesVector Calculus - GATE Study Material in PDFSupriya Santre100% (1)
- Vector Calculus GATE Study Material in PDF 1Document10 pagesVector Calculus GATE Study Material in PDF 1nazeeraNo ratings yet
- XkjijjnnDocument11 pagesXkjijjnnmohit bhardwajNo ratings yet
- Lecture 1 02 10 2022Document8 pagesLecture 1 02 10 2022owronrawan74No ratings yet
- Notes GraphDocument9 pagesNotes GraphFurkan memonNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2 - Discrete-Mathematics-Set-Operations-Discrete-Mathematics-Basic-Structures-SetsDocument76 pagesChapter 2 - Discrete-Mathematics-Set-Operations-Discrete-Mathematics-Basic-Structures-SetsbusatifcNo ratings yet
- Terminologies and Special Types of GraphsDocument5 pagesTerminologies and Special Types of GraphsSean CatapangNo ratings yet
- 1.1 Functions and Continuity QsDocument4 pages1.1 Functions and Continuity QsSri Devi NagarjunaNo ratings yet
- Homework 3Document6 pagesHomework 3Leo ChungNo ratings yet
- M3 Adv. AlgebraDocument4 pagesM3 Adv. AlgebraAngel Von Heart PandesNo ratings yet
- Multiple Choice Questions: Cbse Class 12 Maths MCQ'S & Case StudyDocument7 pagesMultiple Choice Questions: Cbse Class 12 Maths MCQ'S & Case StudyDhayananthNo ratings yet
- HW Checkpoint #5 (Relations and Functions)Document2 pagesHW Checkpoint #5 (Relations and Functions)Menna ArafaNo ratings yet
- Types of FunctionsDocument6 pagesTypes of FunctionsMartin AlonsoNo ratings yet
- Week 8 HomeworkDocument3 pagesWeek 8 HomeworkmoppommtyNo ratings yet
- Function ModuleDocument52 pagesFunction ModulepifodaNo ratings yet
- The Mathematics of GraphsDocument6 pagesThe Mathematics of GraphsJebbrys LargoNo ratings yet
- Class 11 - Maths - Relations and FunctionsDocument19 pagesClass 11 - Maths - Relations and FunctionsAaminNo ratings yet
- A Linverse Nuit Incolore Nuit Incolore - A LinverseDocument3 pagesA Linverse Nuit Incolore Nuit Incolore - A LinverseelearningcorrectionsNo ratings yet
- Terminologies in Graph Theory: Md. Saidur RahmanDocument35 pagesTerminologies in Graph Theory: Md. Saidur RahmanAvi ShekNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2 SolutionsDocument20 pagesChapter 2 SolutionsS.packialakshmiNo ratings yet
- 0026 - Neutrosophic Chromatic NumberDocument68 pages0026 - Neutrosophic Chromatic NumberHenry GarrettNo ratings yet
- Full Solution Manual For Discrete Mathematics With Graph Theory 3 E 3Rd Edition Edgar G Goodaire Michael M Parmenter PDF Docx Full Chapter ChapterDocument36 pagesFull Solution Manual For Discrete Mathematics With Graph Theory 3 E 3Rd Edition Edgar G Goodaire Michael M Parmenter PDF Docx Full Chapter Chaptersquireenmabbyzc7meu100% (24)
- SMT5201Document70 pagesSMT5201Piku MajhiNo ratings yet
- Venn Diagram: Set OperationsDocument6 pagesVenn Diagram: Set OperationsAkim ApallaNo ratings yet
- GB Sir Calculs PrbomDocument607 pagesGB Sir Calculs PrbomAnish VijayNo ratings yet
- Topology 1 KSOU TextbookDocument186 pagesTopology 1 KSOU Textbookindujois021118No ratings yet
- Math in NetworksDocument22 pagesMath in NetworksHannah RasumanNo ratings yet
- Chapter 8Document31 pagesChapter 8Nguyễn Minh HoàngNo ratings yet
- Xii MathsDocument118 pagesXii Mathsmisterrandom006No ratings yet
- Drawing Inverse Function Graphs:: Key Features of The GraphDocument3 pagesDrawing Inverse Function Graphs:: Key Features of The GraphShraddha NayakNo ratings yet
- Eulerian Graph and DigraphDocument9 pagesEulerian Graph and DigraphCantika ValensiaNo ratings yet
- Finding Domain and Range of A Function G8Document27 pagesFinding Domain and Range of A Function G8kennethvilla07No ratings yet
- PlanarGraph (2022 - 02 - 01 16 - 13 - 34 UTC)Document26 pagesPlanarGraph (2022 - 02 - 01 16 - 13 - 34 UTC)ValentinaNo ratings yet