Professional Documents
Culture Documents
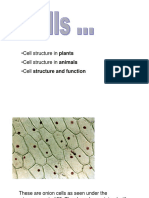
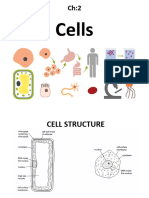
-Cells
-Cells
Uploaded by
Gary Chye0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
2 views1 pageCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pdf or txt
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
2 views1 page-Cells
-Cells
Uploaded by
Gary ChyeCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pdf or txt
You are on page 1of 1
-Cells
Thursday, June 27, 2024 7:08 PM
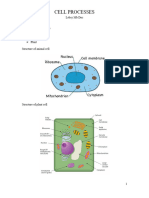
Normal cells
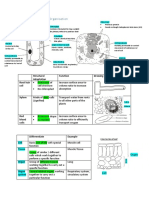
Organelle Structure Function
Cell membrane -Outermost membrane -Selectively controls substances in &out
(partially permeable membrane )
Nucleus -A Nuclear envelope, chromatin -Contain genetic material (DNA) Difference between animal and plant cell
threads , -Controls cell activities
a nucleolus -Controls cell division and reproduction
Cytoplasm -Jelly-like substances between cell -Site where chemical reaction take place
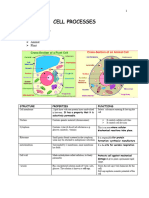
Features Plant cell Animal cell
membrane and nucleus Cell wall V X
Cell wall ( Found in plant cell only) -Made of cellulose -Protect the cell Vacuole Large central vacuole Numerous small vacuole
-Provides strength and support to the plant filled with cell sap
cell Chloroplast V X
-Gives the cell a regular shape
Chloroplast -Oval structure contains chlorophyll -Contain chlorophyll to trap light energy and
convert it into chemical energy through
photosynthesis
Ribosomes -Small spherical structure -Responsible for synthesis/ make protein
Vacuole -Animal cell: Numerous small vacuole -Controls turgidity
-Plant cell : 1 large central vacuole
Mitochondria/ Mitochondrion NIL -Site of respiration where food substances
are broken down to release energy
Specialized cell
Cell structure How is it adapted to its function
Red blood cell -Biconcave-> increases surface area-to-volume ratio, so
oxygen can diffuses in & out faster
-Lacks a nucleus->has more space for haemoglobin, to
transport more oxygen
-Contains haemoglobin-> binds with oxygen and transport it
from the lung to all parts of the body
Root hair cells -Elongated structure-> increases surface area- to - volume
ratio for faster absorption of water and mineral salt
Xylem vessel (dead) -Long and hollow-> transports water and mineral salts to
flow easily
-Thickened with lignin -> provides support to prevent
collapse of xylem vessel
Chapter 1 (cells) Page 1
You might also like
- Learning Activity Sheet Biotechnology 8Document11 pagesLearning Activity Sheet Biotechnology 8Jaeda BaltazarNo ratings yet
- Cellsjw PDFDocument49 pagesCellsjw PDFToriNo ratings yet
- Fifth Quiz Samples BIO 102Document9 pagesFifth Quiz Samples BIO 102Wendy Stephanie AcostaNo ratings yet
- Hindu Gotras and The Science Behind ThemDocument13 pagesHindu Gotras and The Science Behind ThemPankaj SaksenaNo ratings yet
- Science Word SearchDocument1 pageScience Word SearchHashimi IsmailNo ratings yet
- BIO COMPLETE (Repaired)Document117 pagesBIO COMPLETE (Repaired)tonikay219No ratings yet
- Cell PorcessesDocument6 pagesCell PorcessesontlametsetidimaneNo ratings yet
- Cell ProcessesDocument6 pagesCell Processestnkele73No ratings yet
- G6 CellsDocument13 pagesG6 CellsDivisha AgarwalNo ratings yet
- Cell ProcessesDocument8 pagesCell Processesdinakempho3No ratings yet
- Cell ProcessesDocument7 pagesCell Processeskmakabe78No ratings yet
- Lecture/Week 2/ Pre-Recorded Lecture BasedDocument6 pagesLecture/Week 2/ Pre-Recorded Lecture Basedmaria apolonia vergaraNo ratings yet
- Simplified Notes For Biology StudiesDocument56 pagesSimplified Notes For Biology Studiesabi_5dec94100% (5)
- 1 Chem113 LecDocument10 pages1 Chem113 LecJamaica M DanguecanNo ratings yet
- Biology Reviewer Paolo PurisimaDocument7 pagesBiology Reviewer Paolo PurisimaPaolo JoaquinNo ratings yet
- Biology: Prokaryotic CellsDocument7 pagesBiology: Prokaryotic CellsVictoria IlaganNo ratings yet
- Pro Bef Ore Karyotic Nucleus: BloodDocument5 pagesPro Bef Ore Karyotic Nucleus: BloodDanielle Anne Zamora-Matillosa LambanNo ratings yet
- Triple Award 2020Document130 pagesTriple Award 2020Kimberly MojeNo ratings yet
- Biology ReviewerDocument4 pagesBiology ReviewerLycaNo ratings yet
- 2 CellsDocument31 pages2 CellsRashed NadaNo ratings yet
- General Biology ReviewerDocument4 pagesGeneral Biology ReviewerJes NapiñasNo ratings yet
- Biology VCE Chapter 1Document8 pagesBiology VCE Chapter 1Rachel JNo ratings yet
- CELLDocument5 pagesCELLrazshellareignNo ratings yet
- Cañete, Rea May (Cell Bio - Parts and Function of The Cell) - FLTamayao - Nov 14 2 PDFDocument6 pagesCañete, Rea May (Cell Bio - Parts and Function of The Cell) - FLTamayao - Nov 14 2 PDFRheaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2 Cell Structure and Cell Organisation 2.1 Cell StructureDocument9 pagesChapter 2 Cell Structure and Cell Organisation 2.1 Cell StructureCikguAgnesNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3 Cell Structures & Their Functions: Certain Molecules To Enter/exit The Cell)Document5 pagesChapter 3 Cell Structures & Their Functions: Certain Molecules To Enter/exit The Cell)Gellyace A.No ratings yet
- Saura, Jasmin E. - DVM - 2B Biochemistry (Activity 1)Document4 pagesSaura, Jasmin E. - DVM - 2B Biochemistry (Activity 1)Jasmin SauraNo ratings yet
- Cells Longman 4Document23 pagesCells Longman 4phonedaniel152No ratings yet
- Anaphy Topic 3Document4 pagesAnaphy Topic 3RAYNE CHLOIE LASTANo ratings yet
- Yellow Green Blue and Red Handwritten Zones of Regulation SEL Social and Emotional Learning Education PresentationDocument15 pagesYellow Green Blue and Red Handwritten Zones of Regulation SEL Social and Emotional Learning Education PresentationAngel ChrisleneNo ratings yet
- AnaPhy-lab ACTSDocument5 pagesAnaPhy-lab ACTSCEEJNo ratings yet
- Biology NDocument64 pagesBiology NIra Nurarisha IshairiNo ratings yet
- 1.2 Animal and Plant Cells - OdpDocument1 page1.2 Animal and Plant Cells - OdpZaynab ShaikhNo ratings yet
- NOTES FORM 1 CHAPTER 2Document14 pagesNOTES FORM 1 CHAPTER 2riseNo ratings yet
- Year 7 Cell SpecialisationDocument32 pagesYear 7 Cell Specialisationjurymagdi430No ratings yet
- Cell Parts and Functions 2Document3 pagesCell Parts and Functions 2Arshelyn Donna NovenoNo ratings yet
- Parts Structure Function(s) : Cedar Girls Secondary School Biology Notes Chapter 2: CellsDocument3 pagesParts Structure Function(s) : Cedar Girls Secondary School Biology Notes Chapter 2: CellsVinodini RaviNo ratings yet
- Cell TopicDocument29 pagesCell TopicChynna PorneteNo ratings yet
- Cell TopicDocument29 pagesCell TopicChynna PorneteNo ratings yet
- f0452703 CellsDocument34 pagesf0452703 CellsMuhammad Shahwaze WaqarNo ratings yet
- Module 1 (BioChem)Document33 pagesModule 1 (BioChem)cariagatrishaclaireNo ratings yet
- FOLIO: Biology Form 4 Chapter 2: Cell Structure and OrganisationDocument51 pagesFOLIO: Biology Form 4 Chapter 2: Cell Structure and OrganisationSashimi 刺身 Chebby100% (1)
- (M1) The CellDocument14 pages(M1) The CellBSN 1-1No ratings yet
- General Biology 1 1Document9 pagesGeneral Biology 1 1manansalastarringNo ratings yet
- Biology Form 4Document9 pagesBiology Form 4Ashlyn OoiNo ratings yet
- Cell StructuresDocument5 pagesCell StructuresSTEM 15 - John Benedict SebucaoNo ratings yet
- 2 Biology 1 - 2 - 07 Pro Vs Eu CellsDocument37 pages2 Biology 1 - 2 - 07 Pro Vs Eu CellsJuan Jaylou AnteNo ratings yet
- The Beginning of CellDocument4 pagesThe Beginning of CellTrishia Lynn MaldiaNo ratings yet
- Cell Structures 2Document10 pagesCell Structures 2STEM 15 - John Benedict SebucaoNo ratings yet
- Biochem 1Document24 pagesBiochem 1Shane OseñaNo ratings yet
- Biology Periodic ReviewerDocument6 pagesBiology Periodic ReviewerLanz NicoleiNo ratings yet
- Omnis Cellua e Cellula, Which All Cells Only Arise From Pre-Existing CellsDocument3 pagesOmnis Cellua e Cellula, Which All Cells Only Arise From Pre-Existing CellsArvie Jane De TorresNo ratings yet
- Gen Bio-1st Sem (Darlene Palanca 11sf-Stem)Document20 pagesGen Bio-1st Sem (Darlene Palanca 11sf-Stem)dcp.marie98No ratings yet
- Micropara ReviewerDocument13 pagesMicropara ReviewerEmhnaly Kae AggalutNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1Document7 pagesChapter 1EricNo ratings yet
- Plant and Animal Cell WorksheetsDocument28 pagesPlant and Animal Cell WorksheetsMarisol Leal PradoNo ratings yet
- Cell Structure and Organisation: Structural Adaptation Function Drawing (Learn To Draw) Root Hair CellDocument10 pagesCell Structure and Organisation: Structural Adaptation Function Drawing (Learn To Draw) Root Hair CellJules VNo ratings yet
- Cells: Simple or Complex CellsDocument2 pagesCells: Simple or Complex CellsMary Jean BoNo ratings yet
- Anaphy Lec (Chapter 3)Document6 pagesAnaphy Lec (Chapter 3)Aya MojicaNo ratings yet
- Cell Biology 7th Grade Textbook | Children's Biology BooksFrom EverandCell Biology 7th Grade Textbook | Children's Biology BooksRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (2)
- The Basics of Cell Life with Max Axiom, Super Scientist: 4D An Augmented Reading Science ExperienceFrom EverandThe Basics of Cell Life with Max Axiom, Super Scientist: 4D An Augmented Reading Science ExperienceNo ratings yet
- High Speed CentrifugeDocument8 pagesHigh Speed Centrifugedéborah_rosalesNo ratings yet
- Pharmaceuticals-Phage Therapy PDFDocument23 pagesPharmaceuticals-Phage Therapy PDFnassimNo ratings yet
- Chapter 30Document48 pagesChapter 30YekitaSNo ratings yet
- KRV, PLAZMA, HEMATOPOEZADocument35 pagesKRV, PLAZMA, HEMATOPOEZASinisa RisticNo ratings yet
- Mci Screening Test SyllabusDocument9 pagesMci Screening Test Syllabusravi sharma100% (2)
- Governance of Dual-Use Research: An Ethical Dilemma: Michael J SelgelidDocument4 pagesGovernance of Dual-Use Research: An Ethical Dilemma: Michael J SelgelidNika AbashidzeNo ratings yet
- General Biology 1: The CellsDocument71 pagesGeneral Biology 1: The CellsPaula Marie Llido100% (2)
- Cell TheoryDocument6 pagesCell Theoryjanice alquizarNo ratings yet
- Cell Structure Worksheet 1 Bloom TaxonomyDocument4 pagesCell Structure Worksheet 1 Bloom Taxonomy[team nothing] ConvexNo ratings yet
- 224 Magpix BrochureDocument6 pages224 Magpix BrochureankuramityNo ratings yet
- Test Bank For Essentials of Genetics 8th Edition by KlugDocument9 pagesTest Bank For Essentials of Genetics 8th Edition by Klugminhkhoit8cua3No ratings yet
- DNA Fact SheetDocument1 pageDNA Fact SheetAncestry.com100% (1)
- GROUP 9 Edocrine System ReportDocument52 pagesGROUP 9 Edocrine System Reportroyeth montezaNo ratings yet
- ContentServer PDFDocument19 pagesContentServer PDFMoses OntitaNo ratings yet
- Biology SPMDocument17 pagesBiology SPMbloptra18No ratings yet
- Nprot 2016 097Document20 pagesNprot 2016 097Giggly HadidNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1 AnswersDocument3 pagesChapter 1 AnswersSonny JimNo ratings yet
- Inability of Calcium Hydroxide To Induce Reparative Dentinogenesis at Non-Peripheral Sites of Dog Dental PulpDocument5 pagesInability of Calcium Hydroxide To Induce Reparative Dentinogenesis at Non-Peripheral Sites of Dog Dental PulpMihai RusescuNo ratings yet
- Bordoni-Awareness of The Fascial SystemDocument9 pagesBordoni-Awareness of The Fascial SystemOscar Sánchez MartínezNo ratings yet
- Microbial Spoilage Characterization in Tomato Products (III) : Flat-SourDocument1 pageMicrobial Spoilage Characterization in Tomato Products (III) : Flat-Sourabc123No ratings yet
- The Multidisciplinary Nature of Environmental Studies: Definition, Scope and Importance, Need For Public AwarenessDocument28 pagesThe Multidisciplinary Nature of Environmental Studies: Definition, Scope and Importance, Need For Public AwarenessArjun UnnikrishnanNo ratings yet
- CLS Aipmt 17 18 XIII Zoo Study Package 4 SET 1 Chapter 14Document46 pagesCLS Aipmt 17 18 XIII Zoo Study Package 4 SET 1 Chapter 14sdsadddsdaNo ratings yet
- Bharathidasan University, Tiruchirappalli - 620 024. B.Sc. Zoology - Course Structure Under CBCSDocument21 pagesBharathidasan University, Tiruchirappalli - 620 024. B.Sc. Zoology - Course Structure Under CBCSLeena AneesNo ratings yet
- Electrical Impedance: Hematology AnalyzerDocument2 pagesElectrical Impedance: Hematology AnalyzerAzura JKNo ratings yet
- HES 007 2nd Periodical Exam TG Day 17Document3 pagesHES 007 2nd Periodical Exam TG Day 17AlbieRhioneilLatonioMacayanNo ratings yet
- Fibroadenoma Versus Phyllodes TumorDocument12 pagesFibroadenoma Versus Phyllodes TumorNatalindah Jokiem Woecandra T. D.No ratings yet
- Blood BankDocument19 pagesBlood Bankmoonfire2009100% (2)