Professional Documents
Culture Documents
rev_notes_ch04_e
rev_notes_ch04_e
Uploaded by
kazocheungCopyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
rev_notes_ch04_e
rev_notes_ch04_e
Uploaded by
kazocheungCopyright:
Available Formats
4 Enzymes and metabolism
4.1 Enzymes and metabolism
1 Metabolism (新陳代謝) is divided into catabolism (分解代謝) and anabolism (合成代謝):
2 Enzymes (酶) are biological catalysts
(催化劑). They speed up chemical
reactions in organisms by lowering
the activation energy (活化能) of the
reactions.
4.2 Actions and properties of enzymes
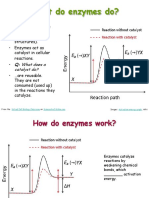
1 The working principle of enzymes:
- Each enzyme has an active site (活性部位).
- Substrate (受質) binds to the active site to form an enzyme-substrate complex
(酶受質複合物). This greatly lowers the activation energy of the reaction.
- The substrate is converted into products (生成物), which then leave the active site.
2 Enzyme actions are specific (專一的):
- Each enzyme has a unique active site, which has a specific shape. It only acts on substrates
that can fit into its active site.
- The specificity of enzyme actions can be explained by the lock-and-key hypothesis
(鎖鑰假說).
New Senior Secondary Mastering Biology Oxford University Press 2020
(Third Edition) -1-
3 Properties of enzymes:
- Enzymes are biological catalysts.
- The actions of enzymes are specific.
- Enzymes are proteins. Their structures and hence their activity are easily affected by
temperature and pH.
- Enzymes are reusable.
- Enzymes are needed in relatively small amounts.
4.3 Factors affecting enzyme activity
Temperature
1 The effects of temperature on enzyme activity:
Temperature Enzyme activity Reason
At low Low - Enzymes are inactive (不活躍). The kinetic energy of
temperatures enzyme and substrate molecules is low.
As temperature Increases - Both enzyme and substrate molecules have more
rises kinetic energy. They collide with each other more
frequently; the chance of forming enzyme-substrate
At optimum Reaches a
complexes increases.
temperature maximum
(最適溫度) - Enzymes work best at their optimum temperature.
At high Decreases - High temperatures cause a change in shape of the
temperatures active site of the enzyme molecule. The enzyme is
denatured (變性).
- The substrate can no longer fit into the active site of
the enzyme to form the enzyme-substrate complex.
- The enzyme loses its catalytic ability permanently.
New Senior Secondary Mastering Biology Oxford University Press 2020
(Third Edition) -2-
pH
2 The effects of pH on enzyme activity:
pH Enzyme activity Reason
At optimum pH Reaches a - Enzymes work best at their optimum pH.
maximum
At unsuitable Decreases - Unsuitable pH causes denaturation of the enzyme.
pH - The substrate can no longer fit into the active site
of the enzyme to form the enzyme-substrate
complex.
- The enzyme loses its catalytic ability permanently.
Inhibitors
3 Inhibitors (抑制劑) are substances that decrease the activity of enzymes. Examples of
inhibitors are cyanide (氰化物) and heavy metals.
New Senior Secondary Mastering Biology Oxford University Press 2020
(Third Edition) -3-
4.4 Applications of enzymes
1 Enzymes are used in many different areas:
Type of enzyme
Area Product Use of enzyme
present
Food industry Cheese Proteases Coagulate (凝固) milk
(蛋白酶)
Fruit juice Pectinase Breaks down the pectin (果膠) in
(果膠酶) plant cell wall to increase the
yield of juice; breaks down the
pectin in the juice to make the
juice looks clear
Liquid-centred Invertase Breaks down the sugars into
chocolate (轉化酶) more soluble forms
Environmental Biofuel (生物燃料) Cellulase Breaks down the cellulose in
protection (e.g. bioethanol (纖維素酶) crops into sugars to increase the
(生物乙醇)) yield of biofuel
Biodegradable An enzyme Breaks down the plastic to
(可生物降解的) plastic extracted from a shorten the time for a plastic bag
bacterium to degrade
Cooking Meat tenderizers Papain (木瓜酶) Breaks down the proteins in meat
(鬆肉粉) to soften the meat
Detergent Biological washing Proteases and Break down the insoluble
powders lipase (脂肪酶) proteins and lipids in stains into
soluble products
Cosmetics Cleansers Papain Breaks down dead cells in the
skin
Textiles Stonewashed jeans Cellulase Breaks down the cellulose fibres
(石磨藍牛仔褲) of the jeans
Medicine Drugs Lysozyme Breaks down the cell wall of
(溶菌酶) certain bacteria to kill them
New Senior Secondary Mastering Biology Oxford University Press 2020
(Third Edition) -4-
2 Advantages of using enzymes in the production of commercial products:
Property of enzyme Advantage
Speed up chemical reactions Shortens production time and allows the mass
production of products
Many work at moderate conditions Does not require extreme conditions, such as very
high temperatures and pressures
Specific in action Produces fewer unwanted products
Reusable and are needed in small Lowers the cost of production
amounts only
3 Limitations of using enzymes in the production of commercial products:
Property of enzyme Limitation
Sensitive to temperature and pH Cannot be used if the production process involves a
changes high temperature or an unsuitable pH
Easily affected by inhibitors All containers used in the production processes
have to be clean to prevent the containers from
being contaminated with inhibitors
New Senior Secondary Mastering Biology Oxford University Press 2020
(Third Edition) -5-
You might also like
- Protective Cabin Crew Smoke Hood PBE 15-40F-11Document2 pagesProtective Cabin Crew Smoke Hood PBE 15-40F-11Me KeenNo ratings yet
- Rev Notes ch04 eDocument5 pagesRev Notes ch04 ekathk2016No ratings yet
- Rev - Notes - ch04 - e EnzymesDocument5 pagesRev - Notes - ch04 - e EnzymesEsther WongNo ratings yet
- Unit 3 - EnzymesDocument5 pagesUnit 3 - EnzymesWaseem AhmedNo ratings yet
- Enzymes Course BioprocessDocument76 pagesEnzymes Course BioprocessiantitosimanjuntakNo ratings yet
- Enzymes Part 1Document23 pagesEnzymes Part 1judevolkovNo ratings yet
- Chapter 5 - Metabolism and EnzymesDocument24 pagesChapter 5 - Metabolism and EnzymesbubabozN aOIDHao8nxNo ratings yet
- Lab 2. Enzyme Action-Effect of Enzyme Concentration, Temperature and PH On Catalase ActivityDocument24 pagesLab 2. Enzyme Action-Effect of Enzyme Concentration, Temperature and PH On Catalase ActivityRicardo SimõesNo ratings yet
- 2 5enzymesDocument28 pages2 5enzymesKhin (Darin) Hnin PhyuNo ratings yet
- MetabolismDocument3 pagesMetabolismFans TimeNo ratings yet
- EnzymesDocument6 pagesEnzymesSarah Farhah2000100% (1)
- Applied MicrobiologyDocument231 pagesApplied Microbiologybrightside6451No ratings yet
- EnzymeDocument16 pagesEnzymesalcedocedmerkNo ratings yet
- MYP 4 EnzymesDocument48 pagesMYP 4 EnzymessaurishberwallNo ratings yet
- EnzymesDocument27 pagesEnzymesKinza fatimaNo ratings yet
- EnzymesDocument43 pagesEnzymesMaryam SabirNo ratings yet
- C5 - Metabolism and Enzyme Part 1Document20 pagesC5 - Metabolism and Enzyme Part 1Daniel LohNo ratings yet
- Dasar Dasar MetabolismeDocument39 pagesDasar Dasar MetabolismeWidychii GadiestchhetyaNo ratings yet
- Biology FinalsDocument2 pagesBiology FinalsbhongskirnNo ratings yet
- A. What Are Enzymes?: Enzymes Prepared by La Vera U. Sombito Natural Sciences Department, CAS - USLSDocument4 pagesA. What Are Enzymes?: Enzymes Prepared by La Vera U. Sombito Natural Sciences Department, CAS - USLSJacqueline Rose Alipo-onNo ratings yet
- $RZ2YE8ODocument2 pages$RZ2YE8OCrow LordNo ratings yet
- Enzyme Brochure Gen Chem PTDocument2 pagesEnzyme Brochure Gen Chem PTAdrielNo ratings yet
- Model Answers: Chapter 5 Metabolism and EnzymesDocument2 pagesModel Answers: Chapter 5 Metabolism and EnzymesireneNo ratings yet
- Gen Chem Peta 2nd QuarterDocument5 pagesGen Chem Peta 2nd QuarterJhames HarveyNo ratings yet
- Research Article Role of EnzymesDocument3 pagesResearch Article Role of Enzymesdwi pambuko anantiNo ratings yet
- $RLW3VJ1Document3 pages$RLW3VJ1Crow LordNo ratings yet
- Mikrobiologi Industri: EnzymeDocument39 pagesMikrobiologi Industri: EnzymeEunike RhizaNo ratings yet
- Biochemistry Midterm ReviewDocument5 pagesBiochemistry Midterm ReviewHuyen Tram NguyenNo ratings yet
- Chapter 02 EnzymesDocument8 pagesChapter 02 Enzymesmiraniwaqar16No ratings yet
- EnzymesDocument25 pagesEnzymesmainakb2003No ratings yet
- Enzymes Part 2Document3 pagesEnzymes Part 2Mar LagmayNo ratings yet
- Application of Enzyme On Woolen Products For Its Value Addition: An OverviewDocument12 pagesApplication of Enzyme On Woolen Products For Its Value Addition: An OverviewNagender SinghNo ratings yet
- Fst613 4 EnzymesDocument41 pagesFst613 4 EnzymesmohamadbarsyikNo ratings yet
- EnzimDocument29 pagesEnzimyasmine aurelliaNo ratings yet
- Enzymes 1Document6 pagesEnzymes 1zarszNo ratings yet
- Enzymes:: "Helper" Protein MoleculesDocument26 pagesEnzymes:: "Helper" Protein MoleculesAyesha JamilNo ratings yet
- Biochem Enzyme NotesDocument8 pagesBiochem Enzyme NotesBeatriz NideaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 5 Metabolism and EnzymesDocument8 pagesChapter 5 Metabolism and Enzymes绿谷出久No ratings yet
- Gen BioDocument35 pagesGen Biomikechristian073No ratings yet
- Enzymes Lecture 1 2015animationDocument80 pagesEnzymes Lecture 1 2015animationSarfaras KKNo ratings yet
- 3.1 Nature of Enzymes: UNIT-3 3. Enzymes 1. Catalytic PropertyDocument5 pages3.1 Nature of Enzymes: UNIT-3 3. Enzymes 1. Catalytic PropertyGashaw Fikir AdugnaNo ratings yet
- IB Biology Notes - 36 EnzymesDocument2 pagesIB Biology Notes - 36 EnzymesJohn Philip D. NapalNo ratings yet
- Enzymes and ReactionsDocument5 pagesEnzymes and Reactionstechninja256No ratings yet
- Enzymes (1ST Shifting) PDFDocument53 pagesEnzymes (1ST Shifting) PDFKwien AustriaNo ratings yet
- Chapter5 Bio f5Document8 pagesChapter5 Bio f5JiayingNo ratings yet
- Chapter 5 - Metabolism and Enzymes: Learning ObjectivesDocument8 pagesChapter 5 - Metabolism and Enzymes: Learning Objectivesthanks btNo ratings yet
- Enzymes Form 3Document4 pagesEnzymes Form 3Ralph MuchingamiNo ratings yet
- Revision Lesson On EnzymesDocument14 pagesRevision Lesson On EnzymesPiper McleanNo ratings yet
- Lec 04Document16 pagesLec 04Muhammad WaseemNo ratings yet
- EnzymesDocument40 pagesEnzymesVeronica HanyNo ratings yet
- ENZYMES Documentation Report Team 1 DINODocument8 pagesENZYMES Documentation Report Team 1 DINOwhyveNo ratings yet
- The Place Where These Molecules Fit Is Called The Active SiteDocument10 pagesThe Place Where These Molecules Fit Is Called The Active SiteNushrat KaziNo ratings yet
- Bio-Ch 5-EnzymesDocument6 pagesBio-Ch 5-EnzymesHassan RiazNo ratings yet
- F4 Chapter 5Document24 pagesF4 Chapter 5lvlysn29No ratings yet
- Immunoglobulins: Immunoglobulins or Antibodies Are Defence Proteins Present in The Blood ToDocument10 pagesImmunoglobulins: Immunoglobulins or Antibodies Are Defence Proteins Present in The Blood ToAbhishek ThakralNo ratings yet
- Pharmaceutical BiochemistryDocument52 pagesPharmaceutical BiochemistryCherryl ValeraNo ratings yet
- EnzymesDocument3 pagesEnzymesDevil HackerNo ratings yet
- Enzyme: Specific Proteins That Catalyze Biochemical: Constituents of Enzyme MoleculeDocument6 pagesEnzyme: Specific Proteins That Catalyze Biochemical: Constituents of Enzyme MoleculeAnya IgnacioNo ratings yet
- Enzymes: The Role of Enzymes in OrganismsDocument9 pagesEnzymes: The Role of Enzymes in OrganismsVikneswaran Gunahlan NeshNo ratings yet
- ChemistryDocument7 pagesChemistryLee LuceroNo ratings yet
- A-level Biology Revision: Cheeky Revision ShortcutsFrom EverandA-level Biology Revision: Cheeky Revision ShortcutsRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (5)
- RBD Tallow PrintDocument37 pagesRBD Tallow PrinthibreNo ratings yet
- Water Handbook - Boiler Blowdown Control - VeoliaDocument8 pagesWater Handbook - Boiler Blowdown Control - Veoliaحسين مهديNo ratings yet
- Journal of EthnopharmacologyDocument8 pagesJournal of EthnopharmacologyMarcelo GanozaNo ratings yet
- Total RNA Isolation From Plant: User ManualDocument25 pagesTotal RNA Isolation From Plant: User ManualVakaliya MohmmadasifNo ratings yet
- SolutionDocument2 pagesSolutionZuber SheikhNo ratings yet
- Section 05 - Louvres and FiltersDocument10 pagesSection 05 - Louvres and FiltersAmro Metwally El HendawyNo ratings yet
- Technology For Production of Surimi Powder and Potential of ApplicationsDocument11 pagesTechnology For Production of Surimi Powder and Potential of ApplicationsWahyu MuhammadNo ratings yet
- CH 10 Precipitation and AgglutinationDocument17 pagesCH 10 Precipitation and AgglutinationFedz FederisoNo ratings yet
- LA Review Midterm 2Document11 pagesLA Review Midterm 2Bob GooberNo ratings yet
- Chem Pre-Year QuizDocument18 pagesChem Pre-Year Quizlokesh G.KNo ratings yet
- Biophysical Chemistry - Molecules To Membranes (PDFDrive)Document346 pagesBiophysical Chemistry - Molecules To Membranes (PDFDrive)Rajamani D.100% (1)
- Mole Conversion Notes KEYDocument3 pagesMole Conversion Notes KEYkossyella848No ratings yet
- Balloon ExperimentDocument4 pagesBalloon Experimentbluearowana02No ratings yet
- Treatment of Industrial WastewaterDocument25 pagesTreatment of Industrial WastewaterdzikreeNo ratings yet
- Chapter 7-Structure and Synthesis of Alkenes Elimination: Study GroupDocument43 pagesChapter 7-Structure and Synthesis of Alkenes Elimination: Study Group張湧浩No ratings yet
- Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2008/0086950 A1Document13 pagesPatent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2008/0086950 A1rat0708No ratings yet
- LG Chem TDS SP988 EnglishDocument1 pageLG Chem TDS SP988 EnglishSérgio BarbosaNo ratings yet
- Margarine Hystorical AproachDocument12 pagesMargarine Hystorical AproachRiandi SaputraNo ratings yet
- Heterogeneous NucleationDocument15 pagesHeterogeneous NucleationDimpy KhatriNo ratings yet
- Biodiesel From Batch and Continuous Oleic Acid Esterification Using Zeolite CatalystsDocument7 pagesBiodiesel From Batch and Continuous Oleic Acid Esterification Using Zeolite CatalystsArif HidayatNo ratings yet
- Pratt & Whitney Standard Practices Manual (PN 585005)Document22 pagesPratt & Whitney Standard Practices Manual (PN 585005)Paul FisherNo ratings yet
- 02.power Transformer-160 &63mvaDocument138 pages02.power Transformer-160 &63mvaraj_stuff006100% (1)
- High Performance Bio-Based Elastomers: Energy Efficient, Sustainable Materials For TiresDocument6 pagesHigh Performance Bio-Based Elastomers: Energy Efficient, Sustainable Materials For Tiresgutha manikantaNo ratings yet
- BP500C MSDSDocument3 pagesBP500C MSDSMiguel GonzalezNo ratings yet
- Lith Printing Technique - Lesson 4: Warmtone Paper: Agfa MCCDocument12 pagesLith Printing Technique - Lesson 4: Warmtone Paper: Agfa MCCchicco pitecoNo ratings yet
- Acumedia Cross ReferenceDocument6 pagesAcumedia Cross ReferenceGRACIELANo ratings yet
- Kamalasanan 2017Document5 pagesKamalasanan 2017HllerdNo ratings yet
- Air Change Load - Vapor Compression NotesDocument9 pagesAir Change Load - Vapor Compression NotesRai OlinoNo ratings yet
- NTSE STAGE - I - 2020 - 2021 Tamil Nadu Part - I Mental Ability Test SolutionsDocument15 pagesNTSE STAGE - I - 2020 - 2021 Tamil Nadu Part - I Mental Ability Test SolutionsarbimbbNo ratings yet