Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Measles talking points
Measles talking points
Uploaded by
kinyerad10Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Measles talking points
Measles talking points
Uploaded by
kinyerad10Copyright:
Available Formats
THE REPUBLIC OF UGANDA
MINISTRY OF HEALTH
MEASLES
TALKING POINTS
1. Introduction no known non-human reservoirs Measles at 9 months during
routine immunisation.
Globally Measles is the leading cause
of death among vaccine preventable 3. Signs and symptoms of w During Supplemental
childhood diseases. Measles include: Immunization Activities (SIAs)
w Fever children aged 6 months to 5 years
In Uganda, Measles is one of the leading w Generalised skin rash will receive a dose of the Measles
causes of death among children under w Cough vaccine by injection irrespective
five and can be prevented through w Running nose of previous immunisation status
immunisation. w Red eyes
w Red lips and sore mouth 7. Justification for Measles
During 2016 and part of 2017 a total of immunisation
2412 suspected cases were reported 4. Complications from Measles
country wide. Out of these 518 (21%) were infection include: w Regular risk analysis shows
clinically and laboratory confirmed. From Uganda is at risk of Measles
January to December 2017, 670 and 335
w Pneumonia and Diarrhoea which outbreaks
clinically and laboratory confirmed cases can lead to death
of Measles were detected from Kampala
w Lifelong disability including w Uganda is already experiencing
and Wakiso districts respectively. blindness, brain damage and Measles outbreaks in some
deafness districts
The WHO recommends the following w Malnutrition and Vitamin A w Evidence shows that many
strategies for achieving and maintaining deficiency children are not yet protected
Measles elimination: against Measles through routine
w Strengthening routine 5. Who is most affected by immunisation
immunisation, and in this area Measles?
w Measles is a highly infectious
Uganda provides one Measles Measles affects all ages but it is
disease and more severe in
dose at 9 months of age more frequent and severe in children
unimmunised children
under 5 years of age who are not
w Providing an opportunity for immunised. The population at POINTS TO NOTE
Measles immunisation through
Supplemental Immunisation
risk of Measles infection includes: • A dose of Measles vaccine is
administered by injection on the
Activities (SIAs) w Unimmunised children left upper arm by qualified health
w Conducting case based Measles workers.
w Pregnant women previously not
surveillance to document progress
in eliminating the disease
immunised with Measles vaccine
during childhood
• The Measles vaccine is SAFE,
EFFECTIVE and FREE. It is
w Proving standard case w Immune suppressed individuals approved by Ministry of Health,
management to Measles WHO and UNICEF
cases according to set standards w Communities living in
overcrowded settlements • Side effects are usually mild
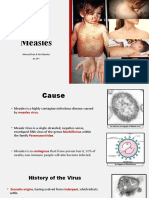
2. What is Measles? and include: a low fever and a
w Communities that cannot easily generalised skin rash
• Measles is an airborne disease, access immunisation services
spread to susceptible persons by 6. Prevention of Measles • We call upon all stakeholders,
respiratory droplets when an infected disease right from the household to the
person coughs or sneezes or by direct national level, to ensure that all
contact with nasal or throat secretions w Immunisation is the best way to eligible children are immunised
of an infected person. Humans are prevent Measles. All children against Measles at 9 months of
the primary hosts and there are should be immunised against age during routine immunisation.
You might also like
- Predict 1 & 2 OverviewDocument34 pagesPredict 1 & 2 OverviewUncoverDCNo ratings yet
- Riverwalk Medical Clinic Influenza Information SheetDocument6 pagesRiverwalk Medical Clinic Influenza Information Sheetcycy143No ratings yet
- Bilingual Medical Certificate Certificado Médico BilingüeDocument2 pagesBilingual Medical Certificate Certificado Médico Bilingüejemal0% (1)
- Vaccines Given at BirthDocument3 pagesVaccines Given at BirthShannon Marcella EvangelinaNo ratings yet
- Measles: Questions and Answers: Information About The Disease and VaccinesDocument4 pagesMeasles: Questions and Answers: Information About The Disease and VaccinesJansher Ali ChohanNo ratings yet
- Measles Vaccine Preventable DiseaseDocument6 pagesMeasles Vaccine Preventable DiseaseluixixixNo ratings yet
- Lesson 9-10 CPHDocument26 pagesLesson 9-10 CPHGeraldine SalonNo ratings yet
- OB 13 Infectious Disease in PregnancyDocument17 pagesOB 13 Infectious Disease in PregnancyJoher100% (1)
- Mumps:: Questions and AnswersDocument4 pagesMumps:: Questions and AnswersGovind DasuNo ratings yet
- Immu 1Document9 pagesImmu 1gsdrfwpfd2No ratings yet
- Pedia - Infectious and Immunization MixDocument28 pagesPedia - Infectious and Immunization MixShakira Fave MaongcoNo ratings yet
- Sexually Transmitted Diseases (STD) 2Document4 pagesSexually Transmitted Diseases (STD) 2easylearning83No ratings yet
- Sabin Immunization Advocates Slide Kit v10.4.19Document21 pagesSabin Immunization Advocates Slide Kit v10.4.19ANo ratings yet
- Grade 9 Integrated Science Week 1 Lesson 2Document4 pagesGrade 9 Integrated Science Week 1 Lesson 2kekeNo ratings yet
- Vaccines & Immunization: How To Realize The Full Benefits of ImmunizationDocument21 pagesVaccines & Immunization: How To Realize The Full Benefits of Immunizationperi umardianaNo ratings yet
- Varicella/Herpes Zoster: Communicable Disease Management ProtocolDocument5 pagesVaricella/Herpes Zoster: Communicable Disease Management Protocolyuliyanto.efendiNo ratings yet
- Infect Dis Clinics NA - Pediatric Infections Marzo 2022Document230 pagesInfect Dis Clinics NA - Pediatric Infections Marzo 2022victorNo ratings yet
- Kinder Impfen ENDocument3 pagesKinder Impfen ENcoleviper95No ratings yet
- Measles Virus (Rubeola) : Anne A. GershonDocument10 pagesMeasles Virus (Rubeola) : Anne A. GershonTammy Utami DewiNo ratings yet
- Measles EpiDocument22 pagesMeasles Epiمحمد صالحNo ratings yet
- Prelims - GMJ Lecture - Module 2 III DisorderDocument3 pagesPrelims - GMJ Lecture - Module 2 III DisorderjuiceNo ratings yet
- Vis FluDocument2 pagesVis FluCarrboro Family MedicineNo ratings yet
- Measles: Symptoms, Diagnosis, Management and Prevention: Continuing Professional DevelopmentDocument7 pagesMeasles: Symptoms, Diagnosis, Management and Prevention: Continuing Professional DevelopmentGedhe PutraNo ratings yet
- MMRDocument2 pagesMMRShrinivas YuvanNo ratings yet
- Vaccine InfoDocument2 pagesVaccine InfoAPhA-ASP BradentonNo ratings yet
- Epidemiology of Measles in The Philippines: Original ArticleDocument10 pagesEpidemiology of Measles in The Philippines: Original ArticlePearlNo ratings yet
- Measles: Not Just A Childhood Rash: ReviewDocument7 pagesMeasles: Not Just A Childhood Rash: ReviewAyuNo ratings yet
- Measles: Ahmad Khan & Ali Sikander A1 64Document13 pagesMeasles: Ahmad Khan & Ali Sikander A1 64Ahmad KhanNo ratings yet
- Care of Mother, Child at Risks With Problems (Acute & Chronic) : Transcript Onsexually Transmitted InfectionDocument4 pagesCare of Mother, Child at Risks With Problems (Acute & Chronic) : Transcript Onsexually Transmitted InfectionMark Gregory Addatu100% (1)
- Saxena 2020 EXCLUDE?Document2 pagesSaxena 2020 EXCLUDE?RabiaNaseemNo ratings yet
- Vaccina Tion: By: Group 4Document77 pagesVaccina Tion: By: Group 4Angela ReyesNo ratings yet
- Questions and Answers: MumpsDocument4 pagesQuestions and Answers: MumpsHannahNo ratings yet
- If Maglalagay Kayo Info. Separate Niyo Narin Yung Ilalagay Sa PPT Na Mga Keywords para Di Na Mahirapan MamayaDocument11 pagesIf Maglalagay Kayo Info. Separate Niyo Narin Yung Ilalagay Sa PPT Na Mga Keywords para Di Na Mahirapan MamayaJhay-r BaldoNo ratings yet
- Emilio Aguinaldo College-Cavite: Communicable Diseases Among InfantsDocument34 pagesEmilio Aguinaldo College-Cavite: Communicable Diseases Among Infantsarlian malihanNo ratings yet
- Varicella Chickenpox VaccineDocument1 pageVaricella Chickenpox Vaccinekhairarohit_30976791No ratings yet
- IJSS Nov RA03 20141119 V11Document4 pagesIJSS Nov RA03 20141119 V11Sri HariNo ratings yet
- Immunize Your ChildDocument1 pageImmunize Your ChildIntan NurulLNo ratings yet
- MeaslesDocument5 pagesMeaslesHameed SabahNo ratings yet
- 308-Article Text-623-1-10-20161213Document3 pages308-Article Text-623-1-10-20161213fadiah maharaniNo ratings yet
- I-CARE-For-Kids-Summary-2023-02-22Document2 pagesI-CARE-For-Kids-Summary-2023-02-22BugMagnetNo ratings yet
- Management of Varicella in Neonates and Infants: Sophie Blumental, Philippe LepageDocument6 pagesManagement of Varicella in Neonates and Infants: Sophie Blumental, Philippe LepageMaria Noviyanti FransiskaNo ratings yet
- Measles: Complications PreventionDocument3 pagesMeasles: Complications PreventionAn NieNo ratings yet
- Measles Eiw2015 enDocument1 pageMeasles Eiw2015 enMarynda RahmadianisyaNo ratings yet
- IMMUNIZATION PamphletDocument3 pagesIMMUNIZATION PamphletSwag MasterNo ratings yet
- Vaccinepreventable DiseasesDocument1 pageVaccinepreventable DiseasesReignNo ratings yet
- Module 2 Day 1 Infection, Infectious Disease, and IsolationDocument6 pagesModule 2 Day 1 Infection, Infectious Disease, and IsolationAndrea DaracanNo ratings yet
- The Infant of An Hiv Positive MotherDocument10 pagesThe Infant of An Hiv Positive Mothernursereview100% (1)
- Chickenpox (Varicella) : Questions and Answers: Information About The Disease and VaccinesDocument3 pagesChickenpox (Varicella) : Questions and Answers: Information About The Disease and VaccinesKailash NagarNo ratings yet
- Prevention of PneumoniaDocument2 pagesPrevention of Pneumoniaella19inaNo ratings yet
- SOGC Interim Guidance On Monkeypox Exposure For Pregnant PeopleDocument6 pagesSOGC Interim Guidance On Monkeypox Exposure For Pregnant PeopleariniNo ratings yet
- VaccinationDocument35 pagesVaccinationmuneebazmat1123No ratings yet
- Zika Virus: Community Health Nursing Ms. ShangrilaDocument34 pagesZika Virus: Community Health Nursing Ms. Shangrilaxr4dmNo ratings yet
- What You Need To Know: Serogroup B Meningococcal Vaccine (Menb) : 1Document2 pagesWhat You Need To Know: Serogroup B Meningococcal Vaccine (Menb) : 1Laurensia Erlina NataliaNo ratings yet
- Kernig Sign, Brudzinski Sign and Nuchal Rigidity By: PutrialishajsgDocument24 pagesKernig Sign, Brudzinski Sign and Nuchal Rigidity By: Putrialishajsgfarah fadzilNo ratings yet
- Measles PDFDocument7 pagesMeasles PDFTwhieNo ratings yet
- Measles: Not Just A Childhood Rash: ReviewDocument7 pagesMeasles: Not Just A Childhood Rash: ReviewTwhieNo ratings yet
- NCP Case Scenario Group 6Document5 pagesNCP Case Scenario Group 6Sean SeanNo ratings yet
- Herpes Zoster: Shingles Acute Posterior GanglionitisDocument23 pagesHerpes Zoster: Shingles Acute Posterior GanglionitisHannah Clarisse Monge IgniNo ratings yet
- Expanded Program On Immunization AbujenDocument2 pagesExpanded Program On Immunization AbujenAlhaisa BejemilNo ratings yet
- Deworming and ImmunizationDocument23 pagesDeworming and ImmunizationKathy Claire BallegaNo ratings yet
- Health Advice and Immunizations for TravelersFrom EverandHealth Advice and Immunizations for TravelersNo ratings yet
- A Primer in Research Methodology and BiostatisticsDocument163 pagesA Primer in Research Methodology and BiostatisticsAdriana Villarreal100% (3)
- UNIT III A in Microbiology and ParasitologyDocument8 pagesUNIT III A in Microbiology and ParasitologyBrixValdrizNo ratings yet
- Production of Germicidal SoapDocument39 pagesProduction of Germicidal Soapapi-233859278No ratings yet
- St. Karen's Secondary School, Patna Subject-Biology Class - 8 Chapter - The Cell Answer Key of (Assignment - 3)Document3 pagesSt. Karen's Secondary School, Patna Subject-Biology Class - 8 Chapter - The Cell Answer Key of (Assignment - 3)Harshit RajNo ratings yet
- Diseases From ParasitesDocument17 pagesDiseases From Parasitestanya jerikaNo ratings yet
- Types of PathogensDocument56 pagesTypes of PathogensMelody DacanayNo ratings yet
- MicroparasitologyDocument28 pagesMicroparasitologyMj BrionesNo ratings yet
- AP Bio F17 Immune System WebquestDocument3 pagesAP Bio F17 Immune System WebquestClaire ParrishNo ratings yet
- Pakistan Kidney and Liver Institute & Research Centre (PKLI)Document1 pagePakistan Kidney and Liver Institute & Research Centre (PKLI)Waqas SaleemNo ratings yet
- Health Care of Farm AnimalsDocument9 pagesHealth Care of Farm AnimalsBindas GuyNo ratings yet
- Microbial Quality Evaluation of Zobo Drink Sold NDocument10 pagesMicrobial Quality Evaluation of Zobo Drink Sold NBRAYANNo ratings yet
- Pathophysiology: HIV Infection and AIDSDocument7 pagesPathophysiology: HIV Infection and AIDSmeylin SNo ratings yet
- Exposé Sur L - Ebola en AnglaisDocument6 pagesExposé Sur L - Ebola en AnglaisMahama GbaneNo ratings yet
- Sebiomo Et AlDocument5 pagesSebiomo Et AlAnkit VermaNo ratings yet
- ASHP Guidelines For S.a.P. (Surgical Antibiotic Prophylaxis)Document3 pagesASHP Guidelines For S.a.P. (Surgical Antibiotic Prophylaxis)ridley45No ratings yet
- Research in MicrobiologyDocument10 pagesResearch in MicrobiologyNithin SakthiNo ratings yet
- Fundamentals of Plant Pathology MSTDocument2 pagesFundamentals of Plant Pathology MSTAshutosh Prakash ChowdharyNo ratings yet
- Diagnostic Parasitology Laboratory Diagnosis Specimens - Fresh Specimens in Sufficient AmountsDocument1 pageDiagnostic Parasitology Laboratory Diagnosis Specimens - Fresh Specimens in Sufficient Amountsmiguel gaquitNo ratings yet
- Paparella: Volume I: Basic Sciences and Related Disciplines Section 6: Pharmacology Chapter 28: Antibiotics Leonard P. RybakDocument16 pagesPaparella: Volume I: Basic Sciences and Related Disciplines Section 6: Pharmacology Chapter 28: Antibiotics Leonard P. RybakDiana Mihaela BadescuNo ratings yet
- WK13 CDN - Cholera, Bacillary Dysentery, Amoebiasis, Typhoid Fever, Hepatitis ADocument38 pagesWK13 CDN - Cholera, Bacillary Dysentery, Amoebiasis, Typhoid Fever, Hepatitis APotato PceeNo ratings yet
- ACORN Double Gloving RecommendationsDocument1 pageACORN Double Gloving RecommendationsEvy MartinsNo ratings yet
- Bakteri Patogen Penyebab Foodborne Diseases: PendahuluanDocument6 pagesBakteri Patogen Penyebab Foodborne Diseases: PendahuluanAmaliatul KhusnaNo ratings yet
- Epidemiology, Prevention and Control of Dengue: DR Tahira JaffarDocument36 pagesEpidemiology, Prevention and Control of Dengue: DR Tahira JaffarRaza UzuNo ratings yet
- Isolation and Microbiological Identification of BacterialDocument6 pagesIsolation and Microbiological Identification of BacterialSumit Sharma PoudelNo ratings yet
- Nephchem ASODocument1 pageNephchem ASOsobujNo ratings yet
- Public Health Recommendation For Fully Vaccinated 3-7-21 3 PM CleanDocument5 pagesPublic Health Recommendation For Fully Vaccinated 3-7-21 3 PM CleanJoseph Adinolfi Jr.No ratings yet
- Oral CandidiasisDocument6 pagesOral CandidiasisKuran NitaNo ratings yet
- Candiduria: Evidence-Based Approach To Management, Are We There Yet?Document10 pagesCandiduria: Evidence-Based Approach To Management, Are We There Yet?ntnquynhproNo ratings yet