Professional Documents
Culture Documents
excretory system
excretory system
Uploaded by
ramtelpuspa06Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
excretory system
excretory system
Uploaded by
ramtelpuspa06Copyright:
Available Formats
Question Answer
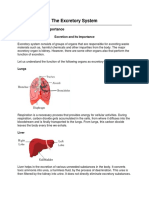
Explain the process of excretion Excretion is the elimination of nitrogenous waste from the
and name some excretory body. Excretory organs include the kidneys, skin, liver, and
organs. intestines.
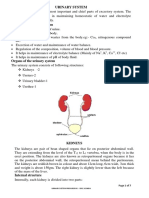
The kidney is enclosed by the renal capsule, adipose
Describe the structure of the capsule, and renal fascia. The hilus renalis allows entry/exit
kidney and its three layers. of blood vessels, lymph vessels, nerves, and ureters.
What is the main function of the The ureter conveys urine from the kidney to the urinary
ureter, and how does it connect bladder. It arises from the hilum of the kidney, traversing the
to the urinary bladder? posterior abdominal cavity before opening into the bladder.
The urinary bladder is a thin-walled, muscular, and elastic
Elaborate on the components bag composed of transitional epithelium. It consists of the
and functions of the urinary body (for urine storage) and trigone (a triangular area formed
bladder. by openings).
The urethra is a muscular tube extending from the urinary
Discuss the role of the urethra bladder. The external sphincter in males is more powerful
and the function of the and can control urethral opening even if the internal
sphincters in males. sphincter is damaged.
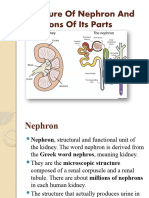
What is the nephron, and The nephron is the functional and structural unit of the kidney,
what is its primary measuring about 3 cm. Its primary function is the filtration of
function? blood.
Differentiate between the The nephron is divided into two parts: the Malpighian body and
Malpighian body and renal renal tubules. The Malpighian body consists of Bowman's
tubules. capsule and glomerulus.
Bowman's capsule is a small, double-walled cup-like structure
Describe the structure of lined with simple epithelium tissue. Podocytes, specialized
Bowman's capsule. epithelial cells, and podopores aid in blood filtration.
Explain the formation and The glomerulus is formed by a network of blood capillaries inside
components of the Bowman's capsule. Afferent renal arterioles enter, divide into
glomerulus. capillaries, and finally exit as efferent renal arterioles.
Question Answer
Renal tubules are part of the nephron located behind
Bowman's capsule. They are long and convoluted,
What is the role of renal differentiated into four parts: proximal convoluted tubules,
tubules in the nephron? Henle's loop, distal convoluted tubule, and conducting duct.
Describe the characteristics PCT, located in the cortex, aids in reabsorption during urine
and function of Proximal formation. It is convoluted and plays a crucial role in
Convoluted Tubules (PCT). maintaining the balance of substances in the urine.
Henle's loop, situated in the medulla, has a U-shaped structure
with ascending and descending limbs. Its main function is to
Explain the structure and maintain urine concentration and act as a counter-current
function of Henle's Loop. system.
Discuss the similarities Both PCT and DCT are convoluted tubules in the cortex,
between Proximal Convoluted playing a role in maintaining urine concentration. While PCT is
Tubules (PCT) and Distal involved in reabsorption, DCT contributes to maintaining the
Convoluted Tubule (DCT). concentration of urine to be excreted.
The conducting duct, located in the medulla, is formed by the
Elaborate on the structure and joining of many tubules. It gives rise to the duct of Bellini,
role of the Conducting Duct in which opens into the renal pelvis. Its function involves the
the nephron. final stages of urine concentration before excretion.
What are the mechanisms The mechanisms of urine formation include ultrafiltration,
involved in urine formation? selective reabsorption, and tubular secretion.
Question Answer
Ultrafiltration is the first step taking place in the glomerulus of
Bowman's capsule. The afferent renal arteriole has a greater
Describe the process of diameter than the efferent arteriole, creating high pressure in
ultrafiltration in urine the glomerulus. This pressure filters blood, forming nephric
formation. filtrate.
Selective reabsorption occurs in the PCT and Henle's loop,
How does selective allowing the reabsorption of useful substances along with
reabsorption contribute to water from the nephric filtrate. This process helps maintain
maintaining the balance of the balance of substances in urine by retaining the essential
substances in urine? ones and excreting harmful substances.
Tubular secretion involves the active transport of substances
from the blood into the renal tubules. It complements the
Briefly discuss the role of processes of ultrafiltration and selective reabsorption by
tubular secretion in urine eliminating additional substances from the blood into the
formation. urine
You might also like
- Surgery OralDocument39 pagesSurgery OralVishva Lalitbhai HirparaNo ratings yet
- Unit 4: Excretion : Cbcs Third Sem GeneralDocument35 pagesUnit 4: Excretion : Cbcs Third Sem Generallegendhere121No ratings yet
- الجهاز البولىDocument6 pagesالجهاز البولىNajwa AbdualgaderNo ratings yet
- Anatomy and Physiology of Urinary SystemDocument5 pagesAnatomy and Physiology of Urinary SystemIan CruzNo ratings yet
- Study of Human Urinary SystemDocument5 pagesStudy of Human Urinary SystemKʀɩsʜʌŋ ĸʀ ƦoƴNo ratings yet
- The Kidneys Are A Pair of Purplish-Brown Organs Is Located Below The Ribs Toward The Middle ofDocument6 pagesThe Kidneys Are A Pair of Purplish-Brown Organs Is Located Below The Ribs Toward The Middle ofJoana Bless PereyNo ratings yet
- Skenario 1 - B2 - 10Document15 pagesSkenario 1 - B2 - 10putriNo ratings yet
- Urinary System Anatomy and PhysiologyDocument13 pagesUrinary System Anatomy and PhysiologyKBDNo ratings yet
- Kidney Anatomy and PhysiologyDocument17 pagesKidney Anatomy and Physiologytemo chachanidzeNo ratings yet
- Lab 7Document6 pagesLab 7InactiveAccountNo ratings yet
- Jigjiga University College of Veterinary Medicine: by DR Mahamud A. (DVM, MSC)Document56 pagesJigjiga University College of Veterinary Medicine: by DR Mahamud A. (DVM, MSC)Shemsu LoveNo ratings yet
- HomeostasisDocument10 pagesHomeostasisSiddhesh YadavNo ratings yet
- Urinary SystemDocument10 pagesUrinary SystemElyka Alivan Valdez PolonioNo ratings yet
- The Excretory SystemDocument31 pagesThe Excretory Systemapi-3759646100% (12)
- Urinary SystemDocument14 pagesUrinary SystemSaadNo ratings yet
- Urinary System Anatomy and PhysiologyDocument12 pagesUrinary System Anatomy and PhysiologyCris Vincent Suma-oy100% (1)
- AnaphyDocument3 pagesAnaphyKenneth DelorinoNo ratings yet
- Histology Urinary SystemDocument6 pagesHistology Urinary SystemHenessey Palisoc ResuelloNo ratings yet
- Untitled 1Document5 pagesUntitled 1YuliaAnggrainiNo ratings yet
- Kidney and NephronDocument41 pagesKidney and NephronMd Atikur AminNo ratings yet
- MRGR Excretory System Ysh17Document13 pagesMRGR Excretory System Ysh17Yash PandeyNo ratings yet
- Topik 2 2021Document26 pagesTopik 2 2021AnnisNo ratings yet
- Biologi CacaDocument4 pagesBiologi CacaRifaa WidasmaraNo ratings yet
- Urinary SystemDocument7 pagesUrinary SystemCurex QANo ratings yet
- Nephron 200328105815Document25 pagesNephron 200328105815Iph anyiNo ratings yet
- Physiology Handouts (Topics 89-103)Document19 pagesPhysiology Handouts (Topics 89-103)bc200411046No ratings yet
- PINK Cream and Green Illustrative Science Project PresentationDocument31 pagesPINK Cream and Green Illustrative Science Project Presentationereneovalerozo22No ratings yet
- Physiology of Kidney and ExcretionDocument57 pagesPhysiology of Kidney and ExcretionWenny KalamiNo ratings yet
- Anatomy Uninary SystemDocument15 pagesAnatomy Uninary SystemSumit PandyaNo ratings yet
- Urinary System (2015 - 06 - 09 22 - 21 - 55 Utc)Document44 pagesUrinary System (2015 - 06 - 09 22 - 21 - 55 Utc)DiazNo ratings yet
- Biology Note PartDocument13 pagesBiology Note PartbnksukantaNo ratings yet
- Online Practice Tests, Live Classes, Tutoring, Study Guides Q&A, Premium Content and MoreDocument42 pagesOnline Practice Tests, Live Classes, Tutoring, Study Guides Q&A, Premium Content and MoreYoAmoNYCNo ratings yet
- Online Practice Tests, Live Classes, Tutoring, Study Guides Q&A, Premium Content and MoreDocument42 pagesOnline Practice Tests, Live Classes, Tutoring, Study Guides Q&A, Premium Content and MoreabctutorNo ratings yet
- Learning Module 8 Lesson 8: Excretory System: 41: M.Opeña, MSCDocument2 pagesLearning Module 8 Lesson 8: Excretory System: 41: M.Opeña, MSCRegina RazoNo ratings yet
- Renal Anatomy and PhysiologyDocument15 pagesRenal Anatomy and PhysiologySapna JainNo ratings yet
- Urinary SystemDocument28 pagesUrinary Systemgabanule brandonNo ratings yet
- ScriptDocument3 pagesScriptAnghelNo ratings yet
- مشروع ابو زنيد1Document15 pagesمشروع ابو زنيد1Hareth mohammad mahmod NawajaNo ratings yet
- 13EXCRETORYDocument3 pages13EXCRETORYDaniellaRuth Cajurao CanalesNo ratings yet
- Urinary SystemDocument15 pagesUrinary SystemrogerstulilewisNo ratings yet
- Urinary SystemDocument29 pagesUrinary Systemhabibsaqib773No ratings yet
- Excretory System Lecture 1 JUWDocument12 pagesExcretory System Lecture 1 JUWamjad.46987No ratings yet
- Histology of The Urinary SystemDocument35 pagesHistology of The Urinary SystemSilvana María Espinoza CuadrosNo ratings yet
- General Anatomy of Urinary SystemDocument62 pagesGeneral Anatomy of Urinary SystemSARABIA, ARVIN JR.No ratings yet
- Hafeezullah: Subject:Anatomy Topic: Anatomy of Excretory System Roll No: 15 Semester: 1 RepeaterDocument10 pagesHafeezullah: Subject:Anatomy Topic: Anatomy of Excretory System Roll No: 15 Semester: 1 RepeaterMuhammad ShahzaibNo ratings yet
- Urinary SystemDocument77 pagesUrinary SystemJushelle Anne Tigoy PilareNo ratings yet
- Xcretory System: BY: Pramod KumarDocument50 pagesXcretory System: BY: Pramod KumarCay C. CordovaNo ratings yet
- Assessment of Patients With Renal Disorders Management of Urinary Tract DisordersDocument16 pagesAssessment of Patients With Renal Disorders Management of Urinary Tract DisordersJhosita Flora LarocoNo ratings yet
- Excretory PDFDocument104 pagesExcretory PDFgerman guazaNo ratings yet
- The Urinary SystemDocument11 pagesThe Urinary SystemInvisible eyeNo ratings yet
- MIRADOR, Kiana AnaphyAct16Document4 pagesMIRADOR, Kiana AnaphyAct16Kiana MiradorNo ratings yet
- Radi 583 Paper Final Draft - HicksDocument26 pagesRadi 583 Paper Final Draft - Hicksapi-356393960No ratings yet
- 13EXCRETORYDocument3 pages13EXCRETORYDaniellaRuth Cajurao CanalesNo ratings yet
- Struktur Dan Mekanisme Kemih Wanita: AbstrakDocument24 pagesStruktur Dan Mekanisme Kemih Wanita: Abstrakrizauddin96 96rizauddinNo ratings yet
- Renal SystemDocument18 pagesRenal SystemS GNo ratings yet
- Urinary SystemDocument4 pagesUrinary SystemAntonioNo ratings yet
- Renal Physiology 1 170407164141Document76 pagesRenal Physiology 1 170407164141Vhutshilo MasithembiNo ratings yet
- The Human Renal SystemDocument8 pagesThe Human Renal SystemRobert CaseyNo ratings yet
- Urinary Tract InfectionDocument10 pagesUrinary Tract InfectionKiara Denise TamayoNo ratings yet
- Renal Reflections: Exploring the Marvels of Nephrology: The Intricate Ballet of Kidney Functions UnveiledFrom EverandRenal Reflections: Exploring the Marvels of Nephrology: The Intricate Ballet of Kidney Functions UnveiledNo ratings yet
- Physiology Practical 1: (Heart Sounds)Document12 pagesPhysiology Practical 1: (Heart Sounds)Dratosh KatiyarNo ratings yet
- 1 Cholinergic & Noradrenergic Transmission IDocument37 pages1 Cholinergic & Noradrenergic Transmission IGeraldine Ong100% (2)
- Cerebrospinal Fluid 1 - Dental Ebook & Lecture Notes PDF Download (Studynama - Com - India's Biggest Website For BDS Study Material Downloads)Document21 pagesCerebrospinal Fluid 1 - Dental Ebook & Lecture Notes PDF Download (Studynama - Com - India's Biggest Website For BDS Study Material Downloads)Vinnie SinghNo ratings yet
- Subtle Energy Module 01 Materials Color Chakra DiagramDocument1 pageSubtle Energy Module 01 Materials Color Chakra Diagramjoyous leeNo ratings yet
- GIT & Urinary SystemDocument50 pagesGIT & Urinary SystemRenishya ManiarasuNo ratings yet
- Phys 4.1 CV Heart ElectricalDocument10 pagesPhys 4.1 CV Heart ElectricalBeverly DatuNo ratings yet
- PhysioEx Nuzla Emira Potensial AksiDocument7 pagesPhysioEx Nuzla Emira Potensial AksiPine's FauNo ratings yet
- MJVH - Volume 4.2 - Issue 2 - Pages 53-55Document3 pagesMJVH - Volume 4.2 - Issue 2 - Pages 53-55Indra YaniNo ratings yet
- Achievement Test Science 5-2023Document5 pagesAchievement Test Science 5-2023Jam AstreroNo ratings yet
- Histology of BreastDocument6 pagesHistology of BreastSusasti HasanahNo ratings yet
- Quiz Organ SysDocument1 pageQuiz Organ SysMelva GuerraNo ratings yet
- CHAPTER-19-REPRODUCTIVE-SYSTEMDocument11 pagesCHAPTER-19-REPRODUCTIVE-SYSTEMVanya YeleniaNo ratings yet
- Human Reproductive System: Development of The Reproductive OrgansDocument11 pagesHuman Reproductive System: Development of The Reproductive OrgansDhion Ardhian NugrohoNo ratings yet
- Atif Afzal Quick HintsDocument54 pagesAtif Afzal Quick Hintssara khanNo ratings yet
- Juan Pekolj, Victoria Ardiles, Juan Glinka Fundamentals of BileDocument162 pagesJuan Pekolj, Victoria Ardiles, Juan Glinka Fundamentals of BileMohamed WerflyNo ratings yet
- Dopa - 26Document6 pagesDopa - 26hhNo ratings yet
- HomeostasisDocument10 pagesHomeostasiszainah jabrNo ratings yet
- Less0n Plan 2nd DemoDocument12 pagesLess0n Plan 2nd DemoJennifer Agsoy DassunNo ratings yet
- Renal Clearance 2Document3 pagesRenal Clearance 2Ine Marthia DanieNo ratings yet
- Special SensesDocument21 pagesSpecial SensesZeeshan Jalil100% (1)
- Chapter 9 - Endocrine System NotesDocument9 pagesChapter 9 - Endocrine System Notesvictoria skoubourisNo ratings yet
- Diseases of The Gastric SystemDocument6 pagesDiseases of The Gastric SystemAaliyaan KhanNo ratings yet
- Control Systems - KeyDocument2 pagesControl Systems - KeySamra ShahzadNo ratings yet
- The Physiology of ImmunityDocument27 pagesThe Physiology of Immunityapi-3823549100% (1)
- Duke - AbdominalDocument75 pagesDuke - AbdominalMihir KatlariwalaNo ratings yet
- (19330693 - Journal of Neurosurgery) Founder of Modern Hydrocephalus Diagnosis and Therapy - Walter Dandy at The Johns Hopkins HospitalDocument6 pages(19330693 - Journal of Neurosurgery) Founder of Modern Hydrocephalus Diagnosis and Therapy - Walter Dandy at The Johns Hopkins HospitalHarry RamoneNo ratings yet
- Nutrition and DigestionDocument47 pagesNutrition and DigestionKhatlya Rivana PutriNo ratings yet
- Aero-Digestive & Respiratory Changes Post TraheostomyDocument36 pagesAero-Digestive & Respiratory Changes Post Traheostomyrahaf abusalahNo ratings yet
- Clinical Imaging of Liver, Gallbladder, BiliaryDocument93 pagesClinical Imaging of Liver, Gallbladder, Biliaryapi-3856051100% (1)