Professional Documents
Culture Documents
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
1 viewsassignment mcqs by bisma
assignment mcqs by bisma
Uploaded by
sara.shinju2Bsn mcqs on carbohydrates
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You might also like
- ScrewsDocument35 pagesScrewsRodel Marata100% (3)
- ChromiumDocument24 pagesChromiumstallone21No ratings yet
- Principles of Biochemical Engg. MCQsDocument18 pagesPrinciples of Biochemical Engg. MCQsasrafarooq57No ratings yet
- Structure of Carbohydrate McqsDocument34 pagesStructure of Carbohydrate Mcqsmaaz khanNo ratings yet
- Carbohydrateprotein and EnzeymeDocument10 pagesCarbohydrateprotein and Enzeymediyarberwari15No ratings yet
- Bio Cheeee MistryDocument16 pagesBio Cheeee Mistrymkhanmughal4No ratings yet
- Exam1 Sp2014 AnswersDocument6 pagesExam1 Sp2014 AnswersEllen LacbayoNo ratings yet
- BIOCHEM I-1st Sem Assignment 2024Document11 pagesBIOCHEM I-1st Sem Assignment 2024teffodennisNo ratings yet
- CarbohydratesDocument7 pagesCarbohydratesjamila abdirahmanNo ratings yet
- Mcqs BiochemDocument10 pagesMcqs Biochemzonishaadan2No ratings yet
- Hidratos de Carbono TallerDocument10 pagesHidratos de Carbono TallerLeidyNo ratings yet
- Sbi4u1 - Biochemistry Unit Test 2010Document11 pagesSbi4u1 - Biochemistry Unit Test 2010alathena alathenaNo ratings yet
- Biochemistry Mcqs and PPR PreprofsDocument15 pagesBiochemistry Mcqs and PPR PreprofsAhmad KhanNo ratings yet
- FeasgsDocument14 pagesFeasgsjan2072650No ratings yet
- Biochemistry Clinical Pathology Sample Paper by NoteskartsDocument6 pagesBiochemistry Clinical Pathology Sample Paper by Noteskartsarshu98172No ratings yet
- BiologyDocument4 pagesBiologysushila dhabaiNo ratings yet
- Bio McqsDocument91 pagesBio Mcqszaim techNo ratings yet
- Exsc 223 CH 24 Practice ExamDocument4 pagesExsc 223 CH 24 Practice Examkimber brownNo ratings yet
- Edited - Chapter 7 Test BankDocument21 pagesEdited - Chapter 7 Test BankRod De GuzmanNo ratings yet
- AnswerDocument7 pagesAnswerloginhani40No ratings yet
- Carbohydrate WorksheetDocument5 pagesCarbohydrate WorksheetReshma MohabeirNo ratings yet
- Foundation Module Questions 2018 D'23Document18 pagesFoundation Module Questions 2018 D'23rk4876001No ratings yet
- Komitte 3Document30 pagesKomitte 3Gizem S.No ratings yet
- Biological Molecules Mcqs 2020Document3 pagesBiological Molecules Mcqs 2020PakistanWaqarMughalNo ratings yet
- Short EssayDocument13 pagesShort EssayYazhiniNo ratings yet
- Biology, 7e (Campbell) : Chapter 41: Animal NutritionDocument7 pagesBiology, 7e (Campbell) : Chapter 41: Animal Nutrition123456789123456789hiNo ratings yet
- FatsDocument15 pagesFatsahsaanahmadNo ratings yet
- Biotechnologya Todos Los HODocument27 pagesBiotechnologya Todos Los HOHanan AmarkiNo ratings yet
- Cytology Lab DR Amal2018 SpringDocument4 pagesCytology Lab DR Amal2018 SpringAhmed Ali SofyNo ratings yet
- 12 Chem CH 10 MCQSDocument12 pages12 Chem CH 10 MCQSSaran.kNo ratings yet
- Smith6e Chapter29 TBDocument12 pagesSmith6e Chapter29 TBandrew.gregory978No ratings yet
- Practice Mult Choice Questions Chapt 3Document5 pagesPractice Mult Choice Questions Chapt 3HyunSung KimNo ratings yet
- FDocument146 pagesFOla GomaaNo ratings yet
- Mock FinalDocument19 pagesMock Finalbuddybbuddy100% (1)
- BIO MOLECULE MCQsDocument8 pagesBIO MOLECULE MCQsdk390381No ratings yet
- 35 doneDocument5 pages35 donemedicolover001No ratings yet
- Carbohydrates Multiple Choice Questions 11 PDJJJDocument8 pagesCarbohydrates Multiple Choice Questions 11 PDJJJbyagni100% (2)
- HSN211 Practice ExamDocument8 pagesHSN211 Practice ExamRaha RajabigamasaeiNo ratings yet
- Biochem 1Document11 pagesBiochem 1Muhammadsiddique khanNo ratings yet
- The1+carbo+ach221+21415, Nokey 1Document18 pagesThe1+carbo+ach221+21415, Nokey 1Shailah Leilene Arce BrionesNo ratings yet
- Sample MCQ 'S Biotechnology DepartmentDocument50 pagesSample MCQ 'S Biotechnology DepartmentSaurabh Kumar RawatNo ratings yet
- Carbohydrates ExercisesDocument5 pagesCarbohydrates Exercisesreemmasri877No ratings yet
- Hda BiologyDocument2 pagesHda BiologyAbdulganiu JubrilNo ratings yet
- Accumulative Test 1Document14 pagesAccumulative Test 1hely shahNo ratings yet
- MCQs Class 9 ScienceDocument3 pagesMCQs Class 9 ScienceHarshima JoshiNo ratings yet
- Biochem Practice TestDocument8 pagesBiochem Practice TestEvette SmithNo ratings yet
- WS Revision Nut Respi 10 Bio SeptDocument5 pagesWS Revision Nut Respi 10 Bio Septanushka109289No ratings yet
- Chemistry Test #9Document3 pagesChemistry Test #9dania.siddiqui195No ratings yet
- Biomolecules Questions WaDocument10 pagesBiomolecules Questions WaYoussef AliNo ratings yet
- BIOMOLECULES Ncert Class 12 Most Important QuestionsDocument6 pagesBIOMOLECULES Ncert Class 12 Most Important QuestionsRamNo ratings yet
- Exam On Proteins & Enzymes and Lipids: I. Multiple Choice. Submit All Your Answers To Google Classroom in PDF FormatDocument7 pagesExam On Proteins & Enzymes and Lipids: I. Multiple Choice. Submit All Your Answers To Google Classroom in PDF Formatsylv ackermanNo ratings yet
- 생화학 답지Document127 pages생화학 답지rndel300No ratings yet
- FST 362 All Objectives Qu.Document14 pagesFST 362 All Objectives Qu.Jyoti SinghNo ratings yet
- QuizDocument7 pagesQuizm_linguistNo ratings yet
- CH - 5 (Nutrition) MCQ/Assertion and ReasoningDocument4 pagesCH - 5 (Nutrition) MCQ/Assertion and ReasoningYashu RawatNo ratings yet
- FST ObjectivesDocument7 pagesFST ObjectivesMaithiliNo ratings yet
- Final Term Bio 2 MedicineDocument10 pagesFinal Term Bio 2 Medicineأم أحمدNo ratings yet
- Secondymcq 12Document5 pagesSecondymcq 12Santosh KathwateNo ratings yet
- Respiration 90 QuestionsDocument92 pagesRespiration 90 QuestionsNITISH KUMARNo ratings yet
- Notes 190612 153750 A96Document6 pagesNotes 190612 153750 A96stuffNo ratings yet
- Chapter 5 The Structure and Function of Large Biological MoleculesDocument20 pagesChapter 5 The Structure and Function of Large Biological Molecules蔡旻珊No ratings yet
- Age Basic Conflict Basic Strength/ Virtue Core Pathology Important Event OutcomeDocument1 pageAge Basic Conflict Basic Strength/ Virtue Core Pathology Important Event OutcomeErnestjohnBelasotoNo ratings yet
- Water Pollution PPT Civil NITHINDocument18 pagesWater Pollution PPT Civil NITHINmudavath jagapathibabuNo ratings yet
- Volume Changes of ConcreteDocument17 pagesVolume Changes of ConcreteAljawhara AlnadiraNo ratings yet
- User Manual - Thermolyne - Benchtop Furnace - Type FD1500M - LT1170X1 Rev - B-1 PDFDocument45 pagesUser Manual - Thermolyne - Benchtop Furnace - Type FD1500M - LT1170X1 Rev - B-1 PDFMartin Fco EncinasNo ratings yet
- A Study To Evaluate The Effectiveness of Patterned Breathing Technique On Pain During First Stage of Labour Among Primigravida Mothers Admitted in Selected Hospital at MoradabadDocument17 pagesA Study To Evaluate The Effectiveness of Patterned Breathing Technique On Pain During First Stage of Labour Among Primigravida Mothers Admitted in Selected Hospital at MoradabadEditor IJTSRDNo ratings yet
- Working at HeightsDocument1 pageWorking at HeightsVictor Quijano JrNo ratings yet
- The Dowser's Handbook - Pendulums, Muscle Testing, Applied Kinesiology by Jimmy MackDocument44 pagesThe Dowser's Handbook - Pendulums, Muscle Testing, Applied Kinesiology by Jimmy MackZach90% (10)
- 74781-Civil Degree PDFDocument14 pages74781-Civil Degree PDFCgpscAspirantNo ratings yet
- CH 111 Experiment 12bDocument8 pagesCH 111 Experiment 12bChala1989No ratings yet
- Kolmeks Pump Catalogue Low PDFDocument260 pagesKolmeks Pump Catalogue Low PDFMykola Titov50% (2)
- D 6730 - 01 AstmDocument55 pagesD 6730 - 01 AstmSebastian GonzalezNo ratings yet
- Exp't 51: Nitration of NitrobenzeneDocument4 pagesExp't 51: Nitration of NitrobenzenelovehopeNo ratings yet
- Comparative Study of HerzbergDocument2 pagesComparative Study of HerzbergRoy Peter DelizoNo ratings yet
- Control of Hospital Acquired Infection PDFDocument36 pagesControl of Hospital Acquired Infection PDFPrakashNo ratings yet
- BSR 560 Jan 2022 Test (w6 Exercise)Document3 pagesBSR 560 Jan 2022 Test (w6 Exercise)Muhammad SahrizatNo ratings yet
- Sika JointDocument16 pagesSika JointnasrulaminzubainiNo ratings yet
- A. Kinesiology of HumanDocument7 pagesA. Kinesiology of HumanleyluuuuuhNo ratings yet
- Chemray420 Service Manual V1.0eDocument77 pagesChemray420 Service Manual V1.0eJose PersiaNo ratings yet
- New Microsoft Word DocumentDocument79 pagesNew Microsoft Word DocumentalexpharmNo ratings yet
- Chap 3 - Reading Essentials Nicholas CeballosDocument5 pagesChap 3 - Reading Essentials Nicholas CeballosNicholasNo ratings yet
- Root Resorption Due To Dental Trauma: General PrinciplesDocument22 pagesRoot Resorption Due To Dental Trauma: General PrinciplesBogdan PopescuNo ratings yet
- SPK Manual 2007-2009Document26 pagesSPK Manual 2007-2009jlhood65No ratings yet
- S.No. Paper Code Title of The Paper Author AffiliationDocument7 pagesS.No. Paper Code Title of The Paper Author AffiliationDanie RoyNo ratings yet
- High-Speed USB PCB Layout Recommendations: Figure 1. Microstrip Model of Differential ImpedanceDocument4 pagesHigh-Speed USB PCB Layout Recommendations: Figure 1. Microstrip Model of Differential ImpedanceopicaNo ratings yet
- ECW748 Advance Water Supply Group 2 Assignment 10NOV2023Document10 pagesECW748 Advance Water Supply Group 2 Assignment 10NOV2023khairie.prominentsynergyNo ratings yet
- SRS Medical ManagementDocument7 pagesSRS Medical ManagementAtharv KatkarNo ratings yet
- QC Case StudyDocument77 pagesQC Case StudyBibhudutta mishraNo ratings yet
- LECTURE 6-Forming and Shaping of Plastics and CompositesDocument52 pagesLECTURE 6-Forming and Shaping of Plastics and CompositesM.k. VarmaNo ratings yet
assignment mcqs by bisma
assignment mcqs by bisma
Uploaded by
sara.shinju20 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
1 views6 pagesBsn mcqs on carbohydrates
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentBsn mcqs on carbohydrates
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as docx, pdf, or txt
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
1 views6 pagesassignment mcqs by bisma
assignment mcqs by bisma
Uploaded by
sara.shinju2Bsn mcqs on carbohydrates
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as docx, pdf, or txt
You are on page 1of 6
ASSIGNMNET
Class: GBSN (2024)
SEMESTER: 1st
Subject: Bio chemistry
Unit: 04
Topic: Carbohydrates
Faculty: Shafeen Amir
Group members:
1. Bisma
2. Celeshia
3. Fazia
4. Bilal Ahmed
5. Faizul Islam
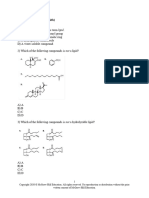
1. What is the general formula of Carbohydrates?
a) CH2 0
b) C6 H1206
c) CH40
d) C2 H4 O2
2. Which of the following is example of Simple Carbohydrates?
a) Starch
b) Cellulose
c) Glucose
d) Glycogen
3. What the main function of Carbohydrates in the body?
a) To provide energy
b) To built protein
c) To Store fat
d) To regulate the body temperature.
4. Which of the following is an example of a complex carbohydrates?
a) fructose
b) Starch
c) Sucrose
d) vibose
5. What is the name of the Process by which carbohydrates broken down in to glucose?
a) Guycolysis
b) Proteolysa
c) Liplosis
d) hydrolysis
6. Which of the following is example of disaccharide?
a) Glucose
b) fructose
c) Sucrose
d) Starch
7. What is the name of hormone that regulate blood sugar levels?
a) Insulin
b) Adrenalin
c) Glucagon
d) Thyroxin
8. Monosaccharide are made up of single unit with a carbon chain of three to
a) Two Carbons.
b) Five Carbons
c) Four carbons
d) Six Carbons
9. Carbohydrates also called
a) Saccharides
b) Elements
c) Carbonyl
d) Carbon
10. Which of the following is an example Carbohydrate that is indigestible by human?
a) Starch
b) Glucose
c) Cellulose
d) Fructose
11. Which of the following is a hexose sugar?
a) Glucose
b) Fructose
c) Galactose
d) All of the above
12. What is the primary source of energy for the body's tissues?
a) Glucose
b) Fructose
c) Galactose
d) Maltose
13. Which of the following is an example of a hexose sugar found in fruit juices?
a) Glucose
b) Fructose
c) Galactose
d) Sucrose
14. What is the term for excess glucose in the blood?
a) Hypoglycemia
b) Hyperglycemia
c) Glucosuria
d) Diabetes mellitus
15. Which of the following is a sign of diabetes mellitus?
a) Excess glucose in the blood
b) Excess glucose in the urine
c) Low blood sugar levels
d) High blood pressure
16. What is the term for the breakdown of starch into glucose?
a) Hydrolysis
b) Glycolysis
c) Gluconeogenesis
d) Glycogenolysis
17. Which of the following sugars is broken down into glucose during digestion?
a) Maltose
b) Lactose
c) Sucrose
d) All of the above
18. What is the normal range of blood glucose levels?
a) 40-60 mg/dL
b) 70-100 mg/dL
c) 100-120 mg/dL
d) 120-140 mg/dL
19. Which of the following is a complication of untreated diabetes mellitus?
a) Hypoglycemia
b) Hyperglycemia
c) Glucosuria
d) Nephropathy
20. What is the term for the regulation of blood glucose levels?
a) Glucose homeostasis
b) Glucose regulation
c) Glycemic control
d) Blood sugar management
21. Which of the following is a hexose sugar?
a) Glucose
b) Fructose
c) Galactose
d) All of the above
22. What is the primary source of energy for the body's tissues?
a) Glucose
b) Fructose
c) Galactose
d) Maltose
23. Which of the following is an example of a hexose sugar found in fruit juices?
a) Glucose
b) Fructose
c) Galactose
d) Sucrose
24. What is the term for excess glucose in the blood?
a) Hypoglycemia
b) Hyperglycemia
c) Glucosuria
d) Diabetes mellitus
25. Which of the following is a sign of diabetes mellitus?
a) Excess glucose in the blood
b) Excess glucose in the urine
c) Low blood sugar levels
d) High blood pressure
26. What is the term for the breakdown of starch into glucose?
a) Hydrolysis
b) Glycolysis
c) Gluconeogenesis
d) Glycogenolysis
27. Which of the following sugars is broken down into glucose during digestion?
a) Maltose
b) Lactose
c) Sucrose
d) All of the above
28. What is the normal range of blood glucose levels?
a) 40-60 mg/dL
b) 70-100 mg/dL
c) 100-120 mg/dL
d) 120-140 mg/dL
29. Which of the following is a complication of untreated diabetes mellitus?
a) Hypoglycemia
b) Hyperglycemia
c) Glucosuria
d) Nephropathy
30. What is the term for the regulation of blood glucose levels?
a) Glucose homeostasis
b) Glucose regulation
c) Glycemic control
d) Blood sugar management
31. What is the Latin word for fruit that Fructose is derived from?
a) Fructus
b) Fruitus
c) Fructosus
d) Fruitis
32. Which of the following is a source of Fructose?
a) Fruit juices
b) Honey
c) Table sugar
d) All of the above
33. What is the main nutritional source of energy for spermatozoa?
a) Glucose
b) Fructose
c) Galactose
d) Sucrose
34. Where can Fructose be converted to Glucose?
a) Liver
b) Pancreas
c) Kidneys
d) Brain
35. Which of the following is a characteristic of Fructose?
a) It is the least sweet sugar
b) It is the sweetest sugar
c) It is found only in animal sources
d) It is not found in honey
36. What is the product of the hydrolysis of Inulin?
a) Glucose
b) Fructose
c) Galactose
d) Sucrose
37. Which of the following is a food that contains Fructose?
a) Bread
b) Milk
c) Fruit juice
d) All of the above
38. What is the primary function of Fructose in the body?
a) Energy source for spermatozoa
b) Energy source for the brain
c) Component of DNA
d) Component of proteins
39. Where is Lactose synthesized?
a) Liver
b) Lactating mammary gland
c) Pancreas
d) Brain
40. What is the common name of Lactose?
a) Table sugar
b) Fruit sugar
c) Milk sugar
d) Honey sugar
41. How sweet is Lactose compared to Sucrose?
a) 50% as sweet
b) 25% as sweet
c) 16% as sweet
d) 75% as sweet
42. What is the primary source of Lactose?
a) Milk
b) Fruit
c) Honey
d) Table sugar
43. Which of the following is the main reason for classifying monosaccharides?
a) To identify their optical activity
b) To determine their sweetness
c) To understand their chemical reactivity
d) To group them based on their number of carbon atoms
44. Which classification of monosaccharides is based on the number of carbon atoms?
a) Aldose and Ketose
b) Triose, Tetrose, Pentose, Hexose
c) Reducing and Non-reducing
d) Optically active and Inactive
45. Why is it important to classify monosaccharides as aldose or ketose?
a) To determine their sweetness
b) To identify their optical activity
c) To understand their chemical reactivity
d) To group them based on their functional group
46. Which classification of monosaccharides is based on their reducing properties?
a) Aldose and Ketose
b) Reducing and Non-reducing
c) Triose, Tetrose, Pentose, Hexose
d) Optically active and Inactive
47. Why is it important to classify monosaccharides as reducing or non-reducing?
a) To determine their sweetness
b) To identify their optical activity
c) To understand their chemical reactivity
d) To predict their ability to form glycosidic bonds
48. What is the chemical nature of the carbonyl group?
a) Hydrophilic and electrophilic
b) Hydrophobic and nucleophilic
c) Hydrophilic and nucleophilic
d) Hydrophobic and electrophilic
49. Which of the following is a characteristic of the carbonyl group?
a) It is a strong base
b) It is a strong acid
c) It is a polar and electrophilic group
d) It is a non-polar and nucleophilic group
50. What is the carbonyl group classified as?
a) A hydrophilic head
b) A hydrophobic tail
c) A polar functional group
d) A non-polar functional group
51. Which of the following is true about the carbonyl group?
a) It is a good leaving group
b) It is a good nucleophile
c) It is a good electrophile
d) It is a poor electrophile
52. What is the chemical nature of the carbonyl carbon?
a) Electropositive
b) Electronegative
c) Neutral
d) Both electropositive and electronegative
53. What is the meaning of Oligosaccharides?
a) A long chain of sugars
b) A short chain of sugars
c) A single sugar molecule
d) A type of protein
54. Which of the following is an example of Oligosaccharides?
a) Starch
b) Cellulose
c) Lactose
d) Maltose
You might also like
- ScrewsDocument35 pagesScrewsRodel Marata100% (3)
- ChromiumDocument24 pagesChromiumstallone21No ratings yet
- Principles of Biochemical Engg. MCQsDocument18 pagesPrinciples of Biochemical Engg. MCQsasrafarooq57No ratings yet
- Structure of Carbohydrate McqsDocument34 pagesStructure of Carbohydrate Mcqsmaaz khanNo ratings yet
- Carbohydrateprotein and EnzeymeDocument10 pagesCarbohydrateprotein and Enzeymediyarberwari15No ratings yet
- Bio Cheeee MistryDocument16 pagesBio Cheeee Mistrymkhanmughal4No ratings yet
- Exam1 Sp2014 AnswersDocument6 pagesExam1 Sp2014 AnswersEllen LacbayoNo ratings yet
- BIOCHEM I-1st Sem Assignment 2024Document11 pagesBIOCHEM I-1st Sem Assignment 2024teffodennisNo ratings yet
- CarbohydratesDocument7 pagesCarbohydratesjamila abdirahmanNo ratings yet
- Mcqs BiochemDocument10 pagesMcqs Biochemzonishaadan2No ratings yet
- Hidratos de Carbono TallerDocument10 pagesHidratos de Carbono TallerLeidyNo ratings yet
- Sbi4u1 - Biochemistry Unit Test 2010Document11 pagesSbi4u1 - Biochemistry Unit Test 2010alathena alathenaNo ratings yet
- Biochemistry Mcqs and PPR PreprofsDocument15 pagesBiochemistry Mcqs and PPR PreprofsAhmad KhanNo ratings yet
- FeasgsDocument14 pagesFeasgsjan2072650No ratings yet
- Biochemistry Clinical Pathology Sample Paper by NoteskartsDocument6 pagesBiochemistry Clinical Pathology Sample Paper by Noteskartsarshu98172No ratings yet
- BiologyDocument4 pagesBiologysushila dhabaiNo ratings yet
- Bio McqsDocument91 pagesBio Mcqszaim techNo ratings yet
- Exsc 223 CH 24 Practice ExamDocument4 pagesExsc 223 CH 24 Practice Examkimber brownNo ratings yet
- Edited - Chapter 7 Test BankDocument21 pagesEdited - Chapter 7 Test BankRod De GuzmanNo ratings yet
- AnswerDocument7 pagesAnswerloginhani40No ratings yet
- Carbohydrate WorksheetDocument5 pagesCarbohydrate WorksheetReshma MohabeirNo ratings yet
- Foundation Module Questions 2018 D'23Document18 pagesFoundation Module Questions 2018 D'23rk4876001No ratings yet
- Komitte 3Document30 pagesKomitte 3Gizem S.No ratings yet
- Biological Molecules Mcqs 2020Document3 pagesBiological Molecules Mcqs 2020PakistanWaqarMughalNo ratings yet
- Short EssayDocument13 pagesShort EssayYazhiniNo ratings yet
- Biology, 7e (Campbell) : Chapter 41: Animal NutritionDocument7 pagesBiology, 7e (Campbell) : Chapter 41: Animal Nutrition123456789123456789hiNo ratings yet
- FatsDocument15 pagesFatsahsaanahmadNo ratings yet
- Biotechnologya Todos Los HODocument27 pagesBiotechnologya Todos Los HOHanan AmarkiNo ratings yet
- Cytology Lab DR Amal2018 SpringDocument4 pagesCytology Lab DR Amal2018 SpringAhmed Ali SofyNo ratings yet
- 12 Chem CH 10 MCQSDocument12 pages12 Chem CH 10 MCQSSaran.kNo ratings yet
- Smith6e Chapter29 TBDocument12 pagesSmith6e Chapter29 TBandrew.gregory978No ratings yet
- Practice Mult Choice Questions Chapt 3Document5 pagesPractice Mult Choice Questions Chapt 3HyunSung KimNo ratings yet
- FDocument146 pagesFOla GomaaNo ratings yet
- Mock FinalDocument19 pagesMock Finalbuddybbuddy100% (1)
- BIO MOLECULE MCQsDocument8 pagesBIO MOLECULE MCQsdk390381No ratings yet
- 35 doneDocument5 pages35 donemedicolover001No ratings yet
- Carbohydrates Multiple Choice Questions 11 PDJJJDocument8 pagesCarbohydrates Multiple Choice Questions 11 PDJJJbyagni100% (2)
- HSN211 Practice ExamDocument8 pagesHSN211 Practice ExamRaha RajabigamasaeiNo ratings yet
- Biochem 1Document11 pagesBiochem 1Muhammadsiddique khanNo ratings yet
- The1+carbo+ach221+21415, Nokey 1Document18 pagesThe1+carbo+ach221+21415, Nokey 1Shailah Leilene Arce BrionesNo ratings yet
- Sample MCQ 'S Biotechnology DepartmentDocument50 pagesSample MCQ 'S Biotechnology DepartmentSaurabh Kumar RawatNo ratings yet
- Carbohydrates ExercisesDocument5 pagesCarbohydrates Exercisesreemmasri877No ratings yet
- Hda BiologyDocument2 pagesHda BiologyAbdulganiu JubrilNo ratings yet
- Accumulative Test 1Document14 pagesAccumulative Test 1hely shahNo ratings yet
- MCQs Class 9 ScienceDocument3 pagesMCQs Class 9 ScienceHarshima JoshiNo ratings yet
- Biochem Practice TestDocument8 pagesBiochem Practice TestEvette SmithNo ratings yet
- WS Revision Nut Respi 10 Bio SeptDocument5 pagesWS Revision Nut Respi 10 Bio Septanushka109289No ratings yet
- Chemistry Test #9Document3 pagesChemistry Test #9dania.siddiqui195No ratings yet
- Biomolecules Questions WaDocument10 pagesBiomolecules Questions WaYoussef AliNo ratings yet
- BIOMOLECULES Ncert Class 12 Most Important QuestionsDocument6 pagesBIOMOLECULES Ncert Class 12 Most Important QuestionsRamNo ratings yet
- Exam On Proteins & Enzymes and Lipids: I. Multiple Choice. Submit All Your Answers To Google Classroom in PDF FormatDocument7 pagesExam On Proteins & Enzymes and Lipids: I. Multiple Choice. Submit All Your Answers To Google Classroom in PDF Formatsylv ackermanNo ratings yet
- 생화학 답지Document127 pages생화학 답지rndel300No ratings yet
- FST 362 All Objectives Qu.Document14 pagesFST 362 All Objectives Qu.Jyoti SinghNo ratings yet
- QuizDocument7 pagesQuizm_linguistNo ratings yet
- CH - 5 (Nutrition) MCQ/Assertion and ReasoningDocument4 pagesCH - 5 (Nutrition) MCQ/Assertion and ReasoningYashu RawatNo ratings yet
- FST ObjectivesDocument7 pagesFST ObjectivesMaithiliNo ratings yet
- Final Term Bio 2 MedicineDocument10 pagesFinal Term Bio 2 Medicineأم أحمدNo ratings yet
- Secondymcq 12Document5 pagesSecondymcq 12Santosh KathwateNo ratings yet
- Respiration 90 QuestionsDocument92 pagesRespiration 90 QuestionsNITISH KUMARNo ratings yet
- Notes 190612 153750 A96Document6 pagesNotes 190612 153750 A96stuffNo ratings yet
- Chapter 5 The Structure and Function of Large Biological MoleculesDocument20 pagesChapter 5 The Structure and Function of Large Biological Molecules蔡旻珊No ratings yet
- Age Basic Conflict Basic Strength/ Virtue Core Pathology Important Event OutcomeDocument1 pageAge Basic Conflict Basic Strength/ Virtue Core Pathology Important Event OutcomeErnestjohnBelasotoNo ratings yet
- Water Pollution PPT Civil NITHINDocument18 pagesWater Pollution PPT Civil NITHINmudavath jagapathibabuNo ratings yet
- Volume Changes of ConcreteDocument17 pagesVolume Changes of ConcreteAljawhara AlnadiraNo ratings yet
- User Manual - Thermolyne - Benchtop Furnace - Type FD1500M - LT1170X1 Rev - B-1 PDFDocument45 pagesUser Manual - Thermolyne - Benchtop Furnace - Type FD1500M - LT1170X1 Rev - B-1 PDFMartin Fco EncinasNo ratings yet
- A Study To Evaluate The Effectiveness of Patterned Breathing Technique On Pain During First Stage of Labour Among Primigravida Mothers Admitted in Selected Hospital at MoradabadDocument17 pagesA Study To Evaluate The Effectiveness of Patterned Breathing Technique On Pain During First Stage of Labour Among Primigravida Mothers Admitted in Selected Hospital at MoradabadEditor IJTSRDNo ratings yet
- Working at HeightsDocument1 pageWorking at HeightsVictor Quijano JrNo ratings yet
- The Dowser's Handbook - Pendulums, Muscle Testing, Applied Kinesiology by Jimmy MackDocument44 pagesThe Dowser's Handbook - Pendulums, Muscle Testing, Applied Kinesiology by Jimmy MackZach90% (10)
- 74781-Civil Degree PDFDocument14 pages74781-Civil Degree PDFCgpscAspirantNo ratings yet
- CH 111 Experiment 12bDocument8 pagesCH 111 Experiment 12bChala1989No ratings yet
- Kolmeks Pump Catalogue Low PDFDocument260 pagesKolmeks Pump Catalogue Low PDFMykola Titov50% (2)
- D 6730 - 01 AstmDocument55 pagesD 6730 - 01 AstmSebastian GonzalezNo ratings yet
- Exp't 51: Nitration of NitrobenzeneDocument4 pagesExp't 51: Nitration of NitrobenzenelovehopeNo ratings yet
- Comparative Study of HerzbergDocument2 pagesComparative Study of HerzbergRoy Peter DelizoNo ratings yet
- Control of Hospital Acquired Infection PDFDocument36 pagesControl of Hospital Acquired Infection PDFPrakashNo ratings yet
- BSR 560 Jan 2022 Test (w6 Exercise)Document3 pagesBSR 560 Jan 2022 Test (w6 Exercise)Muhammad SahrizatNo ratings yet
- Sika JointDocument16 pagesSika JointnasrulaminzubainiNo ratings yet
- A. Kinesiology of HumanDocument7 pagesA. Kinesiology of HumanleyluuuuuhNo ratings yet
- Chemray420 Service Manual V1.0eDocument77 pagesChemray420 Service Manual V1.0eJose PersiaNo ratings yet
- New Microsoft Word DocumentDocument79 pagesNew Microsoft Word DocumentalexpharmNo ratings yet
- Chap 3 - Reading Essentials Nicholas CeballosDocument5 pagesChap 3 - Reading Essentials Nicholas CeballosNicholasNo ratings yet
- Root Resorption Due To Dental Trauma: General PrinciplesDocument22 pagesRoot Resorption Due To Dental Trauma: General PrinciplesBogdan PopescuNo ratings yet
- SPK Manual 2007-2009Document26 pagesSPK Manual 2007-2009jlhood65No ratings yet
- S.No. Paper Code Title of The Paper Author AffiliationDocument7 pagesS.No. Paper Code Title of The Paper Author AffiliationDanie RoyNo ratings yet
- High-Speed USB PCB Layout Recommendations: Figure 1. Microstrip Model of Differential ImpedanceDocument4 pagesHigh-Speed USB PCB Layout Recommendations: Figure 1. Microstrip Model of Differential ImpedanceopicaNo ratings yet
- ECW748 Advance Water Supply Group 2 Assignment 10NOV2023Document10 pagesECW748 Advance Water Supply Group 2 Assignment 10NOV2023khairie.prominentsynergyNo ratings yet
- SRS Medical ManagementDocument7 pagesSRS Medical ManagementAtharv KatkarNo ratings yet
- QC Case StudyDocument77 pagesQC Case StudyBibhudutta mishraNo ratings yet
- LECTURE 6-Forming and Shaping of Plastics and CompositesDocument52 pagesLECTURE 6-Forming and Shaping of Plastics and CompositesM.k. VarmaNo ratings yet