Professional Documents
Culture Documents
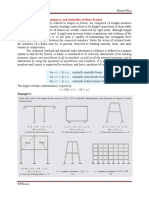
TRUSS ANALYSIS METHOD OF SECTIONS
TRUSS ANALYSIS METHOD OF SECTIONS
Uploaded by
saadCopyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
TRUSS ANALYSIS METHOD OF SECTIONS
TRUSS ANALYSIS METHOD OF SECTIONS
Uploaded by
saadCopyright:
Available Formats
The method of sections is a powerful technique used in truss analysis to determine the
internal forces (such as axial forces and shear forces) in specific members of a truss structure.
Here's a step-by-step guide on how to perform truss analysis using the method of sections:
1. Understand the Truss Structure: Start by familiarizing yourself with the truss structure you
are analyzing. Identify all the members, joints, support conditions, applied loads, and any
other relevant information.
2. Choose a Section: Select a section of the truss where you want to analyze the internal forces
in specific members. The section should ideally cut through only a few members to simplify
the analysis. It's common to choose a section that passes through one or two joints.
3. Isolate the Selected Section: Cut the truss along the chosen section to isolate the part you
are analyzing. This creates a free-body diagram (FBD) of the isolated section, showing only
the forces acting on the members within that section.
4. Apply Equilibrium Equations: Use the equilibrium equations (sum of forces and sum of
moments) to analyze the forces in the isolated section. For a 2D truss, you will have three
equilibrium equations (ΣFx = 0, ΣFy = 0, and ΣM = 0), where ΣFx and ΣFy represent the sum
of horizontal and vertical forces, respectively, and ΣM represents the sum of moments about
a chosen point.
5. Determine Unknown Forces: Solve the equilibrium equations to determine the unknown
forces in the members of the isolated section. These forces may include axial forces (tension
or compression) and shear forces.
6. Consider Member Types: Depending on the type of truss members (such as zero-force
members or members connected to pins or rollers), you may need to apply additional
considerations to accurately determine the internal forces.
7. Repeat for Other Sections (if necessary): If you need to analyze internal forces in multiple
sections or members, repeat the process by selecting different sections and isolating them to
create separate free-body diagrams.
8. Check for Consistency: Ensure that the internal forces obtained from the method of sections
are consistent with the overall equilibrium and compatibility of the entire truss structure. This
includes checking for zero-force members and verifying that the forces satisfy the joint
equilibrium at each node.
The method of sections is particularly useful for analyzing specific sections of a truss without
having to calculate all member forces throughout the entire structure. It's a key tool in
structural engineering for understanding the behavior of truss systems under different loading
conditions.
You might also like
- Chapter 4-Analysis of Simple Structures11Document44 pagesChapter 4-Analysis of Simple Structures11dawitdabale09No ratings yet
- Inclined Loads: Ce 311 Structural Theory August 26, 2020Document2 pagesInclined Loads: Ce 311 Structural Theory August 26, 2020Victor LimNo ratings yet
- Structural AnalysisDocument46 pagesStructural Analysisongica jamesNo ratings yet
- Method of TrussesDocument3 pagesMethod of TrussesRachit AgarwalNo ratings yet
- The Girl Was One of Those Pretty and Charming Young Creatures Who Sometimes Are BornDocument14 pagesThe Girl Was One of Those Pretty and Charming Young Creatures Who Sometimes Are BornGani AnosaNo ratings yet
- Analysis of Structures: Aastu (Civil Engg Department) Engineering Mechanics I (Statics) For Pre-EngineeringDocument7 pagesAnalysis of Structures: Aastu (Civil Engg Department) Engineering Mechanics I (Statics) For Pre-EngineeringGadisaNo ratings yet
- ES 1022y Engineering Statics Structural Analysis - TrussesDocument15 pagesES 1022y Engineering Statics Structural Analysis - TrussesErikNo ratings yet
- BecDocument7 pagesBecron123domingoNo ratings yet
- 6 Structures Marked - 0Document20 pages6 Structures Marked - 0sudhaNo ratings yet
- Structures: Unit IIIDocument27 pagesStructures: Unit IIIDivyanshuVermaNo ratings yet
- Analysis of StructuresDocument6 pagesAnalysis of StructuresGirlie BalabatNo ratings yet
- Chapter 6 Structural AnalysisDocument30 pagesChapter 6 Structural AnalysisOmar AbdullahNo ratings yet
- Concept 1 of IntroductionDocument8 pagesConcept 1 of Introductionk.ghanemNo ratings yet
- Analysis of TrussDocument2 pagesAnalysis of Trussvj5agdalesNo ratings yet
- CE 311 MODULE 5 - Structural Analysis of TrussesDocument11 pagesCE 311 MODULE 5 - Structural Analysis of TrussesBryanHarold BrooNo ratings yet
- Frames Shear and Bending Moment PDFDocument9 pagesFrames Shear and Bending Moment PDFCHA CHANo ratings yet
- ME100-Structural AnalysisDocument20 pagesME100-Structural AnalysisMuhammad NabeelNo ratings yet
- Module 5 - Analysis of StructureDocument42 pagesModule 5 - Analysis of StructureJazmine ValenzonaNo ratings yet
- Documents Null-Staad+sampleDocument50 pagesDocuments Null-Staad+sampleJulio Cesar Santos de JesusNo ratings yet
- Engineering Mechanics I CHAP 4Document9 pagesEngineering Mechanics I CHAP 4nvnrevNo ratings yet
- Structure Report PDFDocument14 pagesStructure Report PDFRawaz KanabieNo ratings yet
- Chapter6 (Analysis of Structures)Document33 pagesChapter6 (Analysis of Structures)April IngramNo ratings yet
- Module 23ADocument2 pagesModule 23AjhacademyhydNo ratings yet
- Pin Jointed SystemsDocument24 pagesPin Jointed SystemsAbu BakarNo ratings yet
- Lecture 19 MechanicsDocument7 pagesLecture 19 MechanicsMuhammad Tehsin RashadNo ratings yet
- Me13A: Chapter Six: Analysis of StructuresDocument33 pagesMe13A: Chapter Six: Analysis of StructuresAndres SalazacaNo ratings yet
- Analysis of Simple Trusses: - Prof. Amba ShettyDocument51 pagesAnalysis of Simple Trusses: - Prof. Amba ShettyShilpashree VNo ratings yet
- CE 3132 Module 05 - Analysis of Statically Determinate Structures (Part 1)Document8 pagesCE 3132 Module 05 - Analysis of Statically Determinate Structures (Part 1)FedieTabaquiraoNo ratings yet
- Lecture 12 (Chapter 6)Document20 pagesLecture 12 (Chapter 6)Adam SurtiNo ratings yet
- Chapter Six Structural AnalysisDocument11 pagesChapter Six Structural AnalysisalpegambarliNo ratings yet
- TrussDocument13 pagesTrussArjun Sharma VNo ratings yet
- Structural AnalysisDocument22 pagesStructural AnalysisJalaluddin JohanNo ratings yet
- Centroid 1Document13 pagesCentroid 1ahmadhashm200577No ratings yet
- Frames & Machine: Frame or Machine Multiforce MemberDocument25 pagesFrames & Machine: Frame or Machine Multiforce MemberFarman AliNo ratings yet
- Answer 1Document2 pagesAnswer 1Shubham imtsNo ratings yet
- Analysis of StructuresDocument15 pagesAnalysis of StructuresFabie BarcenalNo ratings yet
- Truss AnalysisDocument11 pagesTruss AnalysisAdrian ParasNo ratings yet
- Week 14 Coe 112 Module (20231130212210)Document20 pagesWeek 14 Coe 112 Module (20231130212210)channelmindNo ratings yet
- Modeling and Numerical Instability ProblemsDocument3 pagesModeling and Numerical Instability ProblemsSunil PandeyNo ratings yet
- Analysis of StructuresDocument2 pagesAnalysis of StructuresElle HeartfiliaNo ratings yet
- Statically Determinate Plane TrussDocument56 pagesStatically Determinate Plane Trussஅருண்ராஜ் கிருஷ்ணன்சாமிNo ratings yet
- Structural Analysis: Engr. John Marco I. MatiraDocument28 pagesStructural Analysis: Engr. John Marco I. MatiraAIMNo ratings yet
- TRUSSDocument11 pagesTRUSSJanice RamonNo ratings yet
- Truss by RJ AliDocument18 pagesTruss by RJ AliAli AhsanNo ratings yet
- UntitledDocument30 pagesUntitledreema omarNo ratings yet
- Structural Analysis 260224Document17 pagesStructural Analysis 260224mwendwakelvin842No ratings yet
- Chapter 2 Pin Jointed FrameDocument29 pagesChapter 2 Pin Jointed FrameShahul14No ratings yet
- 3-Analysis of StructuresDocument42 pages3-Analysis of StructuresJoylyn BeranNo ratings yet
- Structural Analysis: Mindanao State University Iligan Institute of Technology College of Engineering & TechnologyDocument18 pagesStructural Analysis: Mindanao State University Iligan Institute of Technology College of Engineering & TechnologynikkihipulanNo ratings yet
- Structural AnalysisDocument11 pagesStructural AnalysisErRajivAmieNo ratings yet
- Trusses, Frames & MachinesDocument55 pagesTrusses, Frames & MachinesCivil RguktNo ratings yet
- Lecture 8Document19 pagesLecture 8Hashir ToheedNo ratings yet
- Structures: Applied MechanicsDocument24 pagesStructures: Applied MechanicsArslanNo ratings yet
- Inertia MomentsDocument2 pagesInertia Moments20-08702No ratings yet
- MECH100 Lecture Chapter 4Document42 pagesMECH100 Lecture Chapter 4Kristina PonceNo ratings yet
- CH 1. Theory On Introduction To Design MasterDocument20 pagesCH 1. Theory On Introduction To Design Mastershaikh.anas9912No ratings yet
- LectureNotes Period 21-MinDocument15 pagesLectureNotes Period 21-MinAbu SaydNo ratings yet
- Analysis of Structures: Trusses and Pin-Connected Frames. in The Actual Structure, The Joints May Be WeldedDocument3 pagesAnalysis of Structures: Trusses and Pin-Connected Frames. in The Actual Structure, The Joints May Be WeldedCarlson CaliwanNo ratings yet
- Chapter 4Document29 pagesChapter 4yohannes lemiNo ratings yet
- P6 Delay Analysis Revision 1Document8 pagesP6 Delay Analysis Revision 1saadNo ratings yet
- Carbon Cure and GFRPDocument4 pagesCarbon Cure and GFRPsaadNo ratings yet
- Technical Scope - B7 - AAADocument10 pagesTechnical Scope - B7 - AAAsaadNo ratings yet
- Tiles Thumb RuleDocument2 pagesTiles Thumb RulesaadNo ratings yet
- 2nd Milestone Ground Floor HMR-DeSKTOP-IBAH82SDocument1 page2nd Milestone Ground Floor HMR-DeSKTOP-IBAH82SsaadNo ratings yet
- Propagation of Sound in Reinforced Concrete and Its Soundproofing PAPERDocument31 pagesPropagation of Sound in Reinforced Concrete and Its Soundproofing PAPERsaadNo ratings yet
- Air ShowDocument4 pagesAir ShowsaadNo ratings yet
- Sheet of CostingDocument2 pagesSheet of CostingsaadNo ratings yet
- Daily Work Report 02-05-2024Document2 pagesDaily Work Report 02-05-2024saadNo ratings yet
- Combined StressesDocument2 pagesCombined StressessaadNo ratings yet
- GFRPDocument37 pagesGFRPsaadNo ratings yet
- UntitledDocument1 pageUntitledsaadNo ratings yet
- Sound Proofing of FramesDocument2 pagesSound Proofing of FramessaadNo ratings yet
- UntitledDocument1 pageUntitledsaadNo ratings yet
- UntitledDocument1 pageUntitledsaadNo ratings yet
- Passenger SafetyDocument6 pagesPassenger SafetysaadNo ratings yet
- UntitledDocument1 pageUntitledsaadNo ratings yet
- UntitledDocument1 pageUntitledsaadNo ratings yet
- EuropeDocument2 pagesEuropesaadNo ratings yet
- Earthquake and PandemicDocument1 pageEarthquake and PandemicsaadNo ratings yet
- Aircraft SummitDocument6 pagesAircraft SummitsaadNo ratings yet
- TABLE: Assembled Joint Masses Story Label Point Element UX UY UZ RX RY RZDocument664 pagesTABLE: Assembled Joint Masses Story Label Point Element UX UY UZ RX RY RZsaadNo ratings yet
- CreosotingDocument1 pageCreosotingsaadNo ratings yet
- NTN # 4151994-9 Footing DesignDocument1 pageNTN # 4151994-9 Footing DesignsaadNo ratings yet
- UntitledDocument1 pageUntitledsaadNo ratings yet
- Forces Moment: HMR Waterfront Retaining Wall - 1Document1 pageForces Moment: HMR Waterfront Retaining Wall - 1saadNo ratings yet
- UntitledDocument1 pageUntitledsaadNo ratings yet
- Steel and CompositestructureDocument1 pageSteel and CompositestructuresaadNo ratings yet
- ContouringDocument2 pagesContouringsaadNo ratings yet
- UntitledDocument1 pageUntitledsaadNo ratings yet
- Nuclear Fusion EnergyDocument3 pagesNuclear Fusion EnergyAner Labaka UgarteNo ratings yet
- Testing Machine Testindo RevisiDocument4 pagesTesting Machine Testindo RevisiRayhan AlfazaNo ratings yet
- GD&T WorkbookDocument96 pagesGD&T WorkbookramasandyaNo ratings yet
- Projectile MotionDocument12 pagesProjectile MotionAtharv GoyalNo ratings yet
- EEE241L - Lab 6 - RLC ResonanceDocument4 pagesEEE241L - Lab 6 - RLC ResonanceMd. Imdadul Haque Nayan 2222846643No ratings yet
- Phy SyllabusDocument83 pagesPhy SyllabusBiswa Ranjan PradhanNo ratings yet
- What IS Inorganic ChemistryDocument2 pagesWhat IS Inorganic ChemistryRoja ReddyNo ratings yet
- Unveiling The Mysteries of Particle Physics - A Journey Into The Subatomic WorldDocument3 pagesUnveiling The Mysteries of Particle Physics - A Journey Into The Subatomic WorldLuciferNo ratings yet
- CE Board Nov 2020 - Hydraulics - Set 18Document1 pageCE Board Nov 2020 - Hydraulics - Set 18Justine Ejay MoscosaNo ratings yet
- P.P.10.1 Node Analysis of Phasor CircuitsDocument10 pagesP.P.10.1 Node Analysis of Phasor CircuitsNguyễn Bá HoàngNo ratings yet
- Pages From 5054 - s15 - QP - 21-7 - Chapter KinematicDocument3 pagesPages From 5054 - s15 - QP - 21-7 - Chapter Kinematiclelon81No ratings yet
- SPE 134002 Testing and History Matching ES-SAGD (Using Hexane)Document15 pagesSPE 134002 Testing and History Matching ES-SAGD (Using Hexane)pedro aguilar100% (1)
- Session 1 - Speed-Time GraphDocument7 pagesSession 1 - Speed-Time GraphSelvenNo ratings yet
- JME 3710 September 3, 2020: L X T TDocument1 pageJME 3710 September 3, 2020: L X T TMichael WendlNo ratings yet
- Spin Quantum NumberDocument13 pagesSpin Quantum NumberStela_Tololiu_5920No ratings yet
- 7,62x25mm CIPDocument1 page7,62x25mm CIPJan LippertNo ratings yet
- Lab 5 SolidDocument8 pagesLab 5 SolidSyahmi ChannelNo ratings yet
- New Integrated-Optical Mach-Zehnder ModulatorDocument7 pagesNew Integrated-Optical Mach-Zehnder Modulatorพลวัต โพธิ์รุ้งNo ratings yet
- La Concepcion College, Inc.: Evaluation SheetDocument1 pageLa Concepcion College, Inc.: Evaluation SheetMark MarcosNo ratings yet
- Road-Structure Monitoring With Modern GeodeticDocument15 pagesRoad-Structure Monitoring With Modern GeodeticJahir LudeñaNo ratings yet
- Chapter One Problems Solutions: KJ 51.84 WH 14.4Document8 pagesChapter One Problems Solutions: KJ 51.84 WH 14.4Mohsan HasanNo ratings yet
- Ldpe 2420H PDFDocument1 pageLdpe 2420H PDFjavadmohammadiNo ratings yet
- Aisc Basic Design ValueDocument10 pagesAisc Basic Design ValueTauhidul IslamNo ratings yet
- VMA Mastermatrix-110-Tds PDFDocument2 pagesVMA Mastermatrix-110-Tds PDFpavan6595No ratings yet
- Lecture 4 Characteristics and SomeDocument34 pagesLecture 4 Characteristics and Somelondindlovu410No ratings yet
- Mechanisms of Rock Fragmentation by BlastingDocument9 pagesMechanisms of Rock Fragmentation by BlastingAlvaroNo ratings yet
- Gauge Siphons and SwivelsDocument2 pagesGauge Siphons and SwivelsKailasNo ratings yet
- Arbaminch University: Collage of Natural SicenceDocument7 pagesArbaminch University: Collage of Natural Sicencebereket simonNo ratings yet
- TLKS10 PDFDocument70 pagesTLKS10 PDFCommon E-Mail IDNo ratings yet
- Centrifugal SeparationDocument11 pagesCentrifugal SeparationAbdulla S. MahdiNo ratings yet