Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Hepatitis B
Hepatitis B
Uploaded by
sebastianCopyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Hepatitis B
Hepatitis B
Uploaded by
sebastianCopyright:
Available Formats
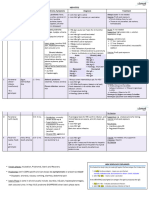
Hepadnavirus family
DNA virus
Enveloped virus
Features
replicates both inside and outside the nucleus
Circular Genome & partially double stranded becomes fully double stranded during replication
reverse transcriptase it is not a retrovirus doesn’t integrate into host chromosome
Sex
Blood
Transmission
Needles
Vertical transmission
Right upper quadrant pain
Acute
Jaundice
Hepatitis
Less likely than Hepatitis C
Adults: 5-10%
Diseases occurrence
Chronic
Newborns: 90-95%
Cirrhosis
Long term sequelae
Hepatocellular carcinoma
Hepatitis B
Rash
Arthralgia
Membranous glomerulonephritis
Prodermal serum sickness-type illness Glomerulonephritis
Membranoproliferative glomerulonephritis
systemic vasculitis
Polyarthritis Nodosa Affects medium to small arteries
Small aneurysms formed have “beads on a string
HbSAg (Hepatitis B surface antigen)
HbeAg
Lab Dx. Anti-HBc (Hepatitis B core antibody)
Anti-HBe
Anti-HBs
Acute cases clear by themselves
Lamivudine
NRTIs
Pregnant women and people with chronic hepatitis
B
Tto of Hep B (only for people with
chronic Hepatitis B
IFN-alpha infection, not to be
used for
pregnant women
Active immunity (Hepatitis B vaccination)
Newborn to Hepatitis B positive mother
Passive immunity (immunoglobulins)
You might also like
- Talal Asad - Anthropology and The Colonial EncounterDocument4 pagesTalal Asad - Anthropology and The Colonial EncounterTania Saha100% (1)
- HEPADNAVIRIDAEDocument14 pagesHEPADNAVIRIDAEnur qistina humaira zulkarshamsiNo ratings yet
- If Ye Know These Things Ross DrysdaleDocument334 pagesIf Ye Know These Things Ross DrysdaleBernardo Rasimo100% (1)
- Viral Hepatitis Etiology and Mode of Transmission Pathogenesis Clinical Manifestations Diagnosis Treatment and Prevention Hepatitis ADocument3 pagesViral Hepatitis Etiology and Mode of Transmission Pathogenesis Clinical Manifestations Diagnosis Treatment and Prevention Hepatitis AJankirk BacierraNo ratings yet
- Family Common Name Characteristics Virus Transmission Disease Detection Treatment Prevention Site of LatencyDocument3 pagesFamily Common Name Characteristics Virus Transmission Disease Detection Treatment Prevention Site of LatencyJessa MongcalNo ratings yet
- He HepatitisDocument4 pagesHe HepatitisMayar JaradNo ratings yet
- Hepatitis D Virus (HDV) : PathogenesisDocument30 pagesHepatitis D Virus (HDV) : PathogenesisJc GaldosNo ratings yet
- Vaccine Vaccine Vaccine: Prevention StepDocument1 pageVaccine Vaccine Vaccine: Prevention StepNUR AMALIA BINTI ABD. AZIZNo ratings yet
- Farmakoterapi SirosisDocument27 pagesFarmakoterapi SirosisfizaNo ratings yet
- Antiviral DrugsDocument2 pagesAntiviral DrugsEzraai HafizNo ratings yet
- Hep BDocument12 pagesHep BGracy PachoriNo ratings yet
- Class notes 1Document56 pagesClass notes 1khodja.amina.mf3No ratings yet
- Acute Viral Hepatitis (Final)Document5 pagesAcute Viral Hepatitis (Final)Kim LompotNo ratings yet
- Hepatitis Virus 2014Document35 pagesHepatitis Virus 2014Rahma MahrozaNo ratings yet
- Hepatitis A, B and C VirusDocument46 pagesHepatitis A, B and C VirusChyzhi SylviaNo ratings yet
- VH NellsonDocument3 pagesVH Nellsontesoro blogNo ratings yet
- Heaptobiliary Disease by Lecturio.Document106 pagesHeaptobiliary Disease by Lecturio.louisegantierNo ratings yet
- Hepatitis: Dr. Amany A. GhazyDocument44 pagesHepatitis: Dr. Amany A. GhazyJosé Luis García GarcíaNo ratings yet
- Gambar Hep BDocument25 pagesGambar Hep BacakNo ratings yet
- Infeksi Virus Pada Sistem Pencernaan Bawah: Hepatitis: Ety AprilianaDocument27 pagesInfeksi Virus Pada Sistem Pencernaan Bawah: Hepatitis: Ety AprilianaAsmorowatiNo ratings yet
- Virus Hepatitis RevDocument83 pagesVirus Hepatitis RevSukma WinahyuNo ratings yet
- HepatitisDocument41 pagesHepatitisitsshaswatNo ratings yet
- Hepatitis BDocument23 pagesHepatitis BMarty Asis100% (1)
- Medical Microbiology: Hepatotrophic Viruses - May 3, 2017Document7 pagesMedical Microbiology: Hepatotrophic Viruses - May 3, 2017Claire DuNo ratings yet
- Virus Hepatitis - KBKDocument53 pagesVirus Hepatitis - KBKfifi anggraeniNo ratings yet
- Viral Hepatitis Training Manual: Federal Ministry of Health National Hepatitis Control Program 2017Document44 pagesViral Hepatitis Training Manual: Federal Ministry of Health National Hepatitis Control Program 2017Eleni HagosNo ratings yet
- 70 - Infections in Patients With CancerDocument1 page70 - Infections in Patients With CancerRica Alyssa PepitoNo ratings yet
- BB Lec - Topic 13 - TTDsDocument4 pagesBB Lec - Topic 13 - TTDscarvajalraizzaeloisseNo ratings yet
- AntiviralsDocument6 pagesAntiviralsNur NajminaNo ratings yet
- HepatitisDocument8 pagesHepatitisglazykimjorquiaNo ratings yet
- Viral Hepatitis VirusDocument8 pagesViral Hepatitis VirusJFNo ratings yet
- Drug Name Mechanism of Action Indication Contraindications Side Effects/Adverse Effects Nursing ConsiderationDocument5 pagesDrug Name Mechanism of Action Indication Contraindications Side Effects/Adverse Effects Nursing ConsiderationWyeth Earl Padar EndrianoNo ratings yet
- HIVDocument5 pagesHIVsarguss14100% (1)
- HepatitisDocument29 pagesHepatitisRose Anne AbivaNo ratings yet
- (LEC) 3.4 Hepatitis Viruses, Prions, and Slow VirusesDocument11 pages(LEC) 3.4 Hepatitis Viruses, Prions, and Slow VirusesKim DeeNo ratings yet
- Virus Board StudyDocument2 pagesVirus Board Studynivik2032No ratings yet
- Viral InfectionsDocument59 pagesViral Infectionsrenato renatoNo ratings yet
- Hepatitis B Kronik Pada Kehamilan - Dr. Dr. Anita Rachmawati, SpOG (K)Document92 pagesHepatitis B Kronik Pada Kehamilan - Dr. Dr. Anita Rachmawati, SpOG (K)Rustan VickyNo ratings yet
- Chapter 48 - Viruses Causing HepatitisDocument164 pagesChapter 48 - Viruses Causing HepatitisKevil LoriyaNo ratings yet
- Hepatitis FinalDocument73 pagesHepatitis FinalAkhil MuraliNo ratings yet
- Hepatitis B: Steve HartDocument36 pagesHepatitis B: Steve HartangelinaNo ratings yet
- Hepatitis Virus: Bagian Mikrobiologi FK UnissulaDocument36 pagesHepatitis Virus: Bagian Mikrobiologi FK UnissulaKarina Mega WNo ratings yet
- HepatitisDocument16 pagesHepatitisSaipulla SaibuNo ratings yet
- Gastroenterology - Viral HepatitisDocument2 pagesGastroenterology - Viral HepatitisEugen MNo ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument7 pagesDrug StudyJoseph Angelo Fortuna CarmonaNo ratings yet
- Acute Viral Hepatitis: Acute Inflamation of The Liver Caused by Primarly Hepatotropic Viruses (A, B, C, D, E)Document35 pagesAcute Viral Hepatitis: Acute Inflamation of The Liver Caused by Primarly Hepatotropic Viruses (A, B, C, D, E)Tarik PlojovicNo ratings yet
- Viral Hepatitis Training Manual: Federal Ministry of Health National Hepatitis Control Program 2021Document11 pagesViral Hepatitis Training Manual: Federal Ministry of Health National Hepatitis Control Program 2021Eleni HagosNo ratings yet
- HEPATITISDocument4 pagesHEPATITISYalin AbouhassiraNo ratings yet
- Advanced Topics:: Viruses, Cancer, and The Immune SystemDocument23 pagesAdvanced Topics:: Viruses, Cancer, and The Immune SystemDaniloFRNo ratings yet
- 15 HepatitisDocument48 pages15 HepatitisAlvin LaurenceNo ratings yet
- Hep B VirusDocument20 pagesHep B VirusBhupesh ChandNo ratings yet
- Etiology:: Viral HepatitisDocument3 pagesEtiology:: Viral HepatitisAhmed almahdiNo ratings yet
- Liver (Dr. Cham)Document4 pagesLiver (Dr. Cham)yayayanizaNo ratings yet
- 05H2_Hepa_HIV_24 (2)Document78 pages05H2_Hepa_HIV_24 (2)Mulugeta DagneNo ratings yet
- Antivirals Pharma Activity 08may23Document17 pagesAntivirals Pharma Activity 08may23Adrian CaballesNo ratings yet
- Gi L17 - HabcdvDocument2 pagesGi L17 - HabcdvIan Evan LeeNo ratings yet
- Togaviruses: FindingsDocument4 pagesTogaviruses: Findingsحسين محمد مطرود كاظمNo ratings yet
- HepatitisDocument8 pagesHepatitisGilankNo ratings yet
- Virus SummaryDocument11 pagesVirus SummaryRenee TristanoNo ratings yet
- MYCOVIRO LECLAB 5 Other Viruses and PrionsDocument3 pagesMYCOVIRO LECLAB 5 Other Viruses and PrionsMarcus Dave MendozaNo ratings yet
- Muhammad Asaad Maidin Departement Microbiology Faculty of Medicine Hasanuddin University, MakassarDocument54 pagesMuhammad Asaad Maidin Departement Microbiology Faculty of Medicine Hasanuddin University, MakassarPratiwi PurnamaNo ratings yet
- Hepatitis C Virus-Host Interactions and Therapeutics: Current Insights and Future PerspectivesFrom EverandHepatitis C Virus-Host Interactions and Therapeutics: Current Insights and Future PerspectivesNo ratings yet
- Trypanosoma bruceiDocument1 pageTrypanosoma bruceisebastianNo ratings yet
- CryptosporidiumDocument1 pageCryptosporidiumsebastianNo ratings yet
- Ebstein BarrDocument1 pageEbstein BarrsebastianNo ratings yet
- CytomegalovirusDocument1 pageCytomegalovirussebastianNo ratings yet
- Medical Genetics (Lecturio)Document54 pagesMedical Genetics (Lecturio)sebastianNo ratings yet
- Crossing The Bar Critique PaperDocument2 pagesCrossing The Bar Critique PapermaieuniceNo ratings yet
- Building 7Document1 pageBuilding 7Arshad AlamNo ratings yet
- Assessment System: Take Assessment - EWAN Chapter 8 - CCNA Exploration: Accessing The WAN (Version 4.0)Document9 pagesAssessment System: Take Assessment - EWAN Chapter 8 - CCNA Exploration: Accessing The WAN (Version 4.0)asceric4363No ratings yet
- Prayerbooklet 1st-EditionDocument16 pagesPrayerbooklet 1st-EditionRexelle Jane ManalaysayNo ratings yet
- IWA City Stories SingaporeDocument2 pagesIWA City Stories SingaporeThang LongNo ratings yet
- 501-453 Universal Cable GalndsDocument1 page501-453 Universal Cable Galndsmeribout adelNo ratings yet
- Whittington 22e Solutions Manual Ch14Document14 pagesWhittington 22e Solutions Manual Ch14潘妍伶No ratings yet
- Types of ParentingDocument13 pagesTypes of ParentingViseshNo ratings yet
- Assignment 04 Solved (NAEEM HUSSAIN 18-CS-47)Document7 pagesAssignment 04 Solved (NAEEM HUSSAIN 18-CS-47)NAEEM HUSSAINNo ratings yet
- Asmaa Mamdouh CVDocument1 pageAsmaa Mamdouh CVAsmaa MamdouhNo ratings yet
- UntitledDocument2 pagesUntitledelleNo ratings yet
- Fundamentals of HydraulicsDocument101 pagesFundamentals of HydraulicswissamhijaziNo ratings yet
- Chinese Vocabulary BodyDocument3 pagesChinese Vocabulary BodyWei LeeNo ratings yet
- UNIT HistoryDocument2 pagesUNIT HistorySanders StephenNo ratings yet
- Teachers' Interview PDFDocument38 pagesTeachers' Interview PDFlalitNo ratings yet
- September 23, Infer The Purpose of The Poem Listened ToDocument4 pagesSeptember 23, Infer The Purpose of The Poem Listened ToLouelle GonzalesNo ratings yet
- Current ElectricityDocument93 pagesCurrent ElectricitySurya SNo ratings yet
- Forms PensionersDocument15 pagesForms PensionersAnimesh DasNo ratings yet
- Cost Leadership Porter Generic StrategiesDocument7 pagesCost Leadership Porter Generic StrategiesRamar MurugasenNo ratings yet
- Tle 7-1st Periodic TestDocument2 pagesTle 7-1st Periodic TestReymart TumanguilNo ratings yet
- Simulation and ModulationDocument89 pagesSimulation and ModulationGuruKPO67% (6)
- 4411 Studio MonitorDocument4 pages4411 Studio MonitorabraxastributetosantanaNo ratings yet
- Quality Supervisor Job DescriptionDocument8 pagesQuality Supervisor Job Descriptionqualitymanagement246No ratings yet
- Taylor Swift LyricsDocument2 pagesTaylor Swift LyricsElsie DomeNo ratings yet
- Parent Involvement in Education: Kathleen Cotton and Karen Reed WikelundDocument17 pagesParent Involvement in Education: Kathleen Cotton and Karen Reed WikelundMohsin khaliqNo ratings yet
- ME-458 Turbomachinery: Muhammad Shaban Lecturer Department of Mechanical EngineeringDocument113 pagesME-458 Turbomachinery: Muhammad Shaban Lecturer Department of Mechanical EngineeringAneeq Raheem50% (2)
- Blue Yellow Playful Illustration Self Care Infographic PosterDocument7 pagesBlue Yellow Playful Illustration Self Care Infographic PosterAin NurasyikinNo ratings yet
- A 182Document20 pagesA 182Thomas100% (1)