Professional Documents
Culture Documents
EVOLUTION ONE PAGER MEMO
EVOLUTION ONE PAGER MEMO
Uploaded by
civilndlovu13Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
EVOLUTION ONE PAGER MEMO
EVOLUTION ONE PAGER MEMO
Uploaded by
civilndlovu13Copyright:
Available Formats
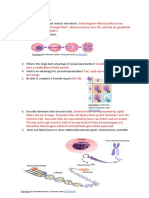
CAUSES OF VARIATION TYPES OF VARIATION EVIDENCE FOR EVOLUTION
1.1 Name the 2 types of variation shown in each diagram Name the 4 types of evidence that support
Name FOUR processes that cause variation Crossing over process in below. evolution using the diagrams as clues.
Continuous variation where there is a
and then fill in the missing words. prophase 1. range of phenotypes eg eye shape 1. Genetics 2. Biogeography
1. Meiosis: because of
.
1.2
2. Fertilisation is random. Random arrangement Discontinuous variation where there
3. Random Mating. of chromosomes in metaphase 1 is no/ a small range of phenotypes.
4. Mutations. or metaphase 2. eg hairline shape
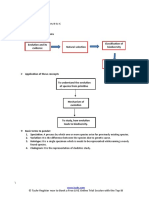
EVOLUTION THEORY 1: APPLYING THEORIES 1 and 3: Fill in the missing words EVOLUTION THEORY 3:
LAMARCKISM below for the theories of Lamarckism and Darwinism (Natural Evolution by the process of NATURAL
LAW 1: ‘Law’ of use and disuse. Selection) for each of the two diagrams shown. SELECTION / DARWINISM.
Law of use: The more you use the LAMARCKISM Describe the theory of evolution by the process of
DARWINISM
structure/ organ/ body part, the bigger/ Law of Favourable
natural selection.
stronger/ more developed it is. eg. Long necks in use. root trait: • Organisms produce a large number of offsrping. 3 Modification by descent 4. Fossil record
Galapagos tortoises. All cacti long roots • There is a great deal of variation amongst the (homologous structures)
had roots Unfavourable offspring, some have the favourable trait and
Law of disuse: The less you use the structure/ that were root trait: some don’t. PRESENT DAY EVOLUTION:
organ/ body part, the smaller/ Tuberculosis (TB MDR-TB XDR-
the same short roots • When there is a change in the environmental
weaker/ less developed it is. eg. Snake legs. length to Therefore conditions or if there is competition, TB)
start. The cacti with
LAW 2: ‘Law’ of the inheritance of roots had to grow to reach water
• the organisms with the unfavourable
long roots
acquired characteristics so roots were longer over time in survive and reproduce. The characteristics, which make them less suited, die.
all cacti. offspring have long roots over time. • The organisms with characteristics which male
The characteristic that developed during the them more suited, survive reproduce and pass on
lifetime of the parent is an acquired trait and will Law of the allele for the favourable characteristic to their
be passed on to the offspring as it is heritable. Use. offspring.
Why was Lamarck’s theory rejected?
All • The next generation will have a higher proportion
giraffes of individuals with the favourable characteristic.
• Acquired characteristics are not inherited / do had the
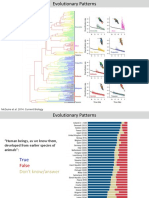
Darwinism is also called Gradualism. 1. Which process of evolution is represented in the
same diagrams above? Natural selection.
not cause change to the DNA of an organism. Darwin called his theory Descent with
length 2. The bacterium with the favourable characteristic is
(genes are inherited, not acquired traits) modification.
neck to bacterium B, whereas the one with the unfavourable
• Lamarck’s theory is deterministic / Organisms start. They stretched to reach the
Favourable neck length: long neck
characteristic is bacterium A in the diagram.
Unfavourable neck length: short
did not evolve because they want to. high leaves and so acquired a Today we call it: The theory of evolution by 3. Explain your answer in question 2 using the theory of
neck. Long neck giraffes survive
(Lamarck had no evidence) long neck. This trait was and the process of natural selection. natural selection.
and reproduce passing the long neck
passed to offspring .
on to their offspring. • In generation 1 there was variation amongst the
bacteria, some had the favourable characteristic of
EVOLUTION THEORY 2: APPLYING THEORY 2: Study the graph below and then answer the questions. antibiotic resistance (Bacterium B) and some did
PUNCTUATED EQUILIBRIUM not (bacterium A).
Describe the theory of punctuated equilibrium. Use the graph to identify the phase at: • Antibiotics were applied and bacteria A had the
• Evolution involves long periods of time where species A. Punctuation phase (rapid change; short time). unfavourable trait and died because the antibiotic
do not change or change gradually through natural B. Equilibrium phase (little or no change; long time). killed them.
selection (known as equilibrium). • Bacterium B had the favourable trait and resisted
the antibiotic, so survived and reproduced passing
• This alternates with (is punctuated by) short periods Circle the correct words from those that are underlined:
on the favourable trait to their offspring.
of time where rapid changes occur through natural 1. At A, the species undergoes rapid/ no or gradual change over a • The next generation (number 4) has a higher
selection long/ short period of time. proportion of individuals with the favourable trait
• During which new species may form in a short period of 2. At B, the species undergoes rapid/ no or gradual change over a of antibiotic resistance.
time. long/ short period of time • The population gradually changed to be antibioitic
You might also like
- ReproductionDocument162 pagesReproductionchumbavictor45967% (3)
- Activity 5.1 - Sanchez, Carl Joshua MDocument3 pagesActivity 5.1 - Sanchez, Carl Joshua MCARL JOSHUA SANCHEZNo ratings yet
- Activity 5.2 - Sanchez, Carl Joshua MDocument3 pagesActivity 5.2 - Sanchez, Carl Joshua MCARL JOSHUA SANCHEZNo ratings yet
- Evolution 1 2018Document60 pagesEvolution 1 2018mimidlali8No ratings yet
- Ib Bio Previous IB Exam Essay QuestionsDocument34 pagesIb Bio Previous IB Exam Essay Questionssrahimi@verizon.net100% (3)
- 01 Microevol-Natl SelDocument7 pages01 Microevol-Natl SelNeha YadavNo ratings yet
- Plant Evolution - 1Document35 pagesPlant Evolution - 1ericsurantaNo ratings yet
- 2nd Grading Reviewer ScienceDocument3 pages2nd Grading Reviewer ScienceLhemar Julia BayocaNo ratings yet
- Theories of EvolutionDocument58 pagesTheories of EvolutionbenitezednacNo ratings yet
- Survival of The FittestDocument5 pagesSurvival of The FittesthaleyNo ratings yet
- Charles and Larmarck Debate CartoonDocument2 pagesCharles and Larmarck Debate CartoonTeerachaiNo ratings yet
- Biology Key Topics 4Document3 pagesBiology Key Topics 4erinNo ratings yet
- Caie Igcse Biology 0610 Theory 64d5a45f13a3a327d3bf9fa9 412Document35 pagesCaie Igcse Biology 0610 Theory 64d5a45f13a3a327d3bf9fa9 412The GamerNo ratings yet
- Edexcel A2 Biology Revision NotesDocument79 pagesEdexcel A2 Biology Revision NotesAasiya SultanaNo ratings yet
- Sci Evolution RevDocument3 pagesSci Evolution RevGertrude Reyes (Geri)No ratings yet
- T2 Science Case Answer KeyDocument3 pagesT2 Science Case Answer KeyDonovan JenkinsNo ratings yet
- Gzoo Midterm ReviewerDocument2 pagesGzoo Midterm ReviewerccccNo ratings yet
- Evolution PPT With AudioDocument45 pagesEvolution PPT With AudioAll about derreonnnNo ratings yet
- Notes Bio TheoryDocument35 pagesNotes Bio Theoryfatimairij2480No ratings yet
- Evidence of EvolutionDocument4 pagesEvidence of EvolutionMarjory De Leon AlbertoNo ratings yet
- Evidence of EvolutionDocument30 pagesEvidence of EvolutionKris Sel Quin TanoNo ratings yet
- Edexcel A2 Biology Revision NotesDocument79 pagesEdexcel A2 Biology Revision NotesAbdalla AhmedNo ratings yet
- Variation and Evolution: Learning OutcomesDocument41 pagesVariation and Evolution: Learning OutcomesOsmany MadrigalNo ratings yet
- Characteristics & Classification of Living Organisms: Biology Short Notes / Shaziyya AliDocument33 pagesCharacteristics & Classification of Living Organisms: Biology Short Notes / Shaziyya Aliv4v26xhfghNo ratings yet
- THEORIES-OF-EVOLUTION Science 10 3rd QuarterDocument24 pagesTHEORIES-OF-EVOLUTION Science 10 3rd Quarterabhus poserNo ratings yet
- Biodiversity and Systematics IIDocument36 pagesBiodiversity and Systematics IIabeesseinantoniNo ratings yet
- Gen Bio Summative ReviewerDocument18 pagesGen Bio Summative ReviewerJOSEMARI YOHAN ESTALILLANo ratings yet
- A2 SNAB Revision NotesDocument80 pagesA2 SNAB Revision Notesbenthemusiclover1512No ratings yet
- TaxonomyDocument7 pagesTaxonomyAtria Mariz Ricamonte OrbistaNo ratings yet
- Symbiotic RelationshipDocument12 pagesSymbiotic RelationshipErrold Paul GagarinNo ratings yet
- General Biology 2 - MidtermDocument9 pagesGeneral Biology 2 - MidtermGerald BajadoNo ratings yet
- The Principles of Modern Zoology Are Derived FromDocument1 pageThe Principles of Modern Zoology Are Derived FromJackelyn SalazarNo ratings yet
- 07 SHS Forces of Evolution 2017-18Document83 pages07 SHS Forces of Evolution 2017-18Jeorge QuiboyNo ratings yet
- Theory of Evolution by Natural SelectionDocument27 pagesTheory of Evolution by Natural Selectionelaine loveluckNo ratings yet
- Chapter 15.2 Evolution: NWRC BIO 30Document38 pagesChapter 15.2 Evolution: NWRC BIO 30nancie8No ratings yet
- Developmental Biology Final Exam Multiple Choice QuestionsDocument12 pagesDevelopmental Biology Final Exam Multiple Choice QuestionsPearl PascuaNo ratings yet
- Unit 3 Evolution Chapter 7 Power Points Student Note 2020 ModifiedDocument38 pagesUnit 3 Evolution Chapter 7 Power Points Student Note 2020 Modifiedlotte worldNo ratings yet
- Earth and Life Science Module 8aDocument5 pagesEarth and Life Science Module 8ajjasmijiNo ratings yet
- All About EvolutionDocument5 pagesAll About EvolutionMohibNo ratings yet
- Phylogeny and The Tree of LifeDocument9 pagesPhylogeny and The Tree of LifesdfsfdsNo ratings yet
- form-4-notes-summaryDocument61 pagesform-4-notes-summarygeofreyokandaNo ratings yet
- Nucleic AcidsDocument24 pagesNucleic Acidshatdog adadaNo ratings yet
- Local Demo IM (FINAL) - CompressedDocument69 pagesLocal Demo IM (FINAL) - Compressedclent girayNo ratings yet
- Molecular-EvidencetheoriesDocument19 pagesMolecular-EvidencetheoriesJean RomeroNo ratings yet
- Bio Factsheet: EvolutionDocument3 pagesBio Factsheet: EvolutionsreenitthiNo ratings yet
- 64d7417cca588200185ca139 - ## - Plant Kingdom Mind MapsDocument3 pages64d7417cca588200185ca139 - ## - Plant Kingdom Mind Mapssohammaity43No ratings yet
- Chapter 5 Summary Notes SL IB ICDocument12 pagesChapter 5 Summary Notes SL IB ICSanaa SamkoNo ratings yet
- Honors Biology Intro To Genetics Review 2021Document4 pagesHonors Biology Intro To Genetics Review 2021Irene AntiriNo ratings yet
- 2 Biological Classification 1628859582527Document73 pages2 Biological Classification 1628859582527l082haripriyakotariNo ratings yet
- EvolutionDocument14 pagesEvolutionCarolina MonteiroNo ratings yet
- 2.evolutionary PatternsDocument40 pages2.evolutionary Patternscamila zapataNo ratings yet
- EVOLUTIONDocument4 pagesEVOLUTIONRansu ChanNo ratings yet
- Lesson 2 Diversity of ProtistsDocument6 pagesLesson 2 Diversity of ProtistsSarah MNo ratings yet
- 1 Reproduction in OrganismsDocument9 pages1 Reproduction in OrganismsTanya PasrichaNo ratings yet
- On the Origin of Species & On the Tendency of Species to Form VarietiesFrom EverandOn the Origin of Species & On the Tendency of Species to Form VarietiesNo ratings yet
- Law of SegregationDocument14 pagesLaw of SegregationAllen Nanqui DadizonNo ratings yet
- Ncert Biology Chapter I0Document11 pagesNcert Biology Chapter I0sai arunNo ratings yet
- Chapter-3. Human Reproduction Case Based QuestionsDocument33 pagesChapter-3. Human Reproduction Case Based QuestionsSania GeorgeNo ratings yet
- Module 2 Week 2Document9 pagesModule 2 Week 2Mycel Ann AcuzarNo ratings yet
- Genetics: Section 1-Solving Genetics ProblemsDocument16 pagesGenetics: Section 1-Solving Genetics ProblemsHaris KhanNo ratings yet
- Botany Guess Paper - 2Document52 pagesBotany Guess Paper - 2dh6hzj7ghxNo ratings yet
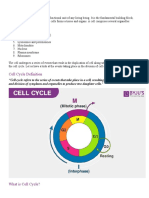
- Cell Cycle & Cell Division - NCERT Based PYQsDocument6 pagesCell Cycle & Cell Division - NCERT Based PYQsAkhil singhNo ratings yet
- Class 11 Biology Botany em Revised Edition-2020 English Medium Book Back Answers C.kishore KumarDocument51 pagesClass 11 Biology Botany em Revised Edition-2020 English Medium Book Back Answers C.kishore KumarRagaviNo ratings yet
- NMAT Part II Reviewer - PersonalDocument38 pagesNMAT Part II Reviewer - PersonalReycel MayNo ratings yet
- Arihant Ncert Exemplar Biology Solution Class 12Document290 pagesArihant Ncert Exemplar Biology Solution Class 12Md Kutubuddin Sardar50% (2)
- Ch07 CellCyclesDocument10 pagesCh07 CellCyclesAna GujabidzeNo ratings yet
- Sains Form 4 MarchDocument10 pagesSains Form 4 MarchJue Hazea GoldshopNo ratings yet
- Q2 Earth and Life Module 10Document25 pagesQ2 Earth and Life Module 10Jomar CarabotNo ratings yet
- Cell DivisionDocument31 pagesCell DivisionShin Thant Ko B10 June SectionNo ratings yet
- Cell Cycle and Cell Division - TESTDocument3 pagesCell Cycle and Cell Division - TESTDoctor BioNo ratings yet
- Ch10 Standard TestDocument2 pagesCh10 Standard TestosamaNo ratings yet
- Grade 8 Module 5Document88 pagesGrade 8 Module 5Lebiram Mabz86% (14)
- Bio 1Document13 pagesBio 1Mary Ann FriasNo ratings yet
- Laboratory 2Document7 pagesLaboratory 2Allexcia AguilaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1. Cell Division: MeiosisDocument16 pagesChapter 1. Cell Division: Meiosisankurbiology100% (1)
- Principle of Genetics and Animal BreedingDocument49 pagesPrinciple of Genetics and Animal BreedingSuresh NepaliNo ratings yet
- Unit 1: Seat of Wisdom Secondary School, Trans Ekulu, EnuguDocument20 pagesUnit 1: Seat of Wisdom Secondary School, Trans Ekulu, EnuguUkwuma Michael ChijiokeNo ratings yet
- 6.1.1 Mutation: Unit 6: Mutation Chapter 1: MutationDocument7 pages6.1.1 Mutation: Unit 6: Mutation Chapter 1: MutationAmit SharmaNo ratings yet
- Science 8 4th Periodical ExamDocument3 pagesScience 8 4th Periodical ExamKimeo Bagyon100% (2)
- Linkage and Genetic Mapping EukaryotesDocument66 pagesLinkage and Genetic Mapping EukaryotesSITI BAZILAH BINTI BILAK KPM-GuruNo ratings yet
- 4HB0 02 Que 20160115Document16 pages4HB0 02 Que 20160115BooksNo ratings yet
- 2011 SBP Bio SkemaDocument33 pages2011 SBP Bio SkemaChe ShazuandyNo ratings yet
- Anaphy Chapter 3 by GetteDocument13 pagesAnaphy Chapter 3 by GetteDUQUE, GEORGETTE FLOREANNE L.No ratings yet
- Nomenclaturas en Saccharomyces Cerevisiae PDFDocument43 pagesNomenclaturas en Saccharomyces Cerevisiae PDFJorge AndrésNo ratings yet
- Gen. Bio 1 Q 1 - Week 4 Module 4Document24 pagesGen. Bio 1 Q 1 - Week 4 Module 4Gyeon Dae-HoNo ratings yet