Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Extra Photogrammetry PDF
Extra Photogrammetry PDF
Uploaded by
Suraj Kumar Singh0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
0 views16 pagesCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF or read online from Scribd
Download as pdf
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
0 views16 pagesExtra Photogrammetry PDF
Extra Photogrammetry PDF
Uploaded by
Suraj Kumar SinghCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF or read online from Scribd
Download as pdf
You are on page 1of 16
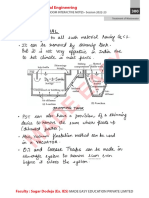
Photogrammetry
Horizontal Photogrammetn
Picture plate
(Positive)
Camera plate
(Negative)
Scale of photo =
x
xX
By Ashish Kumar |@) @me_ashishsir
Important terminolo
Zz Camera Axis
camera axis is the line passing through centre of camera lens and
perpendicular to both plates (positive and negative)
> | Picture/ Positive | it is the plane perpendicular to camera axis at the focal distance in
Plate front of the lens.
3 | Image/ Negative | it is the plane in which images of points in the object space of the
Plate lens are focused.
4 | Principal point (K)
it is defined as the intersection of camera axis with either the
picture plane (positive) or the camera plane ( negative).
The camera shutter controls the interval of time during which light is
allowed to pass through the lens. Since the aircraft moves at high
3 Shutter speed, a fast speed shutter is required to prevent blurring the image
caused by camera vibrations and the forward motion of the aircraft.
6 Dig A diaphragm is placed between the lens elements and acts as a
phragm physical opening of the lens system.
A filter consist of a pieces of coloured glass placed in front of lens.
7 It filters stray light (blue and violet) in the atmosphere caused by
haze and moisture.
It also protects the lens from the flying particles in the environment.
By Ashish Kumar |@) @me_ashishsir
Vertical. Photogrammetr
Vertical photograph:
when axis of camera coincides with the
direction of gravity
Tilted photograph:
When axis of camera is unintentionally
tilted from vertical (generally less than 3°
Angle)
Oblique Photograph:
When axis of camera is intentionally
tilted from vertical.
Line drawn on map to represent the track
of flight.
Flying Height:
Elevation of exposure station above
datum (Mean Sea Level)
yy
WLM
By Ashish Kumar |@ @me_ashishsir
Important terminolo
Exposure Station: (O)
An exposure station is the point in space
occupied by the camera lens at the instant
of exposure.
Altitude:
It is the elevation of aircraft above the
earth’s surface.
Principal point :(K)
it is the point of intersection of axis of
camera and plane of aerial photo.
Isocentre: (i)
It is the point on aerial photograph in which
the bisector of the angle of tilt meets the
photograph.
Nadir point: (N)
It is the point on an aerial photograph
where plumb line dropped from the front
point pierces the photograph.
By Ashish Kumar |@ @me_ashishsir
Scale of Vertical Photograph
Photo Distance
Scale of Photo = ——-? — "ance
Ground Distance
ka eP
Seal hoto = —= —
cale of photo KA Hoh
f= Focal Length of camera
H = Flying height
h = Elevation of ground/ Terrain
ka = length on photo
KA = Length on ground
Note: Elevation of ground may not be same
at all the points, hence in case of undulation
average elevation (Ayq) is taken.
. is
Scalt = ————
‘cale of photo Hevea,
By Ashish Kumar |@ @me_ashishsir
Horizontal Distance
Scale =p
aes ee
Similarly
X= thex, Y= tBey,
nue invent rine
AB= (Xa = Xp)? + Ya — Vp)?
© @me_ashishsir
By Ashish Kumar
Relief Displacement
Displacement of any point on photograph
from its true orthographic position due to
height of object is called relief
displacement.
From AOka & AOKA
R- H=h
TH Th
From AOka,& AOK,A,
N%
=|
he,
R
CONTI...
Releif Displacement = d
r=
Tt NY from principal point
d=r-r, t
d- ees :
“AnH a.
= H-H+h |, Rf*h
a Rf Gone \°> Gam
her
d= A I
If tower is standing on ground of r
elevation Rayg, Then |
her :
tS ae
HohS,
Radial distance of image
By Ashish Kumar
© @me_ashishsir
Flight Planning
In Aerial survey, Photographs are taken such that, it must be overlapped on previously
taken photo in two directions as below;
* End to End Overlap (Longitudinal)- In the direction of flight line
* Side to Side Overlap (Transverse)- in transverse to the flight line
Stereo Pair
By Ashish Kumar |@ @me_ashishsir
$ + 60% -70% Overlap
4@- -® between photos
: { (forwarrd overlap)
» 3. 25% - 40% overlap
between flight lines
--g- (lateral overlap)
y
By Ashish Kumar |@ @me_ashishsir
No of Photos to Cover a Given Area
r=
[sos sass)
Case-1: Area Given (L x B)
Case-2: Area Given A
No of photographs in each strip
L
= G1
G=Pst
No of Strips required
Ny
B
*. PAS
Nz
Total No. of Photos Required
N=N,xN;
Where;
P, = End to end Overlap
P,,= Side to side Overlap
S = Scale of photo
= length of photo
b= Width of photo
Total no of photographs required (Approx.)
A
N=—
a
Where;
A= Total Area of ground
a = Ground Area covered by each
Photo
(-p)Sl x (1-p,) Sb
as
= Cp) A-py) S71 b
By Ashish Kumar |@ @me_ashishsir
CONTI...
Air Base
The distance covered by two successive exposure is
known as Air base
Interval between re
If the ground speed of the aircraft is V
km/h and the ground distance
covered between exposure along the
flight line L km, Interval between
exposure
Drift
Drift is caused by the failure of the photograph to
stay on the predetermined flight line. It is due to
wind in the direction normal to the flight line.
Crab
Angle formed between the flight line and edge of
the photograph in the direction of flight is called
Crab.
By Ashish Kumar
Parallax
m --- Air Base (B)
. Ground
By Ashish Kumar |@ @me_ashishsir
R =
Where; aS)
£1 = First Exposure B = Length of Air Base
£2 = Second Exposure f= Focal Length
A =Top of Tower H = Flying Height
B = Bottom of Tower hypp=Elevation of Top of Tower
N; = Nadir point of First Exposure Asottom = Elevation of Bottom of Tower
N2= Nadir point of Second Exposure Ptop= Parallax for Top
a,= Image of Top of tower at first exposure Peottom = Parallax for Bottom
MSL = Mean Sea Level
a= Image of Top of tower at second exposure | b,,= Photo Base(Mean Principal Base)
The principal Base or Photographic base is the distance between the principal point
of a photograph and the position of transferred principal point of its next
photograph obtained as a result of stereoscopic fusion.
Photo Mean Principal Base:(b,,)
By Ashish Kumar |@ @me_ashishsir
Derivation
Parallax of a point is the displacement of the image of the point on the two successive
exposures. And the difference between the displacements of the images of two points
on successive exposures is called the difference in parallax between two points.
ba
Ff — Hb, = fB
eB fB
Prop = H — Prop: PBottom _ He ha
+Ap = Hbm
PBottom Py elk AS
Hby,
Ar ——_— es
Pp Heh, A h P Bottom
By Ashish Kumar |@ @me_ashishsir
CONTI... Lo
Hb,
Ap = 2.
P * Hooton —AR H—Ppoetom
Dh oe Hb, (H — hgottom —H + Rgottom +4 h)
PS ~(H = Mpottom —4 B) CH — hizottom)
3 Hbyn Ah
(H — hgottom —A h) (H — Rgottom)
Ap
Exact Relation | Approximate Relation
-_ 2
(H hgottom) A p Ni (H- Azoteom)* AP
b,,H + (H — hgottom) AP ~ b,H
By Ashish Kumar |@ @me_ashishsir
You might also like
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeFrom EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (5834)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreFrom EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1093)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItFrom EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (852)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceFrom EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (590)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceFrom EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (903)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeFrom EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (541)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersFrom EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (349)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureFrom EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (474)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesFrom EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (823)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)From EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (122)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerFrom EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (271)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingFrom EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (405)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyFrom EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2259)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)From EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Rating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (98)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaFrom EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (266)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryFrom EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (231)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnFrom EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (234)
- Ee - Uncompressed PDF - Part 1 NotesDocument150 pagesEe - Uncompressed PDF - Part 1 NotesAbhinav TripathiNo ratings yet
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealFrom EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (74)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaFrom EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (45)
- Engineering Mechanics WB NotesDocument19 pagesEngineering Mechanics WB NotesAbhinav TripathiNo ratings yet
- EE - UNCOMPRESSED PDF - Part 2 NotesDocument150 pagesEE - UNCOMPRESSED PDF - Part 2 NotesAbhinav TripathiNo ratings yet
- EE - UNCOMPRESSED PDF - Part 3 NotesDocument127 pagesEE - UNCOMPRESSED PDF - Part 3 NotesAbhinav TripathiNo ratings yet
- Survey Questions PDF NotesDocument3 pagesSurvey Questions PDF NotesAbhinav TripathiNo ratings yet
- Survey WB - 2024 NotesDocument39 pagesSurvey WB - 2024 NotesAbhinav TripathiNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2 Soil Classification NotesDocument5 pagesChapter 2 Soil Classification NotesAbhinav TripathiNo ratings yet