Professional Documents
Culture Documents
BMCT Module-2(part-2)
BMCT Module-2(part-2)
Uploaded by
yatishfinanceCopyright:
Available Formats
You might also like
- Gas Testing Procedures PDFDocument44 pagesGas Testing Procedures PDFAbdelkader BOUKHOUS50% (2)
- Explain Briefly About Preloading. A. Preloading of Soil Is Merely Applying An External Loading For A Long Duration ToDocument10 pagesExplain Briefly About Preloading. A. Preloading of Soil Is Merely Applying An External Loading For A Long Duration Tohimabindugvsd71No ratings yet
- Bmc1-Bearing Capacity of SoilDocument24 pagesBmc1-Bearing Capacity of SoilHridhya mpNo ratings yet
- Effectiveness of Sand Column As A Ground Improvement TechniqueDocument5 pagesEffectiveness of Sand Column As A Ground Improvement TechniqueMuhammad IrfanNo ratings yet
- PierDocument52 pagesPierEngdasew BirhaneNo ratings yet
- Concept of Bearing CapacityDocument6 pagesConcept of Bearing CapacityrahimmullaNo ratings yet
- Department of Collegiate and Technical Education: Civil EngineeringDocument18 pagesDepartment of Collegiate and Technical Education: Civil EngineeringHarsha HarapanahalliNo ratings yet
- Pile FoundationDocument44 pagesPile FoundationKasim MalekNo ratings yet
- 3.bearing Capacity of SoilDocument9 pages3.bearing Capacity of SoilDinuNo ratings yet
- An Overview On Bored Cast in Situ ConcreDocument12 pagesAn Overview On Bored Cast in Situ ConcreElric TambilawanNo ratings yet
- Lecture08 Stone Columns PDFDocument69 pagesLecture08 Stone Columns PDFvijjikewlguy7116100% (2)
- BMCT Module-2(part-1)Document7 pagesBMCT Module-2(part-1)yatishfinanceNo ratings yet
- FoundationDocument60 pagesFoundationSurajNo ratings yet
- Soil StabilizationDocument13 pagesSoil StabilizationAngel MouriNo ratings yet
- Pile DesignDocument15 pagesPile Designmohanty_anantakumar6332100% (1)
- Chapter 3 - Caissons and Piers FinalDocument81 pagesChapter 3 - Caissons and Piers FinalgediongatzNo ratings yet
- Pile FoundationsDocument79 pagesPile FoundationsKoruvada NarendraNo ratings yet
- Plate Load Soil Test ReportDocument5 pagesPlate Load Soil Test ReportJoseph Cloyd L. LamberteNo ratings yet
- AssignmentDocument32 pagesAssignmentsyedNo ratings yet
- Civil Engineering Department: Government Engineering Colleg BilaspurDocument11 pagesCivil Engineering Department: Government Engineering Colleg Bilaspurtinu sahuNo ratings yet
- Sand ColumnDocument16 pagesSand ColumnZulfadli MunfazNo ratings yet
- Well Foundations NotesDocument11 pagesWell Foundations NotesK.manojNo ratings yet
- Handout 3 Earthwork OperationsDocument25 pagesHandout 3 Earthwork OperationsthuraiyaNo ratings yet
- Open Ended Lab For Soil MechanicsDocument27 pagesOpen Ended Lab For Soil Mechanicsعثمان محيب احمدNo ratings yet
- Tagupa, Mara Erna-ResearchworkDocument14 pagesTagupa, Mara Erna-ResearchworkMara Erna TagupaNo ratings yet
- Piles DesignDocument15 pagesPiles Designvenkatesh19701No ratings yet
- Fmcet: Ground ImprovementDocument29 pagesFmcet: Ground ImprovementVijay KumarNo ratings yet
- CE - VIII Sem - Plate Load Test - Rashi ChaurasiaDocument7 pagesCE - VIII Sem - Plate Load Test - Rashi ChaurasiaHamada SaidNo ratings yet
- 14.8.2 Bearing Capacity Based On Tolerable SettlementDocument3 pages14.8.2 Bearing Capacity Based On Tolerable SettlementLenana KoikaiNo ratings yet
- Vibro Ground BrochureDocument12 pagesVibro Ground Brochurealphaboi100% (1)
- Ground Improvement Techniques: Sneha P. Hirkane, N. G. Gore, P. J. SalunkeDocument3 pagesGround Improvement Techniques: Sneha P. Hirkane, N. G. Gore, P. J. SalunkevinodykrNo ratings yet
- Plate Load TestDocument3 pagesPlate Load TestniteshNo ratings yet
- Lecture (7) Foundation (Piles)Document19 pagesLecture (7) Foundation (Piles)علي نصير أبراهيمNo ratings yet
- Kazi MD Shifun NewazDocument21 pagesKazi MD Shifun NewazMd.Bakhtiar Enam SakibNo ratings yet
- An Investigation16Document19 pagesAn Investigation16badisnoveNo ratings yet
- Unit-I: Mr. C SASIDHAR, Asst. Professor, Dept. of Civil Engineering, SRET, TirupatiDocument4 pagesUnit-I: Mr. C SASIDHAR, Asst. Professor, Dept. of Civil Engineering, SRET, TirupatiSasi HoneyNo ratings yet
- Steps To Improve Roads On Black Cotton SoilsDocument9 pagesSteps To Improve Roads On Black Cotton SoilsAmrutha SivaramanNo ratings yet
- Pile DesignDocument16 pagesPile DesignVinod KrishnaNo ratings yet
- 04 Soil Mechanics and Foundation EngineeringDocument19 pages04 Soil Mechanics and Foundation EngineeringMohammed AnwhazNo ratings yet
- Earthwork ExcavationDocument24 pagesEarthwork ExcavationGabriella PrathapsonNo ratings yet
- Vibro Replacement Technique PDFDocument3 pagesVibro Replacement Technique PDFdebpriya1984No ratings yet
- Ground Improvement Techniques 01Document57 pagesGround Improvement Techniques 01tharadev2512No ratings yet
- NPTEL Course: Ground ImprovementDocument35 pagesNPTEL Course: Ground ImprovementmmNo ratings yet
- Piers and CassionsDocument19 pagesPiers and CassionsTsegaye TsegayeNo ratings yet
- Pile Foundation DesignDocument42 pagesPile Foundation DesignBright MuzaNo ratings yet
- Training Report SARNENDU (L-17)Document21 pagesTraining Report SARNENDU (L-17)Monaliza SenNo ratings yet
- Ground Improvement TechniquesDocument35 pagesGround Improvement TechniquesShivamMishra75% (4)
- Pile Foundation Mod 3Document9 pagesPile Foundation Mod 3supreetha k sNo ratings yet
- Ce6012 - Uw 1 - by Civildatas - Blogspot.inDocument29 pagesCe6012 - Uw 1 - by Civildatas - Blogspot.inSaibharathReddy ChavvaNo ratings yet
- GIT Full NotesDocument29 pagesGIT Full NotesHanamant HunashikattiNo ratings yet
- Ground Improvement Technique-1Document13 pagesGround Improvement Technique-1PradeepLokhandeNo ratings yet
- Research Work 1Document14 pagesResearch Work 1Mara Erna TagupaNo ratings yet
- Gte CCHDocument8 pagesGte CCH13 Vedant DamodareNo ratings yet
- Shallow FoundationDocument130 pagesShallow FoundationSanki ChoraNo ratings yet
- Deep CompactionDocument20 pagesDeep CompactionReza Ermawan100% (1)
- Pile FoundationsDocument32 pagesPile Foundationslovepreet singhNo ratings yet
- Chapter 14 Deep Foundation 29Document16 pagesChapter 14 Deep Foundation 29Ambu DeviNo ratings yet
- Review - Shear Strength of SoilDocument6 pagesReview - Shear Strength of SoilBenard OmondiNo ratings yet
- Reinforced Concrete Grade Beams, Piles & Caissons: A Practical Guide for Hillside ConstructionFrom EverandReinforced Concrete Grade Beams, Piles & Caissons: A Practical Guide for Hillside ConstructionNo ratings yet
- Transactions of the American Society of Civil Engineers, vol. LXX, Dec. 1910 Reinforced Concrete Pier ConstructionFrom EverandTransactions of the American Society of Civil Engineers, vol. LXX, Dec. 1910 Reinforced Concrete Pier ConstructionNo ratings yet
- General Catalogue EngDocument4 pagesGeneral Catalogue EngChakchouk MED WALIDNo ratings yet
- Hardness Conversion or Equivalence Table For Many Different ScalesDocument7 pagesHardness Conversion or Equivalence Table For Many Different ScalessureshjeevaNo ratings yet
- Appendix 2: Geomembrane Test MethodsDocument5 pagesAppendix 2: Geomembrane Test MethodsliviuNo ratings yet
- Journal of Photochemistry and Photobiology A: ChemistryDocument9 pagesJournal of Photochemistry and Photobiology A: ChemistryHugo RojasNo ratings yet
- Structural Firefighting Gloves: When Seconds MatterDocument2 pagesStructural Firefighting Gloves: When Seconds MatterHarry Orlando AlvarezNo ratings yet
- Annex B ISO 14731 & ISO 3834Document6 pagesAnnex B ISO 14731 & ISO 3834ioancNo ratings yet
- Physical and Chemical Changes - MCQDocument9 pagesPhysical and Chemical Changes - MCQMinuteBrain LearningNo ratings yet
- Technical Data: Ethacure 300Document2 pagesTechnical Data: Ethacure 300sriatul2006No ratings yet
- Design of Foundation & Structure For 400Kv BpiDocument20 pagesDesign of Foundation & Structure For 400Kv BpiZamfir ConstantinNo ratings yet
- Presentation DelcorteDocument15 pagesPresentation Delcortecarlos2685No ratings yet
- How Long Does Composting TakeDocument5 pagesHow Long Does Composting TakeLadylyn NuñezNo ratings yet
- 2018grandeacs Iecr 8b01483Document7 pages2018grandeacs Iecr 8b01483Alberto TousNo ratings yet
- Nabeel Khan Thesis (Minimum Size)Document76 pagesNabeel Khan Thesis (Minimum Size)Nabeel Ahmed KhanNo ratings yet
- Development of New AC TIG Welding Power Source and Its Improvement of ProductivityDocument8 pagesDevelopment of New AC TIG Welding Power Source and Its Improvement of ProductivityahmetNo ratings yet
- Kelvin Probe Force Microscopy: SynonymsDocument8 pagesKelvin Probe Force Microscopy: SynonymsRaj TokasNo ratings yet
- Overview Data LOCTITE HB S PURBOND-Line July 2015 - 2Document1 pageOverview Data LOCTITE HB S PURBOND-Line July 2015 - 2frankNo ratings yet
- HBI TestingDocument15 pagesHBI Testingreva cmNo ratings yet
- Aluminum Glass and Windows For QuotationDocument2 pagesAluminum Glass and Windows For Quotationjarellano08No ratings yet
- NOCDocument11 pagesNOCVedam Shanmukha HrushikeshNo ratings yet
- Siwes Presentation BY Ameh Ignisius 17BC004976/1701612 Undertaken AT Brains and Hammers FromDocument11 pagesSiwes Presentation BY Ameh Ignisius 17BC004976/1701612 Undertaken AT Brains and Hammers FromIgnisius AmehNo ratings yet
- Effects of Fineness of Cement On Polynaphalene Sulfonate Based Superplasticizers Cement InteractionDocument7 pagesEffects of Fineness of Cement On Polynaphalene Sulfonate Based Superplasticizers Cement Interactionibrahim çavuşoğluNo ratings yet
- Ad0601116 PDFDocument161 pagesAd0601116 PDFVelissarios DemetriouNo ratings yet
- Aluminium Mig WeldingDocument5 pagesAluminium Mig WeldingManish SharmaNo ratings yet
- Flexural Behavior of Ultra-High-Performance Fiber-Reinforced Concrete Beams Reinforced With GFRP and Steel RebarsDocument17 pagesFlexural Behavior of Ultra-High-Performance Fiber-Reinforced Concrete Beams Reinforced With GFRP and Steel Rebarsmohamed ellithyNo ratings yet
- SDS Abbdia Reagent Alinity C GlucoseDocument10 pagesSDS Abbdia Reagent Alinity C GlucoseAMNo ratings yet
- Saic Q 1060Document3 pagesSaic Q 1060Arjun RawatNo ratings yet
- Automated Operation of Topsoe Steam Reformers LTMDocument8 pagesAutomated Operation of Topsoe Steam Reformers LTMrajuNo ratings yet
- Market Price Graph of South Indian Scrap Prices For IronsDocument2 pagesMarket Price Graph of South Indian Scrap Prices For IronsR.JayaprakashNo ratings yet
- Pipe Manufacturer's Data Sheet 1Document231 pagesPipe Manufacturer's Data Sheet 1Mumtaz Ahmed Ghumman100% (1)
BMCT Module-2(part-2)
BMCT Module-2(part-2)
Uploaded by
yatishfinanceCopyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
BMCT Module-2(part-2)
BMCT Module-2(part-2)
Uploaded by
yatishfinanceCopyright:
Available Formats
Building Material & Construction 18CV34
Module- 2
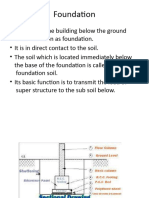
• Foundation: Preliminary investigation of soil, safe bearing capacity of soil, Function and
requirements of good foundation, types of foundation, introduction to spread, combined,
strap, mat and pile foundation
• Masonry: Definition and terms used in masonry. Brick masonry, characteristics and
requirements of good brick masonry, Bonds in brick work, Header, Stretcher, English,
Flemish bond, Stone masonry, Requirements of good stone masonry, Classification,
characteristics of different stone masonry, Joints in stone masonry. Types of walls; load
bearing, partition walls, cavity walls.
Department of Civil Engineering, AIT Page 1
Prepared by- Satish Kumar M, Assistant Professor
Building Material & Construction 18CV34
Methods for determining the bearing capacity of soil
1. Method of loading: The materials required for the test are as follows:
a. Steel square plate: The size of the plate usually varies from 3000 to 7500mm2 in area
and should have minimum thickness of 25mm.
b. Platform: This is usually made of a wooden table having four legs and a top plank
board. The two blocks of wooden beams are placed on the plank board in a well
balanced position.
c. Wooden pegs: The pegs are driven with 50mm projection above the ground level.
They are used to maintain level of bench mark.
d. Dumpy level with staff: This is a levelling instrument used to note the settlement of
the steel plate.
e. Rolled steel sections: They are available in standard size and weights. They are
arranged in two layers over a platform to take the load of sand bags.
f. Sand bags: They are used for incremental loading.
Procedure
i. A square pit of required size is excavated up to required
depth. The side of the pit is equal to 5 times the side of
the steel plate. At the centre, a square hole is dug of size
equal to side of the steel plate. The bottom of the hole
should correspond to the foundation level and the ratio of
breadth to depth of pit should made equal to ratio of
depth to breadth of hole.
ii. The bottom of the hole is made leveled by scraping and
it is well protected against the disturbing forces before
and during the test.
iii. The steel plate placed and platform is prepared as shown
in fig. iv. The amount of initial load is decided according to the type of soil to be tested.
The weights of steel plates, wooden table and wooden beam should be carefully worked
out.
v. A dumpy level is planted to note the settlement of the steel plate with reference to a
permanent bench mark.
vi. The load is to be kept on the platform till the settlement of the ground ceases or stops.
vii. Then the load is increased by a suitable amount, usually by 5KN and the procedure is
continued. For this purpose the weighed sand bags are used.
Department of Civil Engineering, AIT Page 2
Prepared by- Satish Kumar M, Assistant Professor
Building Material & Construction 18CV34
viii. A graph of load-settlement is plotted.
Bearing capacity of Soil in KN/m2= Maximum Load / area of steel Plate
Safe Bearing capacity of soil in KN/m2 = Bearing Capacity of soil / FOS
2. Plate load test: This is the improved refined method and it is widely used for determining
the bearing capacity of soil for important civil engineering structures.
The procedure to carry out the plate load test is as follows:
1. The test pit and the square hole for the steel plate are made as in the previous method.
The plate is firmly seated in the hole. If the ground is slightly uneven, a thin layer of sand
is spread below the plate. The loading is done with the help of sand bags, stones or
concrete blocks.
2. The load is applied in convenient increments say about 1/5th of the expected safe bearing
capacity or 1/10th of the ultimate bearing capacity
Department of Civil Engineering, AIT Page 3
Prepared by- Satish Kumar M, Assistant Professor
Building Material & Construction 18CV34
3. The settlement of the plate is observed by two sensitive dial gauges which are fixed at
diametrically opposite ends and supported independently on a suitable datum bar. The
sensitivity of the dial gauges should be 0.02mm.
4. As the plate settles, the ram of the dial gauges moves down and settlement is recorded.
The load in indicated on the load gauge of the hydraulic jack. The settlement should be
observed for each increment of load after an interval of 1, 4, 10, 20, 40 and 60 min and
thereafter at hourly intervals.
5. The recording of settlement is continued until the rate of settlement becomes less than
0.02mm per hour. The next load increment is then applied. The maximum load that is to
be applied corresponds to 1.50 times the estimated ultimate load or 3 times the proposed
allowable bearing pressure. 6. The load-settlement curve is plotted.
3. Method of dropping a weight or penetration test: In this method, a substance of known
weight is dropped from a known height. The depth of impression made by the weight on
the soil is noted. Then bearing capacity is determined as
follows
R = resistance of soil h = height d = depth of impression w =
weight of the substance
Then Total energy
R*d=w*h
R = w*h/d
A = cross section area of the substance
R/A = resistance of the soil per unit area
Therefore Safe Bearing capacity of soil = R/(A *f)
Where f= factor of safety
4. Analytical methods: The analytical methods involving the use of soil parameters like
angle of internal friction and cohesion are now available to determine the ultimate
bearing capacity of soil.
5. Presumptive values of bearing capacities of soils: The presumptive value of maximum
safe bearing capacity of various soils is now available from codes or other sources which
are adopted for designing the foundations for light loaded structures.
Increasing the bearing Capacity of soil
Sometimes the required safe bearing capacity of the soil is not available at shallow depth or
it is so low that the dimension of the footing works out to be very large and uneconomical.
Under such circumstances, it becomes necessary to increase the bearing capacity of soil.
Department of Civil Engineering, AIT Page 4
Prepared by- Satish Kumar M, Assistant Professor
Building Material & Construction 18CV34
Methods for increasing the bearing capacity of soil
1. Increase in depth of foundation: For granular soils, bearing capacity increases
with the depth of foundation due to confining weight of overlying material. This
method is however not economical because the cost of construction increases with
the depth and the load on the foundation also increases with increase in depth. This
method is adopted only when more depth of foundation can be justified by the type
and nature of structure to be supported over the soil.
2. Compacting Soil: In this method the width of foundation is increased about 450mm
or so and then a layer of 300mm to 450mm rubble is placed over the bottom of the
foundation. This layer of rubble is well rammed and if this is buried completely then
another layer of depth about 150 to 250mm is laid and it is well rammed. At the end
of this process, if the bearing capacity of the soil is tested, it is found to have
increased considerably. This value is used for designing the foundation.
The compaction of soil can also be achieved by various other means like
• Flooding the soil: The bearing capacity of very loose sand can be increased
effectively by flooding the soil.
• Ramming moist soil: The soil is made wet and it is then compacted with the
help of hand, mechanical rammers or vibratory rollers. The voids of the soil
are reduced considerably and it results in the improvement of the bearing
capacity of the soil.
• Vibration: If a layer of granular soils to a depth of 1m to 3m is compacted
with the help of vibratory rollers, there is considerable increase in the safe
bearing capacity of soil and the chances of settlements are minimized.
• Vibroflotation: This is a commercial method and it combines the effect of
vibration with jetting. It is very useful especially when the foundation is
required to support heavy loads spread over a greater area. The process is
carried out as follows:
a. A heavy cylinder, known as vibroflot is inserted into the ground while
the cylinder vibrates due to a rotary action
b. A large amount of water under pressure is supplied from the water jet
provided on the tip of the vibroflot.
c. As the vibroflot sinks, the clean sand is added in the crater which is
formed on the surface.
d. The procedure is repeated to cover desired area of the foundation.
3. Drainage of soil: The presence of water decreases the bearing capacity of soil.
Suitable drains should be provided in the foundation trench to drain off the excess
water. If a spring is met with or if water finds its way through the cracks on the
surface of the rock, the pipes are provided and thereby the uplift pressure is
decreased. The pipes are then sealed at top.
Department of Civil Engineering, AIT Page 5
Prepared by- Satish Kumar M, Assistant Professor
Building Material & Construction 18CV34
4. Sheet Piles: The movement of soil under the action o load can be prevented by
confining the ground by the use of sheet pile. This will result in the increase of
bearing power of soil.
5. Sand Piles: The construction of sand piles proves to be very useful in case of sandy
soils or soft soils.
6. Grouting: The bore holes in sufficient numbers are driven in the ground. The
cement grout is then forced under pressure through these bore holes. The cracks on
the surface of rock are thus filled up, resulting in the increase of bearing power of
soil.
7. Chemical treatment: In this treatment, certain chemicals which can solidify and
gain early strength are used in place of cement paste grout to solidify the soil. But
as this process is costly, it is adopted only in case of important buildings.
8. Stone columns: Stone columns are invariably used in weak soils having very poor
bearing capacity. It is normally used in soft inorganic soils. Pieces of stones are well
compacted in pre-bored holes to form stone column which acts as reinforcement,
confines the soil and improves bearing capacity.
9. Use of geo-synthetics: Geo-synthetics are used as reinforcing material which
improves the ground condition. The bearing capacity of such soils is improved by
300% by using geo-synthetics. The various types of geo-synthetics are
(1) Geo-textiles
(2) Geo-grids
(3) Geo-cells
(4) Geo-drains etc.
The above materials when reinforced in weak soils enhance its shearing resistance.
Nowadays geo-grids are more employed for draining out water from a trench because
of its porous nature.
10. Compaction by deep blasting: In this case a bore hole is dug for a depth of 3/4th or
2/3rd of total depth. Suitable explosive is placed at the bottom of hole and the charge
is carried by cordex and connected to the electric detonator. When the explosive is
detonated, it creates a cavity. The cavity expansion produces shock waves which
densifies the soil. Normally 15 to 45gms of explosive are used for densification of
soil.
Department of Civil Engineering, AIT Page 6
Prepared by- Satish Kumar M, Assistant Professor
You might also like
- Gas Testing Procedures PDFDocument44 pagesGas Testing Procedures PDFAbdelkader BOUKHOUS50% (2)
- Explain Briefly About Preloading. A. Preloading of Soil Is Merely Applying An External Loading For A Long Duration ToDocument10 pagesExplain Briefly About Preloading. A. Preloading of Soil Is Merely Applying An External Loading For A Long Duration Tohimabindugvsd71No ratings yet
- Bmc1-Bearing Capacity of SoilDocument24 pagesBmc1-Bearing Capacity of SoilHridhya mpNo ratings yet
- Effectiveness of Sand Column As A Ground Improvement TechniqueDocument5 pagesEffectiveness of Sand Column As A Ground Improvement TechniqueMuhammad IrfanNo ratings yet
- PierDocument52 pagesPierEngdasew BirhaneNo ratings yet
- Concept of Bearing CapacityDocument6 pagesConcept of Bearing CapacityrahimmullaNo ratings yet
- Department of Collegiate and Technical Education: Civil EngineeringDocument18 pagesDepartment of Collegiate and Technical Education: Civil EngineeringHarsha HarapanahalliNo ratings yet
- Pile FoundationDocument44 pagesPile FoundationKasim MalekNo ratings yet
- 3.bearing Capacity of SoilDocument9 pages3.bearing Capacity of SoilDinuNo ratings yet
- An Overview On Bored Cast in Situ ConcreDocument12 pagesAn Overview On Bored Cast in Situ ConcreElric TambilawanNo ratings yet
- Lecture08 Stone Columns PDFDocument69 pagesLecture08 Stone Columns PDFvijjikewlguy7116100% (2)
- BMCT Module-2(part-1)Document7 pagesBMCT Module-2(part-1)yatishfinanceNo ratings yet
- FoundationDocument60 pagesFoundationSurajNo ratings yet
- Soil StabilizationDocument13 pagesSoil StabilizationAngel MouriNo ratings yet
- Pile DesignDocument15 pagesPile Designmohanty_anantakumar6332100% (1)
- Chapter 3 - Caissons and Piers FinalDocument81 pagesChapter 3 - Caissons and Piers FinalgediongatzNo ratings yet
- Pile FoundationsDocument79 pagesPile FoundationsKoruvada NarendraNo ratings yet
- Plate Load Soil Test ReportDocument5 pagesPlate Load Soil Test ReportJoseph Cloyd L. LamberteNo ratings yet
- AssignmentDocument32 pagesAssignmentsyedNo ratings yet
- Civil Engineering Department: Government Engineering Colleg BilaspurDocument11 pagesCivil Engineering Department: Government Engineering Colleg Bilaspurtinu sahuNo ratings yet
- Sand ColumnDocument16 pagesSand ColumnZulfadli MunfazNo ratings yet
- Well Foundations NotesDocument11 pagesWell Foundations NotesK.manojNo ratings yet
- Handout 3 Earthwork OperationsDocument25 pagesHandout 3 Earthwork OperationsthuraiyaNo ratings yet
- Open Ended Lab For Soil MechanicsDocument27 pagesOpen Ended Lab For Soil Mechanicsعثمان محيب احمدNo ratings yet
- Tagupa, Mara Erna-ResearchworkDocument14 pagesTagupa, Mara Erna-ResearchworkMara Erna TagupaNo ratings yet
- Piles DesignDocument15 pagesPiles Designvenkatesh19701No ratings yet
- Fmcet: Ground ImprovementDocument29 pagesFmcet: Ground ImprovementVijay KumarNo ratings yet
- CE - VIII Sem - Plate Load Test - Rashi ChaurasiaDocument7 pagesCE - VIII Sem - Plate Load Test - Rashi ChaurasiaHamada SaidNo ratings yet
- 14.8.2 Bearing Capacity Based On Tolerable SettlementDocument3 pages14.8.2 Bearing Capacity Based On Tolerable SettlementLenana KoikaiNo ratings yet
- Vibro Ground BrochureDocument12 pagesVibro Ground Brochurealphaboi100% (1)
- Ground Improvement Techniques: Sneha P. Hirkane, N. G. Gore, P. J. SalunkeDocument3 pagesGround Improvement Techniques: Sneha P. Hirkane, N. G. Gore, P. J. SalunkevinodykrNo ratings yet
- Plate Load TestDocument3 pagesPlate Load TestniteshNo ratings yet
- Lecture (7) Foundation (Piles)Document19 pagesLecture (7) Foundation (Piles)علي نصير أبراهيمNo ratings yet
- Kazi MD Shifun NewazDocument21 pagesKazi MD Shifun NewazMd.Bakhtiar Enam SakibNo ratings yet
- An Investigation16Document19 pagesAn Investigation16badisnoveNo ratings yet
- Unit-I: Mr. C SASIDHAR, Asst. Professor, Dept. of Civil Engineering, SRET, TirupatiDocument4 pagesUnit-I: Mr. C SASIDHAR, Asst. Professor, Dept. of Civil Engineering, SRET, TirupatiSasi HoneyNo ratings yet
- Steps To Improve Roads On Black Cotton SoilsDocument9 pagesSteps To Improve Roads On Black Cotton SoilsAmrutha SivaramanNo ratings yet
- Pile DesignDocument16 pagesPile DesignVinod KrishnaNo ratings yet
- 04 Soil Mechanics and Foundation EngineeringDocument19 pages04 Soil Mechanics and Foundation EngineeringMohammed AnwhazNo ratings yet
- Earthwork ExcavationDocument24 pagesEarthwork ExcavationGabriella PrathapsonNo ratings yet
- Vibro Replacement Technique PDFDocument3 pagesVibro Replacement Technique PDFdebpriya1984No ratings yet
- Ground Improvement Techniques 01Document57 pagesGround Improvement Techniques 01tharadev2512No ratings yet
- NPTEL Course: Ground ImprovementDocument35 pagesNPTEL Course: Ground ImprovementmmNo ratings yet
- Piers and CassionsDocument19 pagesPiers and CassionsTsegaye TsegayeNo ratings yet
- Pile Foundation DesignDocument42 pagesPile Foundation DesignBright MuzaNo ratings yet
- Training Report SARNENDU (L-17)Document21 pagesTraining Report SARNENDU (L-17)Monaliza SenNo ratings yet
- Ground Improvement TechniquesDocument35 pagesGround Improvement TechniquesShivamMishra75% (4)
- Pile Foundation Mod 3Document9 pagesPile Foundation Mod 3supreetha k sNo ratings yet
- Ce6012 - Uw 1 - by Civildatas - Blogspot.inDocument29 pagesCe6012 - Uw 1 - by Civildatas - Blogspot.inSaibharathReddy ChavvaNo ratings yet
- GIT Full NotesDocument29 pagesGIT Full NotesHanamant HunashikattiNo ratings yet
- Ground Improvement Technique-1Document13 pagesGround Improvement Technique-1PradeepLokhandeNo ratings yet
- Research Work 1Document14 pagesResearch Work 1Mara Erna TagupaNo ratings yet
- Gte CCHDocument8 pagesGte CCH13 Vedant DamodareNo ratings yet
- Shallow FoundationDocument130 pagesShallow FoundationSanki ChoraNo ratings yet
- Deep CompactionDocument20 pagesDeep CompactionReza Ermawan100% (1)
- Pile FoundationsDocument32 pagesPile Foundationslovepreet singhNo ratings yet
- Chapter 14 Deep Foundation 29Document16 pagesChapter 14 Deep Foundation 29Ambu DeviNo ratings yet
- Review - Shear Strength of SoilDocument6 pagesReview - Shear Strength of SoilBenard OmondiNo ratings yet
- Reinforced Concrete Grade Beams, Piles & Caissons: A Practical Guide for Hillside ConstructionFrom EverandReinforced Concrete Grade Beams, Piles & Caissons: A Practical Guide for Hillside ConstructionNo ratings yet
- Transactions of the American Society of Civil Engineers, vol. LXX, Dec. 1910 Reinforced Concrete Pier ConstructionFrom EverandTransactions of the American Society of Civil Engineers, vol. LXX, Dec. 1910 Reinforced Concrete Pier ConstructionNo ratings yet
- General Catalogue EngDocument4 pagesGeneral Catalogue EngChakchouk MED WALIDNo ratings yet
- Hardness Conversion or Equivalence Table For Many Different ScalesDocument7 pagesHardness Conversion or Equivalence Table For Many Different ScalessureshjeevaNo ratings yet
- Appendix 2: Geomembrane Test MethodsDocument5 pagesAppendix 2: Geomembrane Test MethodsliviuNo ratings yet
- Journal of Photochemistry and Photobiology A: ChemistryDocument9 pagesJournal of Photochemistry and Photobiology A: ChemistryHugo RojasNo ratings yet
- Structural Firefighting Gloves: When Seconds MatterDocument2 pagesStructural Firefighting Gloves: When Seconds MatterHarry Orlando AlvarezNo ratings yet
- Annex B ISO 14731 & ISO 3834Document6 pagesAnnex B ISO 14731 & ISO 3834ioancNo ratings yet
- Physical and Chemical Changes - MCQDocument9 pagesPhysical and Chemical Changes - MCQMinuteBrain LearningNo ratings yet
- Technical Data: Ethacure 300Document2 pagesTechnical Data: Ethacure 300sriatul2006No ratings yet
- Design of Foundation & Structure For 400Kv BpiDocument20 pagesDesign of Foundation & Structure For 400Kv BpiZamfir ConstantinNo ratings yet
- Presentation DelcorteDocument15 pagesPresentation Delcortecarlos2685No ratings yet
- How Long Does Composting TakeDocument5 pagesHow Long Does Composting TakeLadylyn NuñezNo ratings yet
- 2018grandeacs Iecr 8b01483Document7 pages2018grandeacs Iecr 8b01483Alberto TousNo ratings yet
- Nabeel Khan Thesis (Minimum Size)Document76 pagesNabeel Khan Thesis (Minimum Size)Nabeel Ahmed KhanNo ratings yet
- Development of New AC TIG Welding Power Source and Its Improvement of ProductivityDocument8 pagesDevelopment of New AC TIG Welding Power Source and Its Improvement of ProductivityahmetNo ratings yet
- Kelvin Probe Force Microscopy: SynonymsDocument8 pagesKelvin Probe Force Microscopy: SynonymsRaj TokasNo ratings yet
- Overview Data LOCTITE HB S PURBOND-Line July 2015 - 2Document1 pageOverview Data LOCTITE HB S PURBOND-Line July 2015 - 2frankNo ratings yet
- HBI TestingDocument15 pagesHBI Testingreva cmNo ratings yet
- Aluminum Glass and Windows For QuotationDocument2 pagesAluminum Glass and Windows For Quotationjarellano08No ratings yet
- NOCDocument11 pagesNOCVedam Shanmukha HrushikeshNo ratings yet
- Siwes Presentation BY Ameh Ignisius 17BC004976/1701612 Undertaken AT Brains and Hammers FromDocument11 pagesSiwes Presentation BY Ameh Ignisius 17BC004976/1701612 Undertaken AT Brains and Hammers FromIgnisius AmehNo ratings yet
- Effects of Fineness of Cement On Polynaphalene Sulfonate Based Superplasticizers Cement InteractionDocument7 pagesEffects of Fineness of Cement On Polynaphalene Sulfonate Based Superplasticizers Cement Interactionibrahim çavuşoğluNo ratings yet
- Ad0601116 PDFDocument161 pagesAd0601116 PDFVelissarios DemetriouNo ratings yet
- Aluminium Mig WeldingDocument5 pagesAluminium Mig WeldingManish SharmaNo ratings yet
- Flexural Behavior of Ultra-High-Performance Fiber-Reinforced Concrete Beams Reinforced With GFRP and Steel RebarsDocument17 pagesFlexural Behavior of Ultra-High-Performance Fiber-Reinforced Concrete Beams Reinforced With GFRP and Steel Rebarsmohamed ellithyNo ratings yet
- SDS Abbdia Reagent Alinity C GlucoseDocument10 pagesSDS Abbdia Reagent Alinity C GlucoseAMNo ratings yet
- Saic Q 1060Document3 pagesSaic Q 1060Arjun RawatNo ratings yet
- Automated Operation of Topsoe Steam Reformers LTMDocument8 pagesAutomated Operation of Topsoe Steam Reformers LTMrajuNo ratings yet
- Market Price Graph of South Indian Scrap Prices For IronsDocument2 pagesMarket Price Graph of South Indian Scrap Prices For IronsR.JayaprakashNo ratings yet
- Pipe Manufacturer's Data Sheet 1Document231 pagesPipe Manufacturer's Data Sheet 1Mumtaz Ahmed Ghumman100% (1)