Professional Documents
Culture Documents
DE POSTER
DE POSTER
Uploaded by
Rutvika GhadiyaliCopyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
DE POSTER
DE POSTER
Uploaded by
Rutvika GhadiyaliCopyright:
Available Formats
Bhagwan Mahavir University
Bhagwan Arihant Institute of Technology
VIP Road, Barthana – Vesu, Surat - 395007
DIGITAL ELECTRONICS
TOPIC : Universal Gate Design Using CMOS
Introduction The CMOS NAND Gate The CMOS NOR Gate
Universal gate design using CMOS (Complementary MOS) involves creating
logic gates using a combination of n-channel (NMOS) and p-channel (PMOS)
transistors. CMOS logic gates are widely used in digital systems due to their
low static power consumption and high input impedance. Some fundamental
CMOS logic gates include the NOT gate, NAND gate, and NOR gate.
Table 1. The truth table for a two-input NAND circuit. Table 2. The truth table for a two-input NOR circuit.
CMOS Technology
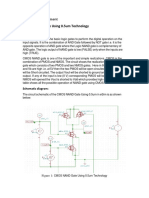
Figure 1. shows a CMOS two-input NAND gate. P-channel transistors Q1 and Figure 2. shows a CMOS two-input NOR gate. P-channel transistors Q1 and
• CMOS (Complementary Metal-Oxide-Semiconductor) is a type of digital Q2 are connected in parallel between +V and the output terminal. N-channel Q2 are connected in series between +V and the output terminal. N-channel
logic gate that uses both NMOS and PMOS transistors to implement logic transistors Q3 and Q4 are connected in series between the output terminal and transistors Q3 and Q4 are connected in parallel between the output and ground.
functions. ground.
• The basic building blocks of CMOS logic gates are the inverter, NAND
gate, and NOR gate.
• The inverter is the simplest CMOS gate, consisting of a series connection of
a PMOS and an NMOS transistor. The NAND and NOR gates can be easily
realized using CMOS logic.
• The PDN (Pull-Down Network) of the AOI (And-Or-Invert) gate is
structurally similar to the PUN (Pull-Up Network) of the OAI (Or-And-
Invert) gate, and vice versa. This makes it possible to realize any logic
function using a combination of NAND and NOR gates. Figure 1. A CMOS two-input NAND gate.
Figure 2. A CMOS two-input NOR gate.
• The truth table is a mathematical model that demonstrates the relationship
between inputs A and B, with inputs being logic 1 and 0 respectively. • The truth table is confirmed when inputs A and B are logic 0, with Q1 and
Q2 being "on" and Q3 and Q4 being "off."
Advantages of CMOS • If Q3 and Q4 transistors are on and Q1 and Q2 are off, the output is a logic
• Low power consumption 0, confirming the lowest row in the truth table. If one input is a logic 1 and • The output is logic 1, confirming the first row. The output is logic 0 for the
• High noise immunity the other is 0 (Q3 and Q2), the output is a logic 1, validating the second and last row. The remaining input combinations have either Q1 and Q3 being
• High packing density third rows. "off" or Q2 and Q4 being "on“.
• Wide operating voltage range
References
1. Basic CMOS Logic Gates - Technical Articles (eepower.com)
1. CMOS Logic Gate – GeeksforGeeks
2. CMOS Gate Circuitry | Logic Gates | Electronics Textbook (allaboutcircuits.com)
Guided By: Prof. Rahul N Gonawala Students Name : 1) Ghadiyali Rutvika | 2) Patel Dhruvi | 3) Rakholiya Honey | 4) Vekariya Bhavyanshu
You might also like
- StopWatch ReportDocument11 pagesStopWatch ReportGeoffrey Chua0% (1)
- MTV 100 User Manual EngDocument11 pagesMTV 100 User Manual EngIbnu AndhikaNo ratings yet
- Unit 4aDocument20 pagesUnit 4asofiashaik414No ratings yet
- UNIT-3 Gate Level Design NotesDocument22 pagesUNIT-3 Gate Level Design NotesPallavi Ch100% (2)
- Philip-Intro To DEDocument32 pagesPhilip-Intro To DEPhilip AustinNo ratings yet
- Anu PDFDocument9 pagesAnu PDFAkhtarNo ratings yet
- Digital ElectronicsDocument7 pagesDigital Electronicsgezaegebre1No ratings yet
- Lab2 PabillaranDocument9 pagesLab2 PabillaranLouise Lope PabillaranNo ratings yet
- Vlsi Design Unit 3 2019Document34 pagesVlsi Design Unit 3 2019Ishan Mahendra PatelNo ratings yet
- Lecture 3 - MOS and ECL TechnologyDocument27 pagesLecture 3 - MOS and ECL TechnologyGhostNo ratings yet
- Two Mark Questions For DSDDocument17 pagesTwo Mark Questions For DSDvnirmalacseNo ratings yet
- Cmos CH 4Document46 pagesCmos CH 4Pinak RoyNo ratings yet
- FinalDocument18 pagesFinalitsaartihere001No ratings yet
- Lab Reports-Vlsi LabDocument42 pagesLab Reports-Vlsi LabHuzaifa AhmedNo ratings yet
- VLSI Design SoC CH 6Document125 pagesVLSI Design SoC CH 6Arqam Ali KhanNo ratings yet
- Cse 3 2 Vlsi Unit 4 PDFDocument44 pagesCse 3 2 Vlsi Unit 4 PDF9966299828100% (1)
- Advance Vlsi Design Practical File: Varun Sahani 04216412811 M.Tech (ECE) 2 SemDocument12 pagesAdvance Vlsi Design Practical File: Varun Sahani 04216412811 M.Tech (ECE) 2 SemVarun SahaniNo ratings yet
- Laboratory Activity 4Document3 pagesLaboratory Activity 4Mark N. Yata ItoNo ratings yet
- Digital Electronics - ArunDocument45 pagesDigital Electronics - ArunArun ANo ratings yet
- Week 3 - CMOS Logic CircuitsDocument33 pagesWeek 3 - CMOS Logic Circuits서종현No ratings yet
- Ec1203 Digital ElectronicsDocument20 pagesEc1203 Digital ElectronicsSiva Prasad PadilamNo ratings yet
- I008 Dem LabfileDocument115 pagesI008 Dem LabfileShireen ChandNo ratings yet
- Introduction To XOR GateDocument13 pagesIntroduction To XOR Gatedhruvivirani2611No ratings yet
- 03 Digital Circuits LMT ELDocument74 pages03 Digital Circuits LMT ELquý dương lêNo ratings yet
- Digital Logic Design Chapter 5Document28 pagesDigital Logic Design Chapter 5Okezaki TemoyoNo ratings yet
- MODULE 4 - Digital ElectronicsDocument45 pagesMODULE 4 - Digital ElectronicsArun ANo ratings yet
- Designing Combinational Logic Gates in CMOSDocument21 pagesDesigning Combinational Logic Gates in CMOSMonica MagnateNo ratings yet
- Nor Gate As Universal Gate:: Power Supply, IC 7400, 7402, LEDDocument4 pagesNor Gate As Universal Gate:: Power Supply, IC 7400, 7402, LEDNkNo ratings yet
- Design of Low Power CMOS Ternary Logic GatesDocument5 pagesDesign of Low Power CMOS Ternary Logic Gatesche2_rathiNo ratings yet
- A Survey Analysis On CMOS Integrated Cir PDFDocument4 pagesA Survey Analysis On CMOS Integrated Cir PDFNK NKNo ratings yet
- SP24 Mid Lecture 3 (1)Document15 pagesSP24 Mid Lecture 3 (1)safwanxd93No ratings yet
- Unit 2 - Logic Gate Devices Characteristics (DBV30023)Document68 pagesUnit 2 - Logic Gate Devices Characteristics (DBV30023)Abd Kadir JailaniNo ratings yet
- Combination Logic CircuitsDocument21 pagesCombination Logic Circuitsamitssaksena100% (1)
- Application of Logic Gates: - Application Note - Andrew Herman ECE480 - Team 5 3/30/2007Document7 pagesApplication of Logic Gates: - Application Note - Andrew Herman ECE480 - Team 5 3/30/2007Norazdila Mohd SallehNo ratings yet
- Logic Gate - WikipediaDocument11 pagesLogic Gate - WikipediayugalkishorNo ratings yet
- Design, Simulation, and Investigation of Basic Logic Gates by Using NAND Logic GateDocument9 pagesDesign, Simulation, and Investigation of Basic Logic Gates by Using NAND Logic Gateswadhinkhamari34No ratings yet
- Chapter 6: Digital Components: ObjectivesDocument17 pagesChapter 6: Digital Components: ObjectivesSteffany RoqueNo ratings yet
- Design Analysis of NAND Gate Using Cascode-Voltage Switch LogicDocument4 pagesDesign Analysis of NAND Gate Using Cascode-Voltage Switch LogicNeha Prashant VermaNo ratings yet
- Contents:: CMOS Inverter Cmos Nand Gate Cmos Nor GateDocument13 pagesContents:: CMOS Inverter Cmos Nand Gate Cmos Nor GateTilottama DeoreNo ratings yet
- Cmos 1Document10 pagesCmos 1mukulgrd1No ratings yet
- Low Power Mix Logic Design Using Line Decoder: A ReviewDocument5 pagesLow Power Mix Logic Design Using Line Decoder: A ReviewEditor IJTSRDNo ratings yet
- Gates Institute of Technology:: Gooty Digital Circuits and Systems 2 Marks With AnswersDocument17 pagesGates Institute of Technology:: Gooty Digital Circuits and Systems 2 Marks With AnswersNaveen YallapuNo ratings yet
- Gates Institute of Technology:: Gooty Digital Circuits and Systems 2 Marks With AnswersDocument20 pagesGates Institute of Technology:: Gooty Digital Circuits and Systems 2 Marks With AnswersNaveen YallapuNo ratings yet
- Unit-Iv Gate Level DesignDocument34 pagesUnit-Iv Gate Level DesignsahithikocharlakotaNo ratings yet
- Aiub Course Solutio N: Dec Lab Report-03 FullDocument19 pagesAiub Course Solutio N: Dec Lab Report-03 FullSifatNo ratings yet
- Switching Theory and Logic Design Lab (ETEC - 253)Document82 pagesSwitching Theory and Logic Design Lab (ETEC - 253)AmanNo ratings yet
- CMOS NAND Gate Using 0.5um Technology Theory:: Title of The ExperimentDocument5 pagesCMOS NAND Gate Using 0.5um Technology Theory:: Title of The ExperimentSIDDHESWAR AMBHORENo ratings yet
- Chukwurah Raluchukwu - Lab Report 2Document11 pagesChukwurah Raluchukwu - Lab Report 2Raluchukwu ChukwurahNo ratings yet
- Algebra Report (Logic Gates)Document27 pagesAlgebra Report (Logic Gates)salah ashrafNo ratings yet
- Lab Manual Logic Design 1-2Document23 pagesLab Manual Logic Design 1-2akahNo ratings yet
- Lesson 3 CMOS Technology Teacher'sDocument7 pagesLesson 3 CMOS Technology Teacher'sMaria Ana DanganNo ratings yet
- Advanced VLSI Design Lab (EC17203) : Experiment No. 3Document4 pagesAdvanced VLSI Design Lab (EC17203) : Experiment No. 3Huzaifa AhmedNo ratings yet
- Logic Families: Designed By: Asadullah JamalovDocument6 pagesLogic Families: Designed By: Asadullah JamalovAsadullah JamalovNo ratings yet
- ECE 3544 Digital Design I: 2: Cmos LogicDocument34 pagesECE 3544 Digital Design I: 2: Cmos LogicZiad Mohmed FawzyNo ratings yet
- DTM w22 22323Document18 pagesDTM w22 22323bhaskarpagare247No ratings yet
- Logic Circuits Design Experiment1 2023Document15 pagesLogic Circuits Design Experiment1 2023Jose Miguel F. BorillaNo ratings yet
- Lecture 8 CMOSDocument32 pagesLecture 8 CMOSAlcanar CarmieNo ratings yet
- UNIT-05-Advanced Techniques by BRRDocument27 pagesUNIT-05-Advanced Techniques by BRRBhargavi NarisettiNo ratings yet
- Logic GatesDocument8 pagesLogic GatesPaul Justine Ruelson MeriolesNo ratings yet
- Dl3 Digital CircuitsDocument14 pagesDl3 Digital Circuitsomgcharlie12No ratings yet
- Index-AAYUSH-OS-1Document1 pageIndex-AAYUSH-OS-1Rutvika GhadiyaliNo ratings yet
- DM - Question BankDocument6 pagesDM - Question BankRutvika GhadiyaliNo ratings yet
- UHV QUESTIONS BANK WITH ANSWERSDocument7 pagesUHV QUESTIONS BANK WITH ANSWERSRutvika GhadiyaliNo ratings yet
- MAIN PRACTICAL DSDocument44 pagesMAIN PRACTICAL DSRutvika GhadiyaliNo ratings yet
- DS PPTDocument17 pagesDS PPTRutvika GhadiyaliNo ratings yet
- Database Management Systems - TheoryDocument3 pagesDatabase Management Systems - TheoryRutvika GhadiyaliNo ratings yet
- Projects 1920 C 5Document95 pagesProjects 1920 C 5Rutvika GhadiyaliNo ratings yet
- B.Tech SEM 1 (BAIT, BMCET, MSCET) PRACTICAL WINTER 2023Document1 pageB.Tech SEM 1 (BAIT, BMCET, MSCET) PRACTICAL WINTER 2023Rutvika GhadiyaliNo ratings yet
- LGBTQ Understanding and AcceptanceDocument6 pagesLGBTQ Understanding and AcceptanceRutvika GhadiyaliNo ratings yet
- ResultDocument5 pagesResultRutvika GhadiyaliNo ratings yet
- Practical 2Document5 pagesPractical 2Rutvika GhadiyaliNo ratings yet
- ACP MCQ Questions Bank: Department of Computer Engineering - 07Document26 pagesACP MCQ Questions Bank: Department of Computer Engineering - 07Rutvika GhadiyaliNo ratings yet
- Source CodeDocument7 pagesSource CodeRutvika GhadiyaliNo ratings yet
- Dynamic CMOS Logic GateDocument14 pagesDynamic CMOS Logic GateAyush SharmaNo ratings yet
- Prakash SIS WordDocument4 pagesPrakash SIS Wordashwini32No ratings yet
- r05320402 Vlsi DesignDocument4 pagesr05320402 Vlsi DesignSRINIVASA RAO GANTANo ratings yet
- Viewnet Diy PricelistDocument2 pagesViewnet Diy PricelistZulhakimMajidNo ratings yet
- Testing of Vlsi CktsDocument12 pagesTesting of Vlsi CktsBharathi MuniNo ratings yet
- 2nd CHAPTER MechatronicsDocument50 pages2nd CHAPTER MechatronicspremscrebdNo ratings yet
- Agricultural RobotDocument70 pagesAgricultural RobotMohammed ZubairNo ratings yet
- Eceg3202 - Computer Architecture and OrganizationDocument41 pagesEceg3202 - Computer Architecture and OrganizationAnonymous AFFiZnNo ratings yet
- Aptio V Status CodesDocument12 pagesAptio V Status Codesdrhollywood2001No ratings yet
- IC Logic Families: Wen-Hung Liao, PH.DDocument40 pagesIC Logic Families: Wen-Hung Liao, PH.Dvenkateshpandu11No ratings yet
- Paper Wcas RevisedDocument4 pagesPaper Wcas RevisedJoão Luiz CarvalhoNo ratings yet
- ECD Presentation1Document9 pagesECD Presentation1Shubham SharmaNo ratings yet
- Design of Low-Power High-Performance 2-4 and 4-16 Mixed-Logic Line DecodersDocument5 pagesDesign of Low-Power High-Performance 2-4 and 4-16 Mixed-Logic Line Decodersjatin guptaNo ratings yet
- Laboratory Manual: Digital System DesignDocument37 pagesLaboratory Manual: Digital System DesignArshad RasheedNo ratings yet
- Master BOM Sample-ElectronicsDocument2 pagesMaster BOM Sample-ElectronicsbmirdhaNo ratings yet
- Protocol: RS-232 Mechanical SpecificationDocument4 pagesProtocol: RS-232 Mechanical SpecificationAashutosh TiwariNo ratings yet
- 8085 Viva-VoiceDocument3 pages8085 Viva-VoiceJoshua DuffyNo ratings yet
- BIST Algorithm For Embedded-DRAM CoresDocument4 pagesBIST Algorithm For Embedded-DRAM CoresespskcNo ratings yet
- Pin Diagram With and GateDocument11 pagesPin Diagram With and GateZahid CoolNo ratings yet
- 周06Document99 pages周06sy1990010111No ratings yet
- Digital Electronics Module 05Document44 pagesDigital Electronics Module 05Yadana1No ratings yet
- 17MB35 Training ManualDocument33 pages17MB35 Training Manualjohnanto100% (1)
- TSRWDocument33 pagesTSRWpalak parmarNo ratings yet
- Lecture 03 - Fault CollapsingDocument40 pagesLecture 03 - Fault Collapsingmayank pNo ratings yet
- Von Neumann ArchitectureDocument30 pagesVon Neumann ArchitectureRochaNavarroNo ratings yet
- DVR ConfigDocument4 pagesDVR ConfigMary ValdezNo ratings yet
- 8051 Instruction - SetDocument48 pages8051 Instruction - SetJibu JoseNo ratings yet
- Dynamic Scheduling Using Tomasulo's Approach: - A Big PictureDocument29 pagesDynamic Scheduling Using Tomasulo's Approach: - A Big PictureSridhar MenonNo ratings yet