Professional Documents
Culture Documents
GEO SCRIPT
GEO SCRIPT
Uploaded by
Leah FernandoCopyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
GEO SCRIPT
GEO SCRIPT
Uploaded by
Leah FernandoCopyright:
Available Formats
1.
Mode of Occurrence of Igneous Rocks
Magmas erupted from volcanoes are either poured out as coherent
fluidal lava flows or blown out as fragments of various sizes. A body
of magma may also be emplaced and cool beneath the surface of the
Earth. Igneous rocks result from the final solidification of magma at
the surface or at variable depths within the Earth, as well as from
the eventual consolidation of fragmented debris. Igneous rocks thus
occur in two ways, either as “extrusive” (on the surface) rocks or
as “intrusive” (below the surface) bodies. Intrusive rocks are also
called “plutonic” (Pluto, the Greek god of infernal regions,
therefore deep-seated) and extrusive rocks “volcanic.” The terms
intrusive and extrusive only refer to the place where the rock
solidified. Extrusive rocks cool rapidly because they have erupted at
the Earth’s surface, but intrusive rocks cool more slowly within an
insulating blanket of surrounding rocks into which they have been
emplaced. The rapid cooling of magma gives a fine-grained rock, which
may even be glassy, whereas slower cooling gives coarse-grained rock
with large crystals.
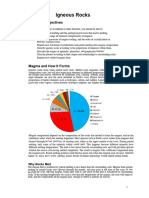
DISTRIBUTION OF IGNEOUS ROCKS
Igneous and metamorphic rocks make up 90–95% of the top 16 kilometers
(9.9 mi) of the Earth's crust by volume. Igneous rocks form about 15% of the
Earth's current land surface. Most of the Earth's oceanic crust is made of
igneous rock.
GRANITE
-rough-cut and polished granite is used as material for the construction of
building walls, bridge piers, monuments, pavements, road curbs, and other
exterior works.
-used as coarse aggregate in concrete, aggregates in road construction,
external wall cladding material, and ballast for railways.
SYENITE
-used as a dimension stone, for cement manufacturing, construction or road
aggregate, for landscaping, etc.
-used for manufacturing natural cement as well as Magnesium & Dolomite
Refractories.
DIORITE
-used as a base material in the construction of roads, buildings, and parking
areas. It is also used as a drainage stone and for erosion control. In the
dimension stone industry, diorite is often cut into facing stone, tile, ashlars,
blocking, pavers, curbing, and a variety of dimension stone products.
GABBRO
Gabbro is widely used as crushed stone for concrete aggregate, road base
material, and railroad ballast. Smaller quantities are cut and polished for
dimension stone and called black granite.
PEGMATITE
Pegmatite are used as architectural stone. If the pegmatite is sound and
attractive, it might be cut into slabs and polished for building facing,
countertops, tile or other decorative stone products and sold commercially as
a “granite.” Pegmatite is used in gemstone mining because of it has large
crystal minerals.
DOLERITE
Dolerite is one of the most widely used road pavement construction materials
in South Africa and is classified as a basic crystalline rock.
A form of dolerite, known as bluestone, is one of the materials used in
the construction of Stonehenge. Diabase also serves as local building
stone. In Tasmania, where it is one of the most common rocks found, it is
used for building, for landscaping and to erect dry-stone farm walls.
BASALT
Today, basalt is commonly used as crushed aggregate in construction
projects. Crushed basalt is used for road base, concrete aggregate, asphalt
pavement aggregate, railroad ballast, filter stone in drain fields. But, basalt is
also cut into dimension stone. In thin slabs it is used for building veneers,
flooring, etc.
You might also like
- Metamorphic, Igneous and Sedimentary Rocks : Sorting Them Out - Geology for Kids | Children's Earth Sciences BooksFrom EverandMetamorphic, Igneous and Sedimentary Rocks : Sorting Them Out - Geology for Kids | Children's Earth Sciences BooksNo ratings yet
- Rocks and The Rock Cycle: Powerpoint PresentationDocument39 pagesRocks and The Rock Cycle: Powerpoint PresentationPriana100% (3)
- What Are Igneous Rocks?Document7 pagesWhat Are Igneous Rocks?Arah Louise ApostolNo ratings yet
- Geo 222 Groupactivity 1 Bsce 2e Group 3Document8 pagesGeo 222 Groupactivity 1 Bsce 2e Group 3YUMUL, ANGELICA. CRUZNo ratings yet
- PETROLOGYDocument28 pagesPETROLOGYCamille T. PajarillagaNo ratings yet
- Rocks in GeologyDocument24 pagesRocks in GeologyQuantity SurveyorNo ratings yet
- Rocks: GEO101-Engineering Geology - Instructor: Engr. Karl Hendrix G. LontocDocument18 pagesRocks: GEO101-Engineering Geology - Instructor: Engr. Karl Hendrix G. LontocJhansen RamosNo ratings yet
- Kinds of Rocks Sedimentary RocksDocument2 pagesKinds of Rocks Sedimentary Rockslhors17No ratings yet
- Materia Stone Cha 2Document6 pagesMateria Stone Cha 2Yosef KirosNo ratings yet
- CE 212 - Rock CycleDocument18 pagesCE 212 - Rock CycleJulius CodiamatNo ratings yet
- Identification of Igneous Rock (Conclusion)Document1 pageIdentification of Igneous Rock (Conclusion)WHfamily100% (3)
- Igneous RocksDocument9 pagesIgneous RocksMartin Simon S Palero0% (1)
- Types of RocksDocument7 pagesTypes of RocksFebrianto Jeremy AllakNo ratings yet
- PetrologyDocument5 pagesPetrologyMar PalmaNo ratings yet
- Building MaterialsDocument5 pagesBuilding MaterialsasdasdadasaNo ratings yet
- Building StonesDocument27 pagesBuilding StonesJeric LaureanoNo ratings yet
- Volcanoes and Plutons: By: Group 2Document54 pagesVolcanoes and Plutons: By: Group 2Anonymous fr268tGNo ratings yet
- Types of Rocks AND ITS ExampleDocument18 pagesTypes of Rocks AND ITS ExampleGerlie ManiquizNo ratings yet
- Lecture 2-Rocks Rocks Are Grouped Into Three Types, Namely Igneous, Metamorphic and SedimentaryDocument13 pagesLecture 2-Rocks Rocks Are Grouped Into Three Types, Namely Igneous, Metamorphic and Sedimentaryeng20072007100% (1)
- Petrology NotesDocument6 pagesPetrology NotesLood RafaelNo ratings yet
- Kuliah 03 Teknologi Bahan, AgregatDocument93 pagesKuliah 03 Teknologi Bahan, AgregatDhanyNo ratings yet
- GranadaDocument1 pageGranadakhavishNo ratings yet
- Stone U1Document45 pagesStone U1mgsvettyNo ratings yet
- Igneous RocksDocument33 pagesIgneous RocksuunsyNo ratings yet
- Rock FormationDocument5 pagesRock FormationGerwin SilvestreNo ratings yet
- Geo ResearchDocument17 pagesGeo Researchdylas0079No ratings yet
- Earth Science Q1 Week2 - FSDocument11 pagesEarth Science Q1 Week2 - FSShemiah Rapah AntonioNo ratings yet
- Stone and Concrete MasonryDocument80 pagesStone and Concrete MasonryMaria VillanuevaNo ratings yet
- Rocks and GeologyDocument7 pagesRocks and GeologySealane TrayaNo ratings yet
- Igneous RocksDocument2 pagesIgneous RocksCyrusquinonesNo ratings yet
- StonesDocument111 pagesStonesSantosh Kumar MNo ratings yet
- Rocks and MineralsDocument5 pagesRocks and MineralsRachelle Monn OcsioNo ratings yet
- 2020 BUILDING TECHNOLOGY 1 Module 1 Lecture 2a - Stone and Concrete MasonryDocument41 pages2020 BUILDING TECHNOLOGY 1 Module 1 Lecture 2a - Stone and Concrete Masonrylia immie rigoNo ratings yet
- Earth and Life Lesson 4 RocksDocument66 pagesEarth and Life Lesson 4 RocksMagdalena TagubaNo ratings yet
- Assignment 4Document2 pagesAssignment 4Prince BalmojaNo ratings yet
- Igneous Sedimentary Metamorphic Rocks ClassDocument14 pagesIgneous Sedimentary Metamorphic Rocks ClasssolivalhovelyNo ratings yet
- Usp Sharing: Let's CheckDocument4 pagesUsp Sharing: Let's Checkronald miguelNo ratings yet
- Chapter Four Building Stone: I) Geological ClassificationDocument5 pagesChapter Four Building Stone: I) Geological ClassificationAbinet AlemuNo ratings yet
- Types of Rocks PDFDocument61 pagesTypes of Rocks PDFziyannn0408No ratings yet
- MINERALS & ROCKS by Mr. OgotDocument8 pagesMINERALS & ROCKS by Mr. Ogotfestus3ndundaNo ratings yet
- Cem Notes by K20ce029Document75 pagesCem Notes by K20ce029Bilal Ahmed BajkaniNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2 Two Arc BLDGDocument19 pagesChapter 2 Two Arc BLDGMikiasNo ratings yet
- Gy 402 2Document29 pagesGy 402 2eliamosha36No ratings yet
- Lecture Notes For Week 4 - Rocks and Minerals - Part 1Document65 pagesLecture Notes For Week 4 - Rocks and Minerals - Part 1Brent banallNo ratings yet
- Building Materials & ConstructionDocument20 pagesBuilding Materials & Constructionharshalraut1215No ratings yet
- 1 Rocks & Stones - 22591467 - 2023 - 11 - 11 - 21 - 52Document40 pages1 Rocks & Stones - 22591467 - 2023 - 11 - 11 - 21 - 52harshalraut1215No ratings yet
- IgneousDocument4 pagesIgneousHafit JuliantNo ratings yet
- PETROLOGY RevisedDocument10 pagesPETROLOGY RevisedKangNo ratings yet
- Muhammad Ghazi Duggal, 241553898Document5 pagesMuhammad Ghazi Duggal, 241553898ghazi duggalNo ratings yet
- Rocks and MineralsDocument6 pagesRocks and Mineralsrosana f.rodriguezNo ratings yet
- Building Stone Specific ObjectivesDocument13 pagesBuilding Stone Specific ObjectivesDavid lumbasiaNo ratings yet
- Group 2 Rocks Handouts 1Document22 pagesGroup 2 Rocks Handouts 1Liezel VillaruzNo ratings yet
- CE 203 Lecture05Document29 pagesCE 203 Lecture05alamin shawonNo ratings yet
- Igneous RocksDocument7 pagesIgneous RocksHamzaBaigNo ratings yet
- RocksDocument14 pagesRocksNovrei YucsonNo ratings yet
- Rocks, Weathering and Landforms o LevelDocument16 pagesRocks, Weathering and Landforms o LevelmanisinkomoNo ratings yet
- Janua Rhey LungayDocument4 pagesJanua Rhey LungayJanua RheyNo ratings yet
- Sedimentary RocksDocument7 pagesSedimentary RocksAllesandro AlbertNo ratings yet
- W3M1 - Igneous RocksDocument39 pagesW3M1 - Igneous Rocksaxieinvestment550No ratings yet
- Classification of Rocks Lecture-3Document20 pagesClassification of Rocks Lecture-3Dr. Daljeet Singh SidhuNo ratings yet
- Petrology Part 2Document12 pagesPetrology Part 2IvoNo ratings yet
- IN THE DAYS OF THY YOUTHDocument17 pagesIN THE DAYS OF THY YOUTHLeah FernandoNo ratings yet
- What Drives Your Life Ecclesiastes 4 Verse 4Document20 pagesWhat Drives Your Life Ecclesiastes 4 Verse 4Leah FernandoNo ratings yet
- Believing Changes Your HeartDocument19 pagesBelieving Changes Your HeartLeah FernandoNo ratings yet
- Be Firm in Your FightDocument15 pagesBe Firm in Your FightLeah FernandoNo ratings yet
- BLESSINGS IN DISGUISE (Romans 8 Verse 18)Document9 pagesBLESSINGS IN DISGUISE (Romans 8 Verse 18)Leah FernandoNo ratings yet
- Geological Classifications and Characteristics of StoneDocument6 pagesGeological Classifications and Characteristics of StoneFretzie CalvesNo ratings yet
- Earth and Life Science First Quarterly Exam 2023 2024 Answer KeyDocument5 pagesEarth and Life Science First Quarterly Exam 2023 2024 Answer KeyDE BELEN JEFFREYNo ratings yet
- Earth & Life Science Lesson 3: The Three Main Categories of RocksDocument30 pagesEarth & Life Science Lesson 3: The Three Main Categories of RocksTeacher MelNo ratings yet
- Geography of East AfricaDocument84 pagesGeography of East AfricaMatabaro Benjamin50% (2)
- 4-Core Subhect-Science-11-Earth - Life Science-Q1-Module-4Document25 pages4-Core Subhect-Science-11-Earth - Life Science-Q1-Module-4agnes joy cepeNo ratings yet
- Andesite Rock (Igneous Rock) ExtrusiveDocument6 pagesAndesite Rock (Igneous Rock) ExtrusiveDewanshu VikramNo ratings yet
- PETROLOGYDocument50 pagesPETROLOGYSarmiento August M.No ratings yet
- Roads 1Document42 pagesRoads 1Musiime AlvinNo ratings yet
- 03 Rocks Key RDocument30 pages03 Rocks Key RRaden AfNo ratings yet
- International Earth Science Olympiad (IESO) : RocksDocument14 pagesInternational Earth Science Olympiad (IESO) : RocksansariNo ratings yet
- Plutonism & Volcanism: Nica B. Raymundo STEM 11-1ADocument13 pagesPlutonism & Volcanism: Nica B. Raymundo STEM 11-1ATina YusonNo ratings yet
- Rocks ClassificationDocument4 pagesRocks ClassificationrockysheddyNo ratings yet
- 4 - Cluster 4 - Rocks, Minerals & Erosion - Manitoba - Grade 4 - Distance LearningDocument48 pages4 - Cluster 4 - Rocks, Minerals & Erosion - Manitoba - Grade 4 - Distance LearningZabrinaNo ratings yet
- Igneous RockDocument2 pagesIgneous RockVenice EdañoNo ratings yet
- Hydrological Study - MineSitesDocument33 pagesHydrological Study - MineSitesDawood MuhammadNo ratings yet
- Types of RocksDocument20 pagesTypes of Rockscourse heroNo ratings yet
- Els m4 RocksDocument27 pagesEls m4 RocksShyra mae PortalizaNo ratings yet
- Rotary - Blasthole Brilling HandbookDocument76 pagesRotary - Blasthole Brilling HandbookLi SaldivarNo ratings yet
- Ce212 Lecture 2 - Geology For Civil Engineering (Geological Concepts Related To Civil Engineering)Document5 pagesCe212 Lecture 2 - Geology For Civil Engineering (Geological Concepts Related To Civil Engineering)KIM JINHWANNo ratings yet
- Igneous RocksDocument15 pagesIgneous RocksRowelyn BakekeNo ratings yet
- A Narrative Report On The Three Major Classes of RocksDocument2 pagesA Narrative Report On The Three Major Classes of RocksRizafel Joy CuencaNo ratings yet
- Types of Rocks Igneous Rock: There Are Two Basic TypesDocument4 pagesTypes of Rocks Igneous Rock: There Are Two Basic TypesBELENNo ratings yet
- 4.3:4.4 GizmoDocument5 pages4.3:4.4 GizmoJaedyn CNo ratings yet
- Minerals and Rocks: Lesson 6Document38 pagesMinerals and Rocks: Lesson 6April Grace MontebanoNo ratings yet
- Physical Geography Mains (GS1) PYQ Notes 2014-2022Document13 pagesPhysical Geography Mains (GS1) PYQ Notes 2014-2022fands sNo ratings yet
- The Rock CycleDocument3 pagesThe Rock CycleMeet PatelNo ratings yet
- Earth Science - Module 2Document38 pagesEarth Science - Module 2Catherine A. PerezNo ratings yet
- 01 Igneous PETROLOGY NotesDocument11 pages01 Igneous PETROLOGY NotesdaanaahishmaelsNo ratings yet
- Rocks and MineralsDocument38 pagesRocks and Mineralsmerry menesesNo ratings yet