Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Mp-7
Mp-7
Uploaded by
Para Commando0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
1 views1 pageCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pdf or txt
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
1 views1 pageMp-7
Mp-7
Uploaded by
Para CommandoCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pdf or txt
You are on page 1of 1
Course code: MP103
L T P C
4 1 0 5
ATOMIC AND NUCLEAR PHYSICS
60 Hrs. Lectures
Objectives:
• To understand the structure of atom and binding forces
• To learn about angular and magnetic momentum and periodicity of elements.
• To learn about radioactive law and nuclear reactions
Unit 1: Atomic Structure of Matter
Thomson, Rutherford Model - Bohr’s theory of Hydrogen atom - Drawbacks of these models -
Bohr’s correspondence principle - Sommerfeld extension to Bohr model - Frank and Hertz
experiment - Types of spectra - Emission and absorption line spectra - Fluorescence and
Phosphorescence-Characteristics of Vector atom model - Related Problems
Unit 2: Alkali spectra, space quantization and Periodicity
Angular and magnetic momenta - Orbital angular momentum - Electron spin and quantum
number-Total angular momentum and magnetic moment of electron-Magnetic quantum numbers
- spin orbit interaction - LS Coupling scheme-selection rules - Pauli exclusion principle-Electron
configuration of atom - Periodic Table - Zeeman effect - Lande’s - g-factor - Paschen back effect -
Stark effect - Stern Gerlach experiment - Hyperfine structure of spectral lines.
Unit 3: Nuclear force and binding
Properties of nuclear force - Ground state properties of deuteron - square well solution of
deuteron; Low energy neutron proton scattering - limits of energy for the scattering of different
partial waves - Binding energy - Weizacker’s semi empirical mass formula - Evidence of shell effects
- Single particle energy levels for infinite square well, harmonic oscillator with spin orbit potential -
Application of shell model for spin and parity.
Unit 4: Radioactive disintegration
Properties of radioactive rays - Law of radioactivity - Radioactive equilibrium - Radioactive series -
Range of alpha particles - Alpha spectrum and Fine structure - Alpha particle disintegration Energy -
Gamow’s theory of Alpha decay - Energies of Beta decay - Beta ray Spectra - Pauli’s neutrino
hypothesis - Properties of neutrino - Gamma emission - Selection rules-internal conversion -
Application of semi empirical formula for alpha decay - mass parabola for stability of nuclei against
beta decay - Fission process on the basis of liquid drop model-Nuclear fission energetic-stability
limits against spontaneous fission - Potential for fission-Bohr - wheeler model.
Unit 5: Nuclear reactions
Types of nuclear reaction - Conservation laws in nuclear reactions- Balance of Mass and Energy in
nuclear reactions - The Q equation and its solution-Proton, deuteron, neutron and alpha induced
reactions-cross section of nuclear reactions - separation of center of mass motion in two body
problem - Partial wave method for scattering and reaction cross section - Compound nucleus
hypothesis - Breitt Wigner one level formula.
You might also like
- commonFileDownloader JSPDocument1 pagecommonFileDownloader JSPBoot BoxNo ratings yet
- Msc. Sem 3Document4 pagesMsc. Sem 3HNHNo ratings yet
- B.Sc. III - Atomic and Nuclear PhysicsDocument3 pagesB.Sc. III - Atomic and Nuclear PhysicsDr. Satish MahadikNo ratings yet
- SSP SyllabusDocument2 pagesSSP SyllabusHaze Subin CNo ratings yet
- I V Savelyev Physics General Course Vol 3Document319 pagesI V Savelyev Physics General Course Vol 3thuongtunhienNo ratings yet
- S.no TopicDocument1 pageS.no TopicsuryaNo ratings yet
- BSC Syllabus at MWU 2012 - 4th SemesterDocument16 pagesBSC Syllabus at MWU 2012 - 4th SemesterKeshav PaudelNo ratings yet
- MSC Final Year Syllabus Semester-Iii: S. No. Contact HoursDocument13 pagesMSC Final Year Syllabus Semester-Iii: S. No. Contact HoursPritam PattanayakNo ratings yet
- MPHS 41 Spectroscopy SLMDocument162 pagesMPHS 41 Spectroscopy SLMSp MNo ratings yet
- Srmjeee SyllabusDocument9 pagesSrmjeee SyllabusSuraj KumarNo ratings yet
- Physics 4061-5061 - Lecture TopicsDocument4 pagesPhysics 4061-5061 - Lecture TopicsNashNo ratings yet
- Part Iii: Syllabus For Entrance Examination Srmjeee (Ug) B.Tech and Health Science (Ug Programs)Document10 pagesPart Iii: Syllabus For Entrance Examination Srmjeee (Ug) B.Tech and Health Science (Ug Programs)Sanskriti MouryaNo ratings yet
- MSC Physics Semester IV, VNSGUDocument19 pagesMSC Physics Semester IV, VNSGUTushar Tk VaghasiyaNo ratings yet
- Srmjeee SyllabusDocument9 pagesSrmjeee SyllabusMd AshfaqNo ratings yet
- 11 - B.Sc.,Physics AlliedDocument8 pages11 - B.Sc.,Physics Alliedroby sorianoNo ratings yet
- Course: Department Specific Elective 2-: HPHDS5021T Nuclear and Particle PhysicsDocument3 pagesCourse: Department Specific Elective 2-: HPHDS5021T Nuclear and Particle PhysicsGrim Reaper Kuro OnihimeNo ratings yet
- 28.3 Physica UG Question Paper Pattern of 5 & 6 Sem PDFDocument41 pages28.3 Physica UG Question Paper Pattern of 5 & 6 Sem PDFthomasgunaseelanNo ratings yet
- PH802 - Atomic and Molecular Spectroscopy (2020) - IRISDocument2 pagesPH802 - Atomic and Molecular Spectroscopy (2020) - IRISken adamsNo ratings yet
- PhysicsDocument3 pagesPhysicsak86No ratings yet
- School of Aeronautics Entrance Examination Syllabus: Syllabus For Physics 1: Units and MeasurementDocument9 pagesSchool of Aeronautics Entrance Examination Syllabus: Syllabus For Physics 1: Units and Measurementquami3quartsNo ratings yet
- SAT Subject Test - PhysicsDocument2 pagesSAT Subject Test - PhysicsBosserz ThanawitNo ratings yet
- AMP SyllabusDocument2 pagesAMP SyllabusfkdjdfjkNo ratings yet
- SyllabusDocument11 pagesSyllabusSavitri BhandariNo ratings yet
- Physics CopoDocument42 pagesPhysics CopoAbujar AnsariNo ratings yet
- PHY1010Document3 pagesPHY1010ms harshithaNo ratings yet
- 2023 24 Syllabus PH122I2C PH222I2CDocument5 pages2023 24 Syllabus PH122I2C PH222I2Caman.kekkarNo ratings yet
- Mathematics-I: Course OutcomesDocument25 pagesMathematics-I: Course OutcomesNishant B MayekarNo ratings yet
- Master in Nuclear Engineering: Second Year - M2Document15 pagesMaster in Nuclear Engineering: Second Year - M2Nur Hidayah AhmadNo ratings yet
- Engg-Phys Course NITADocument4 pagesEngg-Phys Course NITAAkash KumarNo ratings yet
- Research Accomplishments: Summary of My PHD WorkDocument5 pagesResearch Accomplishments: Summary of My PHD WorkVandana SharmaNo ratings yet
- PHY704 Review of Modern PhysicsDocument42 pagesPHY704 Review of Modern Physicsravinesh rattanNo ratings yet
- PHY704 Review of Modern PhysicsDocument42 pagesPHY704 Review of Modern Physicsravinesh rattanNo ratings yet
- M.SC Entrance Exam Syllabus 2024Document10 pagesM.SC Entrance Exam Syllabus 20247sakthivelkumar2004No ratings yet
- Syllabus B.Tech, B.Des and Under Graduate Programs in Health SciencesDocument11 pagesSyllabus B.Tech, B.Des and Under Graduate Programs in Health SciencesChakradhar DNo ratings yet
- Vitee SyllabusDocument8 pagesVitee Syllabusmamtakalra3632No ratings yet
- VITEEE 2024 SyllabusDocument10 pagesVITEEE 2024 Syllabussaikatsarkar409No ratings yet
- Physical Methods in ChemistryDocument117 pagesPhysical Methods in Chemistrypranjalmanitripathi11No ratings yet
- Bpl-401: Elements of Modern PhysicsDocument8 pagesBpl-401: Elements of Modern Physicsasanamikasingh8No ratings yet
- BScPhysics13Batch1to6Semester PDFDocument39 pagesBScPhysics13Batch1to6Semester PDFSidharth SinghNo ratings yet
- Phy6002 - Nuclear-And-Particle-Physics - Eth - 1.0 - 40 - Phy6002 - 55 AcpDocument2 pagesPhy6002 - Nuclear-And-Particle-Physics - Eth - 1.0 - 40 - Phy6002 - 55 AcpAnandajithNo ratings yet
- National University of Engineering: Physics ProgramDocument2 pagesNational University of Engineering: Physics ProgramRicardo ParraNo ratings yet
- Course Description Physics Semester-II: Course Instructor Anuj Kumar Department of Physics, Email:anuj - Kumar@jiet - Ac.inDocument11 pagesCourse Description Physics Semester-II: Course Instructor Anuj Kumar Department of Physics, Email:anuj - Kumar@jiet - Ac.injeevarvinderNo ratings yet
- Std12 Phy EM 1Document237 pagesStd12 Phy EM 1vijaiNo ratings yet
- Syllabus For 2nd Sem (2020) Admitted BatchDocument12 pagesSyllabus For 2nd Sem (2020) Admitted BatchAshutoshNo ratings yet
- I Year CoursesDocument29 pagesI Year Coursesabi niveshNo ratings yet
- Lab Asst HSC STD EngDocument9 pagesLab Asst HSC STD EngkumarNo ratings yet
- Indian Institute of Technology Roorkee: PhysicsDocument3 pagesIndian Institute of Technology Roorkee: PhysicsSankalp RajNo ratings yet
- Scientific Officer PhysicsDocument3 pagesScientific Officer PhysicsabduNo ratings yet
- New Syllabus Physics 5 & 6 Sem PDFDocument41 pagesNew Syllabus Physics 5 & 6 Sem PDFthomasgunaseelanNo ratings yet
- Review of Laser-Driven Ion Sources and Their Applications PDFDocument72 pagesReview of Laser-Driven Ion Sources and Their Applications PDFAjit UpadhyayNo ratings yet
- Syllabus of Minor in Physics, May 2024 - FinalDocument3 pagesSyllabus of Minor in Physics, May 2024 - Finalanagha.karneNo ratings yet
- Chemistry PGDocument33 pagesChemistry PGhrishikeshanandNo ratings yet
- Allied Physics PDFDocument9 pagesAllied Physics PDFrajia1981No ratings yet
- B.SC 2nd and 3rd Year Syllabus SVUDocument16 pagesB.SC 2nd and 3rd Year Syllabus SVUSrinivasulu Pudu100% (1)
- CHEM 359 Atomic and Molecular Spectroscopy Fall 2013Document6 pagesCHEM 359 Atomic and Molecular Spectroscopy Fall 2013abdooufNo ratings yet
- Date: 09.01.2024Document3 pagesDate: 09.01.2024Elder DragonNo ratings yet
- Syllabus For BITSATDocument10 pagesSyllabus For BITSATNilesh PatilNo ratings yet
- JUT Syllabus Chemistry-I Bit SindriDocument4 pagesJUT Syllabus Chemistry-I Bit SindriPalNo ratings yet
- SyllabusDocument4 pagesSyllabusSanthana KaruppuNo ratings yet
- mp90Document1 pagemp90Para CommandoNo ratings yet
- Mp-9Document1 pageMp-9Para CommandoNo ratings yet
- Mp-6Document1 pageMp-6Para CommandoNo ratings yet
- Expenses 1Document5 pagesExpenses 1Para CommandoNo ratings yet
- Big Bang Theory Upsc Notes 86Document2 pagesBig Bang Theory Upsc Notes 86Para CommandoNo ratings yet
- Dashboard 2 - 2024-02-08T143807.301Document1 pageDashboard 2 - 2024-02-08T143807.301Para CommandoNo ratings yet
- Expense InsightsDocument1 pageExpense InsightsPara CommandoNo ratings yet
- Radio Communications Systems II - Session 2 - AdU - Post Test 2Document3 pagesRadio Communications Systems II - Session 2 - AdU - Post Test 2Eugene Embalzado Jr.No ratings yet
- Lecture Notes in Transmission Media and Antenna Systems: Mapua Institute of Technology School of EeceDocument115 pagesLecture Notes in Transmission Media and Antenna Systems: Mapua Institute of Technology School of EecejobertNo ratings yet
- Tutorial Problems-Unit 1-75 PercDocument5 pagesTutorial Problems-Unit 1-75 PercSuseel Jai Krishnan0% (1)
- Excited States and Photochemistry of Organic Molecules - Martin KlessingerDocument281 pagesExcited States and Photochemistry of Organic Molecules - Martin KlessingerCarol SantosNo ratings yet
- X-Ray Absorption Edges, Characteristic X-Ray LinesDocument5 pagesX-Ray Absorption Edges, Characteristic X-Ray LinesUnknownNo ratings yet
- Chapter 21 Nuclear Physics Exercise Short QuestionsDocument4 pagesChapter 21 Nuclear Physics Exercise Short Questionsmursaleen100% (2)
- Padhle 10th - Human Eye & The Colourful World + Integrated PYQsDocument18 pagesPadhle 10th - Human Eye & The Colourful World + Integrated PYQsMadhu Urs100% (1)
- Plancks Constant Version 2016-1Document10 pagesPlancks Constant Version 2016-1MR XNo ratings yet
- Mechanical Vibrations - VP SinghDocument131 pagesMechanical Vibrations - VP SinghROSHNI MERANINo ratings yet
- Physics 17 - General Wave Properties-OrigDocument43 pagesPhysics 17 - General Wave Properties-OrigRodel VerzosaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 11 - Projectiles and Circular MotionDocument56 pagesChapter 11 - Projectiles and Circular Motionascd_msvuNo ratings yet
- X Ray Diffraction Safety InformationDocument48 pagesX Ray Diffraction Safety Informationrenjith2017100% (1)
- Atmosphere: Study Guide For Module No. 6Document12 pagesAtmosphere: Study Guide For Module No. 6Maia GabrielaNo ratings yet
- Minor Project MSS381Document12 pagesMinor Project MSS381Muhamad SyahmiNo ratings yet
- Buoyancy Flow in Water: Created in COMSOL Multiphysics 5.5Document34 pagesBuoyancy Flow in Water: Created in COMSOL Multiphysics 5.5Ahmed Al SayedNo ratings yet
- Master: A Study of Vertical and Horizontal Earthquake SpectraDocument153 pagesMaster: A Study of Vertical and Horizontal Earthquake SpectraAlberto CaínNo ratings yet
- Examen EN1110 TTA PDFDocument2 pagesExamen EN1110 TTA PDFsneakstones9540No ratings yet
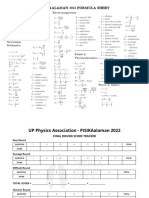
- UPPA PISIKAalaman 2022 Formula and Score Sheet2Document2 pagesUPPA PISIKAalaman 2022 Formula and Score Sheet2Jason YabutNo ratings yet
- Projectile MotionDocument46 pagesProjectile MotionJasha KimNo ratings yet
- Electronics 11 02233 v2Document23 pagesElectronics 11 02233 v2calvin chengNo ratings yet
- Physics WrittenDocument66 pagesPhysics Writtenhp464km2tsNo ratings yet
- Chapter 8Document64 pagesChapter 8aungchanmyatpaingNo ratings yet
- Multiple Choice Portion: Unit 1: VectorsDocument7 pagesMultiple Choice Portion: Unit 1: VectorsMr saifan and Mr shehzadNo ratings yet
- Lecture 5 HvacDocument42 pagesLecture 5 HvacJohn Bennett100% (2)
- Dynamics of Rigid BodiesDocument18 pagesDynamics of Rigid BodiesPatrick Laurence FalcunayaNo ratings yet
- RRB JE - General Awareness + General ScienceDocument17 pagesRRB JE - General Awareness + General ScienceRitesh KaraleNo ratings yet
- Objective Neet Vol 2 DC PandeyDocument500 pagesObjective Neet Vol 2 DC PandeyDx MineNo ratings yet
- EM Spectrum Physics Answer KeyDocument4 pagesEM Spectrum Physics Answer KeyanashechirenjeNo ratings yet
- Oscillarty MotionDocument20 pagesOscillarty MotionAhmed NegmNo ratings yet
- Summative Test Physical ScienceDocument5 pagesSummative Test Physical ScienceARNEL METILLONo ratings yet