Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Algae I KEMSEN World of Botany
Algae I KEMSEN World of Botany
Uploaded by
zakirkashan720Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Algae I KEMSEN World of Botany
Algae I KEMSEN World of Botany
Uploaded by
zakirkashan720Copyright:
Available Formats
KEMSEN World of Botany
Exploring the Plants from Roots to Petals & Bridging the Gap b/w Plants and People
Algae Phycology
Algae are defined as a group of predominantly aquatic, photosynthetic Protists, and nucleus-bearing organisms
that lack the true roots, stems, leaves, and specialized multicellular reproductive structures of plants
(Thallophytes).
History: Aristotle, a Greek philosopher and scientist, is considered the father of algae. He was the first to
describe and classify algae in his book "Historia Plantarum" in the 4th century BCE.
Carl Linnaeus coined the term algae (1753).
Classification: Algae possess diverse characters in their pigments, nature of reserve food, nature of cilia etc.
According to these morphological and physiological differences they are classified by many people.
Fritsch (1935) classified the whole of the algae into Eleven Classes on the basis of type of pigments, nature of
reserve food material, mode of reproduction etc. The classification is published in his book titled
“The Structure and Reproduction of Algae”. They are:
Class Pigments Flagella Reserve Food Examples
Chlorophyceae Chlorophyll a & b Flagella (2-4) Starch Chlamydomonas, Volvox,
Green Algae & Carotenoids Chlorella, Scenedesmus
Xanthophyceae Chl a & b 2 Unequal Oil Vaucheria
Yellow Green Algae Xanthophyll is Flagella (Pyrenoids absent)
predominant
Chrysophyceae Chlorophyll a & b 2 Unequal Laminaran Ochromonas
Golden-Brown Algae & Carotenoids Flagella Chrysosphaera
Bacillariophyceae Chlorophyll a & c 1 Flagella Fat Pinnularia
Diatoms & Carotenoids (Only In Male) Volutin
Cryptophyceae Chl a & c 2 Unequal Starch Chroomonas
Cryptomonads Xanthophyll is Flagella
predominant
Dinophyceae Chl a & c 2 Unequal Starch Dinoflagellate
Pyrrophyta Xanthophyll is Flagella Oil
predominant
Chloromonadineae Chl a & b 2 Equal Flagella Oil Heterosigma
Raphidophytes Xanthophyll is
predominant
Euglenophyceae Chl a & b 1 or 2 Flagella Polysaccharide Euglena
Euglinids Paramylon
Phaeophyceae Chl a, c, 2 Unequal Mannitol as well as Ectocarpus
Brown Algae Carotenes, Flagella Laminarin and Fats Sargassum
Xanthophylls, Kelps
Not chl b
Rhodophyceae Phycoerythrin & No Flagella Floridean Starch Batrachospermum,
Red Algae Phycocyanin, Chl- Polysiphonia
a, d & Carotenes
Myxophyceae Chlorophyll, No Flagella Sugars Oscillatoria
Cyanophyceae or Blue Carotenes, Glycogen Nostoc
Green Algae Xanthophylls,
Phycocyain &
Phycoerythrin
Economic Importance Life Cycles in Algae
Agar – Agar: Gelidium,Gracillaria, Gigartina A. Haplontic life cycle:
Alginic Acid: Laminaria Present in charophyta, spirogyra, Ulothrix,
Carragenin: Chondrus crispus Chlamydomonas and Oedogonium
Iodine: Kelps B. Diplohaplontic life cycle:
Fodder: Kelps, Sargassum Ulva, Cladophora and Ectocarpus
Antibiotics: Chlorellin from Chlorella C. Haplobiotic or Haplohaplontic:
Minerals: Kelps and Sea-Weeds Primitive Red Algae Nemalion
Sewage disposal Chlamydomonas, D. Haplohaplohaplontic: Batrachospermum
Euglena and Chlorella E. Diplodiplohaplontic: Polysiphonia
KEMSEN Competitive Exam Preparations
You might also like
- Algae - Classification (Fritsch PDFDocument5 pagesAlgae - Classification (Fritsch PDFCDB 1st Semester 2077100% (6)
- FLAVONOIDDocument35 pagesFLAVONOIDanisahanifatinrNo ratings yet
- Classification by F.E FRITSCH: AlgaeDocument15 pagesClassification by F.E FRITSCH: AlgaeJatin SwamiNo ratings yet
- Chart - Kingdom ProtistaDocument9 pagesChart - Kingdom ProtistaRegina AbesamisNo ratings yet
- 9.algaeDocument5 pages9.algaeMukbsNo ratings yet
- 9.algaeDocument5 pages9.algaeMukbsNo ratings yet
- Protistans (English Version)Document8 pagesProtistans (English Version)Brian Adam MJfansNo ratings yet
- Diversity of Microorganisms: Part 2: Eucaryotic MicrobesDocument26 pagesDiversity of Microorganisms: Part 2: Eucaryotic MicrobesSri Widia NingsihNo ratings yet
- Bio 102 - Lec 03Document43 pagesBio 102 - Lec 03Aaron John CorpuzNo ratings yet
- Overview of Algae: Presented By:-Neha Sharma Presented To: - Dr. Richa TandonDocument32 pagesOverview of Algae: Presented By:-Neha Sharma Presented To: - Dr. Richa TandonNikhil SinghNo ratings yet
- AlgaeDocument34 pagesAlgaekapil singh solankiNo ratings yet
- Red AlgaeDocument4 pagesRed Algaecastillochristina53No ratings yet
- Types of Algae and Their Pigments Characteristics RepresentatorsDocument1 pageTypes of Algae and Their Pigments Characteristics RepresentatorsManja ĆetkovićNo ratings yet
- Algal PresentationDocument31 pagesAlgal Presentationjeque661100% (3)
- 3 - General CharacteristicsDocument15 pages3 - General CharacteristicsLeslie Ann Ü Dag-umanNo ratings yet
- Algae 1Document31 pagesAlgae 1Biotechnology CaspianNo ratings yet
- Chemotaxonomy Taxonomic EvidencesDocument30 pagesChemotaxonomy Taxonomic EvidencesLouNo ratings yet
- 1.4.1 Eukaryotes - Fungi, Algae, Protozoan - Structure, ClassificationDocument31 pages1.4.1 Eukaryotes - Fungi, Algae, Protozoan - Structure, Classificationjumbergy01No ratings yet
- AlgaeDocument7 pagesAlgaeRavi NagraNo ratings yet
- Plant Kingdom (L2) - 2nd JuneDocument43 pagesPlant Kingdom (L2) - 2nd JuneUpal PramanickNo ratings yet
- Algae Classification and Characters: Phylum Classes Common Names/Examples Food Storage Nutrition Pigments ChromophytaDocument2 pagesAlgae Classification and Characters: Phylum Classes Common Names/Examples Food Storage Nutrition Pigments ChromophytaSimranjit KaurNo ratings yet
- Chlorophyta & EuglenophytaDocument17 pagesChlorophyta & EuglenophytaNia AnandaNo ratings yet
- Classification of Algae by G.M SmithDocument45 pagesClassification of Algae by G.M SmithSarah Pavu100% (2)
- Day 2Document15 pagesDay 2saifali986254No ratings yet
- Types of AlgaeDocument12 pagesTypes of AlgaeHumairah ShabriNo ratings yet
- AlgaeDocument1 pageAlgaeKaren Aki HuangNo ratings yet
- AlgaeDocument34 pagesAlgaeAnand KumarNo ratings yet
- Training Manual On Live Feed - 1Document16 pagesTraining Manual On Live Feed - 1anusoumyaNo ratings yet
- KINGDOM Plantae + Algae For StudentsDocument8 pagesKINGDOM Plantae + Algae For Studentsraahat soniNo ratings yet
- Olutola Assignment MCBDocument7 pagesOlutola Assignment MCBOLUTOLA ADEMOLANo ratings yet
- LC-UV-HRMS dereplication of secondary metabolites from Brazilian Vernonieae (Asteraceae) species supported through in-house databaseDocument12 pagesLC-UV-HRMS dereplication of secondary metabolites from Brazilian Vernonieae (Asteraceae) species supported through in-house databaseJonathanNo ratings yet
- Biology of Scarabaeidad: Department of Entomology, Oregon State College, Corvallis, OregonDocument24 pagesBiology of Scarabaeidad: Department of Entomology, Oregon State College, Corvallis, OregonEugene QuahNo ratings yet
- Higher Secondary Botany Short Notes DR Anil HssliveDocument15 pagesHigher Secondary Botany Short Notes DR Anil Hsslivetobyviru2255No ratings yet
- Comparative Studies On Chlorophyll Concentration in Some Important Plant FamiliesDocument7 pagesComparative Studies On Chlorophyll Concentration in Some Important Plant FamiliesANMOL RajputNo ratings yet
- Screening of Mushrooms Bioactivity Piceatannol Was IdentifiedDocument11 pagesScreening of Mushrooms Bioactivity Piceatannol Was Identifiedela.sofiaNo ratings yet
- Unit 4 MODULE 1 BIODIVERSITYDocument7 pagesUnit 4 MODULE 1 BIODIVERSITYLovely Reianne Rosita ManigbasNo ratings yet
- TLCand HPLCidentificationofflavonoidsDocument8 pagesTLCand HPLCidentificationofflavonoidsNDung NDungNo ratings yet
- General Characteristics of AlgaeDocument21 pagesGeneral Characteristics of AlgaeLeslie Ann Ü Dag-umanNo ratings yet
- Red Algae Short NotesDocument4 pagesRed Algae Short NotesAniket kashyapNo ratings yet
- Art Ingles FlavonoideDocument8 pagesArt Ingles FlavonoideDara ApolinarioNo ratings yet
- β-Cyclodextrins as Carriers of Monoterpenes into theDocument9 pagesβ-Cyclodextrins as Carriers of Monoterpenes into theShield YggdrasilNo ratings yet
- Archae 1Document30 pagesArchae 1Sabiha SheikhNo ratings yet
- Liu IIIDocument8 pagesLiu IIIaji subaktiNo ratings yet
- Classification of Algae - FritchDocument4 pagesClassification of Algae - Fritchsharina NNo ratings yet
- Chlo Rophy TaDocument6 pagesChlo Rophy TaTemiloluwa OluwasegunNo ratings yet
- Classification of AlgaeDocument20 pagesClassification of AlgaeAditya ShawNo ratings yet
- Bahan Alam Laut (Alga)Document22 pagesBahan Alam Laut (Alga)bn_butonNo ratings yet
- Lactic Acid Isolated From Jalapeno PepperDocument9 pagesLactic Acid Isolated From Jalapeno PepperIesanu MaraNo ratings yet
- Phylum AquificiaeDocument2 pagesPhylum AquificiaeAndreu Angeles2No ratings yet
- Ekologi Mikroalga - 2015Document36 pagesEkologi Mikroalga - 2015Dewi S. GadiNo ratings yet
- Carotenoid Content of Chlorophycean Micro Algae Factors Determining Lutein Accumulation in Muriel Lops Is Sp. ChlorophytaDocument9 pagesCarotenoid Content of Chlorophycean Micro Algae Factors Determining Lutein Accumulation in Muriel Lops Is Sp. ChlorophytaVinit BajajNo ratings yet
- II ME NRP B SS 02. Plant KingdomDocument5 pagesII ME NRP B SS 02. Plant KingdomAmit RavindhraNo ratings yet
- How Are Chromobionta Different From The Other Stramenopiles?Document19 pagesHow Are Chromobionta Different From The Other Stramenopiles?sheilaNo ratings yet
- Algae NotesDocument20 pagesAlgae NotesDHARMARAj100% (2)
- Practical Paper 1Document26 pagesPractical Paper 1Ashika AshuNo ratings yet
- Classification of AlgaeDocument10 pagesClassification of AlgaeKrishna Santhosh SanthoshNo ratings yet
- ALKALOIDSDocument12 pagesALKALOIDSAkanksha SharmaNo ratings yet
- Divisi Rhodophyta (The Red Alga) One Classes: RhodophyceaeDocument11 pagesDivisi Rhodophyta (The Red Alga) One Classes: Rhodophyceaerheea_chaNo ratings yet
- General Characters of AlgaeDocument50 pagesGeneral Characters of AlgaeAnilNo ratings yet
- The Total Synthesis of Natural ProductsFrom EverandThe Total Synthesis of Natural ProductsJohn ApSimonNo ratings yet
- Cross Sections of Leaf Stem and RootDocument15 pagesCross Sections of Leaf Stem and Rootlwandlemkhonza96No ratings yet
- Activity Sheet 1 in General Biology - 02Document4 pagesActivity Sheet 1 in General Biology - 02Julianne Maxine FloresNo ratings yet
- Laboratory Exercise 1Document8 pagesLaboratory Exercise 1Xyrene DelloroNo ratings yet
- 1.6 Plantae Bryophytes PteridophytesDocument73 pages1.6 Plantae Bryophytes PteridophytesaixyaehNo ratings yet
- Photosynthetic Plant AlliesDocument11 pagesPhotosynthetic Plant AlliesJohn Christian BorromeoNo ratings yet
- Plant Kingdom - Practice SheetDocument8 pagesPlant Kingdom - Practice Sheetxsparxx16No ratings yet
- Kingdom Plantae Nonvascular and Seedless PlantsDocument11 pagesKingdom Plantae Nonvascular and Seedless PlantsMihnea RotaruNo ratings yet
- What Is Aquatic Botany and Why Algae Are Plants The Importance of Non Taxonomic Terms For Groups of OrganismsDocument5 pagesWhat Is Aquatic Botany and Why Algae Are Plants The Importance of Non Taxonomic Terms For Groups of Organismseunice osei owusuNo ratings yet
- Plenary 2 - Mr. Pedrosa IIIDocument36 pagesPlenary 2 - Mr. Pedrosa IIICalamianes Seaweed Marketing CooperativeNo ratings yet
- Lab Activity 5: Plant Morphology: StemDocument5 pagesLab Activity 5: Plant Morphology: StemPaulNo ratings yet
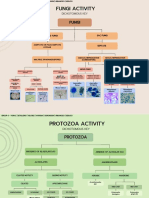
- Group 6 Fungi and Protozoa Activity 1Document2 pagesGroup 6 Fungi and Protozoa Activity 1严子明 Renz Ryan SevillenoNo ratings yet
- Kontrak Profung 2020Document13 pagesKontrak Profung 2020RofiqoNo ratings yet
- 18958-Article Text-39255-1-10-20230501Document7 pages18958-Article Text-39255-1-10-20230501dimas aryaNo ratings yet
- Protists Review WSDocument4 pagesProtists Review WSIZ - 12JR 1013186 Lincoln Alexander SSNo ratings yet
- Gambar ProtistaDocument4 pagesGambar ProtistaGG ChannelNo ratings yet
- (KBA BU HANUM) Senyawa Fenolik AlamDocument134 pages(KBA BU HANUM) Senyawa Fenolik AlamPoppyA.NamiraNo ratings yet
- Algae Botany 2021 B.Sc. 1st YrDocument4 pagesAlgae Botany 2021 B.Sc. 1st YrPET BOTANY 2021No ratings yet
- BRYOPHYTESDocument3 pagesBRYOPHYTESGanesh Rajeshwar100% (1)
- Classification of OrganismsDocument17 pagesClassification of OrganismsManula MuthunayakeNo ratings yet
- First Semester 2074 Final Exam FM 45 PM 22Document167 pagesFirst Semester 2074 Final Exam FM 45 PM 22CDB 1st Semester 2077100% (1)
- Somatic Structures of FungiDocument2 pagesSomatic Structures of FungiSajjad Hossain Shuvo100% (1)
- CHAPTER 1 BiologyDocument13 pagesCHAPTER 1 Biologyparvenassri prabakharanNo ratings yet
- Class 11 Compiled Chintu Notes ..Document76 pagesClass 11 Compiled Chintu Notes ..Mohammed ArifuddinNo ratings yet
- Lecture Note Plant Structure and FunctionDocument22 pagesLecture Note Plant Structure and FunctionMilka Rahman100% (1)
- Levels of ClassificationDocument33 pagesLevels of ClassificationAl Christian YaboNo ratings yet
- Chloro Ky BusDocument1 pageChloro Ky Busx456456456xNo ratings yet
- Morphology of Moulds/ Molds A. ThallusDocument3 pagesMorphology of Moulds/ Molds A. ThallusJane LappaoNo ratings yet
- 9.08 Vascular PlantsDocument3 pages9.08 Vascular PlantsGodfrey ObingoNo ratings yet
- Abraham Darby RoseDocument2 pagesAbraham Darby Rosevero66No ratings yet
- Anatomical Features of Bougainvillea (Nyctaginaceae) : Sarah ChewDocument7 pagesAnatomical Features of Bougainvillea (Nyctaginaceae) : Sarah ChewPratistha ShauryaNo ratings yet