Professional Documents
Culture Documents
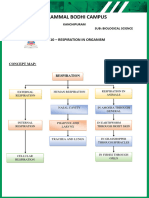
Respiration Assignment 1 2024
Respiration Assignment 1 2024
Uploaded by
ravya.singh.gdgCopyright:
Available Formats
You might also like
- Respiration HandoutDocument4 pagesRespiration Handoutkiran2000tripathiNo ratings yet
- Life Processes - Respiration QB - 2019 PDFDocument4 pagesLife Processes - Respiration QB - 2019 PDFRatheesh HrishikeshNo ratings yet
- Chapter 30 AnswersDocument8 pagesChapter 30 AnswersJuan SandovalNo ratings yet
- Difference Between Breathing and RespirationDocument8 pagesDifference Between Breathing and RespirationpreethaNo ratings yet
- CH 6 E - Notes RespirationDocument5 pagesCH 6 E - Notes RespirationRajvir tradaNo ratings yet
- GRADE-7 RESPIRATION IN ORGANISMS-NOTES-NewDocument9 pagesGRADE-7 RESPIRATION IN ORGANISMS-NOTES-NewsabariqaNo ratings yet
- LIFE PROCESS Respiration FullDocument38 pagesLIFE PROCESS Respiration Fullkabir.official.05No ratings yet
- Life Process RespirationDocument51 pagesLife Process RespirationJatin Kalra 10 DNo ratings yet
- Respiration Is The Process of Breaking Down of Glucose To Produce EnergyDocument5 pagesRespiration Is The Process of Breaking Down of Glucose To Produce EnergyTechnical AyushNo ratings yet
- Bio TestDocument24 pagesBio Testjunaid mehmoodNo ratings yet
- VIESCAaj GENBIO2 ESSAYDocument2 pagesVIESCAaj GENBIO2 ESSAYAnghel jhed ViescaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 8 Exercise Question and AnswersDocument5 pagesChapter 8 Exercise Question and AnswersPooja AgarwalNo ratings yet
- Biology U2Document10 pagesBiology U2Alima IqbalNo ratings yet
- RespirationDocument9 pagesRespirationpriya.kesharwani0557No ratings yet
- Human Respiratory System (Class X) ABK - SSJDocument18 pagesHuman Respiratory System (Class X) ABK - SSJ7B06Asher kharaNo ratings yet
- Gas Exchange Presentation4 Ambot1Document13 pagesGas Exchange Presentation4 Ambot1Archel GalorportNo ratings yet
- Respiration: Raja Fayaz AliDocument12 pagesRespiration: Raja Fayaz AliSuchitra SharmaNo ratings yet
- Respiratory_SystemDocument6 pagesRespiratory_SystemBenedicta AnyaNo ratings yet
- MLP HLP Class VII Respiration in OrganismsDocument4 pagesMLP HLP Class VII Respiration in OrganismsDivyanshi BansalNo ratings yet
- Breathing Exchange of GasesDocument6 pagesBreathing Exchange of GasesprimeeducationalinstituteNo ratings yet
- RESPIRATIONDocument11 pagesRESPIRATIONCREATIVING TAMILANNo ratings yet
- Chapter 13 Biology 1st Year - Prof. Ijaz Ahmed Khan Abbasi (Lecturer Biology PGC) Notes - MDCAT BY FUTURE DOCTORS - Touseef Ahmad Khan - 03499815886Document24 pagesChapter 13 Biology 1st Year - Prof. Ijaz Ahmed Khan Abbasi (Lecturer Biology PGC) Notes - MDCAT BY FUTURE DOCTORS - Touseef Ahmad Khan - 03499815886Tauqeer AhmadNo ratings yet
- Respiration Chapter 7 Biology Form 4Document90 pagesRespiration Chapter 7 Biology Form 4Faida Hamid87% (23)
- Respiration Chapter 7 Biology Form 4Document90 pagesRespiration Chapter 7 Biology Form 4edain84No ratings yet
- Gaseous Exchange MaterialDocument2 pagesGaseous Exchange Materialhafsa.r.yasirNo ratings yet
- Grade - 7 Biology: Chapter-10 Respiration in OrganismsDocument22 pagesGrade - 7 Biology: Chapter-10 Respiration in OrganismsJanardhanNo ratings yet
- Respiration Class 10Document3 pagesRespiration Class 10unknownuwugirl2442No ratings yet
- 1670490268lesson No10 NotesDocument6 pages1670490268lesson No10 NotesVijayaLakshmi KuchimanchiNo ratings yet
- Parts and Functions of Respiratory System - NotesDocument9 pagesParts and Functions of Respiratory System - NotesZaraa BeaNo ratings yet
- Life Procesess - Respiratory System PDFDocument25 pagesLife Procesess - Respiratory System PDFjacob mathewNo ratings yet
- Module 10Document8 pagesModule 10Jamille Nympha C. BalasiNo ratings yet
- Respiration in OrganismsDocument3 pagesRespiration in OrganismsNitesh KohliNo ratings yet
- Gaseous Exchange in Humans PDFDocument6 pagesGaseous Exchange in Humans PDFKevin JacksonNo ratings yet
- Respiratory System Questions and Answers BiosDocument4 pagesRespiratory System Questions and Answers BiosChrispin MsofeNo ratings yet
- Respiratory System of Frog: External RespirationDocument3 pagesRespiratory System of Frog: External RespirationShaira CogollodoNo ratings yet
- Respiration in OrganismsDocument9 pagesRespiration in Organismsshreya kashyapNo ratings yet
- Gaseous ExchangeDocument5 pagesGaseous Exchangehafsa.r.yasirNo ratings yet
- Biology Lecture NotesDocument56 pagesBiology Lecture NotesMaisonette MichNo ratings yet
- Notes RespirationDocument6 pagesNotes Respirationakheel7353No ratings yet
- Respiration NotesDocument7 pagesRespiration NotesKrishna SharmaNo ratings yet
- X Cbse Science Unit Test - Solutions: Life Processes-Nutrition & Respiration Marks: 30 Test Code: 10SUT103 Duration: 1 HRDocument4 pagesX Cbse Science Unit Test - Solutions: Life Processes-Nutrition & Respiration Marks: 30 Test Code: 10SUT103 Duration: 1 HRdayanandan1No ratings yet
- Gaseous Exchange in Plants and AnimalsDocument51 pagesGaseous Exchange in Plants and AnimalsJesimie OriasNo ratings yet
- Chapter-6 LIFE PROCESSES (5.3) NOTESDocument3 pagesChapter-6 LIFE PROCESSES (5.3) NOTESSangeetha DeviNo ratings yet
- J) RespirationDocument3 pagesJ) Respirationamarashah182No ratings yet
- C7 RespirationDocument18 pagesC7 RespirationDharshiniNo ratings yet
- Revision Notes Chapter-10 Respiration in Organisms: Why Do We Respire?Document11 pagesRevision Notes Chapter-10 Respiration in Organisms: Why Do We Respire?Raman -No ratings yet
- Human Resource ManagementDocument15 pagesHuman Resource ManagementKIPNGENO EMMANUELNo ratings yet
- Respiration in Organisms: Question and AnswersDocument4 pagesRespiration in Organisms: Question and AnswersSanvi SinghNo ratings yet
- CLASS 10th RESPIRATIONDocument3 pagesCLASS 10th RESPIRATIONNavkaran SinghNo ratings yet
- Class 7 Lesson 6Document3 pagesClass 7 Lesson 6gunjanrichaNo ratings yet
- Animal Physiology and Physiological Chemistry Paper Mzo503 Paper Mzo503Document19 pagesAnimal Physiology and Physiological Chemistry Paper Mzo503 Paper Mzo503Abhishek Singh ChandelNo ratings yet
- Respiratory SystemDocument10 pagesRespiratory SystemSudip NeupaneNo ratings yet
- L - Life Processes - Respiration Notes and Questions For Note Book WorkDocument7 pagesL - Life Processes - Respiration Notes and Questions For Note Book WorkNotImmortalNo ratings yet
- Assignment Lec 13Document2 pagesAssignment Lec 13LeiNo ratings yet
- Lesson 5 - Respiratory and Circulatory SystemsDocument60 pagesLesson 5 - Respiratory and Circulatory SystemsBeng QuinnNo ratings yet
- Respiration NotesDocument5 pagesRespiration Notesashwathrajan1902No ratings yet
- Respiration Ch-5 Life ProcessesDocument18 pagesRespiration Ch-5 Life Processes7B06Asher kharaNo ratings yet
- Fun Facts about Oxygen : Chemistry for Kids The Element Series | Children's Chemistry BooksFrom EverandFun Facts about Oxygen : Chemistry for Kids The Element Series | Children's Chemistry BooksNo ratings yet
- Circular Above Elbow CastDocument10 pagesCircular Above Elbow CastAmsir LimbongNo ratings yet
- Ch. 18 Reading Guide Ed8Document10 pagesCh. 18 Reading Guide Ed8quinntai97No ratings yet
- Ramipril Drug StudyDocument3 pagesRamipril Drug StudyCheezy Bread0% (1)
- STEMI Algorithm Poster 18x24Document1 pageSTEMI Algorithm Poster 18x24OgizWaraNo ratings yet
- Direct Factors Affecting The PeriodontiumDocument4 pagesDirect Factors Affecting The PeriodontiumHayley WelshNo ratings yet
- Lymphatic Research and BiologyDocument6 pagesLymphatic Research and BiologyJuhiJahan AmanullahNo ratings yet
- ScienceMentalphysics PDFDocument188 pagesScienceMentalphysics PDFGuida Lourenco100% (3)
- Aortic Valve DiseaseDocument25 pagesAortic Valve Diseasesagungw93No ratings yet
- JumpSTART Training Presentation Instructor Course 2016 FinalDocument109 pagesJumpSTART Training Presentation Instructor Course 2016 FinalvictorioNo ratings yet
- Midterm 1 Kahoot Questions Psyc1010Document6 pagesMidterm 1 Kahoot Questions Psyc1010Zekvan DönmezNo ratings yet
- Life Process - NutritionDocument3 pagesLife Process - NutritionYuktha ANo ratings yet
- Nicom CompetencyDocument2 pagesNicom Competencyapi-258141893No ratings yet
- Lecture - 7 - Work - Capacity, - Stress - and - Fatigue (Autosaved)Document51 pagesLecture - 7 - Work - Capacity, - Stress - and - Fatigue (Autosaved)Aizat RomainoNo ratings yet
- Contoh Soal TOEFL StructureDocument15 pagesContoh Soal TOEFL Structureviolla dwivannieNo ratings yet
- Physiology and Neurobiology of Stress and Adaptation - Central Role of The BrainDocument33 pagesPhysiology and Neurobiology of Stress and Adaptation - Central Role of The BrainJSGINo ratings yet
- Sa Overall National Freediving Records 2016Document2 pagesSa Overall National Freediving Records 2016api-326870530No ratings yet
- Navi KriyaDocument5 pagesNavi Kriyavnrkakinada100% (1)
- ScienceDocument52 pagesScienceVannyNo ratings yet
- Ehp 1206136Document7 pagesEhp 1206136SaiKai54No ratings yet
- BIO 160 SyllabusDocument15 pagesBIO 160 SyllabusjoanneoellersNo ratings yet
- Hu Et Al-2017-Journal of Cellular PhysiologyDocument37 pagesHu Et Al-2017-Journal of Cellular PhysiologySorop AndreiNo ratings yet
- Vertebral Canal, DR Adel Bondok 2022Document3 pagesVertebral Canal, DR Adel Bondok 2022Amira Sobh100% (1)
- WorksheetDocument10 pagesWorksheetMomay RojalesNo ratings yet
- Ventral Suspension PositionDocument3 pagesVentral Suspension PositionyangNo ratings yet
- Upper Respiratory Infection Definition and FactsDocument2 pagesUpper Respiratory Infection Definition and FactsBerlian PurnamasariNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2 - Movement of Substances Across Plasma MembraneDocument17 pagesChapter 2 - Movement of Substances Across Plasma MembraneRossliza Yaacob100% (1)
- Recent Advances in NGF and Related Molecules: Laura Calzà Luigi Aloe Luciana Giardino EditorsDocument302 pagesRecent Advances in NGF and Related Molecules: Laura Calzà Luigi Aloe Luciana Giardino EditorsPedro CastroNo ratings yet
- ds103 Evolution Vocabulary BingoDocument6 pagesds103 Evolution Vocabulary Bingoapi-110789702No ratings yet
- Photosynthesis in Higher Plants - DPP 02 (Of Lec 05) - Sequence No. 46 - Pathshala 11th NEET 2024Document3 pagesPhotosynthesis in Higher Plants - DPP 02 (Of Lec 05) - Sequence No. 46 - Pathshala 11th NEET 2024priyanshuranjanroutNo ratings yet
- cc2 Lectures AllDocument256 pagescc2 Lectures AllJayson Dagohoy SudioNo ratings yet
Respiration Assignment 1 2024
Respiration Assignment 1 2024
Uploaded by
ravya.singh.gdgCopyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Respiration Assignment 1 2024
Respiration Assignment 1 2024
Uploaded by
ravya.singh.gdgCopyright:
Available Formats
ASSIGNMENT RESPIRATION (PLANT & ANIMAL)
1.CO2 release is the major activity at night & O2 release is the major activity during daytime in
plants. Discuss.
HINTDuring the day both respiration and photosynthesis takes place and photosynthesis
is the major activity so only O2 is released whereas during night respiration is the major activity so
CO2release is the major activity.
2. Trace the path followed during the exchange of gases in plants.
HINTThere is no major pathway for exchange of gases in plants. Exchange of gases takes place
by the process of diffusion with the help of tiny pores i.e stomata present on the leaf epidermis. The
large intercellular spaces ensure that all cells are in contact with air.
3. How do leaves help in exchange of gases? OR Same as in question 3.
HintLeaves have tiny poresstomatahelp in exchange of gases by the process of
diffusionThe large intercellular spaces ensure that all cells are in contact with air.
4.Why do plants have low energy needs as compared to animals. Explain.
In plants, the movements are usually at the cellular level and so less amount of energy is
required. Animals need to move from one place to another in search of food and to move away from
predators so they need more energy.
5.Why do land plants die if their roots remain waterlogged?
The land plants may die if roots remain waterlogged for a long time because roots also respire and
if water is logged for much time then the process of diffusion will not occur in the roots.
6.Give differences between Breathing and Respiration.
BREATHING RESPIRATION
1 Intake of O2 rich air and removal of Oxidation of food to form CO2,water and
Co2rich air energy.
2 Physical process Biochemical process
3 No energy is released Energy is released in the form of ATP.
4 Extracellular process Intracellular process
5 No enzyme is involved Enzymes are involved
7..How is oxygen and carbon dioxide transported in human beings?
(i) Transport of oxygen : Haemoglobin(respiratory pigment) present in the blood takes up the
oxygen from the air in the lungs. It carries the oxygen to tissues which are deficient in oxygen
before releasing it.
(ii) Transport of carbon dioxide : Carbon dioxide is more soluble in water. Therefore, it is mostly
transported from body tissues in the dissolved form in our blood plasma to lungs. Here it diffuses
from blood to air in the lungs.
8.How does air moves in(inspiration) and out (expiration) in humans?
OR EXPLAIN MECHANISM OF BREATHING.
AnsINSPIRATIN/Air moves inAir enters through nostrils and filtered by fine hairs, lining the
nasal passage. During breathing in, ribs lifts up, diaphragm flattens and contract, chest cavity
becomes large, air moves in. Air enters the lung through trachea and bronchi. In lungs air enters
alveoli, where exchange of gases takes place.
EXPIRATION/Air moves outWhile breathing out, ribs relax, diaphragm relax, chest cavity reduces
and air moves OUT.
9.How is oxygen and carbon dioxide transported in human beings?
Ans(i) Transport of oxygen : Haemoglobin(respiratory pigment) present in the blood takes up the
oxygen from the air in the lungs. It carries the oxygen to tissues which are deficient in oxygen
before releasing it.
(ii) Transport of carbon dioxide : Carbon dioxide is more soluble in water. Therefore, it is mostly
transported from body tissues in the dissolved form in our blood plasma to lungs. Here it diffuses
from blood to air in the lungs.
10.Explain the exchange of respiratory gases in the capillaries surrounding the tissues?
Gas exchange takes place in the alveoli in the lungs and the capillaries that envelop them.
Inhaled oxygen moves from the alveoli to the blood with the help of haemoglobin respiratory
pigment, in the capillaries, and carbon dioxide moves from the blood in the capillaries to
the air in the alveoli.
11. (EXTRA)What is residual volume? Write its significance in human respiratory system.
ANSResidual volume is the amount of gas remaining in the lungs at the end of a maximal
exhalation. Residual Volume is important because it prevents the lungs from collapsing.
You might also like
- Respiration HandoutDocument4 pagesRespiration Handoutkiran2000tripathiNo ratings yet
- Life Processes - Respiration QB - 2019 PDFDocument4 pagesLife Processes - Respiration QB - 2019 PDFRatheesh HrishikeshNo ratings yet
- Chapter 30 AnswersDocument8 pagesChapter 30 AnswersJuan SandovalNo ratings yet
- Difference Between Breathing and RespirationDocument8 pagesDifference Between Breathing and RespirationpreethaNo ratings yet
- CH 6 E - Notes RespirationDocument5 pagesCH 6 E - Notes RespirationRajvir tradaNo ratings yet
- GRADE-7 RESPIRATION IN ORGANISMS-NOTES-NewDocument9 pagesGRADE-7 RESPIRATION IN ORGANISMS-NOTES-NewsabariqaNo ratings yet
- LIFE PROCESS Respiration FullDocument38 pagesLIFE PROCESS Respiration Fullkabir.official.05No ratings yet
- Life Process RespirationDocument51 pagesLife Process RespirationJatin Kalra 10 DNo ratings yet
- Respiration Is The Process of Breaking Down of Glucose To Produce EnergyDocument5 pagesRespiration Is The Process of Breaking Down of Glucose To Produce EnergyTechnical AyushNo ratings yet
- Bio TestDocument24 pagesBio Testjunaid mehmoodNo ratings yet
- VIESCAaj GENBIO2 ESSAYDocument2 pagesVIESCAaj GENBIO2 ESSAYAnghel jhed ViescaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 8 Exercise Question and AnswersDocument5 pagesChapter 8 Exercise Question and AnswersPooja AgarwalNo ratings yet
- Biology U2Document10 pagesBiology U2Alima IqbalNo ratings yet
- RespirationDocument9 pagesRespirationpriya.kesharwani0557No ratings yet
- Human Respiratory System (Class X) ABK - SSJDocument18 pagesHuman Respiratory System (Class X) ABK - SSJ7B06Asher kharaNo ratings yet
- Gas Exchange Presentation4 Ambot1Document13 pagesGas Exchange Presentation4 Ambot1Archel GalorportNo ratings yet
- Respiration: Raja Fayaz AliDocument12 pagesRespiration: Raja Fayaz AliSuchitra SharmaNo ratings yet
- Respiratory_SystemDocument6 pagesRespiratory_SystemBenedicta AnyaNo ratings yet
- MLP HLP Class VII Respiration in OrganismsDocument4 pagesMLP HLP Class VII Respiration in OrganismsDivyanshi BansalNo ratings yet
- Breathing Exchange of GasesDocument6 pagesBreathing Exchange of GasesprimeeducationalinstituteNo ratings yet
- RESPIRATIONDocument11 pagesRESPIRATIONCREATIVING TAMILANNo ratings yet
- Chapter 13 Biology 1st Year - Prof. Ijaz Ahmed Khan Abbasi (Lecturer Biology PGC) Notes - MDCAT BY FUTURE DOCTORS - Touseef Ahmad Khan - 03499815886Document24 pagesChapter 13 Biology 1st Year - Prof. Ijaz Ahmed Khan Abbasi (Lecturer Biology PGC) Notes - MDCAT BY FUTURE DOCTORS - Touseef Ahmad Khan - 03499815886Tauqeer AhmadNo ratings yet
- Respiration Chapter 7 Biology Form 4Document90 pagesRespiration Chapter 7 Biology Form 4Faida Hamid87% (23)
- Respiration Chapter 7 Biology Form 4Document90 pagesRespiration Chapter 7 Biology Form 4edain84No ratings yet
- Gaseous Exchange MaterialDocument2 pagesGaseous Exchange Materialhafsa.r.yasirNo ratings yet
- Grade - 7 Biology: Chapter-10 Respiration in OrganismsDocument22 pagesGrade - 7 Biology: Chapter-10 Respiration in OrganismsJanardhanNo ratings yet
- Respiration Class 10Document3 pagesRespiration Class 10unknownuwugirl2442No ratings yet
- 1670490268lesson No10 NotesDocument6 pages1670490268lesson No10 NotesVijayaLakshmi KuchimanchiNo ratings yet
- Parts and Functions of Respiratory System - NotesDocument9 pagesParts and Functions of Respiratory System - NotesZaraa BeaNo ratings yet
- Life Procesess - Respiratory System PDFDocument25 pagesLife Procesess - Respiratory System PDFjacob mathewNo ratings yet
- Module 10Document8 pagesModule 10Jamille Nympha C. BalasiNo ratings yet
- Respiration in OrganismsDocument3 pagesRespiration in OrganismsNitesh KohliNo ratings yet
- Gaseous Exchange in Humans PDFDocument6 pagesGaseous Exchange in Humans PDFKevin JacksonNo ratings yet
- Respiratory System Questions and Answers BiosDocument4 pagesRespiratory System Questions and Answers BiosChrispin MsofeNo ratings yet
- Respiratory System of Frog: External RespirationDocument3 pagesRespiratory System of Frog: External RespirationShaira CogollodoNo ratings yet
- Respiration in OrganismsDocument9 pagesRespiration in Organismsshreya kashyapNo ratings yet
- Gaseous ExchangeDocument5 pagesGaseous Exchangehafsa.r.yasirNo ratings yet
- Biology Lecture NotesDocument56 pagesBiology Lecture NotesMaisonette MichNo ratings yet
- Notes RespirationDocument6 pagesNotes Respirationakheel7353No ratings yet
- Respiration NotesDocument7 pagesRespiration NotesKrishna SharmaNo ratings yet
- X Cbse Science Unit Test - Solutions: Life Processes-Nutrition & Respiration Marks: 30 Test Code: 10SUT103 Duration: 1 HRDocument4 pagesX Cbse Science Unit Test - Solutions: Life Processes-Nutrition & Respiration Marks: 30 Test Code: 10SUT103 Duration: 1 HRdayanandan1No ratings yet
- Gaseous Exchange in Plants and AnimalsDocument51 pagesGaseous Exchange in Plants and AnimalsJesimie OriasNo ratings yet
- Chapter-6 LIFE PROCESSES (5.3) NOTESDocument3 pagesChapter-6 LIFE PROCESSES (5.3) NOTESSangeetha DeviNo ratings yet
- J) RespirationDocument3 pagesJ) Respirationamarashah182No ratings yet
- C7 RespirationDocument18 pagesC7 RespirationDharshiniNo ratings yet
- Revision Notes Chapter-10 Respiration in Organisms: Why Do We Respire?Document11 pagesRevision Notes Chapter-10 Respiration in Organisms: Why Do We Respire?Raman -No ratings yet
- Human Resource ManagementDocument15 pagesHuman Resource ManagementKIPNGENO EMMANUELNo ratings yet
- Respiration in Organisms: Question and AnswersDocument4 pagesRespiration in Organisms: Question and AnswersSanvi SinghNo ratings yet
- CLASS 10th RESPIRATIONDocument3 pagesCLASS 10th RESPIRATIONNavkaran SinghNo ratings yet
- Class 7 Lesson 6Document3 pagesClass 7 Lesson 6gunjanrichaNo ratings yet
- Animal Physiology and Physiological Chemistry Paper Mzo503 Paper Mzo503Document19 pagesAnimal Physiology and Physiological Chemistry Paper Mzo503 Paper Mzo503Abhishek Singh ChandelNo ratings yet
- Respiratory SystemDocument10 pagesRespiratory SystemSudip NeupaneNo ratings yet
- L - Life Processes - Respiration Notes and Questions For Note Book WorkDocument7 pagesL - Life Processes - Respiration Notes and Questions For Note Book WorkNotImmortalNo ratings yet
- Assignment Lec 13Document2 pagesAssignment Lec 13LeiNo ratings yet
- Lesson 5 - Respiratory and Circulatory SystemsDocument60 pagesLesson 5 - Respiratory and Circulatory SystemsBeng QuinnNo ratings yet
- Respiration NotesDocument5 pagesRespiration Notesashwathrajan1902No ratings yet
- Respiration Ch-5 Life ProcessesDocument18 pagesRespiration Ch-5 Life Processes7B06Asher kharaNo ratings yet
- Fun Facts about Oxygen : Chemistry for Kids The Element Series | Children's Chemistry BooksFrom EverandFun Facts about Oxygen : Chemistry for Kids The Element Series | Children's Chemistry BooksNo ratings yet
- Circular Above Elbow CastDocument10 pagesCircular Above Elbow CastAmsir LimbongNo ratings yet
- Ch. 18 Reading Guide Ed8Document10 pagesCh. 18 Reading Guide Ed8quinntai97No ratings yet
- Ramipril Drug StudyDocument3 pagesRamipril Drug StudyCheezy Bread0% (1)
- STEMI Algorithm Poster 18x24Document1 pageSTEMI Algorithm Poster 18x24OgizWaraNo ratings yet
- Direct Factors Affecting The PeriodontiumDocument4 pagesDirect Factors Affecting The PeriodontiumHayley WelshNo ratings yet
- Lymphatic Research and BiologyDocument6 pagesLymphatic Research and BiologyJuhiJahan AmanullahNo ratings yet
- ScienceMentalphysics PDFDocument188 pagesScienceMentalphysics PDFGuida Lourenco100% (3)
- Aortic Valve DiseaseDocument25 pagesAortic Valve Diseasesagungw93No ratings yet
- JumpSTART Training Presentation Instructor Course 2016 FinalDocument109 pagesJumpSTART Training Presentation Instructor Course 2016 FinalvictorioNo ratings yet
- Midterm 1 Kahoot Questions Psyc1010Document6 pagesMidterm 1 Kahoot Questions Psyc1010Zekvan DönmezNo ratings yet
- Life Process - NutritionDocument3 pagesLife Process - NutritionYuktha ANo ratings yet
- Nicom CompetencyDocument2 pagesNicom Competencyapi-258141893No ratings yet
- Lecture - 7 - Work - Capacity, - Stress - and - Fatigue (Autosaved)Document51 pagesLecture - 7 - Work - Capacity, - Stress - and - Fatigue (Autosaved)Aizat RomainoNo ratings yet
- Contoh Soal TOEFL StructureDocument15 pagesContoh Soal TOEFL Structureviolla dwivannieNo ratings yet
- Physiology and Neurobiology of Stress and Adaptation - Central Role of The BrainDocument33 pagesPhysiology and Neurobiology of Stress and Adaptation - Central Role of The BrainJSGINo ratings yet
- Sa Overall National Freediving Records 2016Document2 pagesSa Overall National Freediving Records 2016api-326870530No ratings yet
- Navi KriyaDocument5 pagesNavi Kriyavnrkakinada100% (1)
- ScienceDocument52 pagesScienceVannyNo ratings yet
- Ehp 1206136Document7 pagesEhp 1206136SaiKai54No ratings yet
- BIO 160 SyllabusDocument15 pagesBIO 160 SyllabusjoanneoellersNo ratings yet
- Hu Et Al-2017-Journal of Cellular PhysiologyDocument37 pagesHu Et Al-2017-Journal of Cellular PhysiologySorop AndreiNo ratings yet
- Vertebral Canal, DR Adel Bondok 2022Document3 pagesVertebral Canal, DR Adel Bondok 2022Amira Sobh100% (1)
- WorksheetDocument10 pagesWorksheetMomay RojalesNo ratings yet
- Ventral Suspension PositionDocument3 pagesVentral Suspension PositionyangNo ratings yet
- Upper Respiratory Infection Definition and FactsDocument2 pagesUpper Respiratory Infection Definition and FactsBerlian PurnamasariNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2 - Movement of Substances Across Plasma MembraneDocument17 pagesChapter 2 - Movement of Substances Across Plasma MembraneRossliza Yaacob100% (1)
- Recent Advances in NGF and Related Molecules: Laura Calzà Luigi Aloe Luciana Giardino EditorsDocument302 pagesRecent Advances in NGF and Related Molecules: Laura Calzà Luigi Aloe Luciana Giardino EditorsPedro CastroNo ratings yet
- ds103 Evolution Vocabulary BingoDocument6 pagesds103 Evolution Vocabulary Bingoapi-110789702No ratings yet
- Photosynthesis in Higher Plants - DPP 02 (Of Lec 05) - Sequence No. 46 - Pathshala 11th NEET 2024Document3 pagesPhotosynthesis in Higher Plants - DPP 02 (Of Lec 05) - Sequence No. 46 - Pathshala 11th NEET 2024priyanshuranjanroutNo ratings yet
- cc2 Lectures AllDocument256 pagescc2 Lectures AllJayson Dagohoy SudioNo ratings yet