Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Chapter 10
Chapter 10
Uploaded by
Rehman uddin0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
2 views4 pagesCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as docx, pdf, or txt
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
2 views4 pagesChapter 10
Chapter 10
Uploaded by
Rehman uddinCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as docx, pdf, or txt
You are on page 1of 4
Heat and Temperature
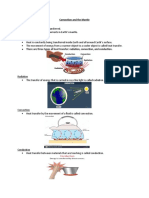
Chapter No 10
1. Temperature of laboratory is 320K.
2. Temperature is the degree of hotness or coldness of a body.
3. Temperature is measured by thermometer.
4. The SI unit of temperature is kelvin.
5. Fahrenheit is used for clinical purposes.
6. While degree centigrade is used in daily life.
7. There are three temperature scales. Kelvin scale, centigrade scale, Fahrenheit scale
8. Thermometer has two reference points. Lower reference point and upper reference point.
9. The gap between these points is called scale which is divided into equal lengths.
10. The freezing point at Kelvin scale is 273 k and the boiling point at Kelvin scale is 373 kelvin.
11. Celsius is the most commonly used temperature scale.
12. The boiling point of water at centigrade scale is 100 and freezing point is 0.
13. Water freezing point at Fahrenheit scale is 32f while water boils at 212 f.
14. Fahrenheit scale has 180 divisions.
15. Conversion formulas of different units of temperature scale.
16. From Celsius to kelvin scale
K = c + 273
17. From Celsius to Fahrenheit scale.
F =…………. `
18. Heat is a form of energy that flow from hotter body to colder body.
19. When water put in a pot and is heated the water becomes hot due to the movement of kinetic
energy of the water.
20. A two body is said to be in thermal equilibrium when the temperature of the hot body becomes
equal to the temperature of the cold body.
21. The SI unit of heat energy is Joule (J).
22. The heat unit is from the name of an English physicist and mathematician James Prescott joule.
23. When a substance is heated its length, area, volume, shape, or density change this change is
called thermal expansion.
24. All three states of matter solid, liquid and gas expand on heating and contract on cooling.
25. The thermal expansion different for the solid liquid and gas of the same substance. Usually gases
expand more than liquid and liquid expand more than solid.
26. In solid particles vibrate about their mean position but do not leave their positions.
27. When solid substances i heated its particles gains heat energy and vibrational kinetic energy
oftheparticle increases and they vibrate with greater amplitude. And the gap between the
neighboring atom increases and hence increases size of the substance.
28. `Heat is always transferred from hot objects to cold objects due to temperature difference.
29. Heat is transferred by three different ways. Conduction convection and radiation.
30. Conduction is the phenomena in which the heat is transferred from the hot body to the cold
body by the vibration of particles.
31. Conduction also takes place from hot part to the cold part of the object.
32. In solid particles are very close to each other on heating one end is hot the other end also get
hot because of the vibrations of the particles.
33. Metal are good conductor of heat because they have free electron. These free electron move
fast and transfer the energy to other part of the metal quickly.
34. Cooking utensils are made up of metals because metals conduct heat fast and cook the food
easily.
35. Non-metals e.g. plastic, wool, fur etc. do not conduct heat easily, they are poor conductors of
heat and are also called insulators.
36. In non-metals electrons are bound they are not free to move in materials.
37. Solid are good conductors of heat than liquid and gases.
38. Air which is mixture of gases is one of the best insulators.
39. Transfer of heat by actual movement of molecules from hot place to cold place is known as
convection.
40. Convection only takes place in liquid and gases only.
41. The upward moving air due to convection is called thermals.
42. The transfer of heat from a hot place to a cold place with or without having a material medium
in between, in the form of electromagnetic waves is called radiation.
43. In radiation energy is transferred without involving matter.
44. The heat transfer that occurs due to a density difference in fluids is called insulation.
Technology in everyday life
Chapter no 11
1. Louse Pasteur is a French chemist and microbiologist was the first to find out that heating at
a certain temperature makes the food microbe free.
2. Pasteurization technique was named after him.
3. Stethoscope is an instrument which is used by doctors to listen the heartbeat of a patient.
4. The best way to preserve vegetables is pickling.
5. In pickling food is soaked in solution of salt and acid
6. The process of food preservation in which bacteria is allowed to grow against the harmful
bacteria is called fermentation.
7. Pasteurization means heating at a certain temperature to keep food microbe free.
Earth and space
Chapter no 12
1. The quantity of matter contain in a body is called mass.
2. The SI unit of mass is kilogram.
3. The bigger unit of mass is ton.
4. The force with which earth attracts anything towards its center is called weight of the
body on earth.
5. The SI unit of force is newton and its symbol is N.
6. Formula of weight is W=mg where m is mass of the body and g is gravitational field
strength.
7. The value of gravitational acceleration on surface of the earth is 9.8 m/sec
8. When you jump on the moon you will raise six times more height than that on earth
because of less gravity.
9. Tides are the rise and fall of water level in the ocean, rivers, lakes etc.
10. High tides are seen in the ocean when the see level rises to its maximum level.
11. When water level falls to its lowest point, it is known as low tide.
12. Gravitational pull of moon and earth, spinning of earth the causes of tides on ocean.
13. The moon has its own gravitational field which attracts everything on earth including
oceans, land structures and people.
14. Spinning motion of the earth involves day and night, while revolution of the earth
around involves change in seasons.
15. Earth has two poles north pole and South Pole.
16. An equator is an imaginary line around the middle of the planet. It is half way between
the North Pole and South Pole. (at 0 degree latitude)
17. Axis is the line around which earth spins.
18. The axial tilt is defined as the angle between the direction of the North Pole and the
perpendicular to the orbital plane.
19. Axial tilt of the earth is 23.5.
20. Earth revolves around the sun with the axial tilt.
21. During the orbital motion of the earth around sun, when the axis of the earth is towards
the sun then summer season is there for that part of earth. When the axis of the earth is
away from the sun then winter season is there for that part of earth. In between these
two times its spring and autumn.
22. Constellation is a group of stars that appear to form a pattern or picture like Orion the
great hunter, Leo the lion or Taurus the bull.
23. Constellation gradually shifted to the west, this is caused by motion of earth around our
sun.
24. There are two main hemisphere of the earth northern hemisphere and southern
hemisphere.
25. The force of gravity is forcing planets to move in orbits.
26. The heat transfer that occurs due to a density difference in fluids is called insulation.
You might also like
- Auriol IAN 392071 Weather StationDocument150 pagesAuriol IAN 392071 Weather Stationmdenis78No ratings yet
- Chapter 9 Heat Form 2 KSSMDocument7 pagesChapter 9 Heat Form 2 KSSMNadhirah Kamarudin80% (5)
- Important Points Science TestDocument7 pagesImportant Points Science Testlunaakatsuki811No ratings yet
- G-8 Physics Unit 4 Note - 07-08-13796168803685 - Gobe - 3Document9 pagesG-8 Physics Unit 4 Note - 07-08-13796168803685 - Gobe - 3AbebechNo ratings yet
- Heat For Form 1 ADocument61 pagesHeat For Form 1 AChrise RajNo ratings yet
- Science Form 1 NoteDocument5 pagesScience Form 1 NoteDaniel ChanNo ratings yet
- Interface Mass TraDocument26 pagesInterface Mass TraWahid AliNo ratings yet
- Heat Chapter NotesDocument9 pagesHeat Chapter NotesMaanya KumarNo ratings yet
- Convection and The Mantle - Gr. 6 Lesson NotesDocument2 pagesConvection and The Mantle - Gr. 6 Lesson NotesJung Ahn HongNo ratings yet
- Earth and Life Science: Quarter 1 - Module 6: Lesson: The Earth's Internal HeatDocument15 pagesEarth and Life Science: Quarter 1 - Module 6: Lesson: The Earth's Internal HeatMigz Arlz14No ratings yet
- Module 2 Warming and Cooling Earth and Its AtmosphereDocument16 pagesModule 2 Warming and Cooling Earth and Its AtmosphereConcepcion Jasmin JodlomanNo ratings yet
- Chapter 7 HeatDocument6 pagesChapter 7 HeatShyeshaNo ratings yet
- HeatDocument12 pagesHeatMayukh ChoudhuryNo ratings yet
- Thermal PhysicsDocument10 pagesThermal PhysicsharshanauocNo ratings yet
- Meteoorology Lecture NotesDocument13 pagesMeteoorology Lecture Notesmalyn bañaresNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1 Earth ScienceDocument5 pagesChapter 1 Earth ScienceLeizel MundoNo ratings yet
- Internal HeatDocument12 pagesInternal Heatbluredgaming05No ratings yet
- ConductionDocument1 pageConductionnikhil.surapuneniNo ratings yet
- Science 7 - Q3 - Episode 6 - SLMDocument5 pagesScience 7 - Q3 - Episode 6 - SLMCaryll BaylonNo ratings yet
- Warming The Earth and The AtmosphereDocument46 pagesWarming The Earth and The AtmosphereSalih TrexieNo ratings yet
- Thermal Physics by Ms. Nudrat Haque: Kinetic Model of MatterDocument6 pagesThermal Physics by Ms. Nudrat Haque: Kinetic Model of MatterNudratNo ratings yet
- Heat and Temperatu-ReDocument11 pagesHeat and Temperatu-ReFedora MefiaNo ratings yet
- Review of Past Terms:: - Define "Energy"Document26 pagesReview of Past Terms:: - Define "Energy"Tapish GoelNo ratings yet
- Thermal Energy ReadingDocument5 pagesThermal Energy Readingapi-189616674No ratings yet
- LAS Earth 03 0Document2 pagesLAS Earth 03 0April Joy EsmaNo ratings yet
- Project in ScienceDocument4 pagesProject in ScienceArsharip Hasim TaupNo ratings yet
- Enl Lesson 6Document21 pagesEnl Lesson 6CjNo ratings yet
- The Earth's Internal HeatDocument15 pagesThe Earth's Internal HeatApril Mae ArcayaNo ratings yet
- Conduction Convection RadiationDocument26 pagesConduction Convection Radiationnavketsharma6280100% (1)
- Lesson 5 - The Earth's Internal HeatDocument39 pagesLesson 5 - The Earth's Internal HeatKirito HatakuNo ratings yet
- Physics Heat NotesDocument20 pagesPhysics Heat NotesHarshwardhan UndeNo ratings yet
- Physics Earth and Space Sciences TopicsDocument8 pagesPhysics Earth and Space Sciences TopicsJanine CerradaNo ratings yet
- Ls-5, HEAT (NOTE: Draw The Diagrams Neatly On The Plain Paper, After Drawing Margins On All Four Sides.)Document3 pagesLs-5, HEAT (NOTE: Draw The Diagrams Neatly On The Plain Paper, After Drawing Margins On All Four Sides.)SashankNo ratings yet
- Las Week 6 (Part 1) Earth's Internal HeatDocument4 pagesLas Week 6 (Part 1) Earth's Internal HeatMargarita EcaldreNo ratings yet
- Chapter 4 HeatDocument5 pagesChapter 4 Heatsahoobijayalaxmi13No ratings yet
- Comprendre Les Différents Modes de Transferts de Chaleur, Conduction, Convection Et RayonnementDocument33 pagesComprendre Les Différents Modes de Transferts de Chaleur, Conduction, Convection Et RayonnementAhmed MobarkiNo ratings yet
- Physics ProjectDocument19 pagesPhysics Projectaditya varteNo ratings yet
- Kavita - Int Sci Heat TransferDocument10 pagesKavita - Int Sci Heat Transfer27h4fbvsy8No ratings yet
- Lecture 4 Transmission of HeatDocument18 pagesLecture 4 Transmission of Heatdinesh11rNo ratings yet
- 5 Lesson Plan On HeatDocument4 pages5 Lesson Plan On HeatJustine Collamar GanabNo ratings yet
- Science Script: Scene 1Document4 pagesScience Script: Scene 1Mikaela MercadoNo ratings yet
- Evelyn C Canonce LAS WK 7Document11 pagesEvelyn C Canonce LAS WK 7malouNo ratings yet
- Ict Assignment 2Document11 pagesIct Assignment 2anis hauraNo ratings yet
- David Physics s3Document12 pagesDavid Physics s3RUKUNDO OliveNo ratings yet
- Methods of Heat Transfer: OjectiveDocument7 pagesMethods of Heat Transfer: OjectiveNadine BernardinoNo ratings yet
- CORE Earth and Life Science Q1Week3Document20 pagesCORE Earth and Life Science Q1Week3Cesar CañonasoNo ratings yet
- Geo 5Document4 pagesGeo 5Prem KukrejaNo ratings yet
- Heat Transfer - G6 Lesson NotesDocument3 pagesHeat Transfer - G6 Lesson NotesJung Ahn HongNo ratings yet
- Heat Notes 2024Document5 pagesHeat Notes 2024saesha2801No ratings yet
- EOG Science Cheat SheetDocument13 pagesEOG Science Cheat SheetClay MarionNo ratings yet
- Sci Oly 2.0Document12 pagesSci Oly 2.0arinaitwejoshua24No ratings yet
- Thermal Energy Transfer PPDocument20 pagesThermal Energy Transfer PPvenkat_09No ratings yet
- Warming The Earth and The AtmosphereDocument46 pagesWarming The Earth and The AtmosphereKylene AlimNo ratings yet
- Lesson 6 The EarthDocument3 pagesLesson 6 The EarthMajo galiciaNo ratings yet
- 3rd Quarter SCIENCE 4 WEEK 6 Heat EnergyDocument25 pages3rd Quarter SCIENCE 4 WEEK 6 Heat EnergyCharlesJames MaruquezNo ratings yet
- Class VII I.I.T.foundation, N.T.S.E.& Science Olympiad Curriculum & Chapter NotesDocument107 pagesClass VII I.I.T.foundation, N.T.S.E.& Science Olympiad Curriculum & Chapter Notesspatel197250% (2)
- The Energy That Warms Us: A Look at HeatFrom EverandThe Energy That Warms Us: A Look at HeatRating: 1 out of 5 stars1/5 (1)
- C.A 6-2019Document2 pagesC.A 6-2019Rehman uddinNo ratings yet
- C.A 3-2020Document3 pagesC.A 3-2020Rehman uddinNo ratings yet
- C.A 2-2020Document3 pagesC.A 2-2020Rehman uddinNo ratings yet
- C.A 12-2019Document6 pagesC.A 12-2019Rehman uddinNo ratings yet
- C.A 11-2019Document5 pagesC.A 11-2019Rehman uddinNo ratings yet
- Traduccion Del Manual PrimusDocument356 pagesTraduccion Del Manual PrimusManzanoCabreraTereso67% (3)
- Chapter Four Heat and ThermodynamicsDocument44 pagesChapter Four Heat and ThermodynamicsmesfinNo ratings yet
- ملخص فارما مختصر جداDocument78 pagesملخص فارما مختصر جداSAMERNo ratings yet
- 4053 02 01 02 SafetyDocument119 pages4053 02 01 02 SafetylokelooksNo ratings yet
- Saacke DictionaryDocument68 pagesSaacke Dictionaryer.tafseer100% (2)
- Copia de CFM - Calculators - 3.80Document18 pagesCopia de CFM - Calculators - 3.80jose mariaNo ratings yet
- R160LC 7 PDFDocument500 pagesR160LC 7 PDFГригорий ГригорянNo ratings yet
- De SolDocument5 pagesDe SolAbegail GarcimoNo ratings yet
- Charts & ReferenceDocument6 pagesCharts & ReferencegicacosmaNo ratings yet
- LolDocument3 pagesLolVrad Neil AustineNo ratings yet
- Labview Day 4: The Case Structure and Rings: Vern LindbergDocument3 pagesLabview Day 4: The Case Structure and Rings: Vern LindbergahNo ratings yet
- AmancioDocument12 pagesAmancioLeizl TolentinoNo ratings yet
- (2-2-1) NPTEL - Properties of Cryogenic FluidsDocument28 pages(2-2-1) NPTEL - Properties of Cryogenic FluidsNirmal JayanthNo ratings yet
- TEXT 6. Solve Linear InequalitiesDocument99 pagesTEXT 6. Solve Linear InequalitiesHector R.100% (1)
- Genius 2 Service ManualDocument16 pagesGenius 2 Service Manualritto05No ratings yet
- DynamicalSystemsWithApplicationsUsingPython 2ed Lynch PDFDocument104 pagesDynamicalSystemsWithApplicationsUsingPython 2ed Lynch PDFcmpmarinho100% (2)
- Conductance Data For Commonly Used Chemicals DataDocument36 pagesConductance Data For Commonly Used Chemicals DataAnshul TomarNo ratings yet
- HX17A Z - SM Manual de ServicioDocument370 pagesHX17A Z - SM Manual de Serviciohernando ramosNo ratings yet
- 04 Linear Equation in Two Variable Subjective QuestionsDocument5 pages04 Linear Equation in Two Variable Subjective Questionsshweta_angel90No ratings yet
- 4 Measurement of Industrial ParametersDocument35 pages4 Measurement of Industrial ParametersumarsaboNo ratings yet
- English at A GlanceDocument111 pagesEnglish at A GlanceLina GaigalaitėNo ratings yet
- Week 4 Third Grade Digital Learning Lesson PlansDocument6 pagesWeek 4 Third Grade Digital Learning Lesson Plansapi-312354951No ratings yet
- Chemical Engineering Principles 2Document60 pagesChemical Engineering Principles 2Ayman HammadNo ratings yet
- Fahrenheit 471 PDFDocument2 pagesFahrenheit 471 PDFCraigNo ratings yet
- Rules of ThumbDocument68 pagesRules of ThumbAnonymous 1Z2HqLVbr100% (1)
- Quick Check: Work = Force - displacement W=F - d W=F cos (Ө) dDocument6 pagesQuick Check: Work = Force - displacement W=F - d W=F cos (Ө) dRowindeNo ratings yet
- Exam Practice: Unit 4: WeatherDocument8 pagesExam Practice: Unit 4: WeatherJean Andrea NiloNo ratings yet
- Year 11 Algebra HSCs 2022 To 2005Document17 pagesYear 11 Algebra HSCs 2022 To 2005Leila FonuaNo ratings yet
- M.Tech Practical ListDocument6 pagesM.Tech Practical ListGitesh NagarNo ratings yet