Professional Documents
Culture Documents
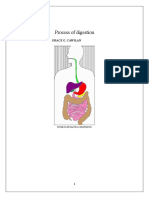
SCIENCE 8 4 ST 1
SCIENCE 8 4 ST 1
Uploaded by
Mary Queen TeroCopyright:
Available Formats
You might also like
- Human Digestive System WorksheetDocument3 pagesHuman Digestive System WorksheetSana Shakeel100% (9)
- SUMMATIVE TEST No 2.4Document1 pageSUMMATIVE TEST No 2.4LV BENDANANo ratings yet
- Human Digestive System WorksheetDocument3 pagesHuman Digestive System WorksheetEvgeni Genev60% (5)
- Unit 5 Anatomy and Physiology in Health and Social CareDocument53 pagesUnit 5 Anatomy and Physiology in Health and Social Caremurdatwotimes90% (31)
- UNIT 325: 1.1 Describe Types of Change They May Occur in The Course of An Individual's LifeDocument7 pagesUNIT 325: 1.1 Describe Types of Change They May Occur in The Course of An Individual's LifemadalinaNo ratings yet
- The Human Digestive System:: Its Functions, Stages, and The Pathway of FoodDocument15 pagesThe Human Digestive System:: Its Functions, Stages, and The Pathway of FoodMichelle Casayuran - Regala100% (2)
- DigestiveDocument2 pagesDigestiveR NovNo ratings yet
- A Holistic Approach To AutismDocument11 pagesA Holistic Approach To AutismNapoleon Gonzalez Gil100% (2)
- Summative Test 4th - DigestiveDocument2 pagesSummative Test 4th - DigestiveMay Joy VitorioNo ratings yet
- Science 8 Quarter 4 Week 1 Long QuizDocument2 pagesScience 8 Quarter 4 Week 1 Long Quizjohn rexNo ratings yet
- Quiz. DigestiveDocument1 pageQuiz. DigestiveALEJANDRO CORTEZNo ratings yet
- The Digestive System Summative Test - Q3 - M1Document2 pagesThe Digestive System Summative Test - Q3 - M1Metchel100% (1)
- Activity 1 - Parts Functions Process of Digestive SystemDocument2 pagesActivity 1 - Parts Functions Process of Digestive SystemHezel MarieNo ratings yet
- Untitled (Flyer) (Flyer)Document10 pagesUntitled (Flyer) (Flyer)Angelica Joy SevillaNo ratings yet
- Digestive System TestDocument4 pagesDigestive System TestDaniel Walsh100% (1)
- B g8 Digestive SystemDocument3 pagesB g8 Digestive SystemnoorlailyNo ratings yet
- Bio Chapter 6 2Document8 pagesBio Chapter 6 2Shamma AhmedNo ratings yet
- Nutrition in Animals AnswersDocument4 pagesNutrition in Animals AnswersSHAJITHA ABDULHALEEMNo ratings yet
- Nutrition in AnimalsDocument1 pageNutrition in Animalsvalentino alvaresNo ratings yet
- Exercise Digestive SystemDocument2 pagesExercise Digestive SystemNathalia GreenNo ratings yet
- Unit 5: Digestive System Test BankDocument8 pagesUnit 5: Digestive System Test Bankjv peridoNo ratings yet
- Final Test For 4th Quarter ScienceDocument1 pageFinal Test For 4th Quarter ScienceLeah DumdumNo ratings yet
- Key For NatSci 2 Prefinal ExamDocument4 pagesKey For NatSci 2 Prefinal ExamManongdo AllanNo ratings yet
- 3.4 Absorption, Assimilasion and Defecation SCIENCE FORM 2Document2 pages3.4 Absorption, Assimilasion and Defecation SCIENCE FORM 2SCNo ratings yet
- Science 8 Summative Exam Q4Document4 pagesScience 8 Summative Exam Q4Kelvin Jason ArellanoNo ratings yet
- LESSON PLAN Bsed 3bDocument12 pagesLESSON PLAN Bsed 3bRjane CañeteNo ratings yet
- Dwnload Full Nutrition For Health and Healthcare 6th Edition Debruyne Solutions Manual PDFDocument35 pagesDwnload Full Nutrition For Health and Healthcare 6th Edition Debruyne Solutions Manual PDFsanjaktouchbox1wfw100% (13)
- Digestive SystemDocument3 pagesDigestive SystemWisdiyan Hadi HastomoNo ratings yet
- Full Download Nutrition For Health and Healthcare 6th Edition Debruyne Solutions ManualDocument35 pagesFull Download Nutrition For Health and Healthcare 6th Edition Debruyne Solutions Manualkeathleyjessiavipfx100% (27)
- Digestive System.Document3 pagesDigestive System.Andri MulyaniNo ratings yet
- Digestive SystemDocument13 pagesDigestive SystemAirene JabagatNo ratings yet
- NCERT Exemplar Class 7 Science Solutions Chapter 2 Nutrition in AnimalsDocument18 pagesNCERT Exemplar Class 7 Science Solutions Chapter 2 Nutrition in AnimalsSiva PrasadNo ratings yet
- Digestion System Science Form 2Document3 pagesDigestion System Science Form 2SCNo ratings yet
- First Written Test in Science 8 QUARTER 4, SY 2021-2022 Instructions: Read Each Question Carefully and Write The Correct Answer in ADocument5 pagesFirst Written Test in Science 8 QUARTER 4, SY 2021-2022 Instructions: Read Each Question Carefully and Write The Correct Answer in Ajoan marie Pelias100% (2)
- Basic Sciences RevuDocument16 pagesBasic Sciences RevuHermann CHEMEUHINo ratings yet
- MCQs of AHN Unit-1 GIT 31 Disorders CompleteDocument36 pagesMCQs of AHN Unit-1 GIT 31 Disorders Completeloferk44No ratings yet
- L2 Nutrition in Animals Worksheet Answerkey 2023 24Document15 pagesL2 Nutrition in Animals Worksheet Answerkey 2023 24Gaming ApocalypseNo ratings yet
- Test - D.2 Digestion - Quizlet - 1Document7 pagesTest - D.2 Digestion - Quizlet - 119092618No ratings yet
- Digestive SystemDocument3 pagesDigestive Systemacahaya880No ratings yet
- 4TH Periodical Test G8 Sy 2022 2023Document4 pages4TH Periodical Test G8 Sy 2022 2023Jayron SuazeNo ratings yet
- Final Exam in ScienceDocument2 pagesFinal Exam in ScienceMarilou VirtudazoNo ratings yet
- Nutrition in Animals - ContentDocument5 pagesNutrition in Animals - ContentJapneesh SidhuNo ratings yet
- Quiz Digestive SystemDocument5 pagesQuiz Digestive SystemutmezduqNo ratings yet
- Science Test Digesty and RespiratoryDocument1 pageScience Test Digesty and RespiratoryANDREA PAOLA DIAZ ANDRADENo ratings yet
- Let'S G EYO: OB NDDocument1 pageLet'S G EYO: OB NDJelaiNo ratings yet
- Activities: Read The Passage and Circle The Appropriate Answer. Circle A, B, C, or D. (Group Work)Document3 pagesActivities: Read The Passage and Circle The Appropriate Answer. Circle A, B, C, or D. (Group Work)Maria Fernanda Disla PerezNo ratings yet
- Digestive System Worksheet A Grade 4Document2 pagesDigestive System Worksheet A Grade 4buena100% (3)
- Human Physiology Digestive System: Name: - ClassDocument3 pagesHuman Physiology Digestive System: Name: - ClassKashaNo ratings yet
- LAS Quarter 4 Week 1 Grace CawilanDocument12 pagesLAS Quarter 4 Week 1 Grace CawilanGRACE CAWILANNo ratings yet
- Science 6 2nd Quarter W3Document10 pagesScience 6 2nd Quarter W3Leo CerenoNo ratings yet
- DIGSTIVE-SYSEM Q4 WK1 Sci8Document26 pagesDIGSTIVE-SYSEM Q4 WK1 Sci8Jasmine kNo ratings yet
- Lesson Plan Digestive SystemDocument5 pagesLesson Plan Digestive SystemglaizaNo ratings yet
- DigestionDocument3 pagesDigestionmuneeza dueveshNo ratings yet
- Digestive System ContinuationDocument38 pagesDigestive System ContinuationLocal ClownNo ratings yet
- Sci ch2 7th 05 01 2023 15 39 SolutionDocument4 pagesSci ch2 7th 05 01 2023 15 39 SolutionBhoomi GoyaniNo ratings yet
- Nutrition and Diet Therapy 9Th Edition Debruyne Test Bank Full Chapter PDFDocument36 pagesNutrition and Diet Therapy 9Th Edition Debruyne Test Bank Full Chapter PDFlaura.francis115100% (10)
- Nutrition and Diet Therapy 9th Edition DeBruyne Test Bank 1Document36 pagesNutrition and Diet Therapy 9th Edition DeBruyne Test Bank 1richardsmithxdqnzoywcb100% (44)
- Digestive System QuizDocument3 pagesDigestive System Quizapi-709247070No ratings yet
- Digestion Test BiologyDocument3 pagesDigestion Test BiologyKatrīna SimanovskaNo ratings yet
- CBSE Class 10 Life Processes MCQ Practice QuestionsDocument8 pagesCBSE Class 10 Life Processes MCQ Practice QuestionsBasavarajNo ratings yet
- 4h Quarter Module FinalDocument98 pages4h Quarter Module Finallevi sanchez100% (1)
- ANimal Nutritoin Exercise 2023Document4 pagesANimal Nutritoin Exercise 2023HjH Nurhazirah Hj Mohd SallehNo ratings yet
- DLP-GROUP-3Document10 pagesDLP-GROUP-3Mary Queen TeroNo ratings yet
- IWARDocument1 pageIWARMary Queen TeroNo ratings yet
- BAGANGA TOURDocument15 pagesBAGANGA TOURMary Queen TeroNo ratings yet
- Daily Lesson Log Q3 WK 1Document4 pagesDaily Lesson Log Q3 WK 1Mary Queen TeroNo ratings yet
- Daily Lesson LogDocument4 pagesDaily Lesson LogMary Queen TeroNo ratings yet
- ATTENDANCEDocument1 pageATTENDANCEMary Queen TeroNo ratings yet
- Storm ClassificationDocument18 pagesStorm ClassificationMary Queen TeroNo ratings yet
- Daily Lesson Log Q2 WK4Document5 pagesDaily Lesson Log Q2 WK4Mary Queen TeroNo ratings yet
- Assessment NotebookDocument4 pagesAssessment NotebookMary Queen TeroNo ratings yet
- Science 8 2 SUMMATIVE TEST (Quarter 2) 2 SUMMATIVE TEST (Quarter 2)Document1 pageScience 8 2 SUMMATIVE TEST (Quarter 2) 2 SUMMATIVE TEST (Quarter 2)Mary Queen TeroNo ratings yet
- Heat Vs TemperatureDocument1 pageHeat Vs TemperatureMary Queen TeroNo ratings yet
- Homeroom Meeting Ppt2Document21 pagesHomeroom Meeting Ppt2Mary Queen Tero100% (1)
- Q1S2 Back PageDocument1 pageQ1S2 Back PageMary Queen TeroNo ratings yet
- Daily Lesson Log 2024 WK 1Document5 pagesDaily Lesson Log 2024 WK 1Mary Queen TeroNo ratings yet
- OutputDocument23 pagesOutputMary Queen TeroNo ratings yet
- Properties of LightDocument29 pagesProperties of LightMary Queen TeroNo ratings yet
- Warm Air Rises and Cold Air SinksDocument1 pageWarm Air Rises and Cold Air SinksMary Queen TeroNo ratings yet
- Pneumatosis Cystoides Intestinalis: Report of Two Cases: M. Turan, M. S En, R. EgılmezDocument3 pagesPneumatosis Cystoides Intestinalis: Report of Two Cases: M. Turan, M. S En, R. EgılmezzixdiddyNo ratings yet
- Sonography of GITDocument11 pagesSonography of GITsononik1674100% (1)
- Intestinal Obstruction: A Report by C2Document22 pagesIntestinal Obstruction: A Report by C2Teanu Jose Gabrillo TamayoNo ratings yet
- Digestive System by Dr. Tehreem FatimaDocument9 pagesDigestive System by Dr. Tehreem FatimaTehreem FatimaNo ratings yet
- Human Body Digestive SystemDocument6 pagesHuman Body Digestive SystemMaria SibauNo ratings yet
- LabEx4 - Eukaryotic CellDocument11 pagesLabEx4 - Eukaryotic CellGlyndel ArcillasNo ratings yet
- Biochemistry of Digestive SystemDocument55 pagesBiochemistry of Digestive SystemSyam UnhasNo ratings yet
- Chapter One Introducing Poultry Production and Describing The Biology of The FowlDocument47 pagesChapter One Introducing Poultry Production and Describing The Biology of The FowlTamiru LegesseNo ratings yet
- Digestive System QuizDocument2 pagesDigestive System QuizAnnaliza Galia JunioNo ratings yet
- Original PDF Physiology of The Gastrointestinal Tract 6th Edition PDFDocument41 pagesOriginal PDF Physiology of The Gastrointestinal Tract 6th Edition PDFnoe.simons469100% (46)
- Animal PhysiologyDocument104 pagesAnimal PhysiologyClara MaeNo ratings yet
- Anat 106Document15 pagesAnat 106markuspinkusNo ratings yet
- Factors Affecting Drug Absorption PDFDocument2 pagesFactors Affecting Drug Absorption PDFRobNo ratings yet
- Test Terminologi MedisDocument4 pagesTest Terminologi MedisDeni PurnamasidiNo ratings yet
- MCQ InfectionsDocument10 pagesMCQ Infectionsعلي الكوافيNo ratings yet
- RMST v1 1 20Document20 pagesRMST v1 1 20Demian AlcaínoNo ratings yet
- Host Resistance FinalDocument12 pagesHost Resistance Finalflyers83No ratings yet
- Silica: There Is No Life Without Silica!Document4 pagesSilica: There Is No Life Without Silica!alerim_mNo ratings yet
- F2 Chap 3 MCQDocument5 pagesF2 Chap 3 MCQSuriya GunalanNo ratings yet
- Achievement Test in Science 6: St. Joseph College of Canlaon, IncDocument10 pagesAchievement Test in Science 6: St. Joseph College of Canlaon, IncALVEN OYANGORINNo ratings yet
- KefirDocument5 pagesKefirsarahsfakeNo ratings yet
- Anph111 Reviewer (Digestive)Document10 pagesAnph111 Reviewer (Digestive)Maria Clarisse ReyesNo ratings yet
- Indian Perspective For Probiotics: A Review: ArticleDocument12 pagesIndian Perspective For Probiotics: A Review: ArticleMurali DathanNo ratings yet
- Parasites EquinesDocument11 pagesParasites EquinesverocoquitoNo ratings yet
- Lecture 8Document21 pagesLecture 8cabdalefarxanomarjimcaleNo ratings yet
- Sub-Topic Digestion in Mammals: by Michael O. Nyaongo (BSC - Ed, MD)Document92 pagesSub-Topic Digestion in Mammals: by Michael O. Nyaongo (BSC - Ed, MD)Michael NyaongoNo ratings yet
- The Digestive System Connected To The Nervous SystemDocument3 pagesThe Digestive System Connected To The Nervous Systemاحمد احمدNo ratings yet
SCIENCE 8 4 ST 1
SCIENCE 8 4 ST 1
Uploaded by
Mary Queen TeroCopyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
SCIENCE 8 4 ST 1
SCIENCE 8 4 ST 1
Uploaded by
Mary Queen TeroCopyright:
Available Formats
SCIENCE 8 Direction: In a ¼ sheet of paper, write the letter of the correct answer.
QUARTER 4, SUMMATIVE 1
1. In what process do animals take in food that provides energy and nutrients?
Direction: In a ¼ sheet of paper, write the letter of the correct answer. A. assimilation C. excretion
1. In what process do animals take in food that provides energy and nutrients? B. digestion D. ingestion
A. assimilation C. excretion 2. The process in which digested foods are distributed into different parts of the body cells are
B. digestion D. ingestion _______.
2. The process in which digested foods are distributed into different parts of the body cells are A. assimilation C. excretion
_______. B. digestion D. ingestion
A. assimilation C. excretion 3. What is the process of turning food into smaller molecules with the aid of
B. digestion D. ingestion enzymes?
3. What is the process of turning food into smaller molecules with the aid of A. churning C. chemical digestion
enzymes? B. mastication D. mechanical digestion
A. churning C. chemical digestion 4. Where does the final stage in digestion of food happen?
B. mastication D. mechanical digestion A. liver C. small intestine
4. Where does the final stage in digestion of food happen? B. mouth D. large intestine
A. liver C. small intestine 5. What type of enzyme present in saliva helps break down starch?
B. mouth D. large intestine A. amylase C. lipase
5. What type of enzyme present in saliva helps break down starch? B. lactase D. maltase
A. amylase C. lipase 6. Which of the following breaks down food into tinier pieces to begin
B. lactase D. maltase mechanical digestion?
6. Which of the following breaks down food into tinier pieces to begin A. esophagus C. teeth
mechanical digestion? B. stomach D. tongue
A. esophagus C. teeth 7. What organ system is responsible for breaking down of large molecules into smaller
B. stomach D. tongue molecules and absorption of organic compounds needed by the body?
7. What organ system is responsible for breaking down of large molecules into smaller molecules A. circulatory system C. Nervous system
and absorption of organic compounds needed by the body? B. digestive system D. respiratory system
A. circulatory system C. Nervous system 8. What is the main function of the large intestine?
B. digestive system D. respiratory system A. It breaks down hemoglobin. C. It regulates the release of bile.
8. What is the main function of the large intestine? B. It secretes digestive enzymes. D. It reabsorbs water from chyme.
A. It breaks down hemoglobin. C. It regulates the release of bile. 9. What do you call the wavelike contraction of the smooth muscles of digestive tract pushes
B. It secretes digestive enzymes. D. It reabsorbs water from chyme. food in small sections through the gastro-intestinal tube?
9. What do you call the wavelike contraction of the smooth muscles of digestive tract pushes food A. mixing movement C. contractile movement
in small sections through the gastro-intestinal tube? B. parietal movement D. peristaltic movement
A. mixing movement C. contractile movement 10. If the liver is severely damaged, metabolism of which nutrients would be most affected?
B. parietal movement D. peristaltic movement A. carbohydrates C. proteins
10. If the liver is severely damaged, metabolism of which nutrients would be most affected? B. lipids D. All of the above
A. carbohydrates C. proteins 11. What is the most essential function of the intestinal villi?
B. lipids D. All of the above A. pushes the fecal matter into the rectum
11. What is the most essential function of the intestinal villi? B. increases surface area for nutrient absorption
A. pushes the fecal matter into the rectum D. secretes mucous to facilitate the movement of chyme via the alimentary canal
B. increases surface area for nutrient absorption 12. Which of the following shows the correct sequence of the processes involved in the human
D. secretes mucous to facilitate the movement of chyme via the alimentary canal digestive system?
12. Which of the following shows the correct sequence of the processes involved in the human A. assimilation, absorption, ingestion, digestion, and egestion
digestive system? B. digestion, ingestion, assimilation, egestion and absorption
A. assimilation, absorption, ingestion, digestion, and egestion C. egestion, absorption, digestion, assimilation and ingestion
B. digestion, ingestion, assimilation, egestion and absorption D. ingestion, digestion, absorption, assimilation and egestion
C. egestion, absorption, digestion, assimilation and ingestion 13. What is the term for the food that is chewed and mixed with saliva that turns into a moist
D. ingestion, digestion, absorption, assimilation and egestion ball?
13. What is the term for the food that is chewed and mixed with saliva that turns into a moist ball? A. bolus C. feces
A. bolus C. feces B. chyme D. gastric juice
B. chyme D. gastric juice 14. What is the process by which the nutrients from the digested food move into the blood
14. What is the process by which the nutrients from the digested food move into the blood vessels passing through the lining of the small intestine?
vessels passing through the lining of the small intestine? A. assimilation C. egestion
A. assimilation C. egestion B. digestion D. elimination
B. digestion D. elimination 15. Which of these substances is an enzyme that digests protein in the stomach?
15. Which of these substances is an enzyme that digests protein in the stomach? A. amylase C. pepsin
A. amylase C. pepsin B. hydrochloric acid D. saliva
B. hydrochloric acid D. saliva 16. The following organs are part of the human digestive system EXCEPT _____.
16. The following organs are part of the human digestive system EXCEPT _____. A. mouth C. small Intestine
A. mouth C. small Intestine B. esophagus D. gastro vascular cavity
B. esophagus D. gastro vascular cavity 17. In which part of the digestive system does the breaking down of food into tinier pieces
17. In which part of the digestive system does the breaking down of food into tinier pieces occur? occur?
A. mouth C. small intestine A. mouth C. small intestine
B. stomach D. large Intestine B. stomach D. large Intestine
18. Which of the following helps in the digestion of food in the mouth? 18. Which of the following helps in the digestion of food in the mouth?
A. amylase C. protease A. amylase C. protease
B. bile D. saliva B. bile D. saliva
19. What enzyme aids the digestion of lipids in the small intestine? 19. What enzyme aids the digestion of lipids in the small intestine?
A. amylase C. lipase A. amylase C. lipase
B. gastric enzyme D. pepsin B. gastric enzyme D. pepsin
20. Which tiny structures line the internal surface of the small intestine to increase its surface 20. Which tiny structures line the internal surface of the small intestine to increase its surface
area for the absorption of nutrients? area for the absorption of nutrients?
A. bile ducts C. salivary glands A. bile ducts C. salivary glands
B. cilia D. villi B. cilia D. villi
21. What aids the passage of food through the digestive tract? 21. What aids the passage of food through the digestive tract?
A. pull from the anus C. movement of the cilia A. pull from the anus C. movement of the cilia
B. chemical absorption D. wavelike muscle contractions B. chemical absorption D. wavelike muscle contractions
22. What is the main work of the digestive system? 22. What is the main work of the digestive system?
A. fights disease C. breaks down food A. fights disease C. breaks down food
B. regenerates cells D. distributes energy throughout the body B. regenerates cells D. distributes energy throughout the body
23. Which of the following is the correct order of the digestive tract? 23. Which of the following is the correct order of the digestive tract?
A. mouth → rectum → esophagus → rectum → anus → small intestine → large intestine A. mouth → rectum → esophagus → rectum → anus → small intestine → large intestine
B. mouth → stomach → esophagus → rectum → anus → small intestine →large intestine B. mouth → stomach → esophagus → rectum → anus → small intestine →large intestine
C. mouth → esophagus → stomach → small intestine → large intestine → rectum → anus C. mouth → esophagus → stomach → small intestine → large intestine → rectum → anus
D. mouth → esophagus → stomach → small intestine → anus → large intestine → rectum D. mouth → esophagus → stomach → small intestine → anus → large intestine → rectum
24. How do nutrients from digested food reach the blood? 24. How do nutrients from digested food reach the blood?
A. by passing through the esophagus into the blood A. by passing through the esophagus into the blood
B. by being absorbed into the blood through the blood vessels B. by being absorbed into the blood through the blood vessels
C. by being absorbed into the blood through the walls of the lungs C. by being absorbed into the blood through the walls of the lungs
D. by passing through the small intestine into the large intestine, then into the blood D. by passing through the small intestine into the large intestine, then into the blood
25. What will happen to the undigested food that pass through the digestive tract? 25. What will happen to the undigested food that pass through the digestive tract?
A. goes to the pancreas to await disposal A. goes to the pancreas to await disposal
B. enters to the stomach and await disposal B. enters to the stomach and await disposal
C. goes to small intestine and await disposal C. goes to small intestine and await disposal
D. moves down to the large intestine and await disposal D. moves down to the large intestine and await disposal
SCIENCE 8
QUARTER 4, SUMMATIVE 1
You might also like
- Human Digestive System WorksheetDocument3 pagesHuman Digestive System WorksheetSana Shakeel100% (9)
- SUMMATIVE TEST No 2.4Document1 pageSUMMATIVE TEST No 2.4LV BENDANANo ratings yet
- Human Digestive System WorksheetDocument3 pagesHuman Digestive System WorksheetEvgeni Genev60% (5)
- Unit 5 Anatomy and Physiology in Health and Social CareDocument53 pagesUnit 5 Anatomy and Physiology in Health and Social Caremurdatwotimes90% (31)
- UNIT 325: 1.1 Describe Types of Change They May Occur in The Course of An Individual's LifeDocument7 pagesUNIT 325: 1.1 Describe Types of Change They May Occur in The Course of An Individual's LifemadalinaNo ratings yet
- The Human Digestive System:: Its Functions, Stages, and The Pathway of FoodDocument15 pagesThe Human Digestive System:: Its Functions, Stages, and The Pathway of FoodMichelle Casayuran - Regala100% (2)
- DigestiveDocument2 pagesDigestiveR NovNo ratings yet
- A Holistic Approach To AutismDocument11 pagesA Holistic Approach To AutismNapoleon Gonzalez Gil100% (2)
- Summative Test 4th - DigestiveDocument2 pagesSummative Test 4th - DigestiveMay Joy VitorioNo ratings yet
- Science 8 Quarter 4 Week 1 Long QuizDocument2 pagesScience 8 Quarter 4 Week 1 Long Quizjohn rexNo ratings yet
- Quiz. DigestiveDocument1 pageQuiz. DigestiveALEJANDRO CORTEZNo ratings yet
- The Digestive System Summative Test - Q3 - M1Document2 pagesThe Digestive System Summative Test - Q3 - M1Metchel100% (1)
- Activity 1 - Parts Functions Process of Digestive SystemDocument2 pagesActivity 1 - Parts Functions Process of Digestive SystemHezel MarieNo ratings yet
- Untitled (Flyer) (Flyer)Document10 pagesUntitled (Flyer) (Flyer)Angelica Joy SevillaNo ratings yet
- Digestive System TestDocument4 pagesDigestive System TestDaniel Walsh100% (1)
- B g8 Digestive SystemDocument3 pagesB g8 Digestive SystemnoorlailyNo ratings yet
- Bio Chapter 6 2Document8 pagesBio Chapter 6 2Shamma AhmedNo ratings yet
- Nutrition in Animals AnswersDocument4 pagesNutrition in Animals AnswersSHAJITHA ABDULHALEEMNo ratings yet
- Nutrition in AnimalsDocument1 pageNutrition in Animalsvalentino alvaresNo ratings yet
- Exercise Digestive SystemDocument2 pagesExercise Digestive SystemNathalia GreenNo ratings yet
- Unit 5: Digestive System Test BankDocument8 pagesUnit 5: Digestive System Test Bankjv peridoNo ratings yet
- Final Test For 4th Quarter ScienceDocument1 pageFinal Test For 4th Quarter ScienceLeah DumdumNo ratings yet
- Key For NatSci 2 Prefinal ExamDocument4 pagesKey For NatSci 2 Prefinal ExamManongdo AllanNo ratings yet
- 3.4 Absorption, Assimilasion and Defecation SCIENCE FORM 2Document2 pages3.4 Absorption, Assimilasion and Defecation SCIENCE FORM 2SCNo ratings yet
- Science 8 Summative Exam Q4Document4 pagesScience 8 Summative Exam Q4Kelvin Jason ArellanoNo ratings yet
- LESSON PLAN Bsed 3bDocument12 pagesLESSON PLAN Bsed 3bRjane CañeteNo ratings yet
- Dwnload Full Nutrition For Health and Healthcare 6th Edition Debruyne Solutions Manual PDFDocument35 pagesDwnload Full Nutrition For Health and Healthcare 6th Edition Debruyne Solutions Manual PDFsanjaktouchbox1wfw100% (13)
- Digestive SystemDocument3 pagesDigestive SystemWisdiyan Hadi HastomoNo ratings yet
- Full Download Nutrition For Health and Healthcare 6th Edition Debruyne Solutions ManualDocument35 pagesFull Download Nutrition For Health and Healthcare 6th Edition Debruyne Solutions Manualkeathleyjessiavipfx100% (27)
- Digestive System.Document3 pagesDigestive System.Andri MulyaniNo ratings yet
- Digestive SystemDocument13 pagesDigestive SystemAirene JabagatNo ratings yet
- NCERT Exemplar Class 7 Science Solutions Chapter 2 Nutrition in AnimalsDocument18 pagesNCERT Exemplar Class 7 Science Solutions Chapter 2 Nutrition in AnimalsSiva PrasadNo ratings yet
- Digestion System Science Form 2Document3 pagesDigestion System Science Form 2SCNo ratings yet
- First Written Test in Science 8 QUARTER 4, SY 2021-2022 Instructions: Read Each Question Carefully and Write The Correct Answer in ADocument5 pagesFirst Written Test in Science 8 QUARTER 4, SY 2021-2022 Instructions: Read Each Question Carefully and Write The Correct Answer in Ajoan marie Pelias100% (2)
- Basic Sciences RevuDocument16 pagesBasic Sciences RevuHermann CHEMEUHINo ratings yet
- MCQs of AHN Unit-1 GIT 31 Disorders CompleteDocument36 pagesMCQs of AHN Unit-1 GIT 31 Disorders Completeloferk44No ratings yet
- L2 Nutrition in Animals Worksheet Answerkey 2023 24Document15 pagesL2 Nutrition in Animals Worksheet Answerkey 2023 24Gaming ApocalypseNo ratings yet
- Test - D.2 Digestion - Quizlet - 1Document7 pagesTest - D.2 Digestion - Quizlet - 119092618No ratings yet
- Digestive SystemDocument3 pagesDigestive Systemacahaya880No ratings yet
- 4TH Periodical Test G8 Sy 2022 2023Document4 pages4TH Periodical Test G8 Sy 2022 2023Jayron SuazeNo ratings yet
- Final Exam in ScienceDocument2 pagesFinal Exam in ScienceMarilou VirtudazoNo ratings yet
- Nutrition in Animals - ContentDocument5 pagesNutrition in Animals - ContentJapneesh SidhuNo ratings yet
- Quiz Digestive SystemDocument5 pagesQuiz Digestive SystemutmezduqNo ratings yet
- Science Test Digesty and RespiratoryDocument1 pageScience Test Digesty and RespiratoryANDREA PAOLA DIAZ ANDRADENo ratings yet
- Let'S G EYO: OB NDDocument1 pageLet'S G EYO: OB NDJelaiNo ratings yet
- Activities: Read The Passage and Circle The Appropriate Answer. Circle A, B, C, or D. (Group Work)Document3 pagesActivities: Read The Passage and Circle The Appropriate Answer. Circle A, B, C, or D. (Group Work)Maria Fernanda Disla PerezNo ratings yet
- Digestive System Worksheet A Grade 4Document2 pagesDigestive System Worksheet A Grade 4buena100% (3)
- Human Physiology Digestive System: Name: - ClassDocument3 pagesHuman Physiology Digestive System: Name: - ClassKashaNo ratings yet
- LAS Quarter 4 Week 1 Grace CawilanDocument12 pagesLAS Quarter 4 Week 1 Grace CawilanGRACE CAWILANNo ratings yet
- Science 6 2nd Quarter W3Document10 pagesScience 6 2nd Quarter W3Leo CerenoNo ratings yet
- DIGSTIVE-SYSEM Q4 WK1 Sci8Document26 pagesDIGSTIVE-SYSEM Q4 WK1 Sci8Jasmine kNo ratings yet
- Lesson Plan Digestive SystemDocument5 pagesLesson Plan Digestive SystemglaizaNo ratings yet
- DigestionDocument3 pagesDigestionmuneeza dueveshNo ratings yet
- Digestive System ContinuationDocument38 pagesDigestive System ContinuationLocal ClownNo ratings yet
- Sci ch2 7th 05 01 2023 15 39 SolutionDocument4 pagesSci ch2 7th 05 01 2023 15 39 SolutionBhoomi GoyaniNo ratings yet
- Nutrition and Diet Therapy 9Th Edition Debruyne Test Bank Full Chapter PDFDocument36 pagesNutrition and Diet Therapy 9Th Edition Debruyne Test Bank Full Chapter PDFlaura.francis115100% (10)
- Nutrition and Diet Therapy 9th Edition DeBruyne Test Bank 1Document36 pagesNutrition and Diet Therapy 9th Edition DeBruyne Test Bank 1richardsmithxdqnzoywcb100% (44)
- Digestive System QuizDocument3 pagesDigestive System Quizapi-709247070No ratings yet
- Digestion Test BiologyDocument3 pagesDigestion Test BiologyKatrīna SimanovskaNo ratings yet
- CBSE Class 10 Life Processes MCQ Practice QuestionsDocument8 pagesCBSE Class 10 Life Processes MCQ Practice QuestionsBasavarajNo ratings yet
- 4h Quarter Module FinalDocument98 pages4h Quarter Module Finallevi sanchez100% (1)
- ANimal Nutritoin Exercise 2023Document4 pagesANimal Nutritoin Exercise 2023HjH Nurhazirah Hj Mohd SallehNo ratings yet
- DLP-GROUP-3Document10 pagesDLP-GROUP-3Mary Queen TeroNo ratings yet
- IWARDocument1 pageIWARMary Queen TeroNo ratings yet
- BAGANGA TOURDocument15 pagesBAGANGA TOURMary Queen TeroNo ratings yet
- Daily Lesson Log Q3 WK 1Document4 pagesDaily Lesson Log Q3 WK 1Mary Queen TeroNo ratings yet
- Daily Lesson LogDocument4 pagesDaily Lesson LogMary Queen TeroNo ratings yet
- ATTENDANCEDocument1 pageATTENDANCEMary Queen TeroNo ratings yet
- Storm ClassificationDocument18 pagesStorm ClassificationMary Queen TeroNo ratings yet
- Daily Lesson Log Q2 WK4Document5 pagesDaily Lesson Log Q2 WK4Mary Queen TeroNo ratings yet
- Assessment NotebookDocument4 pagesAssessment NotebookMary Queen TeroNo ratings yet
- Science 8 2 SUMMATIVE TEST (Quarter 2) 2 SUMMATIVE TEST (Quarter 2)Document1 pageScience 8 2 SUMMATIVE TEST (Quarter 2) 2 SUMMATIVE TEST (Quarter 2)Mary Queen TeroNo ratings yet
- Heat Vs TemperatureDocument1 pageHeat Vs TemperatureMary Queen TeroNo ratings yet
- Homeroom Meeting Ppt2Document21 pagesHomeroom Meeting Ppt2Mary Queen Tero100% (1)
- Q1S2 Back PageDocument1 pageQ1S2 Back PageMary Queen TeroNo ratings yet
- Daily Lesson Log 2024 WK 1Document5 pagesDaily Lesson Log 2024 WK 1Mary Queen TeroNo ratings yet
- OutputDocument23 pagesOutputMary Queen TeroNo ratings yet
- Properties of LightDocument29 pagesProperties of LightMary Queen TeroNo ratings yet
- Warm Air Rises and Cold Air SinksDocument1 pageWarm Air Rises and Cold Air SinksMary Queen TeroNo ratings yet
- Pneumatosis Cystoides Intestinalis: Report of Two Cases: M. Turan, M. S En, R. EgılmezDocument3 pagesPneumatosis Cystoides Intestinalis: Report of Two Cases: M. Turan, M. S En, R. EgılmezzixdiddyNo ratings yet
- Sonography of GITDocument11 pagesSonography of GITsononik1674100% (1)
- Intestinal Obstruction: A Report by C2Document22 pagesIntestinal Obstruction: A Report by C2Teanu Jose Gabrillo TamayoNo ratings yet
- Digestive System by Dr. Tehreem FatimaDocument9 pagesDigestive System by Dr. Tehreem FatimaTehreem FatimaNo ratings yet
- Human Body Digestive SystemDocument6 pagesHuman Body Digestive SystemMaria SibauNo ratings yet
- LabEx4 - Eukaryotic CellDocument11 pagesLabEx4 - Eukaryotic CellGlyndel ArcillasNo ratings yet
- Biochemistry of Digestive SystemDocument55 pagesBiochemistry of Digestive SystemSyam UnhasNo ratings yet
- Chapter One Introducing Poultry Production and Describing The Biology of The FowlDocument47 pagesChapter One Introducing Poultry Production and Describing The Biology of The FowlTamiru LegesseNo ratings yet
- Digestive System QuizDocument2 pagesDigestive System QuizAnnaliza Galia JunioNo ratings yet
- Original PDF Physiology of The Gastrointestinal Tract 6th Edition PDFDocument41 pagesOriginal PDF Physiology of The Gastrointestinal Tract 6th Edition PDFnoe.simons469100% (46)
- Animal PhysiologyDocument104 pagesAnimal PhysiologyClara MaeNo ratings yet
- Anat 106Document15 pagesAnat 106markuspinkusNo ratings yet
- Factors Affecting Drug Absorption PDFDocument2 pagesFactors Affecting Drug Absorption PDFRobNo ratings yet
- Test Terminologi MedisDocument4 pagesTest Terminologi MedisDeni PurnamasidiNo ratings yet
- MCQ InfectionsDocument10 pagesMCQ Infectionsعلي الكوافيNo ratings yet
- RMST v1 1 20Document20 pagesRMST v1 1 20Demian AlcaínoNo ratings yet
- Host Resistance FinalDocument12 pagesHost Resistance Finalflyers83No ratings yet
- Silica: There Is No Life Without Silica!Document4 pagesSilica: There Is No Life Without Silica!alerim_mNo ratings yet
- F2 Chap 3 MCQDocument5 pagesF2 Chap 3 MCQSuriya GunalanNo ratings yet
- Achievement Test in Science 6: St. Joseph College of Canlaon, IncDocument10 pagesAchievement Test in Science 6: St. Joseph College of Canlaon, IncALVEN OYANGORINNo ratings yet
- KefirDocument5 pagesKefirsarahsfakeNo ratings yet
- Anph111 Reviewer (Digestive)Document10 pagesAnph111 Reviewer (Digestive)Maria Clarisse ReyesNo ratings yet
- Indian Perspective For Probiotics: A Review: ArticleDocument12 pagesIndian Perspective For Probiotics: A Review: ArticleMurali DathanNo ratings yet
- Parasites EquinesDocument11 pagesParasites EquinesverocoquitoNo ratings yet
- Lecture 8Document21 pagesLecture 8cabdalefarxanomarjimcaleNo ratings yet
- Sub-Topic Digestion in Mammals: by Michael O. Nyaongo (BSC - Ed, MD)Document92 pagesSub-Topic Digestion in Mammals: by Michael O. Nyaongo (BSC - Ed, MD)Michael NyaongoNo ratings yet
- The Digestive System Connected To The Nervous SystemDocument3 pagesThe Digestive System Connected To The Nervous Systemاحمد احمدNo ratings yet