Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Motion DPP
Motion DPP
Uploaded by
9-E PRADYOT SINHACopyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Motion DPP
Motion DPP
Uploaded by
9-E PRADYOT SINHACopyright:
Available Formats
Motion (Class-9)
Motion DPP-01
SECTION-A
Q. 1 to Q. 7 are multiple choice questions. Each question has four options (1), (2), (3) and (4) out of which only
one option is correct.
1. A boy is sitting on a chair in his study room. The boy is at rest in the room this is because
(1) his position changes with time
(2) his position does not change with time
(3) his position changes but the time does not pass by
(4) none of these
2. Assertion : Two kids are playing in the playground by passing a ball to each other. The ball is in motion
in the playground.
Reason : The position of ball changes with passage of time.
(1) Both assertion and reason are true and reason is correct explanation of assertion
(2) Both assertion and reason are true but reason is not the correct explanation of assertion
(3) Assertion is true but reason is false
(4) Both assertion and reason are false
3. Which part of the moving cycle undergoes rotational motion?
(1) Only A
(2) A and B
(3) A and C
(4) B and D
4. Which of the following types of motion is periodic?
(1) Motion of a car taking a turn on a curved road.
(2) Motion of the Earth around the Sun.
(3) Both (1) and (2).
(4) Neither (1) nor (2).
5. A motion that occurs when an object moves in a repeated pattern over equal periods of time is called
(1) rectilinear motion
(2) rolling motion
(3) periodic motion
(4) None of these
Digital Pvt. Ltd. [1]
Motion (Class-9)
6. Which of the following is an example of rectilinear motion?
(1) Motion of a pendulum
(2) Motion of the piston of a syringe
(3) Motion of a spinning top
(4) Motion of the moon around the earth
7. Which of these is NOT an example of circular motion?
(1) Motion of an electric fan
(2) Motion of Earth around Sun
(3) Motion of a box dropped from a height
(4) Motion of a merry-go-round
Q. 8 to 10 is multiple choice question. This question has four options (1),(2),(3) and (4) out of which ONE or
MORE THAN ONE options may be correct.
8. State of Motion is not described by
(1) Position of Rest only
(2) Position of Motion only
(3) Both by the State of Rest and Motion
(4) All of the above
9. A person, seated in a train in motion, is at rest with reference to
(1) the train
(2) a person watching him from the front seat.
(3) a car moving in the opposite direction to the train.
(4) trees on the ground.
10. In the below picture :
(1) Man standing on the roadside is in motion with respect to man sitting in car.
(2) Tree is at rest with respect to the man standing on the roadside.
(3) Car is in motion with respect to the tree.
(4) Both man standing on the roadside and tree are at rest with respect to car.
Digital Pvt. Ltd. [2]
Motion (Class-9)
SECTION-B
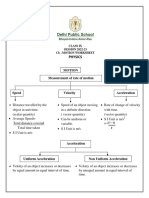
1. Complete the map
Kinematics
Rest
(no change in (change in position
position with time) with time)
Linear ___________ ___________
___________ eg.a spinning eg. a child on
top a swing
2. Match the column
Column-I Column-II
(A) Ball dropped from roof (p) Oscillatory motion
(B) Revolution of Moon around Earth (q) Rest
(C) Book kept on a table (r) Linear motion
(D) Pendulum of a wall clock (s) Circular motion
3. Fill in the blanks
Read the following statement and fill the blanks.
4. A point object is one whose dimension is ______ as compared to the distance it moves.
5. The sun is in ______________ with reference to the earth.
Read the following statements and mark your answer as true or false.
6. A lift operator, who is operating the lift for the people in the shopping mall, is at rest in the lift.
7. A child is mixing bournvita in hot milk in a glass by stirring it with a spoon. The spoon is at rest in the glass.
Digital Pvt. Ltd. [3]
Motion (Class-9)
8. A person is sitting in a boat moving in the river. The person is at rest in the river.
Subjective Questions.
9. What do you understand by reference point or origin ?
10. What do you understand by motion of an object ?
Digital Pvt. Ltd. [4]
Motion (Class-9)
SOLUTIONS DPP-01
SECTION-A
Answer Key
Question 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10
Answer 2 1 3 2 3 2 3 1,2,4 1,2 1,2,3
1. (2)
A boy is sitting on a chair in his study room. The boy is at rest in the room because his position does not
change with time. The objects at rest does not change their position with respect to time and surroundings.
2. (1)
Both assertion and reason are true, reason is correct explanation of assertion.
3. (3)
Wheel and pedal of the moving cycle are exhibiting rotational motion as both of than have their axis of
rotation around with whole body moves.
4. (2)
Motion of the earth around the Sun is a periodic motion as its motion repeat itself after equal interval of time.
5. (3)
A motion that occurs when an object moves in a repeated pattern over equal periods of time is called periodic
motion.
6. (2)
Motion of the piston of a syringe is an example of rectilinear motion as it is in straight line path.
7. (3)
Motion of a box dropped from a height is an example of rectilinear motion.
8. (1,2,4)
State of Motion is described by Both the State of Rest and Motion, as rest and motion are relative terms.
9. (1,2)
A person seated in a train in motion, is at rest with reference to the train and a person watching him from the
front seat as their distance is not changing with respect to time.
10. (1,2,3)
In the given picture a man standing on the roadside is in motion with respect to man sitting in the car. Tree is
at rest with respect to the man standing on the roadside and car is in motion with respect to the tree.
Digital Pvt. Ltd. [5]
Motion (Class-9)
SECTION-B
1.
2. (A) → (r), (B) → (s), (C) → (q), (D) → (p)
3.
4. Negligible
5. Motion
6. True
A lift operator, who is operating the lift for the people in the shopping mall is at rest in the lift.
7. False
A child is mixing bournvita in hot milk in a glass by stirring it with a spoon. The spoon is in motion in the glass.
8. False
A person is sitting in a boat moving in the river. The person is in motion with respect to the river.
9. In order to study motion, we have to choose a fixed position or point with respect to which the motion has to
be studied. Such a point or fixed position is called a reference point or the origin.
10. An object is said to be in motion if its position changes with time.
Digital Pvt. Ltd. [6]
Motion (Class-9)
Motion DPP-02
SECTION-A
Q. 1 to Q. 14 are multiple choice questions. Each question has four options (1),(2),(3) and (4) out of which only
one option is correct.
1. Which of the following is not a vector quantity?
(1) Speed
(2) Velocity
(3) Displacement
(4) Acceleration
2. Which of the following is not a scalar quantity?
(1) Distance
(2) Pressure
(3) Mass
(4) Force
3. A vector quantity can change only when
(1) its magnitude changes
(2) its direction changes
(3) either its magnitude or direction or both change
(4) None of these
4. Two vectors are equal if
(1) they have the same magnitude and different directions.
(2) they have different magnitudes and the same direction.
(3) they have different magnitudes and different directions.
(4) they have the same magnitude and direction.
5. Which of the following quantities has direction but not a vector?
(1) Time
(2) Temperature
(3) Electric current
(4) Energy
6. A person moves 3 km North, then 4 km West and finally 3 km South. His displacement from the
original position is
(1) 4 km West
(2) 7 km West
(3) 3 km East
(4) 10 km East
Digital Pvt. Ltd. [7]
Motion (Class-9)
7. An athlete completes one round of a circular track of radius R in 40 sec. What will be his displacement
at the end of 2 minutes 20 seconds?
(1) 2R
(2) 3R
(3) 7R
(4) Zero
8. Distance is
(1) always straight distance between initial and final point.
(2) a vector quantity.
(3) the length of path followed by an object.
(4) always negative
9. A body travels 50 km on a straight line for 1 hour. Choose the correct statement.
(1) Distance travelled by the body is greater than the displacement.
(2) Distance travelled by the body is less than the displacement.
(3) Distance travelled by the body is equal to the displacement.
(4) None of the above.
10. Two boys A and B start their journey from position P to position Q along two different paths as shown
in the figure below.
(1) Distances travelled by both boys A and B from P to Q are the same.
(2) Distance travelled by boy A is greater than the distance travelled by boy B from P to Q.
(3) Distances travelled by both boys A and B are different but their displacement from P to Q are the same.
(4) Distances travelled by both boys A and B are the same but their displacements from P to Q are different.
11. The distance travelled by a body in the nth second is given by the expression (2+3n). Find the initial
velocity and acceleration. Also, find its velocity at the end of 2 seconds.
(1) u = 1, a = 1, v = 2.5
(2) u = 3.5, a = 3, v = 9.5
(3) u = 3, a = 3.5, v = 9.5
(4) u = 2, a = 1, v = 3.5
Digital Pvt. Ltd. [8]
Motion (Class-9)
12. A three-wheeler starts from rest, accelerates uniformly with 1 ms-1 on a straight road for 10 s, and then
moves with uniform velocity. Plot the distance covered by the vehicle during the nth second (n=1,2,3…)
versus n. Find the velocity at the end of 10th second. What do you expect this plot to be during
accelerated motion: a straight line or a parabola?
(1) 15 m/s, Straight line
(2) 15 m/s Parabola
(3) 10 m/s Straight Line
(4) 10 m/s Parabola
13. Sunita starts from her home P, goes to school S via Q, R. Find the total distance and displacement
travelled respectively made by her to go from her home to school.
S 12 m R
10 m
Q 12 m P
(1) 34 m, 26 m
(2) 36 m, 24 m
(3) 30 m, 20 m
(4) 26 m, 34 m
14. Which of the following is the common characteristics of all moving bodies?
(1) They do not change their position with time.
(2) They change their position with time.
(3) They always travel with uniform speed.
(4) Equations of motion are applicable to them always.
Q. 15 is a multiple choice question. It has four options (1),(2),(3) and (4) out of which ONE or MORE THAN ONE
option may be correct.
15. An ant travels a distance of 8 cm from P to Q and then moves at a distance of 6 cm at right angles to
PQ.
(1) The net displacement of ant is zero.
(2) The net displacement of ant is 10 cm.
(3) The distance covered by ant is 14 cm.
(4) The net displacement of ant is 2 cm.
Digital Pvt. Ltd. [9]
Motion (Class-9)
SECTION-B
1. Crossword
Across
3. Algebraic addition is used for a ________ quantity.
5. Science of describing motion of an object using diagrams, equations etc.
7. An instrument in vehicles to measure distance travelled.
8. Displacement can be positive, ________ or zero.
Down
1. _________ never decreases with time.
2. An object is at rest if its __________ doesn't change with time.
4. Displacement is a ________ quantity.
6. Fixed point with respect to which motion is studied.
Read the following statements and write your answer as true or false (Q. 2 and Q. 3)
2. Odometer in a vehicle measures the displacement of the vehicle.
3. Distance covered by a body is equal to its displacement when it moves in a straight line in a fixed direction.
Read the following statement and fill the blanks. (Q. 4 to Q. 6)
4. If an object moves 1½ cycle on a circular path of 10 m radius, then the displacement of the object is ’10 × z’
m. The value of z is.............
5. The position of a particle going along a straight line is x1 =50 m at 10:30 AM and x2 =58 m at 10:35 AM. Its
displacement between 10:30 AM to 10:35 AM is ‘2 × y’ m. The value of y is..........
6. A body falling from a height of 10 m has __________ distance and ___________ displacement.
Subjective Questions
7. A particle moves along a circular path of radius R as shown in figure. Find distance travelled and displacement
between A and B.
Digital Pvt. Ltd. [10]
Motion (Class-9)
8. A particle moves along a circular path of radius R as shown in figure. Find distance travelled and displacement
between A and B.
9. A particle is moving in a circle of diameter 40 m. What is its distance and displacement as per the table given
below.
Rounds Displacement Distance
1.5
2.5
10. A boat sailing through a river moved eastward for 5 km, then cross the river by moving 3 km south ward. On
reaching the other side it moved westward through 1 km. find the distance and displacement of the boat.
Digital Pvt. Ltd. [11]
Motion (Class-9)
SOLUTIONS DPP-02
SECTION-A
Answer Key
Question 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15
Answer 1 4 3 4 3 1 1 3 3 3 2 3 1 2 2,3
1. (1)
Speed is a scalar quantity.
2. (4)
Force is a vector quantity.
3. (3)
A Vector quantity can be changed if either magnitude or direction of quantity changes
4. (4)
Two vectors are equal if they have the same magnitude and direction.
5. (3)
Electric current has direction but it is not a vector quantity.
6. (1)
N B 4 km A
W E 3 km 3 km
S
(end point) C O (Origin)
4 km
Displacement = xf – xi
= 4 – 0 = 4 km
His displacement from the original position is 4 km west.
7. (1)
(Origin) (end point)
2R
Given time = 2 m 20 sec = 140 sec.
In 40 sec → 1 round
In 140 sec → × 140
= 3.5 round
For 3 complete round displacement = 0
For last half round displacement = 2 R
Digital Pvt. Ltd. [12]
Motion (Class-9)
8. (3)
The distance is the length of path followed by an object.
9. (3)
If a body travels 50 km on a straight line for 1 hour then distance travelled by the body is equal to the
displacement.
10. (3)
Distances travelled by both boys A and B are different but their displacement from P to Q are the same.
11. (2)
Consider the distance travelled by an object in nth second Snth = u +1/2a (2n-1)
So, 2 + 3n = u a (2n – 1)
⇒ 2 + 3n = u + an –
Now equating both parts
an = 3n
⇒ a = 3m/s2
2=u–
⇒ u = = 3.5 m/s
Now as we know that according to the first law of motion.
Speed at the end of t seconds is calculated as v = u + at, where u is the initial velocity and a is the
acceleration.
So, velocity at the end of 2 seconds will be v = 3.5 + 3 × 2 = 9.2 metres/seconds
Hence, the velocity at the end of wo seconds will be 9.5 m/sec.
12. (3)
Distance travelled in nth second,
Snth = u + a/2 (2n-1)
As, u = 0, a = 1ms-2
Snth = 0 + ½(2n-1)
= ½(2n-1) m
So, the distance travelled by the three-wheeler at the end of each second are given by
n(s) 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10
Snth(m) 0.5 1.5 2.5 3.5 4.5 5.5 6.5 7.5 8.5 9.5
Now, velocity of the three-wheeler at the end of 10th second is given by
v = u + at = 0 + 1 x 10 = 10 ms-1
So, the values are linearly increasing, so the graph would be straight line inclined to the x axis.
13. (1)
Sunita starts from her home P, goes to school S via Q, R
S 12 m R O
10 m
Q 12 m P
Digital Pvt. Ltd. [13]
Motion (Class-9)
Distance = PQ + QR + RS
= 12 m + 10 m + 12 m = 34 m
Displacement = length of PS
By Pythagoras theorem (PS)2 = (OP)2 + (OS)2
(PS)2 = (10)2 + (24)2
(PS)2 = 100 + 576 = 676 m
PS = 26 m
14. (2)
An object is said to be in motion only if its position changes with respect to time. If it is not changing, it is said
to be in motion.
15. (2,3)
S
6 cm
P Q
8 cm
Distance = total path length
= 8 cm + 6 cm = 14 cm
Displacement = length of PS
(PS)2 = (PQ)2 + (QS)2
= 64 cm + 36 cm = 100 cm
∴ PS = 10 cm
The net displacement of ant is 10 cm.
The distance covered by ant is 14 cm.
SECTION-B
1. Crossword
Across Down
3. Scalar 1. Distance
5. Kinematics 2. Position
7. Odometer 4. Vector
8. Negative 6. Origin
2. False
Odometer in a vehicle that measures the distance of the vehicle.
3. True
Distance covered by a body is equal to its displacement when it moves in a straight line in a fixed direction.
4. Displacement of the object in 1 ½ cycle on a circular path
= 2 × Radius
= 2 × 10 m
= 20 m
10 (z) = 20 z = 2
Digital Pvt. Ltd. [14]
Motion (Class-9)
5. Displacement between 10 :30 AM to 10 : 35 AM = X2 – X1
= 58 m – 50 m
2y=8
y=4
6. 10 m, 10 m
3
7. R, 2R
2
3
Distance travelled between A and B = × (circumference of circle)
4
3 3
= × 2 R R
4 2
Displacement :-
In right angle triangle AOB
AB2 = R2 + OB2 AB2 = R2 + R2
AB2 = 2R2
AB = 2R 2 R 2
Displacement between A and B = R 2
8. Distance travelled between A and B = 2R
9. Distance travelled in 1 round = circumference of circle
Distance travelled in 1 round = 2 πr
Distance travelled in 1 round = π × 40 m = 40 π m
Displacement travelled in 1 round = 0
Distance travelled in 1.5 round = 1.5 × circumference of circle
Distance travelled in 1.5 round = 1.5 × 2 πr
Distance travelled in 1.5 round = 3 × π × 20 m = 60 π m
Displacement travelled in 1.5 round = 2R = 2 × 20 m = 40 m
Distance travelled in 2 rounds = 2 × circumference of circle
Distance travelled in 2 rounds = 2 × 2 πr
Distance travelled in 2 rounds = 4 × π × 20 m = 80 π m
Displacement travelled in 2 rounds = 0
Distance travelled in 2.5 rounds = 2.5 × circumference of circle
Distance travelled in 2.5 rounds = 2.5 × 2 πr
Distance travelled in 2.5 rounds = 5 × π × 20 m = 100 π m
Displacement travelled in 2.5 rounds = diameter of circle = 2R = 40 m
Digital Pvt. Ltd. [15]
Motion (Class-9)
5 km x N
O A
10. 3 km W E
B
C 1 km
S
Distance travelled by the boat = OA + AB + BC
Distance travelled by the boat = 5 km + 3 km + 1 km
Distance travelled by the boat = 9 km
In right angle triangle OXC
OC2 = OX2 + XC2
OC2 = (4)2 + (3)2 OC2 = 16 + 9
OC2 = 25
OC = 5 km Displacement of the boat = 5 km.
Digital Pvt. Ltd. [16]
Motion (Class-9)
Motion DPP-03
SECTION-A
Q.1 to Q.9 are multiple choice questions. Each question has four options (1),(2),(3) and (4) out of which only
one option is correct.
1. When a body moves with a constant speed in a circle
(1) Its acceleration is zero
(2) Its acceleration is increasing
(3) Its velocity is changing
(4) Its velocity is uniform
2. A boy walks to his school at a distance of 6 km with constant speed of 2.5 km/h and walks back with a
constant speed of 4 km/h. his average speed for round trip expressed in km/h is given as
(1) 24/13
(2) 40/13
(3) 3
(4) ½
3. Bus X travels a distance of 360 km in 5 hours whereas bus Y travels a distance of 476 km in 7 hours.
Which bus travels faster?
(1) Bus X
(2) Bus Y
(3) Buses X and Y both travel at the same speed.
(4) None of the above
4. A ball thrown vertically upwards with speed 'u' from the top of a tower reaches the ground in 9 s.
Another ball is thrown vertically downwards from the same position with speed 'u', takes 4 s to reach
the ground. Calculate the value of 'u'. (Take g=10ms-1)
(1) 125 m/s
(2) 75 m/s
(3) 25 m/s
(4) 175 m/s
Digital Pvt. Ltd. [17]
Motion (Class-9)
5. The motion of a car measured by an odometer is shown below:
S. No. Time Distance
1. 0 min 0 km
2. 1 min 1 km
3. 2 min 2 km
4. 3 min 3 km
5. 4 min 5 km
What is the average speed till the 3rd min of the journey ?
(5) 60 Km/h
(6) 90 Km/h
(7) 100 Km/h
(8) 40 Km/h
6. A car has a speed of 80 km/hr for the first half distance and 50 km/hr for the next half distance. Its
average speed (in km/hr) is
(1) 61.53
(2) 50
(3) 30
(4) 40
7. A car covers 30 km at a uniform speed of 60 km/hr and the next 30 km at a uniform speed of 40 km/hr.
The total time taken by the car, for its journey, is
(1) 30 min
(2) 45 min
(3) 75 min
(4) 120 m
8. A boy covers a distance AB of 2 km with a speed of 2.5 kmph while going A to B and comes back from
B to A with a speed 0.5 kmph. His average speed will be
(1) 1.5 kmph
(2) 1.2 kmph
(3) 0.83 kmph
(4) 3 kmph
9. A radio signal takes 1.3 seconds to reach the earth from the moon. If the speed of the signal is 3 × 108
m/s, then the distance of the moon from the earth is
(1) 3 × 105 km
(2) 3 × 105 m
(3) 3.9 × 105 km
(4) 3.9 × 105 m
Digital Pvt. Ltd. [18]
Motion (Class-9)
Q.10 is a multiple choice question. It has four options (1),(2),(3) and (4) out of which ONE or MORE THAN ONE
option may be correct.
10. A train travels at a speed of 60 Km/hr for 0.52 hr, at 30 Km/hr for next 0.24 hr and then at 70 Km/hr for
0.71 hr. The average speed of the train for its journey is
(1) 31.2 Km/hr
(2) 49.7 m/s
(3) 16.6 m/s
(4) 59.9 Km/hr
Digital Pvt. Ltd. [19]
Motion (Class-9)
SECTION-B
Read the following statements and write your answer as true or false.
1. Speedometer of a vehicle measures the instantaneous speed.
2. If a body moves with uniform speed, its initial speed is equal to final speed.
3. A body having uniform speed will always have uniform velocity.
The answer to are an integer (ranging from -999 to 999 both inclusive). Type that integer.
4. A cyclist ride for first 10 min. at a uniform speed of 20 Kmph and then for next 10 min. at a uniform speed of
30 Kmph. His average speed for the whole journey is (21+y) Kmph. Find y.
5. A teacher starts from his residence at 7:30 AM and reaches his school at 7:50 AM on his scooter. The school is
8 Km away from his residence. The average speed of the scooter is ‘6 x y’ m/s. Find the value of y.
6. A scooter acquires a velocity of 36 km/hr in just 10 seconds after the start. The acceleration of the scooter was
x m/s2. Find x.
7. A car travels a distance of 200 km from Delhi to Ambala towards north in 5 hours. Calculate its speed.
8. From the above question, calculate the magnitude of velocity of the car for this journey.
9. Crossword
Across
1. Shape of distance-time graph in case of uniform motion.
4. Body that covers equal distances in equal intervals of time is moving with uniform _______.
7. Decrease in velocity of an object with time.
8. Velocity can be_______, negative or zero.
Down
2. In uniform motion, average speed is equal to _____________ speed.
3. Instrument used in vehicles to measure instantaneous speed.
5. Acceleration is a ________ quantity.
6. Speed and _______ have the same units.
Digital Pvt. Ltd. [20]
Motion (Class-9)
10. Concept Map
Digital Pvt. Ltd. [21]
Motion (Class-9)
SOLUTIONS DPP-03
SECTION-A
Answer Key
Question 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10
Answer 3 2 1 3 1 1 3 3 3 3,4
1. (3)
When an object is moving with a constant speed in a circular path the direction of motion is changing at every
point of its motion. So its velocity is changing.
2. (2)
Vav = 2UV/U+V = (2)(2.5)(4) / (2.5 + 4) = 20/6.5 = (20x10) / 65 = 40/13
3. (1)
Speed =
Speed of bus X = = 72 km/hr
Speed of bus Y = = 68 km/hr
Speed of bus X is greater than bus Y
4. (3)
Ball is thrown from the top of tower, ⇒ height=−h,
For the first case, velocity = u , Time t=9s,
Using s=ut+ at2 ⇒−h=u×9− ×10×92
⇒−h = 9 u – 405 ....1
For the second case, velocity = −u , Time t=4s,
Using s=ut+ at2 ⇒ − h=−u×4− ×10×42
⇒−h=−4u−80 ....2
Equating equations 1 and 2,
⇒ 9u − 405 = − 4u − 80 ⇒ u = 25ms–1
5. (1)
Average speed =
= = 1 km/min.
[∵ 1 hr = 60 min]
= 60 km/hr
6. (1)
Given, u = 80 min/hr, v = 50 km/hr.
Average speed =
Average speed =
× ×
v= = 61.53 km/hr
Digital Pvt. Ltd. [22]
Motion (Class-9)
7. (3)
Total time = t1 + t2
t1 = = hr
/
t2 =
/
= hr
T = t1 + t2 = + = = hr
Now, × 60 = 75 min
8. (3)
Average speed =
u+v
× . × . .
= =
. .
= 0.83 km/hr
9. (3)
Distance of moon from the earth is
Distance = speed × time
= (3 × 108 × 1.3) m
= 3.9 ×105 km
10. (3,4)
Average speed =
d1 = v1 × t1 = 60 × 0.52
d2 = v2 × t2 = 30 × 0.24
d3 = v3 × t3 = 70 × 0.71
(60 × .52) + (30 × .24) + (70 × .71)
0.52 + 0.24 + 0.71
. . . .
= = = 59.9 km/hr
. .
59.9 × m/s = 16.6 m/s
Digital Pvt. Ltd. [23]
Motion (Class-9)
SECTION-B
1. True
speedometer of a vehicle measures instantaneous speed.
2. True
if a body moves with uniform speed, its initial speed is equal to final speed.
3. False
A body moving with constant speed in a circular motion do not have constant (or uniform) velocity because
the velocity changes its direction continuously.
4. vavg =
vavg = = =
21 + y = 25
y=4
5. time = 20 min, distance = 8 km
v= = = 8 × 3 = 24 m/s
/
6 × y = 24m/s
y=4
6. Given, final velocity = 36 km/hr = 10 m/s, initial velocity = 0, time = 10 sec
–
acceleration =
( ) /
a= =1 m/s2
x=1
7. Given, distance = 200 km, time = 5 hours
speed = = = 40 km/hr
8. magnitude of velocity = 40 km/hr
9. 1. Straight 2.Instantaneous 3.Speedometer 4.Speed 5.Vector
6. Velocity 7.Deceleration
Digital Pvt. Ltd. [24]
Motion (Class-9)
10.
acceleration acceleration
speed speed
uniform non uniform
deceleration
objects changes
it's speed it's
direction or both
Digital Pvt. Ltd. [25]
Motion (Class-9)
Motion DPP-04
SECTION-A
Q.1 to Q.10 are multiple choice questions. Each question has four options (1),(2),(3) and (4) out of which only
one option is correct.
1. A quantity has a value of – 6.0 m/s. It may be the
(1) speed of a particle.
(2) velocity of a particle.
(3) position of a particle.
(4) None of these.
2. Velocity of an object can be changed by changing
(1) the speed of the object.
(2) the direction of motion of the object.
(3) both the speed and direction of motion of the object.
(4) All (1), (2) and (3) are true.
3. An engineer is asked to design a playground slide such that the speed of a child reached at the bottom
does not exceed 6 m/s. Determine height that the slide can be
(1) 2.9m
(2) 1.8m
(3) 14m
(4) 3.2m
4. A car travels a distance of 200 km from point A to point B towards north in 5 hours. Calculate the
velocity of the car for this journey.
(1) 40 km/h towards south
(2) 40 km/h towards north
(3) 0 km/h
(4) 100 km/h towards west
5. An object is moving along a circular path of radius 1 m, with a constant speed of 2 m/s then it's
average velocity for one complete cycle is
(1) 2 m/s
(2) 2π m/s
(3) 1 m/s
(4) 0 m/s
6. A cyclist moving on a circular track of radius 40 m completes half a revolution in 40 sec. Its average
velocity is
(1) zero
(2) 2 m/s
(3) 4π m/s
(4) 8π m/s
Digital Pvt. Ltd. [26]
Motion (Class-9)
7. A cyclist moving on a circular track of radius 40 m completes half a revolution in 40 sec. His average
velocity is nearly
(1) zero
(2) 4π m/s
(3) 2 m/s
(4) 8π m/s
8. A 100 m long train crosses a bridge of length 200 m in 50 seconds with constant velocity. Find the
velocity of the train.
(1) 4 m/s
(2) 5 m/s
(3) 6 m/s
(4) 7 m/s
9. A cat runs 200 m away from a wall in a straight line in 12 s and then runs halfway back in 8 s. Its
average velocity is
(1) 10 m/s
(2) 15 m/s
(3) 20 m/s
(4) 5 m/s
10. A body starts its motion from A and moves along a square path ABCD of side 10 m (path shown in
figure below). After 10 seconds, it reaches point D. Find the average velocity of the body for its journey
from A to D.
(1) 3 m/s
(2) 2 m/s
(3) 1 m/s
(4) 4 m/s
Digital Pvt. Ltd. [27]
Motion (Class-9)
SECTION-B
1. Concept Map
Read the following statements and mark your answer as true or false.
2. An aero plane is flying with a constant speed of 250 m/s at an altitude of 1000 m along north. The motion of
aero plane is non-uniform.
3. Motion of a car along a circular track at a constant speed is a uniform motion.
4. A body having uniform speed will always have uniform velocity.
Read the following statement and choose the correct option to fill the blanks.
5. For an object in uniform motion, both it’s ______________ and _____________ remain constant?
6. If the velocity of body moving in a particular direction changes with time, the ratio of displacement to the time
taken is called its ___________.
7. 5 m/s = _________ km/hr
8. A truck driver drives 20 km down the road in 5 minutes. He then reverses and drives 12 km up the road in 3
minutes what is his average velocity?
9. A man walks 10 km east in 2 hours and then 2.5 km west in 1 hour. Calculate the total average velocity of a
man ?
10. A man starts walking from a point on a circular field of radius 0.5 km and 1 hour later he finds himself at the
same point where he initially started. What is the average velocity of man ?
Digital Pvt. Ltd. [28]
Motion (Class-9)
SOLUTIONS DPP-04
SECTION-A
Answer Key
Question 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10
Answer 2 4 2 2 4 2 3 3 4 3
1. (2)
As velocity can be negative, positive or zero, it is a velocity of particle.
2. (4)
Velocity is a vector quantity. It can be changed by changing speed / direction or both.
3. (2)
V2 – u2 = 2gH, 62 – 0 = 2(10)(H) , 36/20 = 1.8m
4. (2)
Velocity =
200 km
= 40
5 hr
The velocity of the car is 40 km/hr towards north
5. (4)
Total displacement is 0 hence average velocity is zero
6. (2)
Vav = Displacement/time = (R + R)/t = 80/40 = 2m/s
7. (3)
Given, r = 40 m for half revolution, displacement = 2 r
= 20 × 40
= 80 m
Average velocity = =
= 2 m/s
8. (3)
Velocity =
displacement = 100 m + 200 m = 300 m
∴ Velocity =
6 m/s
Digital Pvt. Ltd. [29]
Motion (Class-9)
9. (4)
100 m
Wall
200 m
–
Average velocity =
= =
( )
= 5 m/s
10. (3)
Average velocity =
= = 1 m/s
SECTION-B
1.
Velocity
Rate of change of
distance with a time
Scalar
Average velocity
Total distance m/s
Total time taken
cm/s
2. False
An aeroplane is flying with a constant speed of 250 m/s at an altitude of 1000 m along north. The motion of
aeroplane is uniform.
3. False
As direction of the motion of fan changes continuously it is not performing uniform motion.
Digital Pvt. Ltd. [30]
Motion (Class-9)
4. False
A body moving with constant speed in a circular motion do not have constant (or uniform) velocity because
the velocity changes its direction continuously.
5. For an object in uniform motion, both it’s speed and direction remain constant?
6. If the velocity of body moving in a particular direction changes with time, the ratio of displacement to the time
taken is called its acceleration.
7. × →
m 18 km
× →
s 5 hr
5 m/s × = 18 km/hr
20 km
8.
12 km
8 km
displacement = 8 km, time = 8 minute
displacement
average velocity =
time
8 km
=
8 minute
8 km×60
=
8 hr
= 10 km/hr
9. Given, displacement = (10 - 2.5) km = 7.5 km, time = (2 + 1)hr = 3 hr
displacement
average velocity =
time
.
=
= 2.5 km/hr
10.
Initial point 0.5 km
Final point
displacement
average velocity =
time
= = 0 km/hr
hence average velocity of man will be zero.
Digital Pvt. Ltd. [31]
Motion (Class-9)
Motion DPP-05
SECTION-A
Q.1 to Q.6 are multiple choice questions. Each question has four options (1),(2),(3) and (4) out of which only
one option is correct.
1. Uniform retardation of a moving body shows that
(1) The speed of body increases
(2) The speed of body decreases
(3) The acceleration of body increases
(4) The acceleration of body decreases
2. The velocity of an object reduces from 15 m/s to 5 m/s in 10 seconds. What is the acceleration of the
object?
(1) 1 m/s2
(2) -1 m/s2
(3) 2 m/s2
(4) -2 m/s2
3. Which of the following cases represents retardation?
(1) A car starting from rest.
(2) A stone falling from a height.
(3) A train coming to a halt at the station.
(4) A bus moving with uniform velocity.
4. A scooter acquires a velocity of 36 km per hour in 8 seconds just after the start. Calculate the
acceleration of the scooter.
(1) 4.5 m/s2
(2) 1.5 m/s2
(3) 1.25 m/s2
(4) 2.25 m/s2
5. A trolley starts from rest and goes down an inclined plane with an acceleration of 4 cms–2. What will be
its velocity after 5 s from the start?
(1) 2 m/s
(2) 20 cm/s
(3) 2 cm/s
(4) 20 m/s
Digital Pvt. Ltd. [32]
Motion (Class-9)
6. A block accelerates down a slope, as shown in the figure.
The upper portion of the slope is smooth and lower portion is rough. On
the lower portion,
(i) the speed of the block may increase or remain same.
(ii) the acceleration of block reduces.
(iii) the mass of block reduces
Which of the following is/are correct?
(1) (ii) only
(2) (ii) and (ii) only
(3) (ii) and (iii) only
(4) (i), (ii) and (iii)
Q. 7 to Q. 10 are multiple choice questions. Each question has four options (1),(2),(3) and (4) out of which ONE
or MORE THAN ONE options may be correct.
7. m/s2 is the SI unit of
(1) Acceleration
(2) Retardation
(3) Rate of change of velocity
(4) Velocity
8. Which of the following cases does not represent retardation?
(1) You are moving towards your school.
(2) Bird flying from nest to the sky.
(3) A football going towards goal keeper
(4) A car comes out from the mall.
9. The ratio of CGS to MKS unit of acceleration is
(1) 1:100
(2) 10-1:1
(3) 10-2:1
(4) 100:1
10. The position of a particle moving along the x-axis at certain times is given below:
t (sec) 0 1 2 3
x (m) –2 0 6 16
Which of the following describes the motion correctly?
(1) Uniform, Accelerated
(2) Uniform, Decelerated
(3) Non-uniform, Accelerated
(4) Non-uniform, Decelerated
Digital Pvt. Ltd. [33]
Motion (Class-9)
SECTION-B
The answer to Q. 1 to Q. 3 is an integer (ranging from -999 to 999 both inclusive). Type that integer.
1. A bus-driver applies the brakes and slows down the velocity of bus from 80 Km/hr to 60 Km/hr in 10 minutes.
The acceleration of the bus is (40 x z) Km/hr2. Find the value of z.
2. A car starts from rest and attains a speed of 10 m/s in 10 seconds. The acceleration of the car is x m/s2, find
the value of x ?
3. A scooter acquires a velocity of 72 km/hr in just 10 seconds after the start. The acceleration of the scooter was
x m/s2. Find x.
Read the following statements and write your answer as true or false (Q.4 to Q. 7)
4. If a body moves with non-uniform velocity, its acceleration is zero.
5. It is possible for a body to have non-zero acceleration and zero velocity.
6. Acceleration is a vector quantity.
7. Acceleration and retardation are measured in different units.
Read the following statement and choose the correct option to fill the blanks. (Q. 8 and Q. 9)
8. All objects in free fall at a given place have the same__________.
9. ‘Uniform acceleration’ means magnitude of acceleration is __________, and direction of acceleration is _________.
10. Match the column
Column-I Column-II
(A) Change in the direction of velocity (p) Cyclist going on a straight road at constant speed
(B) Increase in the magnitude of velocity (q) Aeroplane landing on a runway
(C) Decrease in the magnitude of velocity (r) Motion of the tip of second's hand of a clock
(D) Zero acceleration (s) Train starting from a station
Digital Pvt. Ltd. [34]
Motion (Class-9)
SOLUTIONS DPP-05
SECTION-A
Answer Key
Question 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10
Answer 2 2 3 3 2 1 1,2,3 1,2,4 1,3 3,4
[
1. (2)
Uniform retardation means minus sign with magnitude. E.g. – 1 m/s2. In it the speed (magnitude) of the body
decreases.
2. (2)
–
Acceleration = = 10
= 10
= – 1 m/s2
3. (3)
A train coming to a halt at the station represent velocity decreasing, hence there is retardation.
4. (3)
v = 36 × m/s = 10 m/s
–
Acceleration =
a= = 1.25 m/s2
5. (2)
Given, a = 4 cm/s2, u = 0, t = 5 s, v = ?
v = u + at
v = 0 + 4 cm/s2 × 5 s
v = 20 cm/s
6. (1)
The acceleration of the block reduces as it’s a rough surface, so the rate of change in velocity will also
decrease and even an object can come rest.
7. (1,2,3)
Acceleration, retardation and rate of change of velocity has unit m/s2.
8. (1,2,4)
You are moving towards your school, bird flying from nest to the sky, a football going towards goal keeper, a
car comes out from the mall. All these are examples of acceleration and not the retardation.
9. (1,3)
CGS to MKS unit acceleration = =
1cm
∵ = 1: 100
100cm
10. (3,4)
Non-uniform, Accelerated and Non-uniform, Decelerated
Digital Pvt. Ltd. [35]
Motion (Class-9)
SECTION-B
1. Given, u = 80 km/hr, v = 60 km/hr, v = 10 min.
a= = = –120 km/hr
(40 × z) km/hr2 = – 120 km/hr2
z=–3
2. Given, u = 0, v = 10 m/s, t = 10 s
a= = = 1 m/s
Given acceleration of the car is x m/s2
here, x = 1
3. Given, u = 0, v = 72 km/hr = 20 m/s, t = 10 s
a= = = 2 m/s
Given acceleration of the car is x m/s2
here, x = 2
4. False
If a body moves with a uniform velocity, its acceleration is zero.
5. False
If the velocity of a body is zero, then acceleration is also zero.
6. True
Acceleration has both magnitude and direction.
7. False
Acceleration and retardation are measured in same units.
8. Acceleration
9. Constant, constant
10. (A) → (r), (B) → (s), (C) → (q), (D) → (p)
Digital Pvt. Ltd. [36]
Motion (Class-9)
Motion DPP-06
SECTION-A
Q.1 to Q.8 are multiple choice questions. Each question has four options (1),(2),(3) and (4) out of which only
one option is correct.
1. If a body starts from rest and moves with uniform acceleration, then
(1) v ∝ t
(2) s ∝ t
(3) v ∝ s
(4) s ∝ √t
2. A ball is dropped from a high-rise platform at t=0 starting from rest. After 6 seconds another ball is
thrown downwards from the same platform with a speed v. The two balls meet at t=18s. What is the
value of v (in m/s)? (Take g=10m/s2)
(1) 75
(2) 25
(3) 50
(4) 125
3. Tripling the speed of a car multiplies the distance needed for stopping it by
(1) 3
(2) 6
(3) 9
(4) Nothing can be decided
4. A particle starts moving from rest with uniform acceleration. It travels a distance x in
first 2 seconds and distance y in the next 2 seconds. Then
(1) y=x
(2) y=2x
(3) y=3x
(4) y=4x
5. The velocity of a particle increases from u to v in a time t, during which it covers a distance s. If the
particle has a uniform acceleration, which one of the following equations does not apply to the
motion?
(1) 2s = (v + u)t
(2) a =
(3) v2 = u2 – 2as
(4) s = u + at t
Digital Pvt. Ltd. [37]
Motion (Class-9)
6. A particle accelerates uniformly from rest along a straight line. The displacement covered by the
particle in time t is directly proportional to
(1) t
(2) t2
(3) t3
(4) t4
7. A bus accelerates uniformly from rest and acquires a speed of 72 km/hr in 20 sec. The distance covered
by the bus in 20 sec is
(1) 100 m
(2) 200 m
(3) 400 m
(4) 720 m
8. A particle starts with initial velocity 10 m/s. It covers a distance of 50 m along a straight line in two
seconds. The acceleration of the particle is
(1) 30 m/s2
(2) 10 m/s2
(3) 15 m/s2
(4) 20 m/s2
Q.9 and Q.10 are multiple choice questions. Each question has four options (1),(2),(3) and (4) out of which ONE
or MORE THAN ONE option may be correct.
9. A car accelerates uniformly from 36 Kmh-1 to 72 Kmh-1 in 5 seconds. Then,
(1) the acceleration of the car is 2 ms-2.
(2) the acceleration of the car is 7.2 ms-2.
(3) the distance covered by the car in 5 seconds is 75 m.
(4) the distance covered by the car in 5 seconds is 50 m.
10. A ball is thrown vertically upwards. Choose the correct statement.
(1) The instantaneous velocity during the upward motion from A to B is positive
(2) The average velocity of the body travelling from A to C is zero.
(3) The acceleration from B to C is positive
(4) The acceleration at the position B is zero
Digital Pvt. Ltd. [38]
Motion (Class-9)
SECTION-B
Read the following statements and mark your answer as true or false.
1. The first equation of motion gives the relation between initial velocity, final velocity, acceleration and time.
2. The equations of motion are applicable only when the body moves with uniform acceleration.
3. A bus starts from rest and moves with an acceleration of 1 m/s2 for 5 seconds. The distance travelled by the
bus is 25 m.
Read the following statement and choose the correct option to fill the blanks.
4. If a jeep starts from rest and accelerates uniformly, the distance it travels is proportional to the _______ of the
time it travels.
The answer to Q.5 is an integer (ranging from -999 to 999 both inclusive). Type that integer.
5. A car is moving with a velocity 20 ms–1. The brake are applied to retard it at a rate of 2 ms–2. What will be the
velocity after 5 s of applying the brakes?
Passage Based Questions (Q.6 and Q.7)
A particle starts with an initial velocity 2.5 m/s along a direction and it accelerates uniformly at the rate of 0.50
m/s2.
6. What is the distance travelled by particle in first two seconds ?
7. How much time does the particle take to reach the velocity 7.5 m/s ?
Subjective Questions
8. A ball is gently dropped from a height of 20 m. If its velocity increases uniformly at the rate of 10 m/s2, with
what velocity will it strike the ground ? After what time will it strike the ground ?
9. A motor car moving with a uniform velocity of 20 m/s comes to stop, on the application of brakes, after
travelling a distance of 10 m. What is its acceleration ?
10. A bullet moving with 10 m/s hits a wooden plank. The bullet is stopped when it penetrates the plank 20 cm
deep. Calculate the retardation of the bullet.
Digital Pvt. Ltd. [39]
Motion (Class-9)
SOLUTIONS DPP-06
SECTION-A
Answer Key
Question 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10
Answer 1 1 3 3 1 2 2 3 1,3 2,3
1. (1)
If a body starts from rest and moves with uniform acceleration, then
v = u + at, u = 0, a = constant
∴v∝t
2. (1)
The distance travelled by the first ball in 18s is h= (1/2)gt2= (1/2)×10× (18)2=1620m
Now to meet second ball has to cover same distance in (18−6) =12s
So, for second ball,
h=vt +(1/2)gt2
1620=v×12+(1/2)×10× (12)2
v= (1620−720)/12=75m/s
3. (3)
s ∝ u2, if the speed becomes three times then the distance needed for stopping will be nine times.
4. (3)
Let the acceleration of the particle be α.
Initial velocity vi = 0
∴ Distance travelled in 2 seconds : x = vi t + αt2 where t = 2 s
∴ x = 0 + α (2)2 = 2α …………(1)
Distance travelled in 4 seconds: S = vi t + αt2 where t = 4 s
∴ S = 0 + α (4)2 = 8α …………(2)
⇒ Distance traveled in last 2 seconds: y = 8α – 2α = 6α
∴ = ⇒ y = 3x
5. (1)
2s = (v + u)t
If the particle has a uniform acceleration the given equations does not apply to the motion
6. (2)
s = ut + at2
∴ s ∝ t2
Digital Pvt. Ltd. [40]
Motion (Class-9)
7. (2)
Given, u = 0, v = 72 km/hr = 20 m/s, t = 20 s
v = u + at
20 m/s = 0 + a (20 sec)
a = 1 m/s2
v2 = u2 + 2as
(20)2 = 0 + 2 × (1)s
s= = 200 m
The distance covered by the bus in 20 sec is 200 m.
8. (3)
Given, u = 10 m/s, s = 50 m, t = 2 sec
s = ut + at2
50 = 10 × 2 + a × 4
50 = 20 + 2a
2a = 30
a = 15 m/s2
9. (1,3)
Given, v =72 × = 20 m/s
u = 36 × = 10 m/s
=a
–
=a
a = 2 m/s2
v2 = u2 – 2as
(20)2 = (10)2 +2 × 2 × s
s = 75 m
The acceleration of the car is 2 ms-2
The distance covered by the car in 5 seconds is 75 m.
10. (2,3)
The average velocity of the body travelling from A to C is zero as net displacement is 0, the acceleration from B
to C is positive.
SECTION-B
1. False
v = u + at
The first equation of motion gives the relation between initial velocity, final velocity, acceleration and time.
Digital Pvt. Ltd. [41]
Motion (Class-9)
2. False
The equations of motion are applicable only when the body moves with uniform acceleration.
3. False
The distance travelled should be 12.5 meter
4. Square
5. u = 20 m/s, a = 2 m/s2, t = 5 sec
v = u + at
v = 20 + (-2) 5 = 20 – 10 = 10 m/s.
6. u = 2.5 m/s, a = 0.50 m/s2 , s = ?, t = 2 sec.
1 2
s = ut + at
2
1 5
= 2.5 × 2 + × ×2×2
2 10
= 5 + 1 = 6 m.
7. v = u + at
7.5 = 2.5 + 0.5 t
7.5 2.5
=t
.5
t = 10 sec.
8. a = 10 m/s2
v2 = u2 + 2 gh
v2 = 0 + 2 × 10 ×20
v2 = 400 m/s
v = 20 m/s
9. u = 20 m/s, v = 0, s = 10 m
v2 = u2 + 2 as
0 = 400 + 2 × -a × 10
400
= -a
20
a = 20 m/s2
10. u = 10 m/s, v = 0, s = 20 cm = 0.20 m, a = ?
v2 = u2 -2 as
0 – 100 = - 2 × 0.2 × a
1000
=a
4
250 = a
a = 250 m/s2
Digital Pvt. Ltd. [42]
Motion (Class-9)
Motion DPP-07
SECTION-A
Q.1 to Q.8 are multiple choice questions. Each question has four options (1),(2),(3) and (4) out of which only
one option is correct.
1. From the given velocity-time graph, it can be inferred that the object is
v
(1) in uniform motion
(2) is at rest
(3) moving with non-uniform acceleration
(4) moving with uniform acceleration
2. The distance-time graph of an object is shown in figure.
Distance
Time
The object
(1) is at rest.
(2) moves with a constant speed.
(3) moves with a constant velocity.
(4) moves with a constant acceleration.
3. The velocity-time graph of a moving particle is a straight line inclined to the time axis at some angle.
Its acceleration is
(1) zero
(2) constant
(3) increasing
(4) decreasing
4. If the velocity-time graph for a body is parallel to the time axis, then the body is
(1) stationary
(2) moving with constant velocity
(3) moving with constant acceleration
(4) moving with variable speed
Digital Pvt. Ltd. [43]
Motion (Class-9)
5. Figure shows velocity-time graph. Find the interval in which the body is exhibiting retarded motion
v
10 m/s
a 10 20 t
(1) (0 – 10) s
(2) (10 – 20) s
(3) (0 – 20) s
(4) None
6. Which of these graphs is not possible?
Distance →
(1)
Time →
Distance →
(2)
Time
Distance →
(3)
Time →
Distance →
(4)
Time →
Digital Pvt. Ltd. [44]
Motion (Class-9)
7. The velocity-time graph of two cars A and B is shown below.
A
velocity
0 t time
Which car travels a larger distance in a given time interval 't' ?
(1) Both travel equal distance
(2) Both are at rest
(3) Car A
(4) Car B
8. Motion of a particle (l) is shown from the beginning till the end of its journey. The arrows (rays)
represent the distance(s) covered by the particle in equal intervals of time (t).
Begin End
The distance-time graph of the motion of the particle is given by,
(1) s
s
(2)
s
(3)
s
(4)
Digital Pvt. Ltd. [45]
Motion (Class-9)
Q. 9 and 10 are multiple choice questions. Each question has four options (1),(2),(3) and (4) out of which ONE
or MORE THAN ONE option may be correct.
9. The velocity-time graph of a body in uniformly accelerated motion can be
s
(1)
0 t
(2)
0 t
(3)
0 t
(4)
0 t
10. The displacement time graph of a body in uniform motion can be
s
(1)
0 t
(2)
0 t
Digital Pvt. Ltd. [46]
Motion (Class-9)
(3)
0 t
(4)
0 t
SECTION-B
Read the following statements and mark your answer as true or false.
1. Area under velocity-time graph shows displacement.
2. Slope of the displacement-time graph for an object shows its acceleration.
Read the following statement and choose the correct option to fill the blanks
3. If distance-time graph is parallel to time axis, then the body is…………….. .
Numerical Based Questions
4. The velocity-time graph given in fig. represents the motion of a cyclist. Find
(i) its acceleration
(ii) its velocity and
(iii) the distance covered by the cyclist in 15 seconds.
5. The graph represents the velocity of a particle as a function of time.
20
10
0
2.0 4.0 6.0 8.0
–10
–20
6. The diagram shows the velocity-time graph of a car. Use the graph to calculate:
Digital Pvt. Ltd. [47]
Motion (Class-9)
7. The velocity time graph is given below which section of the graph has the highest acceleration among all.
25
Velocity (m/s)
20
15
C
10
B D
5 A
0
0 10 20 30 40 50
Time (s)
Passage Based Questions (Q. 8 and Q.9)
The velocity-time graph of two cars A and B is shown below..
A
velocity
B
0 t time
8. Which car travels larger distance in a given time interval 't' ?
9. Which car has greater acceleration ?
(1) Car A
(2) Car B
(3) Both have equal non-zero acceleration
(4) Acceleration is zero for both
10. Match the column
Column-I Column-II
v
(A) Uniform velocity
(p)
t
a
(B) Uniform acceleration
(q)
t
(C) Uniform retardation Uniform acceleration with initial velocity
(r)
t
s
(D) Uniform acceleration with initial velocity
(s)
t
Digital Pvt. Ltd. [48]
Motion (Class-9)
SOLUTIONS DPP-07
SECTION-A
Answer Key
Question 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10
Answer 4 1 2 2 2 1 3 3 3,4 3,4
1. (4)
The object is moving with uniform acceleration as velocity is changing (increasing) uniformly with time.
2. (1)
As distance is not changing with time, object is at rest.
3. (2)
For a body moving with constant acceleration, the graph is
0 t
4. (2)
As velocity is not changing and only time is changing so body is moving at constant velocity.
5. (2)
Speed is decreasing (10-20)s showing decreasing slope, so it is retardation.
6. (1)
Distance is never decreasing. It is always positive and can only increase for a moving object.
7. (3)
Displacement of A is larger than B at time ‘t’ so car A travels large distance in velocity time graph,
displacement can be found by area under the curve.
8. (3)
The distance travelled by the body gradually decreases in equal interval of time.
9. (3,4)
In given graph change in velocity is constant so it gives uniformly acceleration motion.
10. (3,4)
The given graph shows uniform motion, equal distance in equal interval of time.
Digital Pvt. Ltd. [49]
Motion (Class-9)
SECTION-B
1. True
Area under the velocity time curve gives total displacement.
2. False
It gives velocity, while slope of velocity time graph gives acceleration.
3. If distance-time graph is parallel to time axis, then the body is stationary.
4. (i) a = 0
(ii) v = 20 m/s
(iii) Area = 20 × 15
Distance = 300 m.
y 2 y1 20 0 20
5. (1) acceleration = slope = 10 m/s2
x 2 x1 20 2
y 2 y1 0 10 10 5
(2) acceleration = slope = m/s2 (Negative indicates retardation)
x 2 x1 6 0 6 3
(3) acceleration = slope = 0
(4) Area of rectangle ABCD + Area of triangle BCE
1
= 2 × 20 + × 2 × 20
2
= 40 + 20 = 60 m.
6. (1) 20 m/s
20 5 1
(2) slope = acceleration = = 0.25 m/s2
60 0 4
1
(3) slope = acceleration = m/s2
2
(4) Area of rectangle ABCD + Area of triangle ABC + Area of triangle EFC.
1 1
= 5 × 60 × 60 × 15 + × 100 × 20
2 2
= 300 + 450 + 1000 = 1750 m.
15 0
7. Section A = Acceleration between 0s and 10s = slope = = 1.5 m/s2
10 0
Section B = This section is flat, meaning the acceleration will be 0
25 15
Section C = Acceleration between 20s and 30s = slope = = 1 m/s2
30 20
0 25 25
Section D = Acceleration between 30s and 50s slope = = = –1.25 m/s2
50 30 20
Section A has the largest acceleration = 1.5 m/s2
8. A and B
Distance = area of A is greater & Car A has covered larger distance.
9. Both have equal non – Zero acceleration.
10. A–q;B–s;C–r;D–p
Digital Pvt. Ltd. [50]
Motion (Class-9)
Motion DPP-08
SECTION-A
Q.1 to Q.6 are multiple choice questions. Each question has four options (1),(2),(3) and (4) out of which only
one option is correct.
1. The speed-time graph shows the motion of a car. The distance covered by it in 20 seconds is:
V (ms–1)
50
40
30
20
10
t(s)
0 10 20
(1) 800 m
(2) 40 m
(3) 4 m
(4) Zero
2. Which part of the velocity-time graph given below provides the magnitude of acceleration 5 m/s2?
3. A displacement-time graph of a body in motion is shown here. The corresponding velocity – time graph
will be
s
t
s
t
(1)
Digital Pvt. Ltd. [51]
Motion (Class-9)
v
t
(2)
v
(3) t
v
t
(4)
4. With reference to the following velocity-time graph of a body, what is the net displacement of it?
4
Velocity (m/s)
time (s)
1 2 3 4
(1) 10 m
(2) 16 m
(3) 8 m
(4) 6 m
5. Velocity time (v – t) graph for a moving object is shown in the figure. Total displacement of the object
during the time interval when there is non-zero acceleration and retardation is
v (m/s) 4
3
2
1
0
10 20 30 40 50 60
time (s)
(1) 60 m
(2) 50 m
(3) 30 m
(4) 40 m
Digital Pvt. Ltd. [52]
Motion (Class-9)
6. The velocity time graph of runner is given in the graph. What is the total distance covered by the
runner in 16 s ?
(1) 130 m
(2) 160 m
(3) 100 m
(4) 30 m
Q.7 to Q.10 are multiple choice questions. Each question has four options (1),(2),(3) and (4) out of which ONE
or MORE THAN ONE option may be correct.
7. This is a velocity-time graph of a car moving along a straight road. Which of the following is correct for
it ?
(1) The acceleration of the car is 10 m/s2 (from t = 0 s to t = 5
s).
(2) Total distance travelled by car is 750 m.
(3) The deceleration of car is –5 m/s2.
(4) Car exhibits uniform motion between time t = 5 sec to t =
15 sec.
8. The velocity-time graph of a body in uniformly accelerated motion can be
v
(1)
0 t
v
(2)
0 t
v
(3)
0 t
Digital Pvt. Ltd. [53]
Motion (Class-9)
v
(4)
0 t
9. Four cars A,B,C and D are moving on a levelled road. Their distance versus time graphs are shown in the
adjacent figure. Choose the correct statement.
(1) Car A is faster than car B.
(2) Car B is the slowest
(3) Car D is faster than car C.
(4) Car C is the slowest.
10. A car is moving along a straight road with uniform velocity. It is shown in the graph.
Displacement
(1)
time
velocity
(2)
time
velocity
(3)
time
velocity
(4)
time
Digital Pvt. Ltd. [54]
Motion (Class-9)
SECTION-B
Read the following statements and write your answer as true or false (Q.1 and Q.2)
1. The first equation of motion gives the relation between initial velocity, final velocity, acceleration and time.
2. The equations of motion are applicable only when the body moves with uniform acceleration.
Subjective Questions
3. Derive first equation of motion.
4. Derive second equation of motion graphically.
5. Derive third equation of motion.
Digital Pvt. Ltd. [55]
Motion (Class-9)
SOLUTIONS DPP-08
SECTION-A
Answer Key
Question 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10
Answer 1 3 1 1 4 1 1,2,4 3,4 1,2 1,4
1. (1)
Area under the speed time graph gives the distance travelled
Area = 40 20
distance = 800 m
2. (3)
Slope, OA = = 10 m/s
10−20
BC = 6−4 = −10
2
= −5 m/s2
AB = 0
CD = 0
3. (1)
s
4. (1)
Area under velocity time graph gives displacement.
displacement = × 1 × 4 + [4 × 1] + ×4×2
= 2+ 4 + 4 = 10 m
5. (4)
Area under velocity time graph for non zero acceleration gives,
Displacement = 20 1 + 20 1
= 40 m
6. (1)
Area under velocity time graph gives distance covered distance
1
= × 6 × 10 + 10 × 10
2
= 30 + 100
= 130 m
Digital Pvt. Ltd. [56]
Motion (Class-9)
7. (1,2,4)
( )
(i) Slope = = 10
acceleration = 10 m/s2
(ii) distance = × 5 × 50 + 10 × 50 + × 5 × 50
= 125 + 500 + 125 = 500 + 250
= 750 m
(iii) deceleration = = − = −10 m/s
(iv) Car exhibits uniform motion between time t = 5 sec to t = 15 sec.
8. (3,4)
The velocity-time graph of a body in uniformly accelerated motion is a straight time graph inclining towards
the time axis.
9. (1,2)
more slope =more speed
Car A is faster than car B and Car B is the slowest among all.
10. (1,4)
In (1) displacement time graph slope gives velocity which is constant/uniform.
In (4) velocity is constant as it is parallel to x-axis.
SECTION-B
1. False
v = u + at
The first equation of motion gives the relation between initial velocity, final velocity, acceleration and time.
2. False
The equations of motion are applicable only when the body moves with uniform acceleration.
3. First equation of motion
A body having an initial velocity 'u' acted upon by a uniform acceleration 'a' for time 't' such that final velocity
of the body is 'v'.
Change in velocity Final velocity Initial velocity
Acceleration =
Time taken Time taken
v u
a= , or v – u = at, or
t
Digital Pvt. Ltd. [57]
Motion (Class-9)
1 2
4. Derivation of s = ut + at
2 y-axis
Distance travelled = Area of trapezium ABCE
C
= Area of rectangle ABDE + Area of triangle BCD
Velocity (m/s)
1 1 at
= AB × AE + (BD × CD) = u × t + [t × (v–u)] B
2 2 v
BD AE t D
u u
CD CE DE v u A
x-axis
1 E
=u×t+ [t × (u + at – u)] [ v = u + at] t
2 time (seconds)
1
s ut at2
2
5. Third equation of motion
A body having an initial velocity 'u' moving with a uniform acceleration 'a' for time 't' such that final velocity is
'v' and the distance covered is 's'.
v u
Vav =
2
Distance covered = average velocity × time taken
v u
s= × t ... (1)
2
Now, v = u + at, or v – u = at
v u
or t= ... (2)
a
From (1) & (2), we get,
v u v u v 2 u2
s
2 a 2a
or 2as = v2 – u2 , or
Digital Pvt. Ltd. [58]
Motion (Class-9)
Motion DPP-09
SECTION-A
Q.1 to Q.8 are multiple choice questions. Each question has four options (1),(2),(3) and (4) out of which only
one option is correct.
1. Which of the following statements is wrong for a uniform circular motion ?
(1) Magnitude of velocity is constant.
(2) Magnitude of angular velocity is constant.
(3) Magnitude of centripetal acceleration is constant.
(4) Velocity is constant.
2. An object is moving along a circular track of radius 1 m at constant speed, having a time period of π
seconds. The speed of the object is
(1) 2π m/s
(2) 2 m/sec
(3) π m/s
(4) m/sec
3. An artificial satellite is moving in a circular orbit of radius 30240 km. Find its angular velocity if it takes
24 hours to revolve around the earth.
(1) rad/s
(2) rad/s
(3) 1260 rad/s
(4) rad/s
4. The direction of centripetal acceleration in circular motion is
(1) towards the centre of the circle
(2) away from the centre of the circle
(3) tangential to the circle
(4) along the circular path
5. A car on an amusement-park-ride travels at a constant speed of 4.0 m/s on a circular track that has a
radius of 4.0 m. What is the magnitude of the car's centripetal acceleration?
(1) 1.0 m/s2
(2) 2.0 m/s2
(3) 4.0 m/s2
(4) 16.0 m/s2
Digital Pvt. Ltd. [59]
Motion (Class-9)
6. What is the angular velocity of a second hand and a minute hand of a clock in radian/sec?
Hint (i) Second hand of a clock completes one revolution in 60 sec.
(ii) minute hand of a clock completes one rotation in 60 min
(1) ,
(2) ,
(3) ,
(4) ,
7. A point on the rim of a wheel 3 m in diameter has linear velocity of 18 m/s. The angular velocity of the
wheel is
(1) 12 rad/s
(2) 10 rad/s
(3) 8 rad/s
(4) 6 rad/s
8. A particle moves in a circle of radius 30 cm with a constant speed of 6 m/s. Its centripetal acceleration
is
(1) zero
(2) 20 m/s2
(3) 10.8 m/s2
(4) 120 m/s2
Q.9 & Q.10 are multiple choice questions. Each question has four options (1),(2),(3) and (4) out of which ONE
or MORE THAN ONE option may be correct.
9. Which of the following relations is/are correct ?
(1) =
t
(2) v = r
2
(3) =
t
(4) ac = r2
10. In a uniform circular motion,
(1) object moves in a circular path with uniform speed.
(2) motion of object is always a non-uniform motion.
(3) the direction of motion is always same.
(4) object moves in a circular path with variable speed.
Digital Pvt. Ltd. [60]
Motion (Class-9)
SECTION-B
Read the following statements and mark your answer as true or false
1. The relation between radian and degree is: 360/ 2π Radian = 1 Degree
2. A circular motion is always a non-uniform motion.
3. Centripetal acceleration is towards the tangent of circular path.
4. Angular speed is measured in m/s.
Read the following statement and choose the correct option to fill the blanks. (Q. 5 and Q. 6)
5. Unit of angular displacement is ______.
6. ______ acceleration is needed keep a body in circular motion.
The answer to Q.7 & Q. 8 are an integer (ranging from -999 to 999 both inclusive). Type that integer.
7. Two bodies moving in different circular paths have the ratio of radii of circular paths as 1:4. If both the bodies
take same time to complete one revolution, then the ratio of their respective angular velocities is 1: Z. Find the
value of Z ?
8. A particle is moving along a circular path of radius 5 m with an angular velocity ω. What is the value of ′ω′, if
it’s linear speed is 25 m/s ?
Subjective Questions
9. Mark the following variables on the given circular path of radius r, if a body moves from points P to Q: r, l, , v,
ac, where
l : linear distance
: angular displacement
v : linear velocity
ac : centripetal acceleration
10. Comparison Table
Linear Terms Angular Terms
Linear distance = rθ measured in
Angular displacement θ = measured
________
in __________
Linear speed v = = rω = measured Angular velocity ω = = measured
in _________ in ____________
Linear acceleration a = measured in Centripetal acceleration a = = rω
___________ measured in ___________
Digital Pvt. Ltd. [61]
Motion (Class-9)
SOLUTIONS DPP-09
SECTION-A
Answer Key
Question 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10
Answer 4 2 4 1 3 3 4 4 1,2,4 1,2
1. (4)
Velocity is not constant as its direction changes continuously.
2. (2)
Given, r = 1 m, t = πsec.
Speed = =
= 2 m/sec
3. (4)
Given r = 30240 km, t = 24 hr
Angular velocity = ω =
Now, θ = = ∵ [ = 2πr, for 1 revolution, = circumference of circle]
θ = 2π
ω= = rad/hr
= = rad/sec.
×
4. (1)
The direction of acceleration is towards the centre of the circle.
5. (3)
Given, v = 4.0 m/s, r = 4 m
Centripetal acceleration, ac =
×
= = 4m/s2
6. (3)
for second hand ω=
ω=
Digital Pvt. Ltd. [62]
Motion (Class-9)
for minute hand ω =
ω= =
×
7. (4)
V = rω
ω= = ω = 6 rad/s
8. (4)
V
a =
r
×
= × 100 =
120 m/s2
9. (1,2,4)
The relation given in option 1,2,4 are correct.
10. (1,2)
In uniform circular motion, object moves with a uniform speed. As direction of object changes continuously, it
is a non uniform motion.
SECTION-B
1. False
360 = 2 radian
1° = radian
2. True
A circular motion is always a non-uniform motion as direction change continuously.
3. False
Centripetal acceleration is always towards the centre.
4. False
Angular speed is measured in rad/s
5. Unit of angular displacement is radian.
6. Centripetal acceleration is needed keep a body in circular motion.
Digital Pvt. Ltd. [63]
Motion (Class-9)
/ /
7. For body 1, ω = = = =
t1 t1
/ /
For body 2, ω = = = =
/
= as t1 = t2
/
8. Given, r = 5m, v = 25 m/s
v = rω
ω= = = 5 rad/sec
r V
9.
a P
10.
Linear Terms Angular Terms
Linear distance = rθ measured in meter
Angular displacement θ = measured in radian.
Linear speed v = = rω = measured in Angular velocity ω = = measured in m/s2
m/s
Linear acceleration a = measured in m/s2 Centripetal acceleration a = = rω measured in
m/s2
Digital Pvt. Ltd. [64]
You might also like
- 2: Kinematics (Exercises) : Conceptual QuestionsDocument19 pages2: Kinematics (Exercises) : Conceptual Questions01-Abhinandan Sankar Sadhukhan-12SC2No ratings yet
- Static and Dynamic Balancing of Rigid RotorsDocument20 pagesStatic and Dynamic Balancing of Rigid RotorsTeng Soon Chye100% (2)
- Motion Exercise 1 AND 2Document25 pagesMotion Exercise 1 AND 29-E PRADYOT SINHANo ratings yet
- CBSE-XI Physics - Chap-2 (Motion in A Straight Line)Document14 pagesCBSE-XI Physics - Chap-2 (Motion in A Straight Line)VINEET ffNo ratings yet
- 2 Force and Motion: Class-VII Physics Question BankDocument21 pages2 Force and Motion: Class-VII Physics Question BankGopa BhattacharyyaNo ratings yet
- Class 6 Motion & Measurement of Distances W.S.4Document12 pagesClass 6 Motion & Measurement of Distances W.S.4rajalakshmi boopathiNo ratings yet
- Class Ix Science Compiled Work Book 2023Document124 pagesClass Ix Science Compiled Work Book 2023traptisharma3342No ratings yet
- Class Ix Physics T1 Assignment Booklet 1 2024 25Document6 pagesClass Ix Physics T1 Assignment Booklet 1 2024 25shikha2506No ratings yet
- Kinematics Lecture 1Document18 pagesKinematics Lecture 1aryanNo ratings yet
- Chapter 8Document2 pagesChapter 8ALPA JOSHINo ratings yet
- Class 9 pt1 Two 2023Document2 pagesClass 9 pt1 Two 2023Laxman SdNo ratings yet
- Force, Work, Power and Energy - Daily Home Assignment 02 - (Victory 2024 - ICSE)Document2 pagesForce, Work, Power and Energy - Daily Home Assignment 02 - (Victory 2024 - ICSE)44 A Ritam BeraNo ratings yet
- Motion Class 9Document3 pagesMotion Class 9lavi singhalNo ratings yet
- Theory Question - MotionDocument2 pagesTheory Question - MotionAvik PaulNo ratings yet
- Chapter No 1 Laws of MotionDocument6 pagesChapter No 1 Laws of Motionvg021822No ratings yet
- Sci G 9 CH 7 Pws-1Document2 pagesSci G 9 CH 7 Pws-1gc.freya452No ratings yet
- Sci9 Q4 Mod1Document28 pagesSci9 Q4 Mod1Matthew Agad100% (2)
- 64d7accbab6c57001883f258 - ## - Board Paper 01 PhysicsDocument3 pages64d7accbab6c57001883f258 - ## - Board Paper 01 Physics2019skguptaNo ratings yet
- Motion NOTES N AND ODocument23 pagesMotion NOTES N AND O9-E PRADYOT SINHANo ratings yet
- Kinematics Quiz 1Document3 pagesKinematics Quiz 1Nicholas ChevalierNo ratings yet
- Motion Class 9Document3 pagesMotion Class 9lavi singhalNo ratings yet
- Physics Motion HHWDocument4 pagesPhysics Motion HHWgardenneed3No ratings yet
- General Physics 1 q1 Week 3Document24 pagesGeneral Physics 1 q1 Week 3Chool Cydrick B. BascosNo ratings yet
- Physics Foundation CH-1 ExerciseDocument8 pagesPhysics Foundation CH-1 ExerciseYash TadiNo ratings yet
- Hi GDJDBDDocument6 pagesHi GDJDBDArghya BiswasNo ratings yet
- MOTION WorksheetDocument3 pagesMOTION Worksheets.anoura07No ratings yet
- Gr12_Ch01_S02_Detailed_C_A4_QDocument2 pagesGr12_Ch01_S02_Detailed_C_A4_Qaungthethein844No ratings yet
- CBSE-IX Science_Chap-7 (Motion)Document13 pagesCBSE-IX Science_Chap-7 (Motion)poltokodruNo ratings yet
- Unit 2: Constant AccelerationDocument17 pagesUnit 2: Constant AccelerationMatthew DiDonatoNo ratings yet
- Class-9 Science Extra QuestionsDocument36 pagesClass-9 Science Extra Questionsbhaweshsuda29No ratings yet
- J CAPS 01 (SC+MATH) Class 09Document5 pagesJ CAPS 01 (SC+MATH) Class 09K Geeth SagarNo ratings yet
- Motion in straight dpp -2Document5 pagesMotion in straight dpp -2ruchiamitgargNo ratings yet
- QB PT 1 Class 9 MotionDocument25 pagesQB PT 1 Class 9 MotiongeetasatyapriyaNo ratings yet
- Screenshot 2024-06-20 at 11.17.26Document11 pagesScreenshot 2024-06-20 at 11.17.26muditshakya2828No ratings yet
- 9th Physics Quiz QueDocument9 pages9th Physics Quiz QueNisha PatidarNo ratings yet
- 9th Physics Revision Work-Sheets 2023-24-095745Document6 pages9th Physics Revision Work-Sheets 2023-24-095745Sidhant LodhiNo ratings yet
- Rotational Motion MCQDocument7 pagesRotational Motion MCQVamsi VangaraNo ratings yet
- Case Base Questions CH 7Document6 pagesCase Base Questions CH 7bhavyastudy1No ratings yet
- Q4 - Science 9 - Mod1 - The Horizontal and Vertical Motions of A Projectile - v1 - FinalDocument27 pagesQ4 - Science 9 - Mod1 - The Horizontal and Vertical Motions of A Projectile - v1 - FinalCharina Lopez100% (1)
- Isi Makalah 3Document25 pagesIsi Makalah 3Mely TriastutiNo ratings yet
- Chapter 8 MotionDocument35 pagesChapter 8 Motionminalsharma692No ratings yet
- Physics Rotational Motion MCQDocument7 pagesPhysics Rotational Motion MCQrkjha70867% (3)
- Practice Paper Class Xi Physics Set 2Document6 pagesPractice Paper Class Xi Physics Set 2ARYANNo ratings yet
- General Physics 1: Quarter 2 - Module 1Document30 pagesGeneral Physics 1: Quarter 2 - Module 1Jheremy Charles Morales MorteraNo ratings yet
- Summer H.HW CLASS IXDocument5 pagesSummer H.HW CLASS IXkuro32190No ratings yet
- Generalphysics1 q1 Mod3 Motion-In-Two-Dimensions v1-1Document30 pagesGeneralphysics1 q1 Mod3 Motion-In-Two-Dimensions v1-1Park JiminshiiNo ratings yet
- 9TH MOTION 1-1 QNSDocument7 pages9TH MOTION 1-1 QNSHyagreeva Learning HubNo ratings yet
- FTS 02 - (Code B) - 07 06 2022Document17 pagesFTS 02 - (Code B) - 07 06 2022Pahel AminNo ratings yet
- IX Physics MotionDocument9 pagesIX Physics Motionhaadiya aliNo ratings yet
- Class IX - Physics Worksheet - All ChaptersDocument5 pagesClass IX - Physics Worksheet - All ChaptersaditiNo ratings yet
- Holiday Homework Class 9 PDFDocument15 pagesHoliday Homework Class 9 PDFDisha Tripathi - 10-ENo ratings yet
- AIMT-NEET-UG Sample PaperDocument27 pagesAIMT-NEET-UG Sample Papers11146366No ratings yet
- MCQDocument12 pagesMCQpradNo ratings yet
- SPH43v CH 1 Assignment Page 1Document1 pageSPH43v CH 1 Assignment Page 1elaria hanyNo ratings yet
- class xi motion in a straight lineDocument4 pagesclass xi motion in a straight linewww.jabbalopNo ratings yet
- Class 9 Physics Chapter 8 Motion MCQsDocument2 pagesClass 9 Physics Chapter 8 Motion MCQsKeerthana RamachandranNo ratings yet
- Dynamic Deformation of Earth and Motion Effects Caused by Universe's Gravitational FieldFrom EverandDynamic Deformation of Earth and Motion Effects Caused by Universe's Gravitational FieldNo ratings yet
- Sun and Earth Modern User Reference Guide: Determining earth’s true surface shape as flat using the sunFrom EverandSun and Earth Modern User Reference Guide: Determining earth’s true surface shape as flat using the sunNo ratings yet
- Dynamics of the Rigid Solid with General Constraints by a Multibody ApproachFrom EverandDynamics of the Rigid Solid with General Constraints by a Multibody ApproachNo ratings yet
- Exercise_03 + SolutionsDocument12 pagesExercise_03 + Solutions9-E PRADYOT SINHANo ratings yet
- DPPhkshdahfaDocument4 pagesDPPhkshdahfa9-E PRADYOT SINHANo ratings yet
- Exercise01and02 +SolutionDocument28 pagesExercise01and02 +Solution9-E PRADYOT SINHANo ratings yet
- 9th_Test Paper_Diversity_AdvanceDocument6 pages9th_Test Paper_Diversity_Advance9-E PRADYOT SINHANo ratings yet
- DPP_Diversity in living organisms_AdvanceDocument82 pagesDPP_Diversity in living organisms_Advance9-E PRADYOT SINHANo ratings yet
- Test+SolutionDocument7 pagesTest+Solution9-E PRADYOT SINHANo ratings yet
- Exercise + SolutionsDocument25 pagesExercise + Solutions9-E PRADYOT SINHANo ratings yet
- NotesDocument4 pagesNotes9-E PRADYOT SINHANo ratings yet
- Test+SolutionDocument5 pagesTest+Solution9-E PRADYOT SINHANo ratings yet
- Test+SolutionDocument5 pagesTest+Solution9-E PRADYOT SINHANo ratings yet
- Motion NOTES N AND ODocument23 pagesMotion NOTES N AND O9-E PRADYOT SINHANo ratings yet
- Test FNLMDocument10 pagesTest FNLM9-E PRADYOT SINHANo ratings yet
- Motion ex 3Document35 pagesMotion ex 39-E PRADYOT SINHANo ratings yet
- 1. Verbal Series DPPDocument9 pages1. Verbal Series DPP9-E PRADYOT SINHANo ratings yet
- Exercise - 3Document22 pagesExercise - 39-E PRADYOT SINHANo ratings yet
- Motion Exercise 1 AND 2Document25 pagesMotion Exercise 1 AND 29-E PRADYOT SINHANo ratings yet
- EXERCISE 1 AND 2Document28 pagesEXERCISE 1 AND 29-E PRADYOT SINHANo ratings yet
- Y17 Statics - Couples - ProblemsDocument23 pagesY17 Statics - Couples - ProblemsCristian Julian González Barrera100% (1)
- Review Sample Problems (FINALS) : Work Energy and PowerDocument6 pagesReview Sample Problems (FINALS) : Work Energy and PowerJay BetaizarNo ratings yet
- H10 FlowDocument5 pagesH10 FlowHoracio EspinosaNo ratings yet
- Practical Rotordynamics For Centrifugal Pumps 52pp SulzerDocument52 pagesPractical Rotordynamics For Centrifugal Pumps 52pp Sulzer1mmahoney100% (2)
- Topic 7 Internal Flow V1.0.1Document25 pagesTopic 7 Internal Flow V1.0.1lam tatNo ratings yet
- Biomechanics in DanceDocument2 pagesBiomechanics in DanceLily SweatmanNo ratings yet
- 3 Kater S PendulumDocument11 pages3 Kater S Pendulumjocas100% (1)
- Module 2 Bodies in Pure Rolling ContactDocument11 pagesModule 2 Bodies in Pure Rolling ContactBilly Jhun0% (1)
- Authentic Lab ExperimentDocument4 pagesAuthentic Lab ExperimentKangNo ratings yet
- 2.1.3. Acceleration of The Piston: 2.2. Structure Dynamics of Crankshaft - Connecting RODDocument3 pages2.1.3. Acceleration of The Piston: 2.2. Structure Dynamics of Crankshaft - Connecting RODBùi Quốc VinhNo ratings yet
- Equation Practice 1: P Momentum (KG M/S) M Mass (KG) V Velocity (M/S)Document1 pageEquation Practice 1: P Momentum (KG M/S) M Mass (KG) V Velocity (M/S)DavidAnnorNo ratings yet
- Physics Class XII Term-IIDocument164 pagesPhysics Class XII Term-IIShubham SinghNo ratings yet
- External FlowDocument49 pagesExternal FlowTusanita MapuolaNo ratings yet
- Kinema TicsDocument3 pagesKinema TicsSpammerNo ratings yet
- Apparent Weight. Example PDFDocument5 pagesApparent Weight. Example PDFShamoon WahedNo ratings yet
- Mechanical Vibration Forced UndampedDocument19 pagesMechanical Vibration Forced UndampedShafiq ShapianNo ratings yet
- Speed, Velocity, and Acceleration: Physics Notes GCE Study BuddyDocument14 pagesSpeed, Velocity, and Acceleration: Physics Notes GCE Study Buddycpika520No ratings yet
- The Awesome Life Force 1984Document8 pagesThe Awesome Life Force 1984Roman PetersonNo ratings yet
- Meldes ExperimentDocument5 pagesMeldes ExperimentVivek SharmaNo ratings yet
- IM05-6. Velocity Analysis by Relative VelocityDocument19 pagesIM05-6. Velocity Analysis by Relative Velocityaruna MoonNo ratings yet
- Postdoc List 09032022Document191 pagesPostdoc List 09032022Subhajit BiswasNo ratings yet
- Numerical Simulation of Ultrasonic Wave Propagation in Flawed DomainDocument4 pagesNumerical Simulation of Ultrasonic Wave Propagation in Flawed DomainGrit WingsNo ratings yet
- String Wave PDFDocument8 pagesString Wave PDFrajNo ratings yet
- Fluid Flow Sample Problem-Continuity EquationDocument41 pagesFluid Flow Sample Problem-Continuity EquationJaid Hedriana100% (1)
- Venturi TubeDocument6 pagesVenturi TubefarahnazNo ratings yet
- THE Electromagnetic Spectrum: Unit 2, Module 2 Kiziah F. GranilDocument10 pagesTHE Electromagnetic Spectrum: Unit 2, Module 2 Kiziah F. GranilHannah Joy DulayNo ratings yet
- Assignment 1 - EC3201 - Microwave EngineeringDocument1 pageAssignment 1 - EC3201 - Microwave EngineeringVasudev DwivediNo ratings yet
- Galileo and NewtonDocument25 pagesGalileo and NewtonMarvin Darius LagascaNo ratings yet