Professional Documents
Culture Documents
2. Acids, Bases and Salts
2. Acids, Bases and Salts
Uploaded by
ronakdoda1Copyright:
Available Formats
You might also like
- 10th Acid Base and Salt Notes 2011Document5 pages10th Acid Base and Salt Notes 2011Ashraf Husain100% (4)
- Acide Bases and Salt Class 10Document16 pagesAcide Bases and Salt Class 10Abc Abc100% (1)
- ACID Base By R.MDocument17 pagesACID Base By R.MSwadhinNo ratings yet
- 3 Common Indicators Natural Indicator: Acids, Bases and Salts IndicatorsDocument13 pages3 Common Indicators Natural Indicator: Acids, Bases and Salts IndicatorsJoshenderNo ratings yet
- Acid Base Notes 20230715152315203Document7 pagesAcid Base Notes 20230715152315203NEERAV ANANDNo ratings yet
- Screenshot 2022-11-28 at 3.28.38 PMDocument4 pagesScreenshot 2022-11-28 at 3.28.38 PMAanya AroraNo ratings yet
- Acids Bases and SaltsDocument5 pagesAcids Bases and Saltsteerth taledaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2 - Acids, Bases & SaltesDocument42 pagesChapter 2 - Acids, Bases & SaltesRufosNo ratings yet
- Acid, Bases & Salts 2022-23Document34 pagesAcid, Bases & Salts 2022-23ramkumarsingh12406No ratings yet
- Ch-2 Part-2Document4 pagesCh-2 Part-2Kartik BhardwajNo ratings yet
- Notes Acids Bases and SaltsDocument8 pagesNotes Acids Bases and SaltsWouldn't you like to knowNo ratings yet
- Acids, Bases and Salts Notes - XDocument8 pagesAcids, Bases and Salts Notes - XLizannNo ratings yet
- 69 Topper 21 101 2 2 23 Acids Bases and Salts Up201807101532 1531216973 6174Document8 pages69 Topper 21 101 2 2 23 Acids Bases and Salts Up201807101532 1531216973 6174Vijay RaoNo ratings yet
- Acids, Bases and Salts Notes - Part 4Document7 pagesAcids, Bases and Salts Notes - Part 4Dhyan ShahNo ratings yet
- Acids Bases and SaltsDocument52 pagesAcids Bases and SaltsPrabakaran MNo ratings yet
- Topperrevisionnotes69 Topper 21 101 2-2-23 Acids Bases and Salts Up201807101532 1531216973Document8 pagesTopperrevisionnotes69 Topper 21 101 2-2-23 Acids Bases and Salts Up201807101532 1531216973Jessica SehgalNo ratings yet
- Acids Bases and Salts Notes PDFDocument13 pagesAcids Bases and Salts Notes PDFRajkumari MishraNo ratings yet
- Acid Base and Salts'Document4 pagesAcid Base and Salts'zaidasadsiddiquiNo ratings yet
- Acids Bases and Salts Class 10 NotesDocument8 pagesAcids Bases and Salts Class 10 Notesashlyyyyyy33No ratings yet
- Notes Ch-Acids and Bases-1 - 240530 - 174138Document12 pagesNotes Ch-Acids and Bases-1 - 240530 - 174138Anjani RathoreNo ratings yet
- Acids Bases & Salts Notes (1)Document7 pagesAcids Bases & Salts Notes (1)kiranshrivastava1970No ratings yet
- Acids, Bases and SalltsDocument9 pagesAcids, Bases and SalltsVishal SinghNo ratings yet
- 2 - Acids, Bases and Salts (1)Document6 pages2 - Acids, Bases and Salts (1)HONEY YOYONo ratings yet
- Acids, Bases, & SaltsDocument25 pagesAcids, Bases, & SaltsVidya JayakumarNo ratings yet
- Class 10 Book Ncert OnlyDocument3 pagesClass 10 Book Ncert OnlyVaibhav BhardwajNo ratings yet
- SaltsDocument22 pagesSaltssaanvi katyalNo ratings yet
- Acid Bases and Salts - Shobhit NirwanDocument26 pagesAcid Bases and Salts - Shobhit NirwanAlok RahateNo ratings yet
- PPT-Chapter 2-Acids Bases and SaltsDocument106 pagesPPT-Chapter 2-Acids Bases and Saltsbilalanzar22No ratings yet
- What Is An Acid and A Base?: Classification of MatterDocument11 pagesWhat Is An Acid and A Base?: Classification of MatterNishidh SinghNo ratings yet
- NOTES - Acids, Bases and SaltsDocument31 pagesNOTES - Acids, Bases and SaltsKartik ChauhanNo ratings yet
- Chapter 11 - Acids, Bases, and Salts PDFDocument7 pagesChapter 11 - Acids, Bases, and Salts PDFAarush SharmaNo ratings yet
- Properties of Acids and Bases Acids BasesDocument5 pagesProperties of Acids and Bases Acids BaseszyxisNo ratings yet
- Class 10 Acids Bases and Salts NotesDocument22 pagesClass 10 Acids Bases and Salts NotesShreyash VishwakarmaNo ratings yet
- Acids Bases and Salts NotesDocument8 pagesAcids Bases and Salts Notesadejapeltier3No ratings yet
- CHAPTER 2 Acid Base and SaltDocument37 pagesCHAPTER 2 Acid Base and SaltRaghav ParasharNo ratings yet
- Topic 5: Acids, Bases and Salts Acids: Zase - by DJ Principle - For Comments, Whatsapp: 0978936116Document17 pagesTopic 5: Acids, Bases and Salts Acids: Zase - by DJ Principle - For Comments, Whatsapp: 0978936116Paul MunsakaNo ratings yet
- Acid Bases and SaltsDocument38 pagesAcid Bases and SaltssajjadsafdarNo ratings yet
- Chapter - 2 Acids - Bases - and - Salts-43Document21 pagesChapter - 2 Acids - Bases - and - Salts-43Vikash SinghNo ratings yet
- Ch-2 Part-3Document4 pagesCh-2 Part-3Kartik BhardwajNo ratings yet
- Acid and Base and SaltsDocument14 pagesAcid and Base and SaltsSamarth SinghNo ratings yet
- Acids, Bases and Salts (BBC Site)Document6 pagesAcids, Bases and Salts (BBC Site)Ramesh GoldbergNo ratings yet
- A) Reaction of Acids and Bases With Metals: BaseDocument6 pagesA) Reaction of Acids and Bases With Metals: Baseashok pradhanNo ratings yet
- CLASS X CHEMISTRY Solution-989571Document8 pagesCLASS X CHEMISTRY Solution-989571abiniveshofficial4708No ratings yet
- SaltsDocument14 pagesSaltsKDZ S M O O T H 亗No ratings yet
- Acids Bases and SaltsDocument11 pagesAcids Bases and SaltsCollins Obari AdiyeNo ratings yet
- 10 Science Notes 02 Acid Bases and Salts 1Document11 pages10 Science Notes 02 Acid Bases and Salts 1PANDUNo ratings yet
- Lesson-2 Class 10Document7 pagesLesson-2 Class 10Dishu SinghNo ratings yet
- 4 Acid, Base and SaltDocument8 pages4 Acid, Base and Saltjosephmartinsogbu30No ratings yet
- Class 10 Science Chapter 2 Revision NotesDocument16 pagesClass 10 Science Chapter 2 Revision NotesKriish RatnaniNo ratings yet
- Acids, Bases and Salts - Short NotesDocument7 pagesAcids, Bases and Salts - Short Notesat5527813No ratings yet
- ERT CBSE Notes For Class 10 Science ChemistryDocument8 pagesERT CBSE Notes For Class 10 Science ChemistryshanthaNo ratings yet
- 6.1 Role of Water in Showing Chemical Properties of Acid and AlkaliDocument29 pages6.1 Role of Water in Showing Chemical Properties of Acid and AlkaliNur Shahirah100% (1)
- 10th SCIENCE (English Medium) Must DoDocument63 pages10th SCIENCE (English Medium) Must Doanshu26stNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2 - Acids, Bases and SaltsDocument12 pagesChapter 2 - Acids, Bases and SaltsRAM SINGHNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2 Acids, Bases and SaltsDocument5 pagesChapter 2 Acids, Bases and SaltsSmrita SinghNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2 Acids, Bases and SaltsDocument5 pagesChapter 2 Acids, Bases and SaltsDileep Singh ParmarNo ratings yet
- 2.acids, Bases and SaltsDocument9 pages2.acids, Bases and SaltsayanNo ratings yet
- The Chemistry of Soaps and Salts - Chemistry Book for Beginners | Children's Chemistry BooksFrom EverandThe Chemistry of Soaps and Salts - Chemistry Book for Beginners | Children's Chemistry BooksNo ratings yet
- CH 25Document34 pagesCH 25John Nicholson LanderoNo ratings yet
- Science Lesson 2Document10 pagesScience Lesson 2Krista May Narvarte OlivaNo ratings yet
- United States Patent (19) 11 Patent Number: 5,985,454Document10 pagesUnited States Patent (19) 11 Patent Number: 5,985,454KatNo ratings yet
- Chemical Analysis of Red Lead: Standard Test Methods ofDocument4 pagesChemical Analysis of Red Lead: Standard Test Methods ofPyone Ei ZinNo ratings yet
- Refrigeration & Air Conditioning: Arun Jose Tom, Rac, CcetDocument340 pagesRefrigeration & Air Conditioning: Arun Jose Tom, Rac, CcetRubin JosephNo ratings yet
- Semiconductor Theory and Diode Circuits 2021Document11 pagesSemiconductor Theory and Diode Circuits 2021France DanielNo ratings yet
- WMCIE JU Syllabus 2021 2022Document26 pagesWMCIE JU Syllabus 2021 2022Rajesh RoyNo ratings yet
- Sem 1 Full Notes 2Document81 pagesSem 1 Full Notes 2Shravani PakhaleNo ratings yet
- Extremophiles 2004 PDFDocument149 pagesExtremophiles 2004 PDFChandraprasad S RajanganNo ratings yet
- Reaction Rates: BIG IdeaDocument34 pagesReaction Rates: BIG Ideacarleston thurgoodNo ratings yet
- TLC Method For DEG DetectionDocument7 pagesTLC Method For DEG DetectionAbdullah KhudariNo ratings yet
- All Acrylic Based Thermoplastic Elastomers - Design and SynthesisDocument264 pagesAll Acrylic Based Thermoplastic Elastomers - Design and Synthesisvkr91@yahoo.comNo ratings yet
- Construction Catalogue - Atul LTDDocument16 pagesConstruction Catalogue - Atul LTDSolai LNo ratings yet
- General Chemistry ReviewerDocument6 pagesGeneral Chemistry ReviewerHewlett Pearl BawalanNo ratings yet
- Unit 2 Acids Bases Salts Past QuestionsDocument49 pagesUnit 2 Acids Bases Salts Past QuestionsDwiyasa Irin100% (2)
- Experiment 9 SaponificationDocument6 pagesExperiment 9 Saponificationpatrice green - SteadmanNo ratings yet
- Answer Key Si Worksheet 10Document5 pagesAnswer Key Si Worksheet 10Jersey BarquillaNo ratings yet
- Physical Chemistry: Section 1Document956 pagesPhysical Chemistry: Section 1Mitchel TayimoNo ratings yet
- Polyester (PET) : Zimmer: The Leading Brand in Polymers TechnologyDocument16 pagesPolyester (PET) : Zimmer: The Leading Brand in Polymers TechnologyArash AbbasiNo ratings yet
- Chapter: 1 Stoichiometric Relationships: SubtopicsDocument108 pagesChapter: 1 Stoichiometric Relationships: SubtopicsBNo ratings yet
- UK Standards For Microbiology InvestigationsDocument15 pagesUK Standards For Microbiology InvestigationsBenNo ratings yet
- BASF in Korea Backgrounder 2016 PDFDocument2 pagesBASF in Korea Backgrounder 2016 PDFMunis RaoNo ratings yet
- 13 Cellular RespirationDocument6 pages13 Cellular RespirationJohnNo ratings yet
- INTER CAT FCC Gasoline Sulphur Reduction Using Catalyst Additives Mechanisms and Commercial ExperiencesDocument10 pagesINTER CAT FCC Gasoline Sulphur Reduction Using Catalyst Additives Mechanisms and Commercial ExperiencesKumaresan LoganathanNo ratings yet
- Astm e 1219Document6 pagesAstm e 1219KEN KNo ratings yet
- Steel Making Processes Post-Solidification Treatment: - ESR (Electro-Slag Refining) - VAR (Vacuum-Arc Remelting)Document27 pagesSteel Making Processes Post-Solidification Treatment: - ESR (Electro-Slag Refining) - VAR (Vacuum-Arc Remelting)Asher Ahmed100% (1)
- ACETONE - Sigma Aldrich - MSDSDocument14 pagesACETONE - Sigma Aldrich - MSDSramkarn7989No ratings yet
- Alkalinity ControlDocument15 pagesAlkalinity ControlArdyas Wisnu BaskoroNo ratings yet
- Solvent Extraction Process To RecoverDocument12 pagesSolvent Extraction Process To RecoverJazmiin SoLiis HdzNo ratings yet
- Frame MaterialsDocument29 pagesFrame MaterialsPluviophileNo ratings yet
2. Acids, Bases and Salts
2. Acids, Bases and Salts
Uploaded by
ronakdoda1Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
2. Acids, Bases and Salts
2. Acids, Bases and Salts
Uploaded by
ronakdoda1Copyright:
Available Formats
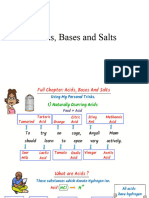
Acids
- Acids have sour taste.
- They turn blue litmus to red.
- They give positive hydrogen (H+) ions in water solution.
Strong Acids – HCl (Hydrochloric Acid), H2SO4 (Sulphuric Acid),
HNO3 (Nitric Acid)
Weak Acids – CH3COOH(Acetic acid), Oxalic Acid, Lactic Acid
Concentrated Acids – More amount of acid + Less amount of
water
Dilute Acids - More amount of water + Less amount of Acid
Litmus turns Red in Sulphuric Acid and Lemon/Orange
Subscribe to my YT channel - https://www.youtube.com/c/GauravSuthar
Chemical properties of acids:
1. Reaction of acid with base:
Acid + Base → Salt + Water
Acid and base together react to produce salt and water. This
reaction is called Neutralization reaction.
Examples -
KOH + HCl → KCl + H2O
2. Reaction of acid with metal:
Acid + Metal → Salt + Hydrogen gas
Examples -
Mg + 2HCl → MgCl2 + H2
3. Reaction of Metallic Oxides with Acids:
Metal oxide + Acid → Salt + Water
Examples -
CuO + HCl → CuCl2 + H2O
Subscribe to my YT channel - https://www.youtube.com/c/GauravSuthar
4. Reaction of acid with metal carbonate and metal hydrogen
carbonates:
Acid + Metal carbonate /Metal hydrogen Carbonate → Salt +
CO2 + H2O
When an acid reacts with a metal carbonate (MCO3) or metal
hydrogen carbonate (MHCO3), it gives the corresponding salt,
carbon dioxide (CO2) gas and water.
Examples -
Na2CO3 + 2HCl → 2NaCl + H2O+ CO2
NaHCO3 + HCl → NaCl + H2O + CO2
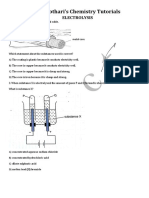
5. Conduction of electricity:
Acidic solutions in water conduct electricity because they
produce hydronium ions. Hydrogen ions cannot exist alone, but
they exist after combining with water molecules. Thus
hydrogen ions must always be shown as H+(aq) or hydronium ion
(H3O+). i.e. H+ + H2O → H3O+.
Strength of Acid
We can test the strength of Acid by using a scale called the
pH scale.
pH value of acids is always less than 7
Subscribe to my YT channel - https://www.youtube.com/c/GauravSuthar
Bases
- Bases are bitter in taste and soapy in touch.
- They turn red litmus to blue.
- They give negative (OH-) ions in water solution.
Strong Bases - NaOH (Sodium Hydroxide), KOH (Potassium
hydroxide), Ca(OH)2 (Calcium hydroxide)
Weak Bases - NH4OH
Alkalis - These are bases which are soluble in water.
Litmus turns Blue in Sodium Hydroxide and Soap/ Colgate
Subscribe to my YT channel - https://www.youtube.com/c/GauravSuthar
Chemical properties of Bases:
1. Reaction of Base with Metal:
Base + Metal → Salt + Hydrogen gas
Examples –
2NaOH + Zn → Na2ZnO2 + H2
Only Some Metals react with Base
2. Base in water:
Bases generate hydroxide (OH–) ions in water.
Water soluble bases are called alkalis.
Examples -
Mg(OH)2 + H2O → Mg+2 + 3OH-
3. Reaction of a Non-metallic Oxide with Base:
Non-Metal oxide + Acid → Salt + Water
Examples –
CO2 + Ca(OH)2 → CaCO3 + H2O
From this reaction, it is clear that Non-metallic oxides are
acidic in nature.
Subscribe to my YT channel - https://www.youtube.com/c/GauravSuthar
4. Conduction of electricity:
Bases in water also conduct electricity as the acids do. As
bases also dissociate into hydroxide ions in water thus
conducts electricity. The process of dissolving a base in
water is a highly exothermic one.
Strength of Base
pH value of Base is always less than 7
More the value of pH is stronger the Base will be.
Subscribe to my YT channel - https://www.youtube.com/c/GauravSuthar
pH Scale:
- A Scale to measure the strength of an Acid or a Base.
- The pH scale is marked with numbers 0 to 14, The pH varies from
0 (very acidic) to 7(neutral) and 14 (very alkaline).
- Higher the pH value then it will be Basic
- Lower the pH value then it will be Acidic.
pH < 7 Acidic
pH = 7 Neutral
pH > 7 Basic
Subscribe to my YT channel - https://www.youtube.com/c/GauravSuthar
Importance of pH in everyday life:
1) Self Defence by Animals & Plants –
When insects like honeybee, Ant etc. bite, they inject an acid
into the skin, that causes pain and irritation. If a mild base
like Baking Soda is applied on affected area, it gives relief.
2) pH of the Soil –
Every Plant requires a specific pH range for healthy growth.
It is also suitable for selecting the Fertilizer for a particular
crop by knowing pH of the Soil.
3) pH of our Digestive System –
HCl is present in our stomach which helps in digestion of food.
As during digestion, the stomach produces too much acid, it
causes pain and irritation. To correct the disturbed pH range,
Milk of Magnesia (a mild base) is used as a medicine, also
called Antacid as it reduces the effect of Acid (or Acidity).
4) pH Change leads to Tooth Decay –
When our mouth has pH less than 5.5 then our tooth decay
starts. After eating, some food particles and sugar left in the
mouth and with the help of its bacteria present in our mouth
releases acid. Thus cause tooth decay. The best way to
prevent this is to clean the mouth after eating food.
To prevent tooth decay, toothpastes (basic) are used which
neutralize the excess acid.
Subscribe to my YT channel - https://www.youtube.com/c/GauravSuthar
Salts
- When an acid reacts with a base then it neutralizes to form salt
and water. This reaction is called neutralization reaction.
Acid + Base → Salt + Water
- The salt we eat is Sodium Chloride. It is formed by the
combination of hydrochloric acid and sodium hydroxide solution.
NaOH + HCl → NaCl + H2O
- Salts of a strong acid and weak base are acidic with pH valve less
than 7. Salts of strong base and weak acid are basic in nature
with pH valve more than 7.
Subscribe to my YT channel - https://www.youtube.com/c/GauravSuthar
Types of Salts:
1. Rock salt (स�धा नमक)
Salt when present in its natural form as a crystalline mineral is
rock salt. When seas of bygone ages dried up, beds of rock salt
were formed in the form of large brown crystals.
(Brown due to impurities present in it).
(काला नमक/ चाट मसाले वाला नमक)
2. Common salt
Salt whose chemical composition is mainly NaCl is common salt.
(Tata Salt - दे श का नमक 😜😜)
Subscribe to my YT channel - https://www.youtube.com/c/GauravSuthar
Chlor-Alkali Process
When we pass electricity through an aqueous solution of
sodium chloride (called brine), it decomposes to form sodium
hydroxide.
2NaCl + 2H2O → 2NaOH + Cl2 + H2
- After this process chlorine gas will be present at Anode, and
Hydrogen gas at Cathode.
- Sodium Hydroxide solution is formed near Cathode.
Bleaching Powder (Calcium Oxychloride, CaOCl2)
Preparation:
Ca(OH)2 + Cl2 → CaOCl2 + H2O
(Slaked lime) (Bleaching
Powder)
Uses of Bleaching Powder:
- To bleach cotton and linen in the textile industry.
- Many chemical industries use it as an oxidizing agent.
- To make drinking water free of germs by disinfecting it.
- Used for making Chloroform.
Subscribe to my YT channel - https://www.youtube.com/c/GauravSuthar
Baking Soda (Sodium Hydrogen Carbonate, NaHCO3)
Preparation:
When common salt is treated with Ammonia in the presence of
water and carbon dioxide then baking soda (NaHCO3) is
formed.
NaCl + H2O + CO2 + NH3 → NH4Cl + NaHCO3
(Ammonia) (Ammonium (Sodium hydrogen
chloride) carbonate)
Uses of Baking Soda:
- It is used for making baking powder (baking soda + mild edible
acid).
- Baking soda is also used in making antacids.
- Used in Soda-acid fire extinguishers.
Washing Soda (Sodium Carbonate, Na2CO3.10H2O)
Preparation:
When we heat baking soda (NaHCO3) it forms sodium
carbonate (Na2CO3). When it combines with the excess of
water than washing soda is obtained.
Subscribe to my YT channel - https://www.youtube.com/c/GauravSuthar
2NaHCO3 + Heat → Na2CO3 + H2O + CO2
(Baking Soda) (Sodium Carbonate)
Na2CO3 + 10H2O → Na2CO3∙10H2O
(Sodium Carbonate) (Washing Soda)
Uses of Washing Soda:
- Washing soda is used in making Glass, Paper and Soap.
- Used in making borax and many other sodium compounds.
- Used in washing Clothes
- Used for removing permanent hardness of water.
Plaster of Paris (CaSO4.½ H2O)
Preparation:
When we heat gypsum at 373K, it loses water molecules and
becomes calcium sulphate hemihydrate (CaSO4 . ½ H2O). This is
Plaster of Paris.
CaSO4 . 2H2O → CaSO4 . ½ H2O + 1½ H2O
(Gypsum) (P.O.P)
Subscribe to my YT channel - https://www.youtube.com/c/GauravSuthar
It is a white powder but on mixing with water, it changes to
hard solid mass i.e gypsum again.
CaSO4 . ½ H2O + 1½ H2O → CaSO4 . 2H2O
(P.O.P) (Gypsum)
Uses of POP:
- Doctor uses as Plaster for supporting fractured bones.
- Making Toys and Sculpture (मू�तर्)
- Used for making Surfaces Smooth
Search “Gaurav Suthar” on YouTube for more Notes.
Love You 3000
Subscribe to my YT channel - https://www.youtube.com/c/GauravSuthar
You might also like
- 10th Acid Base and Salt Notes 2011Document5 pages10th Acid Base and Salt Notes 2011Ashraf Husain100% (4)
- Acide Bases and Salt Class 10Document16 pagesAcide Bases and Salt Class 10Abc Abc100% (1)
- ACID Base By R.MDocument17 pagesACID Base By R.MSwadhinNo ratings yet
- 3 Common Indicators Natural Indicator: Acids, Bases and Salts IndicatorsDocument13 pages3 Common Indicators Natural Indicator: Acids, Bases and Salts IndicatorsJoshenderNo ratings yet
- Acid Base Notes 20230715152315203Document7 pagesAcid Base Notes 20230715152315203NEERAV ANANDNo ratings yet
- Screenshot 2022-11-28 at 3.28.38 PMDocument4 pagesScreenshot 2022-11-28 at 3.28.38 PMAanya AroraNo ratings yet
- Acids Bases and SaltsDocument5 pagesAcids Bases and Saltsteerth taledaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2 - Acids, Bases & SaltesDocument42 pagesChapter 2 - Acids, Bases & SaltesRufosNo ratings yet
- Acid, Bases & Salts 2022-23Document34 pagesAcid, Bases & Salts 2022-23ramkumarsingh12406No ratings yet
- Ch-2 Part-2Document4 pagesCh-2 Part-2Kartik BhardwajNo ratings yet
- Notes Acids Bases and SaltsDocument8 pagesNotes Acids Bases and SaltsWouldn't you like to knowNo ratings yet
- Acids, Bases and Salts Notes - XDocument8 pagesAcids, Bases and Salts Notes - XLizannNo ratings yet
- 69 Topper 21 101 2 2 23 Acids Bases and Salts Up201807101532 1531216973 6174Document8 pages69 Topper 21 101 2 2 23 Acids Bases and Salts Up201807101532 1531216973 6174Vijay RaoNo ratings yet
- Acids, Bases and Salts Notes - Part 4Document7 pagesAcids, Bases and Salts Notes - Part 4Dhyan ShahNo ratings yet
- Acids Bases and SaltsDocument52 pagesAcids Bases and SaltsPrabakaran MNo ratings yet
- Topperrevisionnotes69 Topper 21 101 2-2-23 Acids Bases and Salts Up201807101532 1531216973Document8 pagesTopperrevisionnotes69 Topper 21 101 2-2-23 Acids Bases and Salts Up201807101532 1531216973Jessica SehgalNo ratings yet
- Acids Bases and Salts Notes PDFDocument13 pagesAcids Bases and Salts Notes PDFRajkumari MishraNo ratings yet
- Acid Base and Salts'Document4 pagesAcid Base and Salts'zaidasadsiddiquiNo ratings yet
- Acids Bases and Salts Class 10 NotesDocument8 pagesAcids Bases and Salts Class 10 Notesashlyyyyyy33No ratings yet
- Notes Ch-Acids and Bases-1 - 240530 - 174138Document12 pagesNotes Ch-Acids and Bases-1 - 240530 - 174138Anjani RathoreNo ratings yet
- Acids Bases & Salts Notes (1)Document7 pagesAcids Bases & Salts Notes (1)kiranshrivastava1970No ratings yet
- Acids, Bases and SalltsDocument9 pagesAcids, Bases and SalltsVishal SinghNo ratings yet
- 2 - Acids, Bases and Salts (1)Document6 pages2 - Acids, Bases and Salts (1)HONEY YOYONo ratings yet
- Acids, Bases, & SaltsDocument25 pagesAcids, Bases, & SaltsVidya JayakumarNo ratings yet
- Class 10 Book Ncert OnlyDocument3 pagesClass 10 Book Ncert OnlyVaibhav BhardwajNo ratings yet
- SaltsDocument22 pagesSaltssaanvi katyalNo ratings yet
- Acid Bases and Salts - Shobhit NirwanDocument26 pagesAcid Bases and Salts - Shobhit NirwanAlok RahateNo ratings yet
- PPT-Chapter 2-Acids Bases and SaltsDocument106 pagesPPT-Chapter 2-Acids Bases and Saltsbilalanzar22No ratings yet
- What Is An Acid and A Base?: Classification of MatterDocument11 pagesWhat Is An Acid and A Base?: Classification of MatterNishidh SinghNo ratings yet
- NOTES - Acids, Bases and SaltsDocument31 pagesNOTES - Acids, Bases and SaltsKartik ChauhanNo ratings yet
- Chapter 11 - Acids, Bases, and Salts PDFDocument7 pagesChapter 11 - Acids, Bases, and Salts PDFAarush SharmaNo ratings yet
- Properties of Acids and Bases Acids BasesDocument5 pagesProperties of Acids and Bases Acids BaseszyxisNo ratings yet
- Class 10 Acids Bases and Salts NotesDocument22 pagesClass 10 Acids Bases and Salts NotesShreyash VishwakarmaNo ratings yet
- Acids Bases and Salts NotesDocument8 pagesAcids Bases and Salts Notesadejapeltier3No ratings yet
- CHAPTER 2 Acid Base and SaltDocument37 pagesCHAPTER 2 Acid Base and SaltRaghav ParasharNo ratings yet
- Topic 5: Acids, Bases and Salts Acids: Zase - by DJ Principle - For Comments, Whatsapp: 0978936116Document17 pagesTopic 5: Acids, Bases and Salts Acids: Zase - by DJ Principle - For Comments, Whatsapp: 0978936116Paul MunsakaNo ratings yet
- Acid Bases and SaltsDocument38 pagesAcid Bases and SaltssajjadsafdarNo ratings yet
- Chapter - 2 Acids - Bases - and - Salts-43Document21 pagesChapter - 2 Acids - Bases - and - Salts-43Vikash SinghNo ratings yet
- Ch-2 Part-3Document4 pagesCh-2 Part-3Kartik BhardwajNo ratings yet
- Acid and Base and SaltsDocument14 pagesAcid and Base and SaltsSamarth SinghNo ratings yet
- Acids, Bases and Salts (BBC Site)Document6 pagesAcids, Bases and Salts (BBC Site)Ramesh GoldbergNo ratings yet
- A) Reaction of Acids and Bases With Metals: BaseDocument6 pagesA) Reaction of Acids and Bases With Metals: Baseashok pradhanNo ratings yet
- CLASS X CHEMISTRY Solution-989571Document8 pagesCLASS X CHEMISTRY Solution-989571abiniveshofficial4708No ratings yet
- SaltsDocument14 pagesSaltsKDZ S M O O T H 亗No ratings yet
- Acids Bases and SaltsDocument11 pagesAcids Bases and SaltsCollins Obari AdiyeNo ratings yet
- 10 Science Notes 02 Acid Bases and Salts 1Document11 pages10 Science Notes 02 Acid Bases and Salts 1PANDUNo ratings yet
- Lesson-2 Class 10Document7 pagesLesson-2 Class 10Dishu SinghNo ratings yet
- 4 Acid, Base and SaltDocument8 pages4 Acid, Base and Saltjosephmartinsogbu30No ratings yet
- Class 10 Science Chapter 2 Revision NotesDocument16 pagesClass 10 Science Chapter 2 Revision NotesKriish RatnaniNo ratings yet
- Acids, Bases and Salts - Short NotesDocument7 pagesAcids, Bases and Salts - Short Notesat5527813No ratings yet
- ERT CBSE Notes For Class 10 Science ChemistryDocument8 pagesERT CBSE Notes For Class 10 Science ChemistryshanthaNo ratings yet
- 6.1 Role of Water in Showing Chemical Properties of Acid and AlkaliDocument29 pages6.1 Role of Water in Showing Chemical Properties of Acid and AlkaliNur Shahirah100% (1)
- 10th SCIENCE (English Medium) Must DoDocument63 pages10th SCIENCE (English Medium) Must Doanshu26stNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2 - Acids, Bases and SaltsDocument12 pagesChapter 2 - Acids, Bases and SaltsRAM SINGHNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2 Acids, Bases and SaltsDocument5 pagesChapter 2 Acids, Bases and SaltsSmrita SinghNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2 Acids, Bases and SaltsDocument5 pagesChapter 2 Acids, Bases and SaltsDileep Singh ParmarNo ratings yet
- 2.acids, Bases and SaltsDocument9 pages2.acids, Bases and SaltsayanNo ratings yet
- The Chemistry of Soaps and Salts - Chemistry Book for Beginners | Children's Chemistry BooksFrom EverandThe Chemistry of Soaps and Salts - Chemistry Book for Beginners | Children's Chemistry BooksNo ratings yet
- CH 25Document34 pagesCH 25John Nicholson LanderoNo ratings yet
- Science Lesson 2Document10 pagesScience Lesson 2Krista May Narvarte OlivaNo ratings yet
- United States Patent (19) 11 Patent Number: 5,985,454Document10 pagesUnited States Patent (19) 11 Patent Number: 5,985,454KatNo ratings yet
- Chemical Analysis of Red Lead: Standard Test Methods ofDocument4 pagesChemical Analysis of Red Lead: Standard Test Methods ofPyone Ei ZinNo ratings yet
- Refrigeration & Air Conditioning: Arun Jose Tom, Rac, CcetDocument340 pagesRefrigeration & Air Conditioning: Arun Jose Tom, Rac, CcetRubin JosephNo ratings yet
- Semiconductor Theory and Diode Circuits 2021Document11 pagesSemiconductor Theory and Diode Circuits 2021France DanielNo ratings yet
- WMCIE JU Syllabus 2021 2022Document26 pagesWMCIE JU Syllabus 2021 2022Rajesh RoyNo ratings yet
- Sem 1 Full Notes 2Document81 pagesSem 1 Full Notes 2Shravani PakhaleNo ratings yet
- Extremophiles 2004 PDFDocument149 pagesExtremophiles 2004 PDFChandraprasad S RajanganNo ratings yet
- Reaction Rates: BIG IdeaDocument34 pagesReaction Rates: BIG Ideacarleston thurgoodNo ratings yet
- TLC Method For DEG DetectionDocument7 pagesTLC Method For DEG DetectionAbdullah KhudariNo ratings yet
- All Acrylic Based Thermoplastic Elastomers - Design and SynthesisDocument264 pagesAll Acrylic Based Thermoplastic Elastomers - Design and Synthesisvkr91@yahoo.comNo ratings yet
- Construction Catalogue - Atul LTDDocument16 pagesConstruction Catalogue - Atul LTDSolai LNo ratings yet
- General Chemistry ReviewerDocument6 pagesGeneral Chemistry ReviewerHewlett Pearl BawalanNo ratings yet
- Unit 2 Acids Bases Salts Past QuestionsDocument49 pagesUnit 2 Acids Bases Salts Past QuestionsDwiyasa Irin100% (2)
- Experiment 9 SaponificationDocument6 pagesExperiment 9 Saponificationpatrice green - SteadmanNo ratings yet
- Answer Key Si Worksheet 10Document5 pagesAnswer Key Si Worksheet 10Jersey BarquillaNo ratings yet
- Physical Chemistry: Section 1Document956 pagesPhysical Chemistry: Section 1Mitchel TayimoNo ratings yet
- Polyester (PET) : Zimmer: The Leading Brand in Polymers TechnologyDocument16 pagesPolyester (PET) : Zimmer: The Leading Brand in Polymers TechnologyArash AbbasiNo ratings yet
- Chapter: 1 Stoichiometric Relationships: SubtopicsDocument108 pagesChapter: 1 Stoichiometric Relationships: SubtopicsBNo ratings yet
- UK Standards For Microbiology InvestigationsDocument15 pagesUK Standards For Microbiology InvestigationsBenNo ratings yet
- BASF in Korea Backgrounder 2016 PDFDocument2 pagesBASF in Korea Backgrounder 2016 PDFMunis RaoNo ratings yet
- 13 Cellular RespirationDocument6 pages13 Cellular RespirationJohnNo ratings yet
- INTER CAT FCC Gasoline Sulphur Reduction Using Catalyst Additives Mechanisms and Commercial ExperiencesDocument10 pagesINTER CAT FCC Gasoline Sulphur Reduction Using Catalyst Additives Mechanisms and Commercial ExperiencesKumaresan LoganathanNo ratings yet
- Astm e 1219Document6 pagesAstm e 1219KEN KNo ratings yet
- Steel Making Processes Post-Solidification Treatment: - ESR (Electro-Slag Refining) - VAR (Vacuum-Arc Remelting)Document27 pagesSteel Making Processes Post-Solidification Treatment: - ESR (Electro-Slag Refining) - VAR (Vacuum-Arc Remelting)Asher Ahmed100% (1)
- ACETONE - Sigma Aldrich - MSDSDocument14 pagesACETONE - Sigma Aldrich - MSDSramkarn7989No ratings yet
- Alkalinity ControlDocument15 pagesAlkalinity ControlArdyas Wisnu BaskoroNo ratings yet
- Solvent Extraction Process To RecoverDocument12 pagesSolvent Extraction Process To RecoverJazmiin SoLiis HdzNo ratings yet
- Frame MaterialsDocument29 pagesFrame MaterialsPluviophileNo ratings yet