Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Sample Answers for IELTS writing task 1 PIECHART. WORD
Sample Answers for IELTS writing task 1 PIECHART. WORD
Uploaded by
ponkojs20040 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
3 views6 pagesPdf
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentPdf
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as docx, pdf, or txt
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
3 views6 pagesSample Answers for IELTS writing task 1 PIECHART. WORD
Sample Answers for IELTS writing task 1 PIECHART. WORD
Uploaded by
ponkojs2004Pdf
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as docx, pdf, or txt
You are on page 1of 6
Sample Answers for IELTS writing task 1
By Maiysha Bintey Amir
IELTS Instructor
HEXA’S MAJORTILA
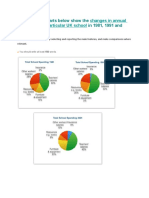
Question: The charts below show American spending patterns
between 1966 and 1996
The pie charts compare how Americans spent on different commodities
in 1996 with that of 1966.
From an overall perspective, it is quite evident that, the spending
pattern of American people was significantly higher on food in 1966
followed by cars, while in 1996 this scenario experienced a massive
incline on cars.
As it is observed from the charts, by 1966, the people of American
spent a huge amount of money on food at 44% which was then
followed by the second highest category where cars consumers made
up around a quarter portion at 23%. Petrol as well as furniture sectors,
meanwhile, took roughly 10% of entire money. At the same time,
people were enthusiastic to expand very little amount on restaurants
along with books which accounted for 7%.
Moving to the second pie chart, it has been observed that, in 1996,
people in American enormously made up 45% of their earning on cars
which was similar to the previous year with food. It is noticeable that,
the rate of entire spending on food witnessed a sharp decline over the
same timeframe at 14%. In terms of restaurants and books, people
used a little amount at 14%. In addition, the total expenditure on
computers got a tremendous upward trend which was 10%. Both,
petrol and furniture sectors saw a light amount at merely 8%.
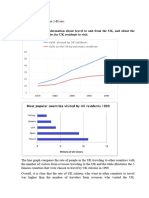
Question: The pie charts below show electricity generation by source
in New Zealand and Germany in 1980 and 2010.
The conferred pie charts enumerate statistical
information about the electricity production from five
different sources in New Zealand and Germany in two
different years 1980 and 2010.
A glance at the pie charts reveal that there were
more units of electricity used in both countries in
2010 than in 1980. In addition, coal was the
predominant one in New Zealand while nuclear
and nutral gas became main fuel sources in
Germany.
Looking at the charts it is clear that New Zealand saw a
significant increase in the units of electricity used from
127 units in 1980 to 200 units in 2010. Similarly, the
figure for Germany also rose remarkably from 105 units
in 1980 to 362 units in 2010. In 1980, the proportion of
electricity generation by coal in New Zealand was 56
units, which was the highest in the total units of sources
of electricity. While electricity sources manufactured by
hydro and nutral gas took up the same units, with 30
units and the figure for petroleum was 11 units.
Regarding Germany, the proportions of electricity
sources were 28 units by coal and nutral gas, about 22
units by petroleum and nuclear, and 7 units by hydro.
Furthermore, in 2010, there were rapid changes in the
sources of electricity generation in both countries. In
New Zealand the figure for coal made up to 150 units in
the total of 200 units of sources of electricity, 50 units
left were in the sources of hydro, petroleum, and nutral
gas. While 155 units were in electricity generation by
nuclear in Germany, which constituted the most of the
total sources of electricity generation in 2010.
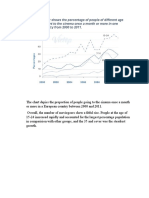
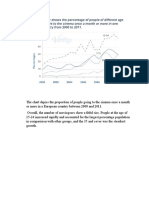
Question: The charts below show the percentage of
water used for different purposes in six areas of the
world.
Summarise the information by selecting the reporting
the main features and make comparisions where
relevant
The rendered pie charts compare the statistical
information regarding the differences in the
proportion of water consumption for three main
purposes in North and South America, Europe, Africa,
Central Asia, and South East Asia.
At the onset, it is explicitly observed that agriculture is
the largest consumer of water in Central Asia, Africa,
South East Asia and South America. While industry
consumes more water than other sectors in Europe
and North America.
As it can be observed in terms of Agricultural use of
water contributes significantly to the total water
consumption across the six regions mentioned. In
Africa, Central Asia and South East Asia, agricultural
use contributes more than 80% of the total water use,
whereas industrial and domestic water consumption
contributes less than 20% to the total across all the
three regions.
On the other hand, in North America and Europe, the
water usage trends are quite similar, with close to 50%
of the total water consumption being done by the
industrial sector. Around 30% – 40% of the water is
used by agriculture and around 15% for domestic use
for both these regions. For South America,
agricultural use of water is 71% of the total, and
industrial and domestic use make up for 19% and
10% of the total, respectively.
You might also like
- Nebosh: Know - Workplace Health and Safety Principles (International)Document18 pagesNebosh: Know - Workplace Health and Safety Principles (International)ARJUN79% (14)
- Cae Writing GuideDocument60 pagesCae Writing Guideelisadp95% (20)
- Louis Hardan Mobile Dental Photography Part I ViaDocument9 pagesLouis Hardan Mobile Dental Photography Part I ViaMuchlis Fauzi ENo ratings yet
- Kraus & Naimer C Switches PDFDocument56 pagesKraus & Naimer C Switches PDFJefMur100% (1)
- Pie ChartDocument6 pagesPie ChartNguyen LeNo ratings yet
- Sample 1: The Given Pie Charts Compare The Expenses in 7 Different Categories in 1966 and 1996 by American CitizensDocument76 pagesSample 1: The Given Pie Charts Compare The Expenses in 7 Different Categories in 1966 and 1996 by American CitizensManoj KumarNo ratings yet
- Writing PieDocument20 pagesWriting PieBishal PunksNo ratings yet
- Task1 Writing.Document15 pagesTask1 Writing.Ánh Ngọc NguyễnNo ratings yet
- 15-4 Writing 9Document94 pages15-4 Writing 9Trung tâm ngoại ngữ English Zone An ĐồngNo ratings yet
- Comparison GraphDocument8 pagesComparison GraphAn ĐỗNo ratings yet
- Ielts Writing Task 1 - Pie ChartDocument53 pagesIelts Writing Task 1 - Pie ChartAmy HicksNo ratings yet
- Task1 WritingDocument16 pagesTask1 WritingÁnh Ngọc NguyễnNo ratings yet
- Writing Task 1Document41 pagesWriting Task 1Ariful Islam Arif100% (1)
- Ielts Writting 1Document25 pagesIelts Writting 1shadman souravNo ratings yet
- Describe Pie ChartDocument11 pagesDescribe Pie ChartAnonymous 7Vl0XCBvNo ratings yet
- Body 1:: Petrol and Oil 1980: Greatest + 2 Times More Than Coal and Natural Gas: in 1980Document4 pagesBody 1:: Petrol and Oil 1980: Greatest + 2 Times More Than Coal and Natural Gas: in 1980Tuấn Hiệp NguyễnNo ratings yet
- More Samples TASK 1Document13 pagesMore Samples TASK 1Ngoc PhamNo ratings yet
- Practice Task 1Document7 pagesPractice Task 1Hương ĐặngNo ratings yet
- Nguyễn Vinh HiểnDocument4 pagesNguyễn Vinh Hiểntt6174811No ratings yet
- 小作文范文六篇Document6 pages小作文范文六篇合并成No ratings yet
- Ielts Task 1 PracticeDocument15 pagesIelts Task 1 PracticeGood GuyNo ratings yet
- Simon's Sample EssaysDocument57 pagesSimon's Sample EssaysNguyễn Ngọc HươngNo ratings yet
- Graph and Chart SampleDocument6 pagesGraph and Chart Samplethrowacc1898No ratings yet
- IELTS Writing Task 1Document21 pagesIELTS Writing Task 1AliWafaNo ratings yet
- Sample Task 1 - 3Document32 pagesSample Task 1 - 3Saeid RajabiNo ratings yet
- The Chart Depics The Proportion of People Going To The Cinema Once A Month or More in An European Country BetDocument13 pagesThe Chart Depics The Proportion of People Going To The Cinema Once A Month or More in An European Country BetÁnh Ngọc NguyễnNo ratings yet
- Vân AnhDocument3 pagesVân AnhthuhoaivtkNo ratings yet
- IELTS Task 1Document12 pagesIELTS Task 1saidur183No ratings yet
- The Bar Chart Shows The Number of Times Per Week (In 1000s), Over Five Weeks, That Three Computer Packages Were Downloaded From The InternetDocument21 pagesThe Bar Chart Shows The Number of Times Per Week (In 1000s), Over Five Weeks, That Three Computer Packages Were Downloaded From The InternetAnonymous 2HWqnKqI4WNo ratings yet
- Practicing The Pie ChartDocument8 pagesPracticing The Pie ChartPhan Phương ThuýNo ratings yet
- Describe ImageDocument4 pagesDescribe ImageRadman Dormendo ItelluNo ratings yet
- Ielts Writing TaskDocument8 pagesIelts Writing TaskLyudmyla GillegoNo ratings yet
- Writing Task 1 - Simon - RemovedDocument25 pagesWriting Task 1 - Simon - Removedngthuthao210104No ratings yet
- Pie ChartDocument8 pagesPie ChartNgọc Ánh LêNo ratings yet
- Ielts Table Write Task 1Document8 pagesIelts Table Write Task 1Anonymous 1IFZQIc30No ratings yet
- Writing Task 1Document19 pagesWriting Task 1Trian NguyenNo ratings yet
- Task 1 ôn tậpDocument29 pagesTask 1 ôn tậpMốcNo ratings yet
- IELTS Writing Task 1 - Tổng Hợp Bài Mẫu Band 9Document32 pagesIELTS Writing Task 1 - Tổng Hợp Bài Mẫu Band 9Đông NguyễnNo ratings yet
- IELTS Writing task 1 - Tổng hợp bài mẫu band 9 PDFDocument32 pagesIELTS Writing task 1 - Tổng hợp bài mẫu band 9 PDFVũ NguyễnNo ratings yet
- Line Graph wt1Document2 pagesLine Graph wt1Gia BảoNo ratings yet
- Sample Task 1Document14 pagesSample Task 1antimabulbulNo ratings yet
- Band 9 Essay Bank: Academic Task 1-Sample 1Document12 pagesBand 9 Essay Bank: Academic Task 1-Sample 1parinaaz kaurNo ratings yet
- Academic Writing Sample Task 1 (56-92)Document57 pagesAcademic Writing Sample Task 1 (56-92)C IB Cibeternal75% (4)
- Writing cùng Trần Phương - Sao chépDocument5 pagesWriting cùng Trần Phương - Sao chépPhuongg MinhhNo ratings yet
- IELTS Rainwater DiagramDocument14 pagesIELTS Rainwater Diagramsaeed haghNo ratings yet
- IELTS Writing Task 1Document30 pagesIELTS Writing Task 1Nguyễn Phương ThảoNo ratings yet
- 4b. BTVN Buoi 4Document3 pages4b. BTVN Buoi 4bichnganhvNo ratings yet
- Ielts Writing Task 1 SimonDocument27 pagesIelts Writing Task 1 SimonQuỳnh Trâm TrầnNo ratings yet
- Dokumen - Tips - Writing Task 1 Tips and Samples Google DocspdfDocument27 pagesDokumen - Tips - Writing Task 1 Tips and Samples Google DocspdfNHI HUỲNH XUÂNNo ratings yet
- 30 Sample Essays Band 9 IELTS of SimonDocument29 pages30 Sample Essays Band 9 IELTS of SimonKhang TranNo ratings yet
- Bài mẫu IELTS Writing Task 1Document4 pagesBài mẫu IELTS Writing Task 1朝陽出暮色No ratings yet
- IELTS READING TEST June 1Document16 pagesIELTS READING TEST June 1Mai LâmNo ratings yet
- Pie Charts With TrendDocument19 pagesPie Charts With TrendHoàng ChiNo ratings yet
- IELTS Writing Task 1 - SimonsDocument28 pagesIELTS Writing Task 1 - SimonsLan Anh HoàngNo ratings yet
- The Line Graph Demonstrates Three Types of Food Which Were Consumed by Mauritian Teenagers Between 1985 and 2015Document10 pagesThe Line Graph Demonstrates Three Types of Food Which Were Consumed by Mauritian Teenagers Between 1985 and 2015cocoNo ratings yet
- Writing PortfolioDocument3 pagesWriting PortfolioCảnh DươngNo ratings yet
- 杨亮雅思写作预测讲义(下)Document16 pages杨亮雅思写作预测讲义(下)wangzhibo0520No ratings yet
- The Diagrams Below Give Information On Transport and Car Use in EdmontonDocument13 pagesThe Diagrams Below Give Information On Transport and Car Use in EdmontonOktiara DwindahNo ratings yet
- Tai Lieu Tong Hop Bai Mau Writing Task 1 Hoc Vien Ielts IReady 1Document17 pagesTai Lieu Tong Hop Bai Mau Writing Task 1 Hoc Vien Ielts IReady 1Mai Linh LinhNo ratings yet
- Academic NotesDocument29 pagesAcademic NotesJaskaranjit Singh GillNo ratings yet
- Chapter 8 PrestressedDocument4 pagesChapter 8 PrestressedMOHAMUD AHMED ABDIKARIM / UPMNo ratings yet
- Task 1Document11 pagesTask 1dinhthao22112005No ratings yet
- Energy Myths and Realities: Bringing Science to the Energy Policy DebateFrom EverandEnergy Myths and Realities: Bringing Science to the Energy Policy DebateRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (4)
- How America Can Stop Importing Foreign Oil & Those Preventing It From HappeningFrom EverandHow America Can Stop Importing Foreign Oil & Those Preventing It From HappeningNo ratings yet
- Water and Its Forms: Name: - DateDocument2 pagesWater and Its Forms: Name: - DateNutrionist Preet PatelNo ratings yet
- House of ConcreteDocument9 pagesHouse of ConcreteArkyadeep ChowdhuryNo ratings yet
- HCR5 Leaflet E 1102 Sheet PDFDocument8 pagesHCR5 Leaflet E 1102 Sheet PDFAmilcar CoutoNo ratings yet
- For UploadsDocument3 pagesFor UploadsMizumi IshiharaNo ratings yet
- Example of A Business Model Canvas Coconut Treat StandDocument2 pagesExample of A Business Model Canvas Coconut Treat StandSabrena FennaNo ratings yet
- 2.2 Evaluating Economic PerformanceDocument12 pages2.2 Evaluating Economic PerformanceMissDangNo ratings yet
- Raj'a (Returning) : Sermon of Amir Ul-MomineenDocument3 pagesRaj'a (Returning) : Sermon of Amir Ul-Momineentausif mewawalaNo ratings yet
- Sublimatex Company ProfileDocument17 pagesSublimatex Company ProfileMohamed MahmoudNo ratings yet
- Definition of DemocracyDocument20 pagesDefinition of DemocracyAnonymous R1SgvNINo ratings yet
- Inorganic Chemistry 1 - Alkali Metals RevisioDocument7 pagesInorganic Chemistry 1 - Alkali Metals RevisioAshleyn Mary SandersNo ratings yet
- Wild Amazon Cradle of Life Film TestDocument2 pagesWild Amazon Cradle of Life Film TestQuratulain MustafaNo ratings yet
- Information On The Desired Degree CourseDocument4 pagesInformation On The Desired Degree CourseAdewumi GbengaNo ratings yet
- D Claves - Examen A2Document1 pageD Claves - Examen A2Anyelin JaimesNo ratings yet
- ScribdDocument66 pagesScribdyeyeu5No ratings yet
- 友谊论文的论点Document6 pages友谊论文的论点gwhjcowlfNo ratings yet
- Neet Code C Question Paper PDFDocument41 pagesNeet Code C Question Paper PDFMagnifestoNo ratings yet
- Cape Sewing - Industrial Sewing TechnologyDocument33 pagesCape Sewing - Industrial Sewing TechnologyMonika GadgilNo ratings yet
- Med Chem IV Sem Pre RuhsDocument1 pageMed Chem IV Sem Pre Ruhsabhay sharmaNo ratings yet
- Discourse Vs - TextDocument11 pagesDiscourse Vs - TextImmo Eagle JuniØrNo ratings yet
- Neonatal Intubation: Past, Present, and Future: Practice GapsDocument9 pagesNeonatal Intubation: Past, Present, and Future: Practice GapskiloNo ratings yet
- Errata Sheet 1.7 - Dropzone Commander Official Update: NEW ADDITIONS/ CHANGES FROM VERSION 1.6 Highlighted in RedDocument2 pagesErrata Sheet 1.7 - Dropzone Commander Official Update: NEW ADDITIONS/ CHANGES FROM VERSION 1.6 Highlighted in RedTecnocastoroNo ratings yet
- English File: Answer KeyDocument4 pagesEnglish File: Answer KeyEvelyn BoccioNo ratings yet
- GEAR 300 75W-90 en DE Motul 34200 20221014Document2 pagesGEAR 300 75W-90 en DE Motul 34200 20221014Marcio AlexandreNo ratings yet
- Edith Stein: Women, Social-Political Philosophy, Theology, Metaphysics and Public HistoryDocument281 pagesEdith Stein: Women, Social-Political Philosophy, Theology, Metaphysics and Public HistorySantiago GarciaNo ratings yet
- Thinclaw THE Ictorious: Paladin 3 (Oath of Devotion) 972 Dragonborn (Gold Dragon Ancestry) KnightDocument1 pageThinclaw THE Ictorious: Paladin 3 (Oath of Devotion) 972 Dragonborn (Gold Dragon Ancestry) KnightAlfonso LópezNo ratings yet
- Pulse OximetryDocument29 pagesPulse OximetryAnton ScheepersNo ratings yet