Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Sexual Reproduction In Flowering Plants_
Sexual Reproduction In Flowering Plants_
Uploaded by
salmasaleema5530 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
1 views2 pagesCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pdf or txt
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
1 views2 pagesSexual Reproduction In Flowering Plants_
Sexual Reproduction In Flowering Plants_
Uploaded by
salmasaleema553Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pdf or txt
You are on page 1of 2
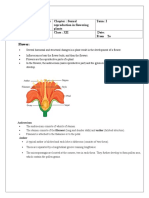
Sexual Reproduction In Flowering Plants
QUESTIONS
1. What is apomixis and what is its importance?
Reproduction by special sporophytic or gametophytic generative tissues
without fertilization (fusion of male and female gamete) is known as apomixis.It
is a mode of asexual reproduction in flowering plants and hence produce
clones, not variations. Apomictic seed production in hybrid plants allows
commercial use of hybrid seeds without conducting hybridization again and
again.
2. Mention two strategies evolved in flowers to prevent self-pollination in flowers.
Self-incompatibility: A condition wherein the pollen is ineffective in fertilizing
the same flower or other flowers on the same plant usually due to inhibition of
the growth of the pollen tube in the stigma and style, thereby preventing
delivery of male gametes to the ovules.
Maturation of pistil before that of stamen (protogyny) or maturation of stamen
before that of the pistil (protandry) inhibit self-pollination.
3. Name the parts of an angiospermic flower in which development of male and
female gametophyte take place.
Pollen is the first cell of male gametophyte while ovule represents female
gametophyte. Development of male and female gametophytes takes place in
anther and ovary, respectively.
4. What is self-incompatibility? Why does self-pollination not lead to seed
formation in self-incompatible species?
Self-incompatibility is a condition where pollen is not able to fertilize the same
flower or other flowers on the same plant due to inhibition of the growth of the
pollen tube in the stigma and style, thereby preventing delivery of male
gametes to the ovules. The absence of fusion of male and female gamete leads
to no seed formation in these plants.
5. Arrange the following terms in the correct developmental sequence: Pollen
grain, sporogenous tissue, microspore tetrad, pollen mother cell, male
gametes.
Each microsporangium has inner sporogenous tissue that differentiates into
microspore/pollen mother cell, they first undergo mitotic divisions to increase
the cell number. The sporogenous cells are diploid and have two complete sets
of chromosomes. These diploid cells undergo meiosis to produce four haploid
microspores/pollen grains (B) that remain suspended in central of each
microsporangium. Pollen grain is the first cell of male gametophyte wherein
male gamete develops. The correct sequence is sporogenous tissue, pollen
mother cell, microspore tetrad, pollen grain and male gamete.
6. What is triple fusion? Where and how does it take place? Name the nuclei
involved in triple fusion.
Fusion of male gamete with diploid secondary nucleus/central cell to form triploid
primary endosperm nucleus is called as triple fusion as it involves three nuceli. It
takes place in embryo sac during double fertilization. Two polar nuclei and male
gamete are involved in it.
7. What is meant by emasculation? When and why does a plant breeder employ
this technique?
The process of removal of anthers from the flower is called as emasculation. It
is done before dehiscence to prevent contamination of stigma with any
undesired pollen and to ensure cross-pollination by desired pollens.
Emasculation is useful in artificial hybridization to pollinate stigma with
selected emasculated pollens only.
8. Differentiate between microsporogenesis and megasporogenesis. Which type
of cell division occurs during these events? Name the structures formed at the
end of these two events.
Microsporogensis involves meiosis in microspore/pollen mother cells to
produce microspores/pollen grains tetrads that remain suspended in central of
each microsporangium. Pollen mother cells are present in each
microsporangium of anther.
Megasporogenesis includes meiosis in megaspore mother cell of ovule to form
megaspore tetrad out of which one megapore is functional.
Meiosis occurs during both megasporogenesis and microsporogenesis to
prodduce haploid male and female gametes. Microsporogenesis forms haploid
microspores while megasporogenesis forms haploid megaspores.
You might also like
- The Sadhana of Buddha AkshobhyaDocument22 pagesThe Sadhana of Buddha AkshobhyaNilo Gelais Costa Junior100% (5)
- Bio Eoc Review Session 1 Questions 11-12Document6 pagesBio Eoc Review Session 1 Questions 11-12api-269873615No ratings yet
- CBSE NCERT Solutions For Class 12 Biology Chapter 2: Back of Chapter QuestionsDocument9 pagesCBSE NCERT Solutions For Class 12 Biology Chapter 2: Back of Chapter QuestionsSatvik MishraNo ratings yet
- CH - 2 - Ncert SolutionsDocument5 pagesCH - 2 - Ncert SolutionsJanani VijayarajNo ratings yet
- CHAPTER 2 - TEXTUAL EXERCISE - Sexual Reproduction in Flowering PlantsDocument6 pagesCHAPTER 2 - TEXTUAL EXERCISE - Sexual Reproduction in Flowering PlantsSyed Mohdammad AliNo ratings yet
- Modes of ReproductionDocument5 pagesModes of ReproductionSandeep638No ratings yet
- Solved AsingnmentDocument8 pagesSolved Asingnmentsalmaburney77No ratings yet
- 2 Sexual Reproduction in Flowering PlantsDocument5 pages2 Sexual Reproduction in Flowering PlantsPreeti AgrawalNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2 Sexual Reproduction in Flowering PlantsDocument7 pagesChapter 2 Sexual Reproduction in Flowering Plantslavishbhati691No ratings yet
- NCERT Solutions For Class 12 March 30 Biology Chapter 2 Sexual Reproduction in Flowering PlantsDocument7 pagesNCERT Solutions For Class 12 March 30 Biology Chapter 2 Sexual Reproduction in Flowering PlantsRaveena GhodeswarNo ratings yet
- Pollination and Reproduction in Crop PlantsDocument66 pagesPollination and Reproduction in Crop PlantsGaurab NeupaneNo ratings yet
- Class 12 - Biology - Sexual Reproduction in Flowering PlantsDocument7 pagesClass 12 - Biology - Sexual Reproduction in Flowering PlantsAstha SaxenaNo ratings yet
- Modes of ReproductionDocument33 pagesModes of ReproductionMohaajanan AliNo ratings yet
- G 5 R HCUyfm 1 N23 O6 o 4 QduDocument10 pagesG 5 R HCUyfm 1 N23 O6 o 4 Qdudhairyasuthar2749No ratings yet
- Biology Project 11Document10 pagesBiology Project 11K.KAVIARASINo ratings yet
- Bilogy PASSIN Package 3Document55 pagesBilogy PASSIN Package 3dhanushgovindaraju2006No ratings yet
- Chapter 2 - Male and Female GametophytesDocument10 pagesChapter 2 - Male and Female Gametophyteskangethemoses371No ratings yet
- Sexual Reproduction in Flowering PlantsDocument35 pagesSexual Reproduction in Flowering PlantsKumar Munendra PrfNo ratings yet
- MF009 5A Plant Reproduction James L2Document27 pagesMF009 5A Plant Reproduction James L2PikuNo ratings yet
- Seed Formation and DevelopmentDocument12 pagesSeed Formation and DevelopmentSabir Ahamed90% (20)
- 12 Biology NcertSolutions Chapter 2 PDFDocument10 pages12 Biology NcertSolutions Chapter 2 PDFKaran bhatiaNo ratings yet
- Fertilization in PlantsDocument17 pagesFertilization in PlantsManisha KumariNo ratings yet
- GSB Textback ch.1. Reproduction in Lower and Higher Plants DR - Phemie FernandesDocument8 pagesGSB Textback ch.1. Reproduction in Lower and Higher Plants DR - Phemie Fernandespranavjain558No ratings yet
- Chapter 2 Sexual Reproduction in Flowering PlantsDocument22 pagesChapter 2 Sexual Reproduction in Flowering PlantsSushil RajbharNo ratings yet
- Chapter-2 Sexual Reproduction in Flowering Plants FlowerDocument7 pagesChapter-2 Sexual Reproduction in Flowering Plants FlowerbpmbhamoraNo ratings yet
- 203RZDocument13 pages203RZSohan PkNo ratings yet
- Ncert Soln Cl 12 Bio Ch 2Document7 pagesNcert Soln Cl 12 Bio Ch 2glimpsesofworld0No ratings yet
- Lecture notes-XII-Sexual Reproduction in Flowering PlantsDocument11 pagesLecture notes-XII-Sexual Reproduction in Flowering Plantsaditya100% (3)
- Sexual Reproduction in PlantsDocument28 pagesSexual Reproduction in Plantsasadukimbugwe20No ratings yet
- Biology 2 PucDocument23 pagesBiology 2 PucTULASI BAINo ratings yet
- Plant Reproduction and DevelopmentDocument16 pagesPlant Reproduction and Developmentits james de guzmanNo ratings yet
- Sexual Repro 1Document5 pagesSexual Repro 1Sudhir Kumar YadavNo ratings yet
- Group 3 Plants and Animals ReproductionDocument25 pagesGroup 3 Plants and Animals ReproductionPateña Nicole Ferdilette DiñozoNo ratings yet
- Pollination - Biology Science Fair Project IdeasDocument10 pagesPollination - Biology Science Fair Project IdeasSwaraj KhedekarNo ratings yet
- Anther&Pollen CultureDocument17 pagesAnther&Pollen CulturenadyaawlNo ratings yet
- Plant Reproductin NotesDocument7 pagesPlant Reproductin NotesTasneem HamdyNo ratings yet
- Double Fertilization - WikipediaDocument27 pagesDouble Fertilization - WikipediaBashiir NuurNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2 - Sexual Reproduction in Flowering Plnts-12thDocument14 pagesChapter 2 - Sexual Reproduction in Flowering Plnts-12thMadhav GourNo ratings yet
- Plant ReproductionDocument8 pagesPlant ReproductionayanurhidayahNo ratings yet
- 2.sexual Reproduction in Flowering PlantsDocument39 pages2.sexual Reproduction in Flowering PlantsIshvaryaNo ratings yet
- Bot01 Lec4Document11 pagesBot01 Lec4Jan Leo QuinioNo ratings yet
- Biology HolidayDocument3 pagesBiology Holidayshikeb aliNo ratings yet
- Sexual Reproduction in Flowering PlantsDocument35 pagesSexual Reproduction in Flowering PlantsDiksha TNo ratings yet
- 12 Biology NcertSolutions Chapter 2Document10 pages12 Biology NcertSolutions Chapter 2Manas Ranjan JenaNo ratings yet
- Plant ReproductionDocument30 pagesPlant ReproductionBitan DasNo ratings yet
- Plant KingdomDocument61 pagesPlant KingdomUdayveer SinghNo ratings yet
- Double Fertilization - WikipediaDocument27 pagesDouble Fertilization - WikipediaNaniNo ratings yet
- Plus Two Botany - Public Exam - Express RevisionDocument170 pagesPlus Two Botany - Public Exam - Express RevisionLena AlbertNo ratings yet
- Module 2 Sexual Reproduction in Flowering PlantsDocument9 pagesModule 2 Sexual Reproduction in Flowering PlantsMorgan BrownNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2 Sexual Reproduction in Flowering PlantsDocument10 pagesChapter 2 Sexual Reproduction in Flowering PlantsSuvidNo ratings yet
- Reprodcution in PlantsDocument10 pagesReprodcution in Plantsargin.dhtNo ratings yet
- XX 3 LOl An 45 G OG7 Eo Dam FDocument9 pagesXX 3 LOl An 45 G OG7 Eo Dam FGauri PopalghatNo ratings yet
- 1. Reproduction in Lower and Higher PlantsDocument19 pages1. Reproduction in Lower and Higher Plantsshivamkadam563No ratings yet
- BIODocument16 pagesBIOVeankatapathy 613 Xl group BNo ratings yet
- Sexual Reproduction in PlantsDocument7 pagesSexual Reproduction in PlantshithereNo ratings yet
- 12 THDocument4 pages12 THguptaamrita5335No ratings yet
- CBSE Test Paper 02 Ch-2 Sexual Reproduction in Flowering PlantsDocument4 pagesCBSE Test Paper 02 Ch-2 Sexual Reproduction in Flowering PlantsShahid ansariNo ratings yet
- Chapter 4. Reproductive SystemsDocument35 pagesChapter 4. Reproductive Systemsalemneh bayehNo ratings yet
- Biology Class 12 ProjectDocument13 pagesBiology Class 12 ProjectKartikey RaiNo ratings yet
- Gardener's Guide to Seed Catalogs: Gardener's Guide Series, #3From EverandGardener's Guide to Seed Catalogs: Gardener's Guide Series, #3No ratings yet
- Change Your Diet Change Your Mind DR Georgia Ede Full Chapter PDFDocument69 pagesChange Your Diet Change Your Mind DR Georgia Ede Full Chapter PDFsygamagobas3100% (6)
- Nursing Lab Articles As Per Indian Nursing CouncilDocument52 pagesNursing Lab Articles As Per Indian Nursing CouncilRahul KashyapNo ratings yet
- Hitachi Trouble ShootingDocument18 pagesHitachi Trouble Shootingjacklyn ade putra75% (4)
- CommunicationsDocument30 pagesCommunicationsChristine PuaNo ratings yet
- Worksheet 5 CSDocument2 pagesWorksheet 5 CSPal KansaraNo ratings yet
- Types of Research - For QuizDocument3 pagesTypes of Research - For QuizDexter Lloyd Chavez CatiagNo ratings yet
- Announcement EnrolmentDocument20 pagesAnnouncement EnrolmentRomeo BalingaoNo ratings yet
- Artificial Retina: Presented byDocument6 pagesArtificial Retina: Presented bySai KrishnaNo ratings yet
- SQL ExceriseDocument10 pagesSQL ExceriseSri VatsaNo ratings yet
- 1 Microbiology Course ContentDocument16 pages1 Microbiology Course ContentAziz AnisahNo ratings yet
- ANP 202 Principles of Animal Production PDFDocument207 pagesANP 202 Principles of Animal Production PDFBELKYS100% (1)
- Hardness Test: Materials Science and TestingDocument6 pagesHardness Test: Materials Science and TestingCharlyn FloresNo ratings yet
- Chapter-9-Soil VIIDocument8 pagesChapter-9-Soil VIIPreeti BansalNo ratings yet
- Minebea Stepper Motor Part Number Decoding TableDocument5 pagesMinebea Stepper Motor Part Number Decoding TableWijebNo ratings yet
- Irodov Basic Laws of ElectromagnetismDocument314 pagesIrodov Basic Laws of Electromagnetismharmanpunn94No ratings yet
- Seal Design For High Pressure Offshore-Morton & EvansDocument10 pagesSeal Design For High Pressure Offshore-Morton & EvansMachineryengNo ratings yet
- Gradsaleh PDFDocument257 pagesGradsaleh PDFميرفت بكرى نمرNo ratings yet
- Assg1 200501Document7 pagesAssg1 200501SHARIFAH NURIN ZAHIRAH BINTI SYED ZAINAL ABIDINNo ratings yet
- PPM Rebuilt Unit Manual: Testing MethodDocument35 pagesPPM Rebuilt Unit Manual: Testing MethodNGUYENTHEPHAT100% (3)
- Build Tight RangeDocument8 pagesBuild Tight RangeMihai MunteanuNo ratings yet
- Elizardo PerzDocument79 pagesElizardo PerzRODRINo ratings yet
- SEMIKRON DataSheet SKiiP 36NAB126V1 25230120Document4 pagesSEMIKRON DataSheet SKiiP 36NAB126V1 25230120Merter TolunNo ratings yet
- Empowering A Poor Threatened CommunityDocument405 pagesEmpowering A Poor Threatened CommunityJul JulNo ratings yet
- Eta Line 150-250Document32 pagesEta Line 150-250tafseerahmadNo ratings yet
- 3374 PDFDocument10 pages3374 PDFCornel DumitruNo ratings yet
- Modeling Studies To Asses Long Term Settlement PLAXISDocument105 pagesModeling Studies To Asses Long Term Settlement PLAXISAnonymous 5exSerNo ratings yet
- Soal Latihan Persiapan Us Bahasa InggrisDocument6 pagesSoal Latihan Persiapan Us Bahasa InggrisNurrul Hadhya ZaraNo ratings yet
- Xenon 2.2 4x2 148HP DC PDFDocument4 pagesXenon 2.2 4x2 148HP DC PDFshiksha torooNo ratings yet