Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Introduction to Philosophy
Introduction to Philosophy
Uploaded by
gaminokaycee0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
3 views6 pagesCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as docx, pdf, or txt
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
3 views6 pagesIntroduction to Philosophy
Introduction to Philosophy
Uploaded by
gaminokayceeCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as docx, pdf, or txt
You are on page 1of 6
INTRODUCTION TO not be signed by the government,
PHILOSOPHY then we will have no recourse
but to go to the war.”
OPINIONS – are statements that go APPEAL TO EMOTION –
beyond providing facts using emotions such as pity or
sympathy
CONCLUSION – a judgement based on
ex. “all these charges are
certain facts
baseless; this is just plain
BELIEFS – are statements that expresses harassment- can’t you see how
convictions that are not easily and clearly this is affecting my family?”
explained by facts.
APPEAL TO THE POPULAR
EXPLANATIONS – are statements that – the idea is presented as
assume the claim to be true and provide acceptable because a lot of
reasons why the statement is true people accept it.
ex. “every boy your age already
ARGUMENTS – are a series of
has a girlfriend. You should go
statements that provide reasons to
find one!”
convince the reader or listener that a claim
or opinion is truthful.
APPEAL TO TRADITION –
FALLACIES – are arguments based on the idea is acceptable because it
faulty reasoning. has been true for a long time.
ex. “marriage should be between
BIAS – a disproportionate weight in favor a man and a woman. It has been
of or against an idea or thing, usually in a so for a long time in this
way that is close-minded, prejudicial or country; it should remain so
unfair. today and in the future”
BEGGING THE QUESTION
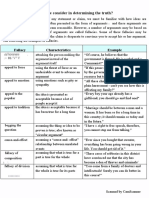
FALLACY, CHARACTERISTICS AND – assuming the thing or idea to
EXAMPLES be proven is true; also known as
circular argument.
AD HOMINEM – attacking the ex. “I have the right to free
person presenting the argument speech, therefore you cannot
instead of the argument itself. stop me from talking.”
ex. “of course, he believes that
the government is flawed, he is a CAUSE-AND-EFFECT –
rebel and a communist!” assuming ‘cause-and-effect’
relationship between unrelated
APPEAL TO FORCE – using events.
the threat or force or an ex. ”ever since you bought that
undesirable event to advance an sweater, everything has been
argument. going wrong in your life. You
ex. “if this peace agreement will should get rid of it.”
cause of the plane crash, but
FALLACY OF investigators are currently
COMPOSITION – assuming focusing on the possibility of
that what is true for the whole pilot error”
ex. “these cases of robbery in
this district have convinced me HINDSIGHT – the tendency to
that the city has become a den of see past events as predictable, or
thieves and criminals.” to ascribe a pattern to historical
events.
FALLACY OF DIVISION – ex.” Magellan’s assault on
assuming that what is true for the Mactan island was a foolhardy
whole is true for its parts. venture, made by an
ex. “you come from a family of overconfident, careless man who
doctors and intellectuals! Surely underestimated the valor of the
you can do better in this course!” native Filipinos.”
BIAS, CHARACTERISTICS AND CONFLICT OF INTREST – a
EXAMPLES person or group is connected to
or has a vested interest in the
issue being discussed.
CORRESPONDENCE BIAS Ex. “as the daughter of the
OR ATTRIBUTION EFFECT accused, I believe I have the
– tendency to judge a person’s right to express my opinion on
personally by his or her actions, the issue of his alleged corrupted
without regard for the external practices.”
factors or influence.
ex. “these soldiers who fought in CULTURAL BIAS – analyzing
the war are all bloodthirsty an event or issue based on one’s
murderers!” cultural standards.
ex. “ I do not agree with this
CONFIRMATION BIAS – Western practice of placing aged
tendency to look for and readily parents in retirement homes. We
accept information which fits Filipinos take care of our family
one’s own beliefs or views and members.”
to reject ideas or views that go
METHODS OF PHILOSOPHIZING
against it.
ex.”how can I accept his view There are four methods of philosophizing,
that there is no God? I’m a these are:
Christian!”
Logic
FRAMING – focusing on a Existentialism
certain aspect of a problem while Analytic tradition
ignoring other aspects. Phenomenology
ex. “preliminary evidence has
still not pointed out the actual
LOGIC – it is a truth which is based on their life, follows through or does not
reasoning and critical thinking. It is the follow through on that decision and begins
analysis and construction of argument and to create their essence. The idea of
serves as the path to freedom from half existentialism is a person will create their
truths and deception. essence over their lifetime and will be
finished or fully formed in existentialism.
Logic is also one of the major branches of In existentialism, the existence comes first
philosophy which increases one’s ability to and the essence comes second.
reason correctly and distinguish rational
reasoning.
ANALYTIC TRADITION – this
philosophy was founded by Gottlob Frege
TWO TYPES OF REASONING in the late 19th century. It is said that the
Philosophy should apply logical
1. DEDUCTIVE REASONING
techniques to attain conceptual clarity.
(from conclusion to
Analytic philosophy is also called
introduction) – in this type of
linguistic philosophy, a related set of
reasoning, conclusion comes
approaches to philosophical problems.
first followed by main points,
and the last will be the This philosophy means the using common
supporting data, facts, examples experience and ordinary language to
and evidences. General idea analyze concepts and language in
comes first before the specific or philosophy. Example o analytic philosophy
particular area. is The Star Strek’s Mr. Spock. Gene
Roddenberry, the creator of the original
2. INDUCTIVE REASONING show was famous for his intense interest in
(from introduction to philosophy and religion and he was
conclusion) – in this type of probably aware of the developments in
reasoning, supporting data, facts, analytic philosophy during the 1960’s
examples and evidences come when Star Trek was first made.
first followed by the main points
and conclusion will be the last
part. This is the opposite of PHENOMENOLOGY – a broad
deductive reasoning because a discipline and methods of inquiry in
particular idea comes first before philosophy which is based on the premise
the general idea. that reality consists of objects and events
(“phenomena”) as they are perceived or
understood in human consciousness and
EXISTENSIALISM – it is a philosophy not of anything independent of human
that emphasizes the importance of free consciousness. It is the study of structures
individual choice, regardless of the power
of other people to influence and coerce our
desires, beliefs and decisions.
An example of existentialism would be
when a person makes a decision about
of consciousness as experienced from the For St. Thomas, the total vision of man
first point of view. This philosophy was would be the embodied spirit.
founded by Edmund Husserl who worked
copiously to establish it as a rigorous
science.
THE HUMAN BODY IN IMPOSING
Maslow’s Hierarchy of needs LIMITS AND POSSIBILITIES
SOCRATIC METHOD – an Mental and emotional
argumentative dialogue between disorders (e.g. anxiety,
individuals, based on asking and intellectual disability)
answering questions. Disabilities (e.g. amputated leg,
deafness)
Diseased and illness (3.g.
OCCAM’S RAZOR – it is a problem- hypertension, cough)
solving device used by the philosophers in Failures and experiences (e.g.
analyzing possible explanations regarding failing a subject)
a phenomenon. Location of neighborhood (e.g.
armed, disorganized, or violent
neighborhood)
PYTHAGORAS – a Greek philosopher,
from the Greek island of Samos. A mystic,
mathematician, and founder of SOCIAL AND ENVIRONMENTAL
Pythagorean theorem. LIMITATIONS
Abusive relationships (e.g.
emotional abuse)
THE HUMAN PERSON AS AN Negative influence (e.g. drug
EMBODIED SPIRIT abuse, smoking)
”MAN IS A RATIONAL ANIMAL/ HUMAN PERSON IN THE
BEING.” ENVIRONMENT
“Happiness is the meaning and the
purpose of life, the whole aim and end of
human existence.” – Aristotle HUMAN PERSON
A human person is a living being
that contains real and existing to
direct its own development
toward fulfilment through
perfect, unconditional and
infinite, truth, love, goodness,
beauty, and unity, and will do so
if all the proper conditions are
met (Spitzer 1999)
ENVIRONMENT
It is the sum total of all
surroundings o a living
organism, including natural DIFFERENT ENVIRONMENTAL
forces and other living things, THEORIES
which provide conditions for
DEEP ECOLOGY
development and growth as well
SOCIAL ECOLOGY
as of danger and damage
ECOFEMINISIM
(Endriga 2017)
This means that as a human
person we interact not only with
our fellow human beings, but DEEP ECOLOGY – for this theory,
also with other living and non- ecological crisis is an outcome of
living elements in our anthropocentrism, which is already
environment. Like other discussed. The controlling attitude of
sciences, philosophy also seeks humankind is extended to nature, when in
to explore the relationship fact, humanity is part of nature. Deep
between humanity and the ecologists encourage humanity to shift
environmental philosophy or away from anthropocentrism to
environmental ethics. ecocentrism.
ENVIRONMENTAL PHILOSOPHY SOCIAL ECOLOGY – for this theory,
OR ENVIRONMENTAL ETHICS ecological crisis results from authoritarian
social structures. Destroying nature is a
As defined by Abella (2016), reflection wherein few people overpower
environmental philosophy or others while exploiting the environment
environmental ethics is the for profit or self interest.
discipline that studies the moral
relationship of human beings Social ecologists call for small scale
with the environment and its societies which recognize that humanity is
non-human contents. linked with the well being of the natural
He also described environmental world in which human life depends.
philosophers as philosophers
who tackle issues that is related
to humanity’s role in the natural ECOFEMINISM – male traits as in the
world, the interaction between anthropocentric model are superior as
nature and human activities, and opposed to female traits as in the
humanity’s response to ecocentric model.
environmental challenges. And
that environmental philosophers
have radical views which argue
that a paradigm shift or cultural
revolution is what will save all
from ecological crisis.
PRUDENCE – is defined as the ability to
have a good judgment that allows
avoidance of dangers and risks.
Meanwhile,
FRUGALITY – is the act of using money
or other resources wisely and practically.
You might also like
- Nathaniel Ross - The As If ConceptDocument24 pagesNathaniel Ross - The As If ConceptAndrea ParedesNo ratings yet
- Culler, Jonathan - Theory of The Lyric - CH 1 and 2Document105 pagesCuller, Jonathan - Theory of The Lyric - CH 1 and 2EC Tilley100% (1)
- Philosophy ReviewerDocument5 pagesPhilosophy ReviewerpoisoncedrickNo ratings yet
- PHILOSOPHY Reviewer 12 STEM 5 1Document4 pagesPHILOSOPHY Reviewer 12 STEM 5 1VITAL, Jay Ann S.No ratings yet
- Methods in Philosophizing: Types of Fallacy Characteristics ExampleDocument2 pagesMethods in Philosophizing: Types of Fallacy Characteristics ExampleyounggirldavidNo ratings yet
- Lesson 3-Determining TruthDocument14 pagesLesson 3-Determining TruthFrancis Lawrence TubidNo ratings yet
- Fallacies and BiasesDocument18 pagesFallacies and BiasesRudolph Basil SiloterioNo ratings yet
- Lesson 3 - Determining The TruthDocument14 pagesLesson 3 - Determining The TruthJBNo ratings yet
- Lesson 2.1 - Methods of Philosophizing and Deteremining The TruthDocument31 pagesLesson 2.1 - Methods of Philosophizing and Deteremining The Truththaline acero cabantogNo ratings yet
- Determining TruthDocument33 pagesDetermining TruthDELA PEÑA, ALTHEA B.No ratings yet
- Lesson 2.1 Philosophy Power Point 1Document15 pagesLesson 2.1 Philosophy Power Point 1Sanemi ShinazugawaNo ratings yet
- Lesson 2method of PhilosophizingDocument41 pagesLesson 2method of Philosophizingtjhunter077No ratings yet
- Methods of PhilosophizingDocument20 pagesMethods of PhilosophizingCelesty JasminNo ratings yet
- PhilosophyDocument5 pagesPhilosophyKervin LibunaoNo ratings yet
- 0 - New - Doc - 2020-02-01 - 21.30.35 - WPS PDF ConvertDocument2 pages0 - New - Doc - 2020-02-01 - 21.30.35 - WPS PDF ConvertIrene Almonia CaroNo ratings yet
- Fallacies and BiasDocument18 pagesFallacies and BiasFrancheska BuencaminoNo ratings yet
- Doing PhilosophyDocument58 pagesDoing PhilosophyMicro MickoNo ratings yet
- Determining The TruthDocument30 pagesDetermining The TruthEliNo ratings yet
- Intro To The Philosophy of The HP Q1 Module 2 - 022831Document3 pagesIntro To The Philosophy of The HP Q1 Module 2 - 022831Dankhel Nicho PadayaoNo ratings yet
- ArgumentsDocument11 pagesArgumentsJules GajesNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2Document13 pagesChapter 2Jhon Kennedy RiñaNo ratings yet
- Philo Class 3Document52 pagesPhilo Class 3KIP AIZA GABAWANo ratings yet
- Reporting in PhiloDocument24 pagesReporting in PhiloFSINCO, PRINCESS KATENo ratings yet
- PHILOSOPHYDocument5 pagesPHILOSOPHYSyntheria YashikaNo ratings yet
- Determining TruthDocument40 pagesDetermining TruthKathlyn Dae Quipit100% (1)
- Truth and OpinionDocument23 pagesTruth and OpinionSlade VexareNo ratings yet
- MODULE 2. PhiloDocument3 pagesMODULE 2. PhiloMarieden RimandoNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Philosophy of Human NatureDocument20 pagesIntroduction To Philosophy of Human NatureFrancheska GalisanaoNo ratings yet
- Briffault's Work ReviewDocument2 pagesBriffault's Work ReviewJonatan CarminatiNo ratings yet
- Module 2 Methods of Philo. 1Document31 pagesModule 2 Methods of Philo. 1Maou AstarolinNo ratings yet
- Truth From OpinionsDocument20 pagesTruth From OpinionsDhea Brenyile LadaranNo ratings yet
- By Friedrich Nietzsche: The Gay ScienceDocument10 pagesBy Friedrich Nietzsche: The Gay ScienceKaustav BoseNo ratings yet
- Ariel IM Philosophy Week 2 Day 2Document4 pagesAriel IM Philosophy Week 2 Day 2Editha BalolongNo ratings yet
- Fallacies On Reasonong PhilosophyDocument38 pagesFallacies On Reasonong Philosophybexbexgirl14No ratings yet
- Philo Lesson 2Document4 pagesPhilo Lesson 2John SmithNo ratings yet
- Considerations in Arguments or OpinionsDocument11 pagesConsiderations in Arguments or OpinionsPia GNo ratings yet
- Germanphilosophy 002600 MBPDocument152 pagesGermanphilosophy 002600 MBPChan ThorpeNo ratings yet
- Philo 12Document2 pagesPhilo 12Wriznym SampangNo ratings yet
- Traits Revisited: Harvard UniversityDocument10 pagesTraits Revisited: Harvard UniversityKyle GreggNo ratings yet
- Wising Up Guy Claxton April 05Document10 pagesWising Up Guy Claxton April 05Ana Betel SolorzanoNo ratings yet
- Poetics of Relation: Edouard GlissantDocument7 pagesPoetics of Relation: Edouard GlissantSavio de QueirozNo ratings yet
- Feminism and Pragmatism RortyDocument12 pagesFeminism and Pragmatism RortyIdrilNo ratings yet
- Bias and FallacyDocument21 pagesBias and Fallacydotaonly474No ratings yet
- Essays On Islamic P 00 ParkDocument70 pagesEssays On Islamic P 00 ParkMuʿādh KapodrawiNo ratings yet
- The Will to Believe, Human Immortality, and Other Essays in Popular PhilosophyFrom EverandThe Will to Believe, Human Immortality, and Other Essays in Popular PhilosophyNo ratings yet
- Determining Truth: Danilo F. Maribao Paliparan Iii Senior High School Dasmarinas City, CaviteDocument66 pagesDetermining Truth: Danilo F. Maribao Paliparan Iii Senior High School Dasmarinas City, CaviteWc-mark ChuvachucHuNo ratings yet
- Methods of PhilosophizingDocument4 pagesMethods of Philosophizingmichelle manliguezNo ratings yet
- Lesson 2b - Arguments and FallaciesDocument2 pagesLesson 2b - Arguments and FallaciesAndrea Marie LaquiñaNo ratings yet
- Media and Information LiteracyDocument7 pagesMedia and Information LiteracyJessa Pearl VedaniaNo ratings yet
- Pranav EssayDocument5 pagesPranav Essaycharvi.khullarug2023No ratings yet
- Lesson 7 Engl 10Document25 pagesLesson 7 Engl 10altheaclaireluteroNo ratings yet
- Quining QualiaDocument19 pagesQuining QualiaNando NNo ratings yet
- Chapter I - Prejudices of PhilosophersDocument5 pagesChapter I - Prejudices of PhilosophersBokolo KokoloNo ratings yet
- Primitives and The Supernatural - Lévy-Bruhl (1935)Document416 pagesPrimitives and The Supernatural - Lévy-Bruhl (1935)Babilonia Cruz100% (2)
- Women's Writings Notes (Short Stories)Document9 pagesWomen's Writings Notes (Short Stories)rupal aroraNo ratings yet
- Methods of PhilosophizingDocument37 pagesMethods of PhilosophizingElias SantosNo ratings yet
- To Philosophy of The Human Person: 1 Quarter: Module 5Document9 pagesTo Philosophy of The Human Person: 1 Quarter: Module 5Jewel Emerald C. Cudiamat100% (6)
- Study Guide Module 2Document10 pagesStudy Guide Module 2mark paul cabidoNo ratings yet
- Types of Informal FallacyDocument3 pagesTypes of Informal Fallacylouis adonis silvestre100% (1)
- AbsurdDocument10 pagesAbsurdDivya PavithranNo ratings yet
- Stanislavski in Rehearsal The Final YearsDocument232 pagesStanislavski in Rehearsal The Final YearsCesar MéndezNo ratings yet
- The Indwelling of The Holy Spirit in The Souls of The Just According To The Teaching of St. Thomas Aquinas (1921)Document264 pagesThe Indwelling of The Holy Spirit in The Souls of The Just According To The Teaching of St. Thomas Aquinas (1921)MDStevens100% (2)
- The Tunnel: The Architecture of The Anti-Novel: William H. Gass'sDocument5 pagesThe Tunnel: The Architecture of The Anti-Novel: William H. Gass'sadSFQE GVSNo ratings yet
- International Baccalaureate Diploma Program: CAS GuidebookDocument21 pagesInternational Baccalaureate Diploma Program: CAS GuidebookRAJVEER GHOSHNo ratings yet
- The Allegory of The Chariot: ReferencesDocument1 pageThe Allegory of The Chariot: Referencesbernoel semaneroNo ratings yet
- 60 75 La Systemologie de Stephane Lupasco. La Propension VersDocument16 pages60 75 La Systemologie de Stephane Lupasco. La Propension VersCryptopher KNo ratings yet
- Translations of Poems From Morpo: Jose Perez Beduya Allan Popa Ateneo de Manila UniversityDocument14 pagesTranslations of Poems From Morpo: Jose Perez Beduya Allan Popa Ateneo de Manila UniversityAna SaladagaNo ratings yet
- Uts Lesson 1Document25 pagesUts Lesson 1Ma Cyril Dawn MuncadaNo ratings yet
- THE DEVIL'S DISCIPLE Title Significance-1Document5 pagesTHE DEVIL'S DISCIPLE Title Significance-1M irfan hashmiNo ratings yet
- Nagendra Haraya Trilochanaya Lyrics - Shiva Panchakshara StotramDocument8 pagesNagendra Haraya Trilochanaya Lyrics - Shiva Panchakshara Stotramkishan24.ks24No ratings yet
- Dark LeadershipDocument2 pagesDark LeadershipdddxNo ratings yet
- Adverbials of ProbabilityDocument3 pagesAdverbials of ProbabilityFaye FernandezNo ratings yet
- ReflectionsDocument10 pagesReflectionsBenflor J. BiongNo ratings yet
- Political Science Research MethodsDocument6 pagesPolitical Science Research MethodsZuleira ParraNo ratings yet
- Keluarga Gerilya by Pramoedya Ananta Toer - Translation of ChapterDocument92 pagesKeluarga Gerilya by Pramoedya Ananta Toer - Translation of ChaptertabeeNo ratings yet
- A Historical-Materialist Response To New MaterialismDocument16 pagesA Historical-Materialist Response To New MaterialismJudhajit SarkarNo ratings yet
- Universidad de Manila College of Public AdministrationDocument8 pagesUniversidad de Manila College of Public AdministrationRavien QuesadaNo ratings yet
- Advanced Communication NotesDocument7 pagesAdvanced Communication NotesMitchie FaustinoNo ratings yet
- How To Concentrate Like Einstein - The Lazy Student's Way To Instantly Improve Memory & Grades With The Doctor Vittoz Secret Concentration Technique. (PDFDrive)Document66 pagesHow To Concentrate Like Einstein - The Lazy Student's Way To Instantly Improve Memory & Grades With The Doctor Vittoz Secret Concentration Technique. (PDFDrive)Muhammad HabibNo ratings yet
- 10 Design Principles ExamplesDocument17 pages10 Design Principles ExamplesAbinav NatarajanNo ratings yet
- Reverse Name GuessDocument13 pagesReverse Name GuessSpockCritical CriticalNo ratings yet
- Response To "Can We Be Good Without God?"Document12 pagesResponse To "Can We Be Good Without God?"Mike SampatNo ratings yet
- Consumer Attitude Formation and ChangeDocument40 pagesConsumer Attitude Formation and ChangeSachin RaiNo ratings yet
- BourdieuDocument4 pagesBourdieuShraddha PandeyNo ratings yet
- BIOL 205 Biostatistics Scales of MeasurementDocument3 pagesBIOL 205 Biostatistics Scales of MeasurementSaba ButtNo ratings yet
- GE9 (7504) - Ethics 1st Exam ReviewerDocument3 pagesGE9 (7504) - Ethics 1st Exam ReviewerSin BadNo ratings yet
- Thoilga, 1 and Ib: L'Tiu"""Pii)Document479 pagesThoilga, 1 and Ib: L'Tiu"""Pii)Konchok nyimaNo ratings yet
- Hand OutDocument2 pagesHand OutSai-na Suzane VelitarioNo ratings yet