Professional Documents
Culture Documents
KCC Classification of plants Short Notes
KCC Classification of plants Short Notes
Uploaded by
mangnalenr111Copyright:
Available Formats
You might also like
- Chapter 1 - Introduction To The Food and Beverage IndustryDocument64 pagesChapter 1 - Introduction To The Food and Beverage IndustryPn Firdaus92% (12)
- 2007 Rolls Royce Propulsion ProductsDocument24 pages2007 Rolls Royce Propulsion ProductsMiguel Ángel Montiel Hernández67% (3)
- PlantsDocument22 pagesPlantsPotato ManNo ratings yet
- Speech & Language Therapy in Practice, Spring 2002Document32 pagesSpeech & Language Therapy in Practice, Spring 2002Speech & Language Therapy in PracticeNo ratings yet
- 5thGr Sci Bundle 4Document7 pages5thGr Sci Bundle 4Emma YulionoNo ratings yet
- Vallorec P91 BOOKDocument69 pagesVallorec P91 BOOKhassan100% (2)
- Let's Sing A Song Let's Sing A SongDocument33 pagesLet's Sing A Song Let's Sing A SongGracio Bintang WijayaNo ratings yet
- Classification of PlantsDocument12 pagesClassification of Plantsprathmfed100% (1)
- 05 Plant KingdomDocument88 pages05 Plant Kingdomlucia.benito.sanz12No ratings yet
- Kingdom Plantae: Unit 3Document49 pagesKingdom Plantae: Unit 3senjicsNo ratings yet
- Plant Diversity: The Evolution and Classification of PlantsDocument23 pagesPlant Diversity: The Evolution and Classification of PlantsJose CariasNo ratings yet
- Kingdom Plantae: - CharacteristicsDocument20 pagesKingdom Plantae: - CharacteristicsJunaedi Ahmad AlzNo ratings yet
- Plant-Kingdom Part 2Document3 pagesPlant-Kingdom Part 2Vidushi KapoorNo ratings yet
- Dr. Abhinandan R Patil Research ScientistDocument59 pagesDr. Abhinandan R Patil Research ScientistAbhinandan PatilNo ratings yet
- Plant Anatomy Ruel-VelosoDocument70 pagesPlant Anatomy Ruel-VelosoKhy Renz BajajNo ratings yet
- Angeospermic Plant MorphologyDocument60 pagesAngeospermic Plant MorphologyMr. Balwant SinghNo ratings yet
- Kingdom Plantae 2023Document28 pagesKingdom Plantae 2023Shawn Xed De La VictoriaNo ratings yet
- Unit 5 - Plants - (Students)Document41 pagesUnit 5 - Plants - (Students)ajtorresbritoNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1: Plant Classification (Root, Stem and Leaf Morfologi)Document180 pagesChapter 1: Plant Classification (Root, Stem and Leaf Morfologi)FITRINESSA IBOLNo ratings yet
- Classification of Living Organisms - 2Document20 pagesClassification of Living Organisms - 2Jeyakumar SNo ratings yet
- 3.2 The PlantsDocument50 pages3.2 The PlantsMohammed Faraaz MustafaNo ratings yet
- F Kingdom Plantae Part 1Document11 pagesF Kingdom Plantae Part 1JNo ratings yet
- Plant Diversity Part One + Two - 2024Document10 pagesPlant Diversity Part One + Two - 2024alshalabinezardonia96No ratings yet
- SN Chapter 3Document90 pagesSN Chapter 3Mohd Razin F2025No ratings yet
- Life Sciences Grade 11 Term 1 Week 4 - 2021Document8 pagesLife Sciences Grade 11 Term 1 Week 4 - 2021Mpho MashediNo ratings yet
- Prokaryote Eukaryote: Unicellular MulticellularDocument26 pagesProkaryote Eukaryote: Unicellular MulticellularKhairy IestNo ratings yet
- Bryophte and Gymno NotesDocument3 pagesBryophte and Gymno Notessaikatmajee727No ratings yet
- Plant Diversity 2024Document47 pagesPlant Diversity 2024pieterhansconsultantNo ratings yet
- Seed Biology: Martha Rosemeyer Farm To Table 14 April 2005Document15 pagesSeed Biology: Martha Rosemeyer Farm To Table 14 April 2005AhmedNo ratings yet
- 1.classification of The Plant KingdomDocument5 pages1.classification of The Plant Kingdomyasmineamari759No ratings yet
- Angiosperms and GynospermsDocument20 pagesAngiosperms and GynospermsMicaszen MendozaNo ratings yet
- Kingdom Plantae: Botany - The Study of PlantsDocument26 pagesKingdom Plantae: Botany - The Study of PlantsEric cruzNo ratings yet
- Maharashtra Board Class 9 Science Chapter 6Document7 pagesMaharashtra Board Class 9 Science Chapter 6drushti luteNo ratings yet
- Chap - 05 Morphology of Flowering PlantsDocument10 pagesChap - 05 Morphology of Flowering PlantsgprasadatvuNo ratings yet
- Notes Plant Function and StructureDocument5 pagesNotes Plant Function and StructureellenialrafeneNo ratings yet
- Anatomy of PlantsDocument52 pagesAnatomy of Plantseshu 1No ratings yet
- Reproduction in PlantsDocument17 pagesReproduction in Plantswafa eliasNo ratings yet
- Roots, Plant Tissues, Morphology and Plant Hormones: by DR Vipan GoyalDocument120 pagesRoots, Plant Tissues, Morphology and Plant Hormones: by DR Vipan Goyalbabaaijaz01No ratings yet
- CH 3 8Document17 pagesCH 3 8Sifatullah HamidiNo ratings yet
- p.4 Science Lesson NotesDocument115 pagesp.4 Science Lesson NotesEcungu George williamNo ratings yet
- VegetationDocument14 pagesVegetationChris P. BeaconNo ratings yet
- PlantsDocument84 pagesPlantsYanyan PaydaNo ratings yet
- p.4 Primary Four Sci Notes Teacher - AcDocument125 pagesp.4 Primary Four Sci Notes Teacher - Acsebuddenoah1No ratings yet
- 06 Anatomy MorphologyDocument53 pages06 Anatomy MorphologyEliash stanfordNo ratings yet
- 2.hafta EngDocument19 pages2.hafta EngKUTAY ÖZELNo ratings yet
- AnatomyDocument84 pagesAnatomygiaNo ratings yet
- 8 TH PLANTDocument22 pages8 TH PLANTyasukaellahNo ratings yet
- AngiospermDocument14 pagesAngiospermJoy EscamillasNo ratings yet
- Morphology.BKK SirDocument20 pagesMorphology.BKK Sirkrishnabaniya17125No ratings yet
- Science B. G8 3rdDocument16 pagesScience B. G8 3rdBen sik ali mohamedNo ratings yet
- Scince Notes Part II Edited 21 OctDocument11 pagesScince Notes Part II Edited 21 OctSANJAY GANGANNo ratings yet
- Activity Sheet 1 GenBio2Document4 pagesActivity Sheet 1 GenBio2Sean MatuguinasNo ratings yet
- Bio ReviwerDocument3 pagesBio Reviweranmbeltran31No ratings yet
- Reproduction PPT 3 ANGIOSPERMSDocument76 pagesReproduction PPT 3 ANGIOSPERMSlisanames.23No ratings yet
- SG-Life of Plants 2012Document39 pagesSG-Life of Plants 2012niku007No ratings yet
- 1 VELS Vegetative Morphology TheoryDocument38 pages1 VELS Vegetative Morphology TheoryManjunath K JNo ratings yet
- Plant Diversity Part Two 2021Document6 pagesPlant Diversity Part Two 2021sulimansmart22No ratings yet
- PK Notes Ncert Detail ExplnDocument33 pagesPK Notes Ncert Detail Explnarjun shindeNo ratings yet
- Class 10 How Do Organisms ReproduceDocument19 pagesClass 10 How Do Organisms ReproduceniranjannandkishoregiriNo ratings yet
- 1 Plant Classification (Root, Stem and Leaf Morfologi)Document180 pages1 Plant Classification (Root, Stem and Leaf Morfologi)Guru temp id-04 for Sekolah-8252 Moe100% (1)
- Lecture 1 Plant Morpho-Anatomy Intro PDFDocument113 pagesLecture 1 Plant Morpho-Anatomy Intro PDFLance CarandangNo ratings yet
- Botany 101Document87 pagesBotany 101lizette Rubi Rendón ValladaresNo ratings yet
- Plant & Animal KingdomDocument31 pagesPlant & Animal Kingdomsindhibabarali2No ratings yet
- p.4 Topical Breakdown & LnDocument68 pagesp.4 Topical Breakdown & Lnmosesenacu635No ratings yet
- The Incredible World of Plants - Cool Facts You Need to Know - Nature for Kids | Children's Nature BooksFrom EverandThe Incredible World of Plants - Cool Facts You Need to Know - Nature for Kids | Children's Nature BooksNo ratings yet
- Manual Nikon AF-S Nikkor 500mm F - 5.6E PF ED VR (Español - 2 Páginas)Document2 pagesManual Nikon AF-S Nikkor 500mm F - 5.6E PF ED VR (Español - 2 Páginas)domingo lunaNo ratings yet
- Dhuvarageesh VaasthuDocument100 pagesDhuvarageesh VaasthuKs SenthilKumarNo ratings yet
- Investigate The Impact of Social Media On Students: Cardiff Metropolitan UniversityDocument57 pagesInvestigate The Impact of Social Media On Students: Cardiff Metropolitan UniversityKarlo JayNo ratings yet
- Suplemente - Junio - VIRTUAL REALITY Exam UGRDocument1 pageSuplemente - Junio - VIRTUAL REALITY Exam UGRAnaGarcíaReyesNo ratings yet
- Narrative Text by Marco Class A Morning Lectuer: Hamid Asman, S.PDDocument12 pagesNarrative Text by Marco Class A Morning Lectuer: Hamid Asman, S.PDMardiana DhyanNo ratings yet
- Form 2 - Industrial Training Visitation ReportDocument2 pagesForm 2 - Industrial Training Visitation ReportWong Mun HoeNo ratings yet
- KFC Case StudyDocument7 pagesKFC Case StudyOfficial WorkNo ratings yet
- City PumpsDocument2 pagesCity PumpsJohan ConradieNo ratings yet
- BPSCL Industrial TrainingDocument28 pagesBPSCL Industrial TrainingAbhigyan PrakashNo ratings yet
- No. in Sq. Ft. Sq. Yds. MarlasDocument7 pagesNo. in Sq. Ft. Sq. Yds. MarlasYasir ButtNo ratings yet
- Logistics and Transportation ServicesDocument2 pagesLogistics and Transportation ServicesEllatroy AycoNo ratings yet
- Bone Marrow and Stem Cell TranspplantDocument28 pagesBone Marrow and Stem Cell TranspplantVILLEJO JHOVIALENNo ratings yet
- Prince Ea-I Just Sued The School SystemDocument3 pagesPrince Ea-I Just Sued The School SystemTizioNo ratings yet
- Shaheed Suhrawardy Medical College HospitalDocument3 pagesShaheed Suhrawardy Medical College HospitalDr. Mohammad Nazrul IslamNo ratings yet
- Shri A.D.K.Mahila Polytechnic, Mathura: Summer Training ReportDocument46 pagesShri A.D.K.Mahila Polytechnic, Mathura: Summer Training Reportanand011No ratings yet
- Self-Velocity Manipulation - Superpower Wiki - FandomDocument8 pagesSelf-Velocity Manipulation - Superpower Wiki - Fandomalex masonNo ratings yet
- JSA Wet End or Dryer Bearing Inspection Paper MillDocument6 pagesJSA Wet End or Dryer Bearing Inspection Paper MillMlayeh MohamedNo ratings yet
- Knights of The Dinner Table 254Document70 pagesKnights of The Dinner Table 254Royce A R Porter100% (2)
- Eng1 Q3 Mod20 Asking-Permission V4Document21 pagesEng1 Q3 Mod20 Asking-Permission V4Silverangel Gayo100% (1)
- The Iconic Influence of Queen Elizabeth IIDocument2 pagesThe Iconic Influence of Queen Elizabeth IIpatriciasusckind_574No ratings yet
- Prequalif Doc Contractor Construction RECHQDocument43 pagesPrequalif Doc Contractor Construction RECHQNazir Hussain100% (1)
- Engl 316 Resume FinalDocument1 pageEngl 316 Resume Finalapi-466382256No ratings yet
- KBI - Group 2 - Community Mapping (RRA & PRA)Document13 pagesKBI - Group 2 - Community Mapping (RRA & PRA)Yudha OkpriandaNo ratings yet
- Application Form NNT EFDocument5 pagesApplication Form NNT EFRizky Aulya AkbarNo ratings yet
- CIMAP Charges For AnalysisDocument11 pagesCIMAP Charges For AnalysisSaloman RaviNo ratings yet
KCC Classification of plants Short Notes
KCC Classification of plants Short Notes
Uploaded by
mangnalenr111Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
KCC Classification of plants Short Notes
KCC Classification of plants Short Notes
Uploaded by
mangnalenr111Copyright:
Available Formats
Class- IX Biology Topic: Classification of Plants
Short Notes:
➢ Robert Whittaker in 1959 proposed Five Kingdom System- Monera, Protista,
Fungi, Plantae, Animalia.
➢ Eichler (botanist) in 1883 classified kingdom Plantae in two Sub Kingdoms.
1) Cryptogams: i) Thallophyta ii) Bryophyta iii) Pteridophyta
2) Phanerogams: i) Gymnosperm ii) Angiosperm
➢ Basis of Classification:
• Presence or absence of organs.
• Presence or absence of separate conducting tissue (Xylem or phloem).
• Presence or absence of Seed.
• If present then, Seeds are enclosed in fruit of not.
• Number of cotyledon- Monocot or dicot
❖ Cryptogams:
- Cryptos- Hidden, Gams- Reproductive organs
- Flowers and seeds are absent
- Reproductive organs are inconspicuous
- It includes lower plants that have necked embryo called Spores
Prepared by- Amol Sir
1) Division-I : Thallophyta
• Mainly grow in water
• Does not have specific parts.
• Includes autotrophic algae (presence of chlorophyll)
• They may be Unicellular or multicellular.
• Some found in fresh water while some in saline water.
• Plants usually have Soft & Fibre like body
• Fungi like Yeast & Moulds, which do not have Chlorophyll also included
in Thallophyta.
Examples: 1) Spirogyra
2) Sargassum
3) Ulva
4) Ulothrix
2) Division-II : Bryophyta
• During rainy season grow on old bricks and rocks in rainy season.
• Known as Amphibians of Plant kingdom.
• Reason: Grow in moist soil But Need water for reproduction.
• Reproduce by- Spore Formation.
• Plant body- Flat, ribbon-like long.
• Without true roots, stem & leaves but have stem-like or leaf-like parts and
Root-like: Rhizoids.
• Vascular bundles (Xylem & Phloem) are absent.
• Furns are known as Ornamental plants in Garden.
Examples : 1) Moss (Funaria)
2) Marchantia
3) Anthoceros
4) Riccia
3) Division- III : Pteridophyta
• Have well developed Roots, stem & Leaves and separate tissues for
conduction of food and water.
• Do not bear flower & Fruit.
• Have well developed conduction system (Xylem & Phloem)
• Reproduce with the help of Spores formed along the back or posterior
surface of their leaves.
Prepared by- Amol Sir
• These plants Reproduce by both asexually & sexually.
Asexually by- Spore Formation
Sexually by- Zygote formation
Examples: 1) Adiantum
2) Equisetum
3) Lycopodium
4) Marsilea
5) Nephrolepis
6) Selaginella
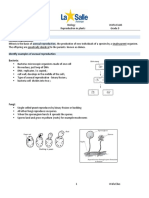
❖ Phanerogams:
- Plants with special structures for Reproduction & produce seeds are c/as
Phanerogams.
- In these plants after process of reproduction, seeds are formed which
contains the embryo and stored food.
- During germination of seed, the stored food is used for initial growth of
embryo.
- Classified in 2 groups
1) Gymnosperm- Seeds are necked
2) Angiosperm- Seeds are enclosed in Fruit.
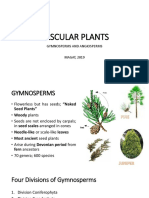
4) Division-I : Gymnosperm
• Gymnos: Necked ; Sperms: Seeds
• Mostly Evergreen, perennial and woody.
• Stems are without branches.
• Leaves form a crown
• Gymnosperm plants bear male and female flower on different
sporophylls of the same plant.
• Seeds do not have natural covering i.e. these plants do not form
Fruits.
Examples: 1) Cycas
2) Picea (Christmas tree)
3) Pinus ( Deodar)
4) Thuja (Morpankhi)
Prepared by- Amol Sir
5) Division- II : Angiosperms
• Angio- Cover ; Sperms- seeds
• The flower of these plants are their reproductive organs.
• Classified in to two groups-
1) Dicot- The plants whose seeds can be divided into two equal halves
or dicotyledons are called Dicot Plants
Example: Ground nuts, Pea, Pulses etc
2) Monocot- The plants whose seeds can not be divides into two parts
are called Monot Plants.
Example: Onion, Bamboo, Banana, Rice, Maize, Wheat, Mustard.
Characters Monocotyledonous Plant Dicotyledonous Plant
Single cotyledon Two cotyledons
Seed
Fibrous Root Well developed, Primary
Root
root (Tap root)
Hollow Ex- Bamboo Strong, Hard
Stem False Ex- Banana Ex: Banyan Tree
Disc-like Ex- Onion
Parallel venation Reticulate Venation
Leaf
Flower with 3 parts or in multiples of Flowers with 4 or 5 parts or
three (Trimerous) in their multiples
Flower
(Tetramerous or
Pentamerous)
Prepared by- Amol Sir
You might also like
- Chapter 1 - Introduction To The Food and Beverage IndustryDocument64 pagesChapter 1 - Introduction To The Food and Beverage IndustryPn Firdaus92% (12)
- 2007 Rolls Royce Propulsion ProductsDocument24 pages2007 Rolls Royce Propulsion ProductsMiguel Ángel Montiel Hernández67% (3)
- PlantsDocument22 pagesPlantsPotato ManNo ratings yet
- Speech & Language Therapy in Practice, Spring 2002Document32 pagesSpeech & Language Therapy in Practice, Spring 2002Speech & Language Therapy in PracticeNo ratings yet
- 5thGr Sci Bundle 4Document7 pages5thGr Sci Bundle 4Emma YulionoNo ratings yet
- Vallorec P91 BOOKDocument69 pagesVallorec P91 BOOKhassan100% (2)
- Let's Sing A Song Let's Sing A SongDocument33 pagesLet's Sing A Song Let's Sing A SongGracio Bintang WijayaNo ratings yet
- Classification of PlantsDocument12 pagesClassification of Plantsprathmfed100% (1)
- 05 Plant KingdomDocument88 pages05 Plant Kingdomlucia.benito.sanz12No ratings yet
- Kingdom Plantae: Unit 3Document49 pagesKingdom Plantae: Unit 3senjicsNo ratings yet
- Plant Diversity: The Evolution and Classification of PlantsDocument23 pagesPlant Diversity: The Evolution and Classification of PlantsJose CariasNo ratings yet
- Kingdom Plantae: - CharacteristicsDocument20 pagesKingdom Plantae: - CharacteristicsJunaedi Ahmad AlzNo ratings yet
- Plant-Kingdom Part 2Document3 pagesPlant-Kingdom Part 2Vidushi KapoorNo ratings yet
- Dr. Abhinandan R Patil Research ScientistDocument59 pagesDr. Abhinandan R Patil Research ScientistAbhinandan PatilNo ratings yet
- Plant Anatomy Ruel-VelosoDocument70 pagesPlant Anatomy Ruel-VelosoKhy Renz BajajNo ratings yet
- Angeospermic Plant MorphologyDocument60 pagesAngeospermic Plant MorphologyMr. Balwant SinghNo ratings yet
- Kingdom Plantae 2023Document28 pagesKingdom Plantae 2023Shawn Xed De La VictoriaNo ratings yet
- Unit 5 - Plants - (Students)Document41 pagesUnit 5 - Plants - (Students)ajtorresbritoNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1: Plant Classification (Root, Stem and Leaf Morfologi)Document180 pagesChapter 1: Plant Classification (Root, Stem and Leaf Morfologi)FITRINESSA IBOLNo ratings yet
- Classification of Living Organisms - 2Document20 pagesClassification of Living Organisms - 2Jeyakumar SNo ratings yet
- 3.2 The PlantsDocument50 pages3.2 The PlantsMohammed Faraaz MustafaNo ratings yet
- F Kingdom Plantae Part 1Document11 pagesF Kingdom Plantae Part 1JNo ratings yet
- Plant Diversity Part One + Two - 2024Document10 pagesPlant Diversity Part One + Two - 2024alshalabinezardonia96No ratings yet
- SN Chapter 3Document90 pagesSN Chapter 3Mohd Razin F2025No ratings yet
- Life Sciences Grade 11 Term 1 Week 4 - 2021Document8 pagesLife Sciences Grade 11 Term 1 Week 4 - 2021Mpho MashediNo ratings yet
- Prokaryote Eukaryote: Unicellular MulticellularDocument26 pagesProkaryote Eukaryote: Unicellular MulticellularKhairy IestNo ratings yet
- Bryophte and Gymno NotesDocument3 pagesBryophte and Gymno Notessaikatmajee727No ratings yet
- Plant Diversity 2024Document47 pagesPlant Diversity 2024pieterhansconsultantNo ratings yet
- Seed Biology: Martha Rosemeyer Farm To Table 14 April 2005Document15 pagesSeed Biology: Martha Rosemeyer Farm To Table 14 April 2005AhmedNo ratings yet
- 1.classification of The Plant KingdomDocument5 pages1.classification of The Plant Kingdomyasmineamari759No ratings yet
- Angiosperms and GynospermsDocument20 pagesAngiosperms and GynospermsMicaszen MendozaNo ratings yet
- Kingdom Plantae: Botany - The Study of PlantsDocument26 pagesKingdom Plantae: Botany - The Study of PlantsEric cruzNo ratings yet
- Maharashtra Board Class 9 Science Chapter 6Document7 pagesMaharashtra Board Class 9 Science Chapter 6drushti luteNo ratings yet
- Chap - 05 Morphology of Flowering PlantsDocument10 pagesChap - 05 Morphology of Flowering PlantsgprasadatvuNo ratings yet
- Notes Plant Function and StructureDocument5 pagesNotes Plant Function and StructureellenialrafeneNo ratings yet
- Anatomy of PlantsDocument52 pagesAnatomy of Plantseshu 1No ratings yet
- Reproduction in PlantsDocument17 pagesReproduction in Plantswafa eliasNo ratings yet
- Roots, Plant Tissues, Morphology and Plant Hormones: by DR Vipan GoyalDocument120 pagesRoots, Plant Tissues, Morphology and Plant Hormones: by DR Vipan Goyalbabaaijaz01No ratings yet
- CH 3 8Document17 pagesCH 3 8Sifatullah HamidiNo ratings yet
- p.4 Science Lesson NotesDocument115 pagesp.4 Science Lesson NotesEcungu George williamNo ratings yet
- VegetationDocument14 pagesVegetationChris P. BeaconNo ratings yet
- PlantsDocument84 pagesPlantsYanyan PaydaNo ratings yet
- p.4 Primary Four Sci Notes Teacher - AcDocument125 pagesp.4 Primary Four Sci Notes Teacher - Acsebuddenoah1No ratings yet
- 06 Anatomy MorphologyDocument53 pages06 Anatomy MorphologyEliash stanfordNo ratings yet
- 2.hafta EngDocument19 pages2.hafta EngKUTAY ÖZELNo ratings yet
- AnatomyDocument84 pagesAnatomygiaNo ratings yet
- 8 TH PLANTDocument22 pages8 TH PLANTyasukaellahNo ratings yet
- AngiospermDocument14 pagesAngiospermJoy EscamillasNo ratings yet
- Morphology.BKK SirDocument20 pagesMorphology.BKK Sirkrishnabaniya17125No ratings yet
- Science B. G8 3rdDocument16 pagesScience B. G8 3rdBen sik ali mohamedNo ratings yet
- Scince Notes Part II Edited 21 OctDocument11 pagesScince Notes Part II Edited 21 OctSANJAY GANGANNo ratings yet
- Activity Sheet 1 GenBio2Document4 pagesActivity Sheet 1 GenBio2Sean MatuguinasNo ratings yet
- Bio ReviwerDocument3 pagesBio Reviweranmbeltran31No ratings yet
- Reproduction PPT 3 ANGIOSPERMSDocument76 pagesReproduction PPT 3 ANGIOSPERMSlisanames.23No ratings yet
- SG-Life of Plants 2012Document39 pagesSG-Life of Plants 2012niku007No ratings yet
- 1 VELS Vegetative Morphology TheoryDocument38 pages1 VELS Vegetative Morphology TheoryManjunath K JNo ratings yet
- Plant Diversity Part Two 2021Document6 pagesPlant Diversity Part Two 2021sulimansmart22No ratings yet
- PK Notes Ncert Detail ExplnDocument33 pagesPK Notes Ncert Detail Explnarjun shindeNo ratings yet
- Class 10 How Do Organisms ReproduceDocument19 pagesClass 10 How Do Organisms ReproduceniranjannandkishoregiriNo ratings yet
- 1 Plant Classification (Root, Stem and Leaf Morfologi)Document180 pages1 Plant Classification (Root, Stem and Leaf Morfologi)Guru temp id-04 for Sekolah-8252 Moe100% (1)
- Lecture 1 Plant Morpho-Anatomy Intro PDFDocument113 pagesLecture 1 Plant Morpho-Anatomy Intro PDFLance CarandangNo ratings yet
- Botany 101Document87 pagesBotany 101lizette Rubi Rendón ValladaresNo ratings yet
- Plant & Animal KingdomDocument31 pagesPlant & Animal Kingdomsindhibabarali2No ratings yet
- p.4 Topical Breakdown & LnDocument68 pagesp.4 Topical Breakdown & Lnmosesenacu635No ratings yet
- The Incredible World of Plants - Cool Facts You Need to Know - Nature for Kids | Children's Nature BooksFrom EverandThe Incredible World of Plants - Cool Facts You Need to Know - Nature for Kids | Children's Nature BooksNo ratings yet
- Manual Nikon AF-S Nikkor 500mm F - 5.6E PF ED VR (Español - 2 Páginas)Document2 pagesManual Nikon AF-S Nikkor 500mm F - 5.6E PF ED VR (Español - 2 Páginas)domingo lunaNo ratings yet
- Dhuvarageesh VaasthuDocument100 pagesDhuvarageesh VaasthuKs SenthilKumarNo ratings yet
- Investigate The Impact of Social Media On Students: Cardiff Metropolitan UniversityDocument57 pagesInvestigate The Impact of Social Media On Students: Cardiff Metropolitan UniversityKarlo JayNo ratings yet
- Suplemente - Junio - VIRTUAL REALITY Exam UGRDocument1 pageSuplemente - Junio - VIRTUAL REALITY Exam UGRAnaGarcíaReyesNo ratings yet
- Narrative Text by Marco Class A Morning Lectuer: Hamid Asman, S.PDDocument12 pagesNarrative Text by Marco Class A Morning Lectuer: Hamid Asman, S.PDMardiana DhyanNo ratings yet
- Form 2 - Industrial Training Visitation ReportDocument2 pagesForm 2 - Industrial Training Visitation ReportWong Mun HoeNo ratings yet
- KFC Case StudyDocument7 pagesKFC Case StudyOfficial WorkNo ratings yet
- City PumpsDocument2 pagesCity PumpsJohan ConradieNo ratings yet
- BPSCL Industrial TrainingDocument28 pagesBPSCL Industrial TrainingAbhigyan PrakashNo ratings yet
- No. in Sq. Ft. Sq. Yds. MarlasDocument7 pagesNo. in Sq. Ft. Sq. Yds. MarlasYasir ButtNo ratings yet
- Logistics and Transportation ServicesDocument2 pagesLogistics and Transportation ServicesEllatroy AycoNo ratings yet
- Bone Marrow and Stem Cell TranspplantDocument28 pagesBone Marrow and Stem Cell TranspplantVILLEJO JHOVIALENNo ratings yet
- Prince Ea-I Just Sued The School SystemDocument3 pagesPrince Ea-I Just Sued The School SystemTizioNo ratings yet
- Shaheed Suhrawardy Medical College HospitalDocument3 pagesShaheed Suhrawardy Medical College HospitalDr. Mohammad Nazrul IslamNo ratings yet
- Shri A.D.K.Mahila Polytechnic, Mathura: Summer Training ReportDocument46 pagesShri A.D.K.Mahila Polytechnic, Mathura: Summer Training Reportanand011No ratings yet
- Self-Velocity Manipulation - Superpower Wiki - FandomDocument8 pagesSelf-Velocity Manipulation - Superpower Wiki - Fandomalex masonNo ratings yet
- JSA Wet End or Dryer Bearing Inspection Paper MillDocument6 pagesJSA Wet End or Dryer Bearing Inspection Paper MillMlayeh MohamedNo ratings yet
- Knights of The Dinner Table 254Document70 pagesKnights of The Dinner Table 254Royce A R Porter100% (2)
- Eng1 Q3 Mod20 Asking-Permission V4Document21 pagesEng1 Q3 Mod20 Asking-Permission V4Silverangel Gayo100% (1)
- The Iconic Influence of Queen Elizabeth IIDocument2 pagesThe Iconic Influence of Queen Elizabeth IIpatriciasusckind_574No ratings yet
- Prequalif Doc Contractor Construction RECHQDocument43 pagesPrequalif Doc Contractor Construction RECHQNazir Hussain100% (1)
- Engl 316 Resume FinalDocument1 pageEngl 316 Resume Finalapi-466382256No ratings yet
- KBI - Group 2 - Community Mapping (RRA & PRA)Document13 pagesKBI - Group 2 - Community Mapping (RRA & PRA)Yudha OkpriandaNo ratings yet
- Application Form NNT EFDocument5 pagesApplication Form NNT EFRizky Aulya AkbarNo ratings yet
- CIMAP Charges For AnalysisDocument11 pagesCIMAP Charges For AnalysisSaloman RaviNo ratings yet