Professional Documents
Culture Documents
MICROSCOPY - HISTO
MICROSCOPY - HISTO
Uploaded by
smrande94Copyright:
Available Formats
You might also like
- Lens Problems WorksheetDocument1 pageLens Problems WorksheetWardah50% (2)
- ElecComTomasi Chapter 13Document2 pagesElecComTomasi Chapter 13jerson eyas0% (1)
- Parts of MicroscopeDocument4 pagesParts of MicroscopeJohn Rey F. CastroNo ratings yet
- Microscope Parts and FunctionsDocument4 pagesMicroscope Parts and FunctionsChris ChanNo ratings yet
- Detailed Explanation of MicroscopeDocument3 pagesDetailed Explanation of MicroscopestsrinidiNo ratings yet
- Detailed Explanation of MicroscopeDocument3 pagesDetailed Explanation of MicroscopestsrinidiNo ratings yet
- HSC Lab 1Document3 pagesHSC Lab 1Reshma MohabeirNo ratings yet
- Biology (Reviewer)Document4 pagesBiology (Reviewer)Claire SerafinNo ratings yet
- MicroscopeDocument3 pagesMicroscopeJannette Jane DavidNo ratings yet
- Parts of A MicroscopeDocument2 pagesParts of A MicroscopeRonJen VlogsNo ratings yet
- HISTO TRANS Overview of Histology and Its MethodsDocument6 pagesHISTO TRANS Overview of Histology and Its MethodsLovely ViernesNo ratings yet
- The MicroscopeDocument6 pagesThe MicroscopejustRizzeNo ratings yet
- Laboratory IIDocument9 pagesLaboratory IIDecemei CuaboNo ratings yet
- Lesson 8 MicroscopeDocument6 pagesLesson 8 MicroscopeCristina AnganganNo ratings yet
- Compound Microscop EDocument26 pagesCompound Microscop EDixie MerinNo ratings yet
- Worksheet 1-Word FinalDocument6 pagesWorksheet 1-Word FinalPrince SalvaNo ratings yet
- Sci Ed 5 Laboratory Exercise 3Document6 pagesSci Ed 5 Laboratory Exercise 3AlibabaNo ratings yet
- Parts and Function of A MicroscopeDocument4 pagesParts and Function of A MicroscopeFria mae AbellanoNo ratings yet
- Parts of A MicroscopeDocument5 pagesParts of A MicroscopeShankey Faith BediaNo ratings yet
- A1.1 Parts of The MicroscopeDocument2 pagesA1.1 Parts of The MicroscopehzntrpNo ratings yet
- Biotech - Microscope (8 - Leeuwenhoek)Document4 pagesBiotech - Microscope (8 - Leeuwenhoek)Leila Nicole FulgencioNo ratings yet
- The MicroscopeDocument5 pagesThe Microscopeeasylearning83No ratings yet
- The Microscope: Dr. S.M. ReyesDocument9 pagesThe Microscope: Dr. S.M. ReyesSheryl Reyes100% (1)
- Give Detail Function of Parts of The MicroscopeDocument2 pagesGive Detail Function of Parts of The MicroscopeLiam GonzalesNo ratings yet
- Science Process Skills - MicroscopeDocument2 pagesScience Process Skills - MicroscopeCharina May Lagunde-SabadoNo ratings yet
- Demonstration of Microscope and Its PartsDocument5 pagesDemonstration of Microscope and Its PartsSujoy Tontubay100% (1)
- MicroscopeDocument12 pagesMicroscopeHEXALANE E. LABRADORNo ratings yet
- Activity 1A MicroscopeDocument4 pagesActivity 1A MicroscopeClarito ManaayNo ratings yet
- Microscope WorksheetDocument5 pagesMicroscope WorksheetDaxx Kenu TanNo ratings yet
- MICROPARADocument8 pagesMICROPARALaureen CordovaNo ratings yet
- 1 Microscope 20Document5 pages1 Microscope 20Daxx Kenu TanNo ratings yet
- Parts of A MicroscopeDocument3 pagesParts of A Microscopeazaanhasnat345No ratings yet
- Lab Exercises For BiologyDocument13 pagesLab Exercises For BiologyMari SoleiNo ratings yet
- 1 Microscope 20-SalvaDocument5 pages1 Microscope 20-SalvaPrince SalvaNo ratings yet
- Parts of A MicroscopeDocument17 pagesParts of A MicroscopedamyangdcsNo ratings yet
- Compound Microscope Definitions For LabelsDocument9 pagesCompound Microscope Definitions For LabelsDURANO, ROSELLE Z.SCINo ratings yet
- Specimen: Compound MicroscopeDocument7 pagesSpecimen: Compound MicroscopeAres WellsNo ratings yet
- The Compund Microscope (Hardcopy)Document11 pagesThe Compund Microscope (Hardcopy)JheanAlphonsineT.MeansNo ratings yet
- Activity 1 MicroscopeDocument7 pagesActivity 1 MicroscopeRalc RamsNo ratings yet
- Parts of The Microscope Microscope Part Function Structural Parts of A MicroscopeDocument6 pagesParts of The Microscope Microscope Part Function Structural Parts of A Microscopelarry machonNo ratings yet
- Microscopy ReviewDocument2 pagesMicroscopy ReviewKimberley MendozaNo ratings yet
- PracticalDocument2 pagesPracticalNim RaNo ratings yet
- The Compound Light MicroscopeDocument2 pagesThe Compound Light MicroscopeIsabela MartinezNo ratings yet
- Batch-B7, Roll No-2111240, Microscopy PracticalDocument6 pagesBatch-B7, Roll No-2111240, Microscopy PracticalBaishali SurNo ratings yet
- MicrosDocument7 pagesMicrosJaeyun RuiNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3 Ana LabDocument28 pagesChapter 3 Ana LabJyrus Quim CrusperoNo ratings yet
- Assignment - Type of MicroscopeDocument4 pagesAssignment - Type of Microscopeuypaul97100% (1)
- Microscope: B. Type of MicroscopeDocument3 pagesMicroscope: B. Type of MicroscopeFati Andari AlmahdiniNo ratings yet
- Science 7 q2 m1 - PDF FILEDocument6 pagesScience 7 q2 m1 - PDF FILEEzzel Jan FranciscoNo ratings yet
- Anaphy Lab 1Document5 pagesAnaphy Lab 1DIANNE PLANANo ratings yet
- What Are MicroscopesDocument10 pagesWhat Are MicroscopesmonsterjannkingNo ratings yet
- Structural Parts of The Microscope (Biology)Document4 pagesStructural Parts of The Microscope (Biology)Nemie VelascoNo ratings yet
- Experiment 4: Microscopy: Compound Light MicroscopeDocument4 pagesExperiment 4: Microscopy: Compound Light MicroscopeEhazNo ratings yet
- MOd 1Document2 pagesMOd 1A. MagnoNo ratings yet
- Practical Handbook 2020Document41 pagesPractical Handbook 2020davidsalome199No ratings yet
- I. Microscope Parts and FunctionsDocument1 pageI. Microscope Parts and FunctionsRowie WanawanNo ratings yet
- Chemistry 2Document3 pagesChemistry 2Neuron Jess Delos ReyesNo ratings yet
- Handout Compound Microscope 2023 2024Document1 pageHandout Compound Microscope 2023 2024reece sayamNo ratings yet
- Laboratory Report 1Document5 pagesLaboratory Report 1ANIS HNo ratings yet
- Biochem No. 1Document7 pagesBiochem No. 1Allesa San JoseNo ratings yet
- Parasitology Practical HandbookDocument41 pagesParasitology Practical Handbookmaximazarov100% (1)
- Topic 15 (1) - Spectacle Lenses and Their Subsidiary EffectsDocument11 pagesTopic 15 (1) - Spectacle Lenses and Their Subsidiary EffectsshadowosNo ratings yet
- The MicroscopeDocument21 pagesThe MicroscopeKatie HolmesNo ratings yet
- User Manual Trinocular Compound LED Microscope: Model M8311Z SeriesDocument22 pagesUser Manual Trinocular Compound LED Microscope: Model M8311Z SeriesMarcelo WillyNo ratings yet
- Light - Reflection - Refraction - Diffraction - ReviewDocument42 pagesLight - Reflection - Refraction - Diffraction - ReviewLester MarquezNo ratings yet
- Chapter Three:: Anatomy of A Curved MirrorDocument23 pagesChapter Three:: Anatomy of A Curved MirrorKay LagunaNo ratings yet
- A Guide To Macro and Close Up Photography PDFDocument90 pagesA Guide To Macro and Close Up Photography PDFtavu39100% (3)
- Pract. Exam Crim 2 Key 2Document4 pagesPract. Exam Crim 2 Key 2Jerome CometaNo ratings yet
- Optical Devices - Science 10Document4 pagesOptical Devices - Science 10B04 Joenathan Gabriel ChuaNo ratings yet
- Ray Optics Class NotesDocument5 pagesRay Optics Class NotescutebeneNo ratings yet
- Sylvania Photolamps Catalog 1969Document52 pagesSylvania Photolamps Catalog 1969Alan Masters100% (2)
- CCTV SYSTEMS Module1 LensesDocument25 pagesCCTV SYSTEMS Module1 LensesmuddogNo ratings yet
- Microbiology Laboratory: Lab Report # 2 (MICROSCOPY)Document4 pagesMicrobiology Laboratory: Lab Report # 2 (MICROSCOPY)Kyla Nicole100% (1)
- 12 Physics Test Paper CH 9 1Document6 pages12 Physics Test Paper CH 9 1ChinmayiNo ratings yet
- FORSEM7Document5 pagesFORSEM7Arvy ArvyNo ratings yet
- Worksheet Light 1Document16 pagesWorksheet Light 1M. Amaan AamirNo ratings yet
- Quantel Optimis II Service Manual 51 60Document10 pagesQuantel Optimis II Service Manual 51 60Vladimir LevchenkoNo ratings yet
- Problem 1: Fabry-Perot Displacement Sensor: EE 231, Lasers Spring 2007 Problem Set 2 Due 5PM 25 AprilDocument2 pagesProblem 1: Fabry-Perot Displacement Sensor: EE 231, Lasers Spring 2007 Problem Set 2 Due 5PM 25 AprilHusam Abduldaem MohammedNo ratings yet
- Instant Download Cost Accounting Foundations and Evolutions 7th Edition Kinney Test Bank PDF Full ChapterDocument32 pagesInstant Download Cost Accounting Foundations and Evolutions 7th Edition Kinney Test Bank PDF Full ChapterMauriceJacksonjafqk100% (11)
- LBYPH03Document2 pagesLBYPH03Alwyn Dave AmbataliNo ratings yet
- Exercise No 1 Microscopy 1Document5 pagesExercise No 1 Microscopy 1Diana BoladoNo ratings yet
- Screenshot 2023-12-27 at 3.40.36 AMDocument1 pageScreenshot 2023-12-27 at 3.40.36 AMridumaheshkumarNo ratings yet
- Final Exam Questions #2 - Spherical MirrorsDocument2 pagesFinal Exam Questions #2 - Spherical Mirrorsanonslu2012No ratings yet
- Wxyz Logo TableDocument5 pagesWxyz Logo TableJudy Dawson NelsonNo ratings yet
- Aberrations Introduced in Off-Axis Testing of Spherical Surfaces - MalacaraDocument5 pagesAberrations Introduced in Off-Axis Testing of Spherical Surfaces - Malacarautente489133No ratings yet
- Science Word Search Light: Sciws1 Kms/03/2000Document1 pageScience Word Search Light: Sciws1 Kms/03/2000pepac414No ratings yet
- Rise Time BudgetDocument11 pagesRise Time Budgetsectiona100% (5)
- 12th Physics Sheet Soltuion PDFDocument288 pages12th Physics Sheet Soltuion PDFaman btechNo ratings yet
- Kodak Vollenda 620Document13 pagesKodak Vollenda 620Mihnea Vulpe100% (1)
MICROSCOPY - HISTO
MICROSCOPY - HISTO
Uploaded by
smrande94Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
MICROSCOPY - HISTO
MICROSCOPY - HISTO
Uploaded by
smrande94Copyright:
Available Formats
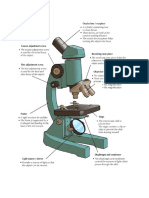
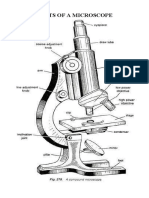
LIGHT MICROSCOPE
Thursday, 20 June 2024 7:48 pm
• visualize very minute objects
• constructed with special components that enable them to achieve high magnification levels
TYPES OF MICROSCOPE
1. Light microscope
2. Dark-field microscope
3. Phase contrast microscope
4. Electron microscope
5. Fluorescent microscope
THREE STRUCTURAL PARTS
1. Head - holds the eyepiece lens at one end and connects to the nose piece at other end. the
light coming from objectives will bend inside this tube. they are adjustable so that the
viewer can adjust the eyepiece for maximum visualization.
2. Arm - connecting the base to the head and the eyepiece tube to the base of the
microscope. it supports the head of the microscope and is also used when carrying the
microscope.
3. Base - lowermost part of the microscope that support that entire microscope structure.
provides stability for the microscope.
OPTICAL PARTS
1. Eyepiece - closest to the viewer's eye and located at the top of the microscope. lenses come
in different magnification powers from 5X to 30X, but the most common ocular lenses are
of 10X or 15X magnification.
2. Eyepiece tube - carries the eyepiece just above the objective lens.
3. Nose piece - movable circular structure that houses all the objective lenses. it is connected
to the body tube and lies just above the stage. it can be rotated clockwise or
counterclockwise to increase or decrease the magnification.
4. Objective lenses - a standard microscope has 3 to 4 objective lenses of different magnifying
powers: 4X, 10X, 40X, and 100X.
○ Scanner
○ Lower Power Objective
○ High Power Objective
○ Oil Immersion Objective
5. Fine adjustment knobs - a smaller knob and is used to move the stage up or down very
slowly. used to sharpen the image.
6. Coarse adjustment knobs - focusing the image under low power magnification. a larger
knob and is used to move the stage up or down very rapidly.
7. Stage - the section in which the specimen is placed for viewing. have stage clips that hold
New Section 1 Page 1
7. Stage - the section in which the specimen is placed for viewing. have stage clips that hold
the specimen slides in place.
8. Stage control knobs - are the control knobs used to move the stage mechanically. there are
two knobs; one for moving left and right and the other for moving forward and backward.
9. Aperture - this is a hole in the microscope stage through which the transmitted light from
the source reaches the stage.
10. Microscopic illuminator - light source
11. Condenser - lenses that are used to collect and focus light from the illuminator into the
specimen. found under the stage next to the diaphragm of the microscope. play a major
role in ensuring clear, sharp images are produced with a high magnification of 400X and
above.
12. Diaphragm - also known as the iris. found under the stage of the microscope, and its
primary role is to control the amount of light that reaches the specimen. controlling the
light intensity and the size of the beam of light that gets to the specimen.
13. Light switch - is an electrical control device.
14. Brightness adjustment - controls the voltage supplied to the light bulb, controlling the
intensity of the light bulb.
LAB ACTIVITY
New Section 1 Page 2
New Section 1 Page 3
You might also like
- Lens Problems WorksheetDocument1 pageLens Problems WorksheetWardah50% (2)
- ElecComTomasi Chapter 13Document2 pagesElecComTomasi Chapter 13jerson eyas0% (1)
- Parts of MicroscopeDocument4 pagesParts of MicroscopeJohn Rey F. CastroNo ratings yet
- Microscope Parts and FunctionsDocument4 pagesMicroscope Parts and FunctionsChris ChanNo ratings yet
- Detailed Explanation of MicroscopeDocument3 pagesDetailed Explanation of MicroscopestsrinidiNo ratings yet
- Detailed Explanation of MicroscopeDocument3 pagesDetailed Explanation of MicroscopestsrinidiNo ratings yet
- HSC Lab 1Document3 pagesHSC Lab 1Reshma MohabeirNo ratings yet
- Biology (Reviewer)Document4 pagesBiology (Reviewer)Claire SerafinNo ratings yet
- MicroscopeDocument3 pagesMicroscopeJannette Jane DavidNo ratings yet
- Parts of A MicroscopeDocument2 pagesParts of A MicroscopeRonJen VlogsNo ratings yet
- HISTO TRANS Overview of Histology and Its MethodsDocument6 pagesHISTO TRANS Overview of Histology and Its MethodsLovely ViernesNo ratings yet
- The MicroscopeDocument6 pagesThe MicroscopejustRizzeNo ratings yet
- Laboratory IIDocument9 pagesLaboratory IIDecemei CuaboNo ratings yet
- Lesson 8 MicroscopeDocument6 pagesLesson 8 MicroscopeCristina AnganganNo ratings yet
- Compound Microscop EDocument26 pagesCompound Microscop EDixie MerinNo ratings yet
- Worksheet 1-Word FinalDocument6 pagesWorksheet 1-Word FinalPrince SalvaNo ratings yet
- Sci Ed 5 Laboratory Exercise 3Document6 pagesSci Ed 5 Laboratory Exercise 3AlibabaNo ratings yet
- Parts and Function of A MicroscopeDocument4 pagesParts and Function of A MicroscopeFria mae AbellanoNo ratings yet
- Parts of A MicroscopeDocument5 pagesParts of A MicroscopeShankey Faith BediaNo ratings yet
- A1.1 Parts of The MicroscopeDocument2 pagesA1.1 Parts of The MicroscopehzntrpNo ratings yet
- Biotech - Microscope (8 - Leeuwenhoek)Document4 pagesBiotech - Microscope (8 - Leeuwenhoek)Leila Nicole FulgencioNo ratings yet
- The MicroscopeDocument5 pagesThe Microscopeeasylearning83No ratings yet
- The Microscope: Dr. S.M. ReyesDocument9 pagesThe Microscope: Dr. S.M. ReyesSheryl Reyes100% (1)
- Give Detail Function of Parts of The MicroscopeDocument2 pagesGive Detail Function of Parts of The MicroscopeLiam GonzalesNo ratings yet
- Science Process Skills - MicroscopeDocument2 pagesScience Process Skills - MicroscopeCharina May Lagunde-SabadoNo ratings yet
- Demonstration of Microscope and Its PartsDocument5 pagesDemonstration of Microscope and Its PartsSujoy Tontubay100% (1)
- MicroscopeDocument12 pagesMicroscopeHEXALANE E. LABRADORNo ratings yet
- Activity 1A MicroscopeDocument4 pagesActivity 1A MicroscopeClarito ManaayNo ratings yet
- Microscope WorksheetDocument5 pagesMicroscope WorksheetDaxx Kenu TanNo ratings yet
- MICROPARADocument8 pagesMICROPARALaureen CordovaNo ratings yet
- 1 Microscope 20Document5 pages1 Microscope 20Daxx Kenu TanNo ratings yet
- Parts of A MicroscopeDocument3 pagesParts of A Microscopeazaanhasnat345No ratings yet
- Lab Exercises For BiologyDocument13 pagesLab Exercises For BiologyMari SoleiNo ratings yet
- 1 Microscope 20-SalvaDocument5 pages1 Microscope 20-SalvaPrince SalvaNo ratings yet
- Parts of A MicroscopeDocument17 pagesParts of A MicroscopedamyangdcsNo ratings yet
- Compound Microscope Definitions For LabelsDocument9 pagesCompound Microscope Definitions For LabelsDURANO, ROSELLE Z.SCINo ratings yet
- Specimen: Compound MicroscopeDocument7 pagesSpecimen: Compound MicroscopeAres WellsNo ratings yet
- The Compund Microscope (Hardcopy)Document11 pagesThe Compund Microscope (Hardcopy)JheanAlphonsineT.MeansNo ratings yet
- Activity 1 MicroscopeDocument7 pagesActivity 1 MicroscopeRalc RamsNo ratings yet
- Parts of The Microscope Microscope Part Function Structural Parts of A MicroscopeDocument6 pagesParts of The Microscope Microscope Part Function Structural Parts of A Microscopelarry machonNo ratings yet
- Microscopy ReviewDocument2 pagesMicroscopy ReviewKimberley MendozaNo ratings yet
- PracticalDocument2 pagesPracticalNim RaNo ratings yet
- The Compound Light MicroscopeDocument2 pagesThe Compound Light MicroscopeIsabela MartinezNo ratings yet
- Batch-B7, Roll No-2111240, Microscopy PracticalDocument6 pagesBatch-B7, Roll No-2111240, Microscopy PracticalBaishali SurNo ratings yet
- MicrosDocument7 pagesMicrosJaeyun RuiNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3 Ana LabDocument28 pagesChapter 3 Ana LabJyrus Quim CrusperoNo ratings yet
- Assignment - Type of MicroscopeDocument4 pagesAssignment - Type of Microscopeuypaul97100% (1)
- Microscope: B. Type of MicroscopeDocument3 pagesMicroscope: B. Type of MicroscopeFati Andari AlmahdiniNo ratings yet
- Science 7 q2 m1 - PDF FILEDocument6 pagesScience 7 q2 m1 - PDF FILEEzzel Jan FranciscoNo ratings yet
- Anaphy Lab 1Document5 pagesAnaphy Lab 1DIANNE PLANANo ratings yet
- What Are MicroscopesDocument10 pagesWhat Are MicroscopesmonsterjannkingNo ratings yet
- Structural Parts of The Microscope (Biology)Document4 pagesStructural Parts of The Microscope (Biology)Nemie VelascoNo ratings yet
- Experiment 4: Microscopy: Compound Light MicroscopeDocument4 pagesExperiment 4: Microscopy: Compound Light MicroscopeEhazNo ratings yet
- MOd 1Document2 pagesMOd 1A. MagnoNo ratings yet
- Practical Handbook 2020Document41 pagesPractical Handbook 2020davidsalome199No ratings yet
- I. Microscope Parts and FunctionsDocument1 pageI. Microscope Parts and FunctionsRowie WanawanNo ratings yet
- Chemistry 2Document3 pagesChemistry 2Neuron Jess Delos ReyesNo ratings yet
- Handout Compound Microscope 2023 2024Document1 pageHandout Compound Microscope 2023 2024reece sayamNo ratings yet
- Laboratory Report 1Document5 pagesLaboratory Report 1ANIS HNo ratings yet
- Biochem No. 1Document7 pagesBiochem No. 1Allesa San JoseNo ratings yet
- Parasitology Practical HandbookDocument41 pagesParasitology Practical Handbookmaximazarov100% (1)
- Topic 15 (1) - Spectacle Lenses and Their Subsidiary EffectsDocument11 pagesTopic 15 (1) - Spectacle Lenses and Their Subsidiary EffectsshadowosNo ratings yet
- The MicroscopeDocument21 pagesThe MicroscopeKatie HolmesNo ratings yet
- User Manual Trinocular Compound LED Microscope: Model M8311Z SeriesDocument22 pagesUser Manual Trinocular Compound LED Microscope: Model M8311Z SeriesMarcelo WillyNo ratings yet
- Light - Reflection - Refraction - Diffraction - ReviewDocument42 pagesLight - Reflection - Refraction - Diffraction - ReviewLester MarquezNo ratings yet
- Chapter Three:: Anatomy of A Curved MirrorDocument23 pagesChapter Three:: Anatomy of A Curved MirrorKay LagunaNo ratings yet
- A Guide To Macro and Close Up Photography PDFDocument90 pagesA Guide To Macro and Close Up Photography PDFtavu39100% (3)
- Pract. Exam Crim 2 Key 2Document4 pagesPract. Exam Crim 2 Key 2Jerome CometaNo ratings yet
- Optical Devices - Science 10Document4 pagesOptical Devices - Science 10B04 Joenathan Gabriel ChuaNo ratings yet
- Ray Optics Class NotesDocument5 pagesRay Optics Class NotescutebeneNo ratings yet
- Sylvania Photolamps Catalog 1969Document52 pagesSylvania Photolamps Catalog 1969Alan Masters100% (2)
- CCTV SYSTEMS Module1 LensesDocument25 pagesCCTV SYSTEMS Module1 LensesmuddogNo ratings yet
- Microbiology Laboratory: Lab Report # 2 (MICROSCOPY)Document4 pagesMicrobiology Laboratory: Lab Report # 2 (MICROSCOPY)Kyla Nicole100% (1)
- 12 Physics Test Paper CH 9 1Document6 pages12 Physics Test Paper CH 9 1ChinmayiNo ratings yet
- FORSEM7Document5 pagesFORSEM7Arvy ArvyNo ratings yet
- Worksheet Light 1Document16 pagesWorksheet Light 1M. Amaan AamirNo ratings yet
- Quantel Optimis II Service Manual 51 60Document10 pagesQuantel Optimis II Service Manual 51 60Vladimir LevchenkoNo ratings yet
- Problem 1: Fabry-Perot Displacement Sensor: EE 231, Lasers Spring 2007 Problem Set 2 Due 5PM 25 AprilDocument2 pagesProblem 1: Fabry-Perot Displacement Sensor: EE 231, Lasers Spring 2007 Problem Set 2 Due 5PM 25 AprilHusam Abduldaem MohammedNo ratings yet
- Instant Download Cost Accounting Foundations and Evolutions 7th Edition Kinney Test Bank PDF Full ChapterDocument32 pagesInstant Download Cost Accounting Foundations and Evolutions 7th Edition Kinney Test Bank PDF Full ChapterMauriceJacksonjafqk100% (11)
- LBYPH03Document2 pagesLBYPH03Alwyn Dave AmbataliNo ratings yet
- Exercise No 1 Microscopy 1Document5 pagesExercise No 1 Microscopy 1Diana BoladoNo ratings yet
- Screenshot 2023-12-27 at 3.40.36 AMDocument1 pageScreenshot 2023-12-27 at 3.40.36 AMridumaheshkumarNo ratings yet
- Final Exam Questions #2 - Spherical MirrorsDocument2 pagesFinal Exam Questions #2 - Spherical Mirrorsanonslu2012No ratings yet
- Wxyz Logo TableDocument5 pagesWxyz Logo TableJudy Dawson NelsonNo ratings yet
- Aberrations Introduced in Off-Axis Testing of Spherical Surfaces - MalacaraDocument5 pagesAberrations Introduced in Off-Axis Testing of Spherical Surfaces - Malacarautente489133No ratings yet
- Science Word Search Light: Sciws1 Kms/03/2000Document1 pageScience Word Search Light: Sciws1 Kms/03/2000pepac414No ratings yet
- Rise Time BudgetDocument11 pagesRise Time Budgetsectiona100% (5)
- 12th Physics Sheet Soltuion PDFDocument288 pages12th Physics Sheet Soltuion PDFaman btechNo ratings yet
- Kodak Vollenda 620Document13 pagesKodak Vollenda 620Mihnea Vulpe100% (1)