Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Dna
Dna
Uploaded by
dangerwoman180Copyright:
Available Formats
You might also like
- Class 12 - Genetics NotesDocument1 pageClass 12 - Genetics NotesDimas HernadyNo ratings yet
- Protein SynthesisDocument8 pagesProtein SynthesisDebbie NsefikNo ratings yet
- IB Diploma Biology: Essential Idea: Transcription and Translation Allow The GeneticDocument37 pagesIB Diploma Biology: Essential Idea: Transcription and Translation Allow The GeneticClàudia VicenteNo ratings yet
- Transcription & TranslationDocument8 pagesTranscription & TranslationDr DapperNo ratings yet
- Protein Synthesis- DNA Transcription and Translation-2Document51 pagesProtein Synthesis- DNA Transcription and Translation-2limshinyen22No ratings yet
- Genetic Code, DNA, RNA, Protein SynthesisDocument46 pagesGenetic Code, DNA, RNA, Protein SynthesisdeepakNo ratings yet
- Transcription Study GuideDocument5 pagesTranscription Study GuideSubhajit AdakNo ratings yet
- Types of RNA-Worksheet Omar IbrahimDocument5 pagesTypes of RNA-Worksheet Omar IbrahimOmar Ibrahim LNo ratings yet
- Lesson: SynthesisDocument3 pagesLesson: Synthesisisaspiegel2018No ratings yet
- Transcription and Translation NarrativeDocument3 pagesTranscription and Translation NarrativeBridget Anne BenitezNo ratings yet
- Polypeptide Synthesis: TranscriptionDocument3 pagesPolypeptide Synthesis: TranscriptionliklyNo ratings yet
- Replication and Transciption of DnaDocument29 pagesReplication and Transciption of DnaTri Hiu AmborowatiNo ratings yet
- Lesson 3A - RNA Types and StructuresDocument3 pagesLesson 3A - RNA Types and Structureshannah CorpuzNo ratings yet
- THE CENTRAL DOGMA HandoutDocument6 pagesTHE CENTRAL DOGMA HandoutLeah AturoNo ratings yet
- Protein Synthesis, Brief NoteDocument4 pagesProtein Synthesis, Brief NoteosunfisanayomideNo ratings yet
- Rna DnaDocument12 pagesRna DnaChandanaNo ratings yet
- Protein SynthesisDocument54 pagesProtein SynthesisYousef WardatNo ratings yet
- Nucleic AcidsDocument16 pagesNucleic AcidsRockingsouvikNo ratings yet
- DNA Replication and Protein SynthesisDocument2 pagesDNA Replication and Protein SynthesislibbyNo ratings yet
- Transes Biochem ProteinsynthesisDocument6 pagesTranses Biochem ProteinsynthesisPia LouiseNo ratings yet
- Dna Replication PDFDocument6 pagesDna Replication PDFCarpioNo ratings yet
- DNADocument64 pagesDNAsapphireriego01No ratings yet
- Dna Rna Protsin 2020Document48 pagesDna Rna Protsin 2020RaragloriaaNo ratings yet
- DNA and Protein PowerpointDocument13 pagesDNA and Protein PowerpointKashish ShahNo ratings yet
- Protein SynthesisDocument3 pagesProtein Synthesis423003157No ratings yet
- Dna ReplicationDocument3 pagesDna ReplicationRachel ReneeNo ratings yet
- 3D Molecular Translation Worksheetv21Document3 pages3D Molecular Translation Worksheetv21Jonas WelliverNo ratings yet
- Bio Keypoints ReviewerDocument4 pagesBio Keypoints ReviewerFrancisNo ratings yet
- Sunshine23 Biochem-Ch21Document4 pagesSunshine23 Biochem-Ch21Alexa Nicole PamaNo ratings yet
- RNA and Protein Synthesis WorksheetDocument4 pagesRNA and Protein Synthesis WorksheetJo JoNo ratings yet
- 3.10 Protein-SynthesisDocument20 pages3.10 Protein-SynthesisPratika MNo ratings yet
- Structure and Function of RNA - Microbiology - OpenStaxDocument5 pagesStructure and Function of RNA - Microbiology - OpenStaxAleksandra Sanja MartinovicNo ratings yet
- Transcription & TranslationDocument5 pagesTranscription & TranslationJerico NaveraNo ratings yet
- The Central Dogma of Molecular BiologyDocument4 pagesThe Central Dogma of Molecular BiologyJoshuaMondejarNo ratings yet
- Dna Replication and Protein SynthesisDocument9 pagesDna Replication and Protein Synthesisbravebrave2005No ratings yet
- LESSON 3.3 Heredity NotesdocxDocument2 pagesLESSON 3.3 Heredity NotesdocxJedy IvoryNo ratings yet
- Molecular Structure of DNA, RNA, and Proteins DNA Replication and Protein Synthesis (Cenabre, Fortun, Ibal)Document2 pagesMolecular Structure of DNA, RNA, and Proteins DNA Replication and Protein Synthesis (Cenabre, Fortun, Ibal)Jessa Mae IbalNo ratings yet
- Sci Q3 Protein Synthesis and MutationDocument7 pagesSci Q3 Protein Synthesis and MutationMel GonzalesNo ratings yet
- Protein SynthesisDocument2 pagesProtein SynthesisEverly Joy JingcoNo ratings yet
- Life Science Needs To KnowDocument3 pagesLife Science Needs To KnowRudzi UdziNo ratings yet
- Nucleic Acid StructureDocument3 pagesNucleic Acid StructureChris RichardsNo ratings yet
- Protein Synthesis NotesDocument6 pagesProtein Synthesis NotesRokunuz Jahan RudroNo ratings yet
- Lecture 5Document27 pagesLecture 5Animikh RayNo ratings yet
- HvhyvugvDocument35 pagesHvhyvugvahanasauNo ratings yet
- 8c) Transcription Summary - 9744 - 2018Document1 page8c) Transcription Summary - 9744 - 20182022 EMMA WEN XUAN HANSONNo ratings yet
- Sandra Loranger Stacie Daer Mike ReillyDocument9 pagesSandra Loranger Stacie Daer Mike ReillyBabasChongNo ratings yet
- Translation Gn22Document59 pagesTranslation Gn22RosyidNo ratings yet
- Lesson 0Document6 pagesLesson 0Francesca YanzonNo ratings yet
- Reviewer Biochem For NucleotidesDocument3 pagesReviewer Biochem For NucleotidesNino D. AtilanoNo ratings yet
- RNA Structure and TypesDocument39 pagesRNA Structure and Typesshubham sachdeva100% (2)
- Lesson 0-1Document10 pagesLesson 0-1Francesca YanzonNo ratings yet
- Dna StructureDocument42 pagesDna StructureCedric BaldozaNo ratings yet
- CYTO PL4 TranslationDocument9 pagesCYTO PL4 TranslationDanielle Anne Zamora-Matillosa LambanNo ratings yet
- Nucleic Acids: DNA Nucleotide or RNA Nucleotide?Document2 pagesNucleic Acids: DNA Nucleotide or RNA Nucleotide?Rachell RequellNo ratings yet
- 2006 CHM6108 L9L10 SlidesDocument40 pages2006 CHM6108 L9L10 Slidesaidar.seralinNo ratings yet
- Genbio Lesson 1 4Document26 pagesGenbio Lesson 1 4Greenard Imperial GualbertoNo ratings yet
- Key Notes Genetic Material and Central DogmaDocument2 pagesKey Notes Genetic Material and Central DogmaSeiza WinchesterNo ratings yet
- Chapter 13 Prescott S 10 THDocument4 pagesChapter 13 Prescott S 10 THiamayesha725No ratings yet
- TranscriptionDocument15 pagesTranscriptioncamila hartmannNo ratings yet
- Kandungan Senyawa Kimia Pada Tumbuhan Daun Salam (Syzygium Polyanthum)Document25 pagesKandungan Senyawa Kimia Pada Tumbuhan Daun Salam (Syzygium Polyanthum)Rafli NaufalNo ratings yet
- Biosynthesis of Steroid Hormones / Steriodgenesis Steroid HormoneDocument10 pagesBiosynthesis of Steroid Hormones / Steriodgenesis Steroid Hormoneajay004004No ratings yet
- BIO 1412 Molecular Biology and Genetics Module - Prof C. Katongo - 2019Document119 pagesBIO 1412 Molecular Biology and Genetics Module - Prof C. Katongo - 2019JOHN MVULA IINo ratings yet
- Lab Properties of LipidsDocument5 pagesLab Properties of LipidsIyap LazatinNo ratings yet
- CH 20 4 Regulation Enzyme Activity GOB Structures 5th EdDocument13 pagesCH 20 4 Regulation Enzyme Activity GOB Structures 5th Edchairam rajkumarNo ratings yet
- Glycoproteins and Proteoglycans TTVDocument34 pagesGlycoproteins and Proteoglycans TTVcraigNo ratings yet
- Bio Molecule Review WorksheetDocument4 pagesBio Molecule Review WorksheetBianca BiancaNo ratings yet
- EnzymesDocument5 pagesEnzymesJica MedrosoNo ratings yet
- Protein PPT PrelimDocument8 pagesProtein PPT PrelimMacchi MagsNo ratings yet
- Isoenzyme - Lactate Dehydrogenase: By, Ishaque P K Biochemistry Pondicherry UniversityDocument17 pagesIsoenzyme - Lactate Dehydrogenase: By, Ishaque P K Biochemistry Pondicherry UniversityBETTYNo ratings yet
- ABCDocument12 pagesABCIrfan AfriliansyahNo ratings yet
- Protein Intake PTC8 PDFDocument110 pagesProtein Intake PTC8 PDFvNo ratings yet
- Chemistry of LipidsDocument23 pagesChemistry of Lipidsbrian mgabiNo ratings yet
- 2016 Art96Document23 pages2016 Art96Nguyễn Ngọc NamNo ratings yet
- 70 Multiple Choice QuestionsDocument10 pages70 Multiple Choice QuestionsChiku MteghaNo ratings yet
- DNA and RNA Comparison WorksheetDocument4 pagesDNA and RNA Comparison WorksheetH DNo ratings yet
- Peel Meals As Feed Ingredients in Poultry Diets Chemical Composition, Dietary Recommendations and ProspectsDocument12 pagesPeel Meals As Feed Ingredients in Poultry Diets Chemical Composition, Dietary Recommendations and ProspectsShanNo ratings yet
- Amino Acids and Proteins - Lecture NotesDocument17 pagesAmino Acids and Proteins - Lecture NotesAyukafangha EtandoNo ratings yet
- Ekstrak Etanol Daun Kecombrang (Nicolaia Speciosa Horan.)Document3 pagesEkstrak Etanol Daun Kecombrang (Nicolaia Speciosa Horan.)Detdet343No ratings yet
- Oil Seeds and Palm Oil: Presented By: Section: G Group: 11Document20 pagesOil Seeds and Palm Oil: Presented By: Section: G Group: 11Joshika AgarwalNo ratings yet
- Vitamins Krok 1Document5 pagesVitamins Krok 1Ahmed EzzatNo ratings yet
- Chapter 23: Nucleotide Metabolism: MatchingDocument14 pagesChapter 23: Nucleotide Metabolism: MatchingAbe345123No ratings yet
- Amino Acid MetabolismDocument23 pagesAmino Acid MetabolismZ ZNo ratings yet
- MCAT BiochemistryDocument41 pagesMCAT BiochemistrydaniyayaqubNo ratings yet
- Hsslive Xii CH 10 Biomolecules AnilDocument8 pagesHsslive Xii CH 10 Biomolecules AnilFathima NithinshaNo ratings yet
- Module 2Document29 pagesModule 2Erica Jazzanne LopezNo ratings yet
- Prohance Nutritional Supplement For Adults in IndiaDocument1 pageProhance Nutritional Supplement For Adults in IndiasunpharmaprohanceNo ratings yet
- Central Dogma ActivityDocument4 pagesCentral Dogma ActivityAlyssa MelegritoNo ratings yet
- Hal 216 - 231 116 GondokesumoDocument16 pagesHal 216 - 231 116 GondokesumoDila AprianiNo ratings yet
- Midterm 1 Chem 251 2011Document6 pagesMidterm 1 Chem 251 2011Orlando CastilloNo ratings yet
Dna
Dna
Uploaded by
dangerwoman180Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Dna
Dna
Uploaded by
dangerwoman180Copyright:
Available Formats
16/10/2023, 08:32 print.
html
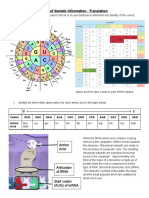
3 types of RNA-mRNA
3 types of RNA- tRNA
mRNA=messenger RNA
tRNA= transfer RNA Carries instructions for polypeptide synthesis from
Transfer RNA is found only in the cytoplasm nucleus to ribosomes in the cytoplasm
3 types of RNA -rRNA=ribosomal RNA The function of tRNA is to attach to one of the 20 amino Messenger RNA is a copy of a gene from DNA
acids and transfer this amino acid to the ribosome to mRNA is created in the nucleus and it then leaves the
create the polypeptide chain. nucleus to carry the copy of the genetic code of one gene
rRNA=ribosomal RNA
Specific amino acids attach to specific tRNA molecules to a ribosome in the cytoplasm
and this is determined by 3 bases found on the tRNA DNA is too large to leave the nucleus and would be at
Forms an important part of both subunits of the
which are complementary to the 3 bases on mRNA risk of being damaged by enzymes. Therefore destroying
ribosomes
These are called anticodon, because they are the genetic code permanently.
Ribosomal RNA is the type of RNA that makes up the
complementary to the codon on mRNA. mRNA is much shorter because it is only the length of
bulk of ribosome
carries amino acids to the ribosome and matches them to one gene and therefore leave the nucleus
rRNA Function combines with protein to form make a
the coded mRNA messages mRNA is short lived as it is only needed temporarily to
ribosome
It is singled stranded ,but folded to create a shape that help create a protein,therefore by the time any enzyme
looks like a cloverleaf. This cloverleaf shape is held in could break it down it would have already carried out its
place by hydrogen bonds function.
mRNA is single stranded and every 3 bases in the
sequence codes for a specific amino acid.These bases are
called codons
Complementary base pairing.
Two DNA polynucleotide strands join together by
hydrogen bonds between the bases.
Each base can only join with one particular partner —
this is called complementary base pairing (or specific
base pairing).
Adenine always pairs with thymine (A - T) .They are held DIfference between RNA and DNA monomers
together with 2 hydrogen bonds DIfferenf ein size
guanine always pairs with cytosine (G - C) .these are held DNA contains the base thymine , whereas RNA contains
together with 3 hydrogen bond uracil instead
DNA is long where as RNA is short
This means there are always equal amounts of adenine DNA contains the pentose sugar deoxyribose, whereas
and thymine in a DNA molecule and equal amounts of RNA contains the pentose sugar ribose
cytosine and guanine.
These base pairing ensure that the 2 polynucleotide
chains are always the same distance apart(parallel) but
run in opposite directions(anti parallel)
The two polynucleotide strands are antiparallel — they
run in opposite directions. Two antiparallel strands twist
to form a DNA double helix.
16/10/2023, 08:32 print.html
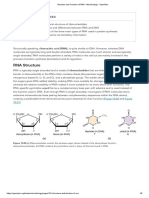
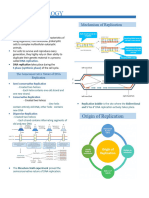
DNA structure-DNA nucleotide structure.
DNA and RNA function. A DNA nucleotide is made from a phosphate group, the
pentose sugar deoxyribose and a nitrogen-containing
organic base.
DNA and RNA are both types of nucleic acid. They’re Each DNA nucleotide has the same sugar and
found in all living cells and they both carry information. phosphate.
DNA (deoxyribonucleic acid) is used to store your The base on each nucleotide can vary though. DNA structure-DNA polynucleotides structure.
genetic information — that’s all the instructions needed to There are four possible bases — adenine (A),
grow and develop from a fertilised egg to a fully grown thymine (T), cytosine (C) and guanine (G). The DNA polymer occurs in pairs, and these pairs are
adult. There’s more on the role of DNA The structure of a DNA nucleotide is illustrated in Figure joined together by hydrogen bonds between the
RNA (ribonucleic acid) is similar in structure to DNA. 4. bases.This is how the double helix structure is created , as
One of its main functions is to transfer genetic
two chains twist
information from the DNA to the ribosomes.
Ribosomes are the body’s ‘protein factories’ — they read
the RNA to make polypeptides (proteins) in a process
called translation
Ribosomes themselves are made from RNA and proteins.
DNA structure.
DNA has a double helix structure. This means that a DNA
molecule is formed from two separate strands which wind
How the structure related to the function
around each other to form a spiral
The strands are polynucleotides.
They’re made up of lots of nucleotides joined together in Difference between the polymers Stable structure due to sugar phosphate backbone
a long chain (covalent bond) and the double helix
DNA molecules are really long and are coiled up very Double stranded so replication can occur using one strand
DNA is much larger because it contains approximately
tightly, so a lot of genetic information can fit into a small as template
23,000 genes(the entire genome_ whereas RNA is much
space in the cell nucleus. Weak hydrogen bonds for easy unzipping of the 2 strands
shorter because it is only the length of one gene
in the double helix during replication
DNA is double stranded whereas RNA is single stranded
Large molecule to carry lots of information
Complementary base pairing allows identical copies to be
made
16/10/2023, 08:32 print.html
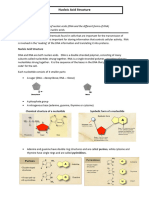
Polynucleotide structure,
The polymer of these nucleotides is called a
polynucleotide. RNA structure.
Many nucleotides join together to form polynucleotide
strands (or chains). Like DNA, RNA is made of nucleotides that contain a sugar, a
The nucleotides join up via a condensation reaction phosphate group and one of four different bases.
between the phosphate group of one nucleotide and The nucleotides also form a polynucleotide strand with a sugar-
Nucleotide structure.
the deoxyribose sugar. phosphate backbone. But the structure of RNA differs from
Molecules of DNA and RNA are polymers of nucleotides. A This forms a phosphodiester bond (consisting of the DNA in four main ways:
nucleotide is a type of biological molecule which is made from phosphate group and two ester bonds).
Phosphodiester bonds are strong covalent bonds and The sugar in RNA nucleotides is a ribose sugar (not
three different components:
therefore help ensure that the genetic code is not broken deoxyribose). It’s still a pentose sugar though.
a pentose sugar (that’s a sugar with 5 carbon atoms), down Uracil (U, a pyrimidine) replaces thymine as a base.
a nitrogen-containing organic base (organic means that it The chain of phosphates and sugars is known as the Uracil always pairs with adenine in RNA.
contains carbon), and a phosphate group sugar-phosphate backbone. It is a single polynucleotide chain and can fold back on
The nitrogenous base can either be guanine, The backbone chains are made from alternating sugar itself if complimentary base form hydrogen bonds
phosphate groups joined together by phosphodiester The nucleotides form a single polynucleotide strand (not
cytosine,adenine and thymine
bonds. which adds stability to the double helix a double one).
The nitrogenous bases contain the element nitrogen along
with carbon ,hydrogen and oxygen This is describing the strong covalent bonds between the RNA strands are much shorter than most DNA
Nucleotides are really important. For a start they’re the sugar and [phosphate groups that hold the polymer polynucleotides
monomers that make up DNA and RNA. together
Phosphate ,sugar deoxyribose,nitrogenous join rother by
condensation reaction to from nucleotides
Nucleotides join by condensation to form polynucleotides
with phosphodiester links
Nucleotides are joined by condensation reaction between
sugar and phosphate group for form a double helix
RNA is a polymer of a nucleotide formed of ribose, a
nitrogenous base and a phosphate group
The nitrogenous bases in RNA are adenine, guanine
Polynucleotide-large molecule to store a lot of genetic ,cytosine and uracil
information The function of RNA is to copy and transfer the genetic
Polynucleotide chains are held together by weak code from DNA is the nucleus to the ribosomes. Some
hydrogen bonds between bases- as each hydrogen bond is RNA is also combined with proteins to create ribosomes.
weak the polynucleotide chains can be easily separated
as there are a Lot of hydrogen bonds collectively they
stabilise the helix
16/10/2023, 08:32 print.html
The nitrogenous bases-how are the bases joined to each other
The bases join by hydrogen bonds
Pirine -double ringed structure -this include adenine and
guanine
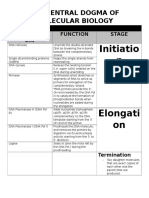
Relationship between DNA,mRNA ,ribosomes and tRNA difference in shape
DNA is to large to leave the nucleus.RNA carries the Pyrimidines are single ringed structures for example DNA is double stranded - wteisted into a double helix
genetic code to the ribosomes in the cytoplasm and it thymine and cytosine held together hy hydrogen bonds where as RNA is single
usually helps synthesis protein stranded
Purine base always base pair with a pyrimidine base -means the
2 strands are parallel and allows DNA to be replicated and
transfer information
You might also like
- Class 12 - Genetics NotesDocument1 pageClass 12 - Genetics NotesDimas HernadyNo ratings yet
- Protein SynthesisDocument8 pagesProtein SynthesisDebbie NsefikNo ratings yet
- IB Diploma Biology: Essential Idea: Transcription and Translation Allow The GeneticDocument37 pagesIB Diploma Biology: Essential Idea: Transcription and Translation Allow The GeneticClàudia VicenteNo ratings yet
- Transcription & TranslationDocument8 pagesTranscription & TranslationDr DapperNo ratings yet
- Protein Synthesis- DNA Transcription and Translation-2Document51 pagesProtein Synthesis- DNA Transcription and Translation-2limshinyen22No ratings yet
- Genetic Code, DNA, RNA, Protein SynthesisDocument46 pagesGenetic Code, DNA, RNA, Protein SynthesisdeepakNo ratings yet
- Transcription Study GuideDocument5 pagesTranscription Study GuideSubhajit AdakNo ratings yet
- Types of RNA-Worksheet Omar IbrahimDocument5 pagesTypes of RNA-Worksheet Omar IbrahimOmar Ibrahim LNo ratings yet
- Lesson: SynthesisDocument3 pagesLesson: Synthesisisaspiegel2018No ratings yet
- Transcription and Translation NarrativeDocument3 pagesTranscription and Translation NarrativeBridget Anne BenitezNo ratings yet
- Polypeptide Synthesis: TranscriptionDocument3 pagesPolypeptide Synthesis: TranscriptionliklyNo ratings yet
- Replication and Transciption of DnaDocument29 pagesReplication and Transciption of DnaTri Hiu AmborowatiNo ratings yet
- Lesson 3A - RNA Types and StructuresDocument3 pagesLesson 3A - RNA Types and Structureshannah CorpuzNo ratings yet
- THE CENTRAL DOGMA HandoutDocument6 pagesTHE CENTRAL DOGMA HandoutLeah AturoNo ratings yet
- Protein Synthesis, Brief NoteDocument4 pagesProtein Synthesis, Brief NoteosunfisanayomideNo ratings yet
- Rna DnaDocument12 pagesRna DnaChandanaNo ratings yet
- Protein SynthesisDocument54 pagesProtein SynthesisYousef WardatNo ratings yet
- Nucleic AcidsDocument16 pagesNucleic AcidsRockingsouvikNo ratings yet
- DNA Replication and Protein SynthesisDocument2 pagesDNA Replication and Protein SynthesislibbyNo ratings yet
- Transes Biochem ProteinsynthesisDocument6 pagesTranses Biochem ProteinsynthesisPia LouiseNo ratings yet
- Dna Replication PDFDocument6 pagesDna Replication PDFCarpioNo ratings yet
- DNADocument64 pagesDNAsapphireriego01No ratings yet
- Dna Rna Protsin 2020Document48 pagesDna Rna Protsin 2020RaragloriaaNo ratings yet
- DNA and Protein PowerpointDocument13 pagesDNA and Protein PowerpointKashish ShahNo ratings yet
- Protein SynthesisDocument3 pagesProtein Synthesis423003157No ratings yet
- Dna ReplicationDocument3 pagesDna ReplicationRachel ReneeNo ratings yet
- 3D Molecular Translation Worksheetv21Document3 pages3D Molecular Translation Worksheetv21Jonas WelliverNo ratings yet
- Bio Keypoints ReviewerDocument4 pagesBio Keypoints ReviewerFrancisNo ratings yet
- Sunshine23 Biochem-Ch21Document4 pagesSunshine23 Biochem-Ch21Alexa Nicole PamaNo ratings yet
- RNA and Protein Synthesis WorksheetDocument4 pagesRNA and Protein Synthesis WorksheetJo JoNo ratings yet
- 3.10 Protein-SynthesisDocument20 pages3.10 Protein-SynthesisPratika MNo ratings yet
- Structure and Function of RNA - Microbiology - OpenStaxDocument5 pagesStructure and Function of RNA - Microbiology - OpenStaxAleksandra Sanja MartinovicNo ratings yet
- Transcription & TranslationDocument5 pagesTranscription & TranslationJerico NaveraNo ratings yet
- The Central Dogma of Molecular BiologyDocument4 pagesThe Central Dogma of Molecular BiologyJoshuaMondejarNo ratings yet
- Dna Replication and Protein SynthesisDocument9 pagesDna Replication and Protein Synthesisbravebrave2005No ratings yet
- LESSON 3.3 Heredity NotesdocxDocument2 pagesLESSON 3.3 Heredity NotesdocxJedy IvoryNo ratings yet
- Molecular Structure of DNA, RNA, and Proteins DNA Replication and Protein Synthesis (Cenabre, Fortun, Ibal)Document2 pagesMolecular Structure of DNA, RNA, and Proteins DNA Replication and Protein Synthesis (Cenabre, Fortun, Ibal)Jessa Mae IbalNo ratings yet
- Sci Q3 Protein Synthesis and MutationDocument7 pagesSci Q3 Protein Synthesis and MutationMel GonzalesNo ratings yet
- Protein SynthesisDocument2 pagesProtein SynthesisEverly Joy JingcoNo ratings yet
- Life Science Needs To KnowDocument3 pagesLife Science Needs To KnowRudzi UdziNo ratings yet
- Nucleic Acid StructureDocument3 pagesNucleic Acid StructureChris RichardsNo ratings yet
- Protein Synthesis NotesDocument6 pagesProtein Synthesis NotesRokunuz Jahan RudroNo ratings yet
- Lecture 5Document27 pagesLecture 5Animikh RayNo ratings yet
- HvhyvugvDocument35 pagesHvhyvugvahanasauNo ratings yet
- 8c) Transcription Summary - 9744 - 2018Document1 page8c) Transcription Summary - 9744 - 20182022 EMMA WEN XUAN HANSONNo ratings yet
- Sandra Loranger Stacie Daer Mike ReillyDocument9 pagesSandra Loranger Stacie Daer Mike ReillyBabasChongNo ratings yet
- Translation Gn22Document59 pagesTranslation Gn22RosyidNo ratings yet
- Lesson 0Document6 pagesLesson 0Francesca YanzonNo ratings yet
- Reviewer Biochem For NucleotidesDocument3 pagesReviewer Biochem For NucleotidesNino D. AtilanoNo ratings yet
- RNA Structure and TypesDocument39 pagesRNA Structure and Typesshubham sachdeva100% (2)
- Lesson 0-1Document10 pagesLesson 0-1Francesca YanzonNo ratings yet
- Dna StructureDocument42 pagesDna StructureCedric BaldozaNo ratings yet
- CYTO PL4 TranslationDocument9 pagesCYTO PL4 TranslationDanielle Anne Zamora-Matillosa LambanNo ratings yet
- Nucleic Acids: DNA Nucleotide or RNA Nucleotide?Document2 pagesNucleic Acids: DNA Nucleotide or RNA Nucleotide?Rachell RequellNo ratings yet
- 2006 CHM6108 L9L10 SlidesDocument40 pages2006 CHM6108 L9L10 Slidesaidar.seralinNo ratings yet
- Genbio Lesson 1 4Document26 pagesGenbio Lesson 1 4Greenard Imperial GualbertoNo ratings yet
- Key Notes Genetic Material and Central DogmaDocument2 pagesKey Notes Genetic Material and Central DogmaSeiza WinchesterNo ratings yet
- Chapter 13 Prescott S 10 THDocument4 pagesChapter 13 Prescott S 10 THiamayesha725No ratings yet
- TranscriptionDocument15 pagesTranscriptioncamila hartmannNo ratings yet
- Kandungan Senyawa Kimia Pada Tumbuhan Daun Salam (Syzygium Polyanthum)Document25 pagesKandungan Senyawa Kimia Pada Tumbuhan Daun Salam (Syzygium Polyanthum)Rafli NaufalNo ratings yet
- Biosynthesis of Steroid Hormones / Steriodgenesis Steroid HormoneDocument10 pagesBiosynthesis of Steroid Hormones / Steriodgenesis Steroid Hormoneajay004004No ratings yet
- BIO 1412 Molecular Biology and Genetics Module - Prof C. Katongo - 2019Document119 pagesBIO 1412 Molecular Biology and Genetics Module - Prof C. Katongo - 2019JOHN MVULA IINo ratings yet
- Lab Properties of LipidsDocument5 pagesLab Properties of LipidsIyap LazatinNo ratings yet
- CH 20 4 Regulation Enzyme Activity GOB Structures 5th EdDocument13 pagesCH 20 4 Regulation Enzyme Activity GOB Structures 5th Edchairam rajkumarNo ratings yet
- Glycoproteins and Proteoglycans TTVDocument34 pagesGlycoproteins and Proteoglycans TTVcraigNo ratings yet
- Bio Molecule Review WorksheetDocument4 pagesBio Molecule Review WorksheetBianca BiancaNo ratings yet
- EnzymesDocument5 pagesEnzymesJica MedrosoNo ratings yet
- Protein PPT PrelimDocument8 pagesProtein PPT PrelimMacchi MagsNo ratings yet
- Isoenzyme - Lactate Dehydrogenase: By, Ishaque P K Biochemistry Pondicherry UniversityDocument17 pagesIsoenzyme - Lactate Dehydrogenase: By, Ishaque P K Biochemistry Pondicherry UniversityBETTYNo ratings yet
- ABCDocument12 pagesABCIrfan AfriliansyahNo ratings yet
- Protein Intake PTC8 PDFDocument110 pagesProtein Intake PTC8 PDFvNo ratings yet
- Chemistry of LipidsDocument23 pagesChemistry of Lipidsbrian mgabiNo ratings yet
- 2016 Art96Document23 pages2016 Art96Nguyễn Ngọc NamNo ratings yet
- 70 Multiple Choice QuestionsDocument10 pages70 Multiple Choice QuestionsChiku MteghaNo ratings yet
- DNA and RNA Comparison WorksheetDocument4 pagesDNA and RNA Comparison WorksheetH DNo ratings yet
- Peel Meals As Feed Ingredients in Poultry Diets Chemical Composition, Dietary Recommendations and ProspectsDocument12 pagesPeel Meals As Feed Ingredients in Poultry Diets Chemical Composition, Dietary Recommendations and ProspectsShanNo ratings yet
- Amino Acids and Proteins - Lecture NotesDocument17 pagesAmino Acids and Proteins - Lecture NotesAyukafangha EtandoNo ratings yet
- Ekstrak Etanol Daun Kecombrang (Nicolaia Speciosa Horan.)Document3 pagesEkstrak Etanol Daun Kecombrang (Nicolaia Speciosa Horan.)Detdet343No ratings yet
- Oil Seeds and Palm Oil: Presented By: Section: G Group: 11Document20 pagesOil Seeds and Palm Oil: Presented By: Section: G Group: 11Joshika AgarwalNo ratings yet
- Vitamins Krok 1Document5 pagesVitamins Krok 1Ahmed EzzatNo ratings yet
- Chapter 23: Nucleotide Metabolism: MatchingDocument14 pagesChapter 23: Nucleotide Metabolism: MatchingAbe345123No ratings yet
- Amino Acid MetabolismDocument23 pagesAmino Acid MetabolismZ ZNo ratings yet
- MCAT BiochemistryDocument41 pagesMCAT BiochemistrydaniyayaqubNo ratings yet
- Hsslive Xii CH 10 Biomolecules AnilDocument8 pagesHsslive Xii CH 10 Biomolecules AnilFathima NithinshaNo ratings yet
- Module 2Document29 pagesModule 2Erica Jazzanne LopezNo ratings yet
- Prohance Nutritional Supplement For Adults in IndiaDocument1 pageProhance Nutritional Supplement For Adults in IndiasunpharmaprohanceNo ratings yet
- Central Dogma ActivityDocument4 pagesCentral Dogma ActivityAlyssa MelegritoNo ratings yet
- Hal 216 - 231 116 GondokesumoDocument16 pagesHal 216 - 231 116 GondokesumoDila AprianiNo ratings yet
- Midterm 1 Chem 251 2011Document6 pagesMidterm 1 Chem 251 2011Orlando CastilloNo ratings yet