Professional Documents
Culture Documents
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
2 viewsDFS and BFS
DFS and BFS
Uploaded by
keerthi2k6Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOC, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You might also like
- Untitled DocumentDocument2 pagesUntitled Documentdebasis nagNo ratings yet
- Ai Dfs Bfs PrintDocument2 pagesAi Dfs Bfs PrintAvadhut KaleNo ratings yet
- DFS & BFS Implementation in PythonDocument2 pagesDFS & BFS Implementation in PythonayushstwtNo ratings yet
- DFS Teb01Document2 pagesDFS Teb01utkarshNo ratings yet
- BFS DFSDocument3 pagesBFS DFSCO2061- Suyash ShishupalNo ratings yet
- Deatri Nari Ratih - Tugas WKBDocument7 pagesDeatri Nari Ratih - Tugas WKBDeatri Nari RatihNo ratings yet
- PROGRAMDocument4 pagesPROGRAMvijayyc5104No ratings yet
- AI Lab2 MustafaDocument2 pagesAI Lab2 MustafaMustafa AliasgharNo ratings yet
- AI lp2 DfsbfsDocument1 pageAI lp2 Dfsbfs03rajput.kiNo ratings yet
- AI Exp 3Document5 pagesAI Exp 3Ganesh PanigrahiNo ratings yet
- Assignmnet 1Document6 pagesAssignmnet 1Muhammad UsamaNo ratings yet
- Selection Sort Algo1Document3 pagesSelection Sort Algo1karthi maniNo ratings yet
- Ai Lab Manual 202PDocument23 pagesAi Lab Manual 202PBhuvana ThimmiReddyNo ratings yet
- BFS & DFSDocument6 pagesBFS & DFSsnehaguptavvNo ratings yet
- 19CS413 LabManualDocument42 pages19CS413 LabManualGurunathanNo ratings yet
- BFS Teb01Document2 pagesBFS Teb01utkarshNo ratings yet
- lab manual 3rd yrDocument5 pageslab manual 3rd yrSindhuNo ratings yet
- AI and ML Lab ManualDocument29 pagesAI and ML Lab ManualRoobesh RoobeshNo ratings yet
- Airline Removed MergedDocument12 pagesAirline Removed MergedOm PasalkarNo ratings yet
- Breadth First Search: # List For Visited Nodes. #Initialize A Queue #Function For BFSDocument31 pagesBreadth First Search: # List For Visited Nodes. #Initialize A Queue #Function For BFSdhruv kumarNo ratings yet
- Week 12Document1 pageWeek 12gowrishankar nayanaNo ratings yet
- Harini 2Document6 pagesHarini 2Chakri ChakradharNo ratings yet
- Bfs PDFDocument1 pageBfs PDFAnkita SahaNo ratings yet
- Lab Algorithm Assignment 8Document6 pagesLab Algorithm Assignment 8Pruthweesha SalianNo ratings yet
- Algo LearningDocument3 pagesAlgo Learningkarthi maniNo ratings yet
- Selection Sort Algo1Document3 pagesSelection Sort Algo1karthi maniNo ratings yet
- Exno 1,2Document3 pagesExno 1,2kpramya19No ratings yet
- Ai&ml RecordDocument57 pagesAi&ml Recordhemapardeep8No ratings yet
- # BFS Algorithm in Python: ImportDocument7 pages# BFS Algorithm in Python: ImportM annonymousNo ratings yet
- AI Practical FileDocument36 pagesAI Practical FileGourav PatelNo ratings yet
- Lab Manual: Spring 2021Document33 pagesLab Manual: Spring 2021Tariz ShahidNo ratings yet
- Lab Manual AI Lab VI SemDocument34 pagesLab Manual AI Lab VI SemYashika AggarwalNo ratings yet
- COMSATS University Islamabad, Lahore Campus: Lab Assignment 1 Statement - FALL 2021Document3 pagesCOMSATS University Islamabad, Lahore Campus: Lab Assignment 1 Statement - FALL 2021Tech TropNo ratings yet
- AIML MANUAL Word FinalDocument38 pagesAIML MANUAL Word FinalitnbaNo ratings yet
- Implement DFS and BFS Search AlgorithmDocument7 pagesImplement DFS and BFS Search AlgorithmYashaswini SNo ratings yet
- Social Media Influence AnalyzerDocument5 pagesSocial Media Influence AnalyzerVijay DpvNo ratings yet
- Aiml Exp 2 Adarsh PandeyDocument3 pagesAiml Exp 2 Adarsh Pandeyveer371karanNo ratings yet
- Practical 1Document2 pagesPractical 1Praju ThoratNo ratings yet
- Heuristic Search AlgorithmsDocument8 pagesHeuristic Search Algorithmsfaheemmahmood1No ratings yet
- Innoctf: 'Hex64' 'R' "" '/N' '' 'Innoctf (' 'Base64' 'Hex'Document8 pagesInnoctf: 'Hex64' 'R' "" '/N' '' 'Innoctf (' 'Base64' 'Hex'Srikanth SatyaNo ratings yet
- Ai LabDocument2 pagesAi Labಚೇತನ್ ಕುಮಾರ್No ratings yet
- Lab Assignment 2 Ai 2019bite045Document4 pagesLab Assignment 2 Ai 2019bite045SwatiNo ratings yet
- Lab Manual AI Lab VI SemDocument50 pagesLab Manual AI Lab VI SemNikhil KumarNo ratings yet
- Implementing Uninformed Search Techniques: CodeDocument6 pagesImplementing Uninformed Search Techniques: Codesarim shahzadNo ratings yet
- Cs-3491 Lab ManualDocument44 pagesCs-3491 Lab Manualpawim69917No ratings yet
- 20CSE020Document19 pages20CSE020mdabdullah2020805No ratings yet
- Final AI PR 15Document5 pagesFinal AI PR 15Sana PathanNo ratings yet
- CN Final FileDocument6 pagesCN Final FileBT20ECE021 MINALNo ratings yet
- Gen Shortest PTHDocument1 pageGen Shortest PTHdadanmakyokNo ratings yet
- P03 A Star Algorithm 35 Anushka ShettyDocument23 pagesP03 A Star Algorithm 35 Anushka ShettyanohanabrotherhoodcaveNo ratings yet
- BFS ExampleDocument6 pagesBFS ExampleAmara ManikantaNo ratings yet
- DFS BFS Assignment 49340 Maqbool AhmedDocument2 pagesDFS BFS Assignment 49340 Maqbool Ahmedmaqboolahmed0303No ratings yet
- Aiml Lab Manual 2023Document17 pagesAiml Lab Manual 2023shamilie17No ratings yet
- Lab Manual AI Lab VI SemDocument34 pagesLab Manual AI Lab VI SemAssoc.Prof, CSE , Vel Tech, ChennaiNo ratings yet
- AIML Manual DocDocument123 pagesAIML Manual DocGuna SeelanNo ratings yet
- OutputDocument65 pagesOutputit's technicalNo ratings yet
- OutputDocument65 pagesOutputit's technicalNo ratings yet
- AI JournalDocument33 pagesAI Journallaxman gupttaNo ratings yet
- AI Lab Report CSIT 4th SemesterDocument28 pagesAI Lab Report CSIT 4th SemesterHrideshNo ratings yet
DFS and BFS
DFS and BFS
Uploaded by
keerthi2k60 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
2 views2 pagesCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
DOC, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOC, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as doc, pdf, or txt
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
2 views2 pagesDFS and BFS
DFS and BFS
Uploaded by
keerthi2k6Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOC, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as doc, pdf, or txt
You are on page 1of 2
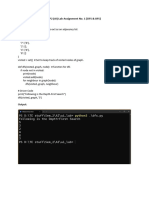
DFS:
# Using a Python dictionary to act as an adjacency list
graph = {
'5' : ['3','7'],
'3' : ['2', '4'],
'7' : ['8'],
'2' : [],
'4' : ['8'],
'8' : []
}
visited = set() # Set to keep track of visited nodes of graph.
def dfs(visited, graph, node): #function for dfs
if node not in visited:
print (node)
visited.add(node)
for neighbour in graph[node]:
dfs(visited, graph, neighbour)
# Driver Code
print("Following is the Depth-First Search")
dfs(visited, graph, '5')
OUTPUT:
Following is the Depth-First Search
5
3
2
4
8
7
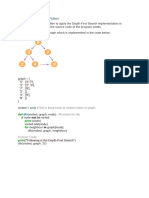
BFS:
'5' : ['3','7'],
'3' : ['2', '4'],
'7' : ['8'],
'2' : [],
'4' : ['8'],
'8' : []
}
visited = [] # List for visited nodes.
queue = [] #Initialize a queue
def bfs(visited, graph, node): #function for BFS
visited.append(node)
queue.append(node)
while queue: # Creating loop to visit each node
m = queue.pop(0)
print (m, end = " ")
for neighbour in graph[m]:
if neighbour not in visited:
visited.append(neighbour)
queue.append(neighbour)
# Driver Code
print("Following is the Breadth-First Search")
bfs(visited, graph, '5') # function calling
OUTPUT:
Following is the Breadth-First Search
537248
You might also like
- Untitled DocumentDocument2 pagesUntitled Documentdebasis nagNo ratings yet
- Ai Dfs Bfs PrintDocument2 pagesAi Dfs Bfs PrintAvadhut KaleNo ratings yet
- DFS & BFS Implementation in PythonDocument2 pagesDFS & BFS Implementation in PythonayushstwtNo ratings yet
- DFS Teb01Document2 pagesDFS Teb01utkarshNo ratings yet
- BFS DFSDocument3 pagesBFS DFSCO2061- Suyash ShishupalNo ratings yet
- Deatri Nari Ratih - Tugas WKBDocument7 pagesDeatri Nari Ratih - Tugas WKBDeatri Nari RatihNo ratings yet
- PROGRAMDocument4 pagesPROGRAMvijayyc5104No ratings yet
- AI Lab2 MustafaDocument2 pagesAI Lab2 MustafaMustafa AliasgharNo ratings yet
- AI lp2 DfsbfsDocument1 pageAI lp2 Dfsbfs03rajput.kiNo ratings yet
- AI Exp 3Document5 pagesAI Exp 3Ganesh PanigrahiNo ratings yet
- Assignmnet 1Document6 pagesAssignmnet 1Muhammad UsamaNo ratings yet
- Selection Sort Algo1Document3 pagesSelection Sort Algo1karthi maniNo ratings yet
- Ai Lab Manual 202PDocument23 pagesAi Lab Manual 202PBhuvana ThimmiReddyNo ratings yet
- BFS & DFSDocument6 pagesBFS & DFSsnehaguptavvNo ratings yet
- 19CS413 LabManualDocument42 pages19CS413 LabManualGurunathanNo ratings yet
- BFS Teb01Document2 pagesBFS Teb01utkarshNo ratings yet
- lab manual 3rd yrDocument5 pageslab manual 3rd yrSindhuNo ratings yet
- AI and ML Lab ManualDocument29 pagesAI and ML Lab ManualRoobesh RoobeshNo ratings yet
- Airline Removed MergedDocument12 pagesAirline Removed MergedOm PasalkarNo ratings yet
- Breadth First Search: # List For Visited Nodes. #Initialize A Queue #Function For BFSDocument31 pagesBreadth First Search: # List For Visited Nodes. #Initialize A Queue #Function For BFSdhruv kumarNo ratings yet
- Week 12Document1 pageWeek 12gowrishankar nayanaNo ratings yet
- Harini 2Document6 pagesHarini 2Chakri ChakradharNo ratings yet
- Bfs PDFDocument1 pageBfs PDFAnkita SahaNo ratings yet
- Lab Algorithm Assignment 8Document6 pagesLab Algorithm Assignment 8Pruthweesha SalianNo ratings yet
- Algo LearningDocument3 pagesAlgo Learningkarthi maniNo ratings yet
- Selection Sort Algo1Document3 pagesSelection Sort Algo1karthi maniNo ratings yet
- Exno 1,2Document3 pagesExno 1,2kpramya19No ratings yet
- Ai&ml RecordDocument57 pagesAi&ml Recordhemapardeep8No ratings yet
- # BFS Algorithm in Python: ImportDocument7 pages# BFS Algorithm in Python: ImportM annonymousNo ratings yet
- AI Practical FileDocument36 pagesAI Practical FileGourav PatelNo ratings yet
- Lab Manual: Spring 2021Document33 pagesLab Manual: Spring 2021Tariz ShahidNo ratings yet
- Lab Manual AI Lab VI SemDocument34 pagesLab Manual AI Lab VI SemYashika AggarwalNo ratings yet
- COMSATS University Islamabad, Lahore Campus: Lab Assignment 1 Statement - FALL 2021Document3 pagesCOMSATS University Islamabad, Lahore Campus: Lab Assignment 1 Statement - FALL 2021Tech TropNo ratings yet
- AIML MANUAL Word FinalDocument38 pagesAIML MANUAL Word FinalitnbaNo ratings yet
- Implement DFS and BFS Search AlgorithmDocument7 pagesImplement DFS and BFS Search AlgorithmYashaswini SNo ratings yet
- Social Media Influence AnalyzerDocument5 pagesSocial Media Influence AnalyzerVijay DpvNo ratings yet
- Aiml Exp 2 Adarsh PandeyDocument3 pagesAiml Exp 2 Adarsh Pandeyveer371karanNo ratings yet
- Practical 1Document2 pagesPractical 1Praju ThoratNo ratings yet
- Heuristic Search AlgorithmsDocument8 pagesHeuristic Search Algorithmsfaheemmahmood1No ratings yet
- Innoctf: 'Hex64' 'R' "" '/N' '' 'Innoctf (' 'Base64' 'Hex'Document8 pagesInnoctf: 'Hex64' 'R' "" '/N' '' 'Innoctf (' 'Base64' 'Hex'Srikanth SatyaNo ratings yet
- Ai LabDocument2 pagesAi Labಚೇತನ್ ಕುಮಾರ್No ratings yet
- Lab Assignment 2 Ai 2019bite045Document4 pagesLab Assignment 2 Ai 2019bite045SwatiNo ratings yet
- Lab Manual AI Lab VI SemDocument50 pagesLab Manual AI Lab VI SemNikhil KumarNo ratings yet
- Implementing Uninformed Search Techniques: CodeDocument6 pagesImplementing Uninformed Search Techniques: Codesarim shahzadNo ratings yet
- Cs-3491 Lab ManualDocument44 pagesCs-3491 Lab Manualpawim69917No ratings yet
- 20CSE020Document19 pages20CSE020mdabdullah2020805No ratings yet
- Final AI PR 15Document5 pagesFinal AI PR 15Sana PathanNo ratings yet
- CN Final FileDocument6 pagesCN Final FileBT20ECE021 MINALNo ratings yet
- Gen Shortest PTHDocument1 pageGen Shortest PTHdadanmakyokNo ratings yet
- P03 A Star Algorithm 35 Anushka ShettyDocument23 pagesP03 A Star Algorithm 35 Anushka ShettyanohanabrotherhoodcaveNo ratings yet
- BFS ExampleDocument6 pagesBFS ExampleAmara ManikantaNo ratings yet
- DFS BFS Assignment 49340 Maqbool AhmedDocument2 pagesDFS BFS Assignment 49340 Maqbool Ahmedmaqboolahmed0303No ratings yet
- Aiml Lab Manual 2023Document17 pagesAiml Lab Manual 2023shamilie17No ratings yet
- Lab Manual AI Lab VI SemDocument34 pagesLab Manual AI Lab VI SemAssoc.Prof, CSE , Vel Tech, ChennaiNo ratings yet
- AIML Manual DocDocument123 pagesAIML Manual DocGuna SeelanNo ratings yet
- OutputDocument65 pagesOutputit's technicalNo ratings yet
- OutputDocument65 pagesOutputit's technicalNo ratings yet
- AI JournalDocument33 pagesAI Journallaxman gupttaNo ratings yet
- AI Lab Report CSIT 4th SemesterDocument28 pagesAI Lab Report CSIT 4th SemesterHrideshNo ratings yet