Professional Documents
Culture Documents
EG11_Heath
EG11_Heath
Uploaded by
bhanukafelixCopyright:
Available Formats
You might also like
- Rhivda-Rapid Hiv Diagnostic AlgorithmDocument12 pagesRhivda-Rapid Hiv Diagnostic Algorithmninafatima allam100% (2)
- Basic Immunology Functions and Disorders of Immune System PDFDocument3 pagesBasic Immunology Functions and Disorders of Immune System PDFMusa TadzNo ratings yet
- Bio Project - 1 InvestigatoryDocument12 pagesBio Project - 1 Investigatoryanonymous user 345No ratings yet
- Understanding The Self Part 2 The Sexual SelfDocument8 pagesUnderstanding The Self Part 2 The Sexual SelfRemart DejosNo ratings yet
- NSTPDocument2 pagesNSTPBernadette ArrojoNo ratings yet
- Exually Ransmitted IseasesDocument52 pagesExually Ransmitted Iseasesjanjan eresoNo ratings yet
- Bio ProjectDocument13 pagesBio ProjectKarishma TiwariNo ratings yet
- Sexual Trasmission DiseaseDocument9 pagesSexual Trasmission Diseasevivekanand100% (2)
- Sex Stories IndonesiaDocument3 pagesSex Stories IndonesiausahamerekaNo ratings yet
- Sexual Health STDs ppt1Document90 pagesSexual Health STDs ppt120154712No ratings yet
- Remulta ExamDocument3 pagesRemulta Examgerone remultaNo ratings yet
- Health 8: Issues and Problems Related To Human SexualityDocument14 pagesHealth 8: Issues and Problems Related To Human SexualityAizel Mae Consas /Amado HernandezNo ratings yet
- What Is SyphilisDocument12 pagesWhat Is SyphilisBheru LalNo ratings yet
- STD 101Document42 pagesSTD 101Clarice BedicoNo ratings yet
- Chapter 4 Communicable DiseaseDocument33 pagesChapter 4 Communicable DiseaseAyro Business CenterNo ratings yet
- Grade 8Document89 pagesGrade 8Regie Apilado Cayosa100% (1)
- Sexually Transmitted DiseaseDocument3 pagesSexually Transmitted DiseaseKim FresnilloNo ratings yet
- Report in HS - HIV and AIDSDocument29 pagesReport in HS - HIV and AIDSJolina Mae NatuelNo ratings yet
- STDs HIVsAIDsDocument26 pagesSTDs HIVsAIDsMarco AvenillaNo ratings yet
- Issues and Problems Related To Human SexualityDocument23 pagesIssues and Problems Related To Human SexualityGeeya Mariel AntonioNo ratings yet
- UTS-STDs-TOMAS SF. COLARINADocument15 pagesUTS-STDs-TOMAS SF. COLARINAAngela Kim T. DaragNo ratings yet
- Sexually Transmitted DiseasesDocument9 pagesSexually Transmitted DiseasespromiseNo ratings yet
- 3 Percent: Ivy Marie R. Maratas BSED Mathematics 1-2 Understanding The Self (GE 1)Document8 pages3 Percent: Ivy Marie R. Maratas BSED Mathematics 1-2 Understanding The Self (GE 1)Ivy Marie MaratasNo ratings yet
- Hiv Aids: Presented By: Chavez - Galang - Kaur - Noguera 2DcnDocument24 pagesHiv Aids: Presented By: Chavez - Galang - Kaur - Noguera 2DcnKate ChavezNo ratings yet
- Term PaperDocument11 pagesTerm PaperclarencecalignerNo ratings yet
- Sexually Transmitted DiseasesDocument4 pagesSexually Transmitted DiseasesTamilore WilliamsNo ratings yet
- Student WorkDocument12 pagesStudent Workapi-376705276No ratings yet
- Lesson 10: Sexually Transmitted Disease Types of StdsDocument19 pagesLesson 10: Sexually Transmitted Disease Types of StdsJeya Plays YTNo ratings yet
- Sexually Transmitted DiseasesDocument76 pagesSexually Transmitted Diseasessomaya abdulhakimNo ratings yet
- Sexually Transmitted Infections PowerpointDocument12 pagesSexually Transmitted Infections Powerpointkriss ellisNo ratings yet
- Quiz Answer Key: Personal Health SeriesDocument3 pagesQuiz Answer Key: Personal Health SeriesYehla marie ArnaizNo ratings yet
- Case Study On SyphillisDocument18 pagesCase Study On Syphillisdia_pee100% (1)
- Understanding Sexually Transmitted Diseases (STD) : A Guidebook To Better Sexual Health (Men) - Free EbookDocument22 pagesUnderstanding Sexually Transmitted Diseases (STD) : A Guidebook To Better Sexual Health (Men) - Free EbookDr Tan & PartnersNo ratings yet
- Human Immunodeficiency Virus (HIV)Document7 pagesHuman Immunodeficiency Virus (HIV)Ambar WulanNo ratings yet
- Health 9 Venereal Diseases: - Caused by A Bacteria Named Chlamydia TrachomatisDocument8 pagesHealth 9 Venereal Diseases: - Caused by A Bacteria Named Chlamydia TrachomatisClaire MedianaNo ratings yet
- Term PaperDocument13 pagesTerm PaperclarencecalignerNo ratings yet
- Aids:: (Acquired Immune Deficiency Syndrome)Document6 pagesAids:: (Acquired Immune Deficiency Syndrome)Farwa DarNo ratings yet
- 1 Summarization-Updated (AutoRecovered)Document6 pages1 Summarization-Updated (AutoRecovered)Joan SevillaNo ratings yet
- Gay Sex and Risk Booklet WebDocument36 pagesGay Sex and Risk Booklet WebryasakijilhaniNo ratings yet
- Being An HFLE Teacher Portfolio1Document23 pagesBeing An HFLE Teacher Portfolio1raianna rogersNo ratings yet
- STD OutlineDocument16 pagesSTD OutlineLory TangpusNo ratings yet
- UntitledDocument40 pagesUntitledHam FeliasNo ratings yet
- 7 Most Common Sexually Transmitted DiseasesDocument3 pages7 Most Common Sexually Transmitted DiseasesTrixon B. LapidNo ratings yet
- The Basics: Cervical Cancer PregnancyDocument9 pagesThe Basics: Cervical Cancer PregnancyOm DarnalNo ratings yet
- Sexually Transmitted Disease or STI Complete SymtomsDocument11 pagesSexually Transmitted Disease or STI Complete SymtomsPowerzNo ratings yet
- Hiv/AidsDocument5 pagesHiv/Aidspaulporras93No ratings yet
- Human Immunodeficiency Virus Infection / Acquired Immunodeficiency Syndrome (HIV/AIDS) IsDocument4 pagesHuman Immunodeficiency Virus Infection / Acquired Immunodeficiency Syndrome (HIV/AIDS) IsL.a.ZumárragaNo ratings yet
- Basic Facts On HIVDocument16 pagesBasic Facts On HIVTimon AgarNo ratings yet
- Sexually Transmitted DiseaseDocument38 pagesSexually Transmitted Diseaserana arslanNo ratings yet
- Expose AidsDocument7 pagesExpose AidsKouadio Bi RichardNo ratings yet
- Adapted From: Sexually Transmitted Infections Pamphlet. Public Health Agency of Canada, 2007Document25 pagesAdapted From: Sexually Transmitted Infections Pamphlet. Public Health Agency of Canada, 2007Mohamoud MohamedNo ratings yet
- The Difference Between HIV and AidsDocument14 pagesThe Difference Between HIV and AidsAnonymous bq4KY0mcWGNo ratings yet
- Group 6Document12 pagesGroup 6Joy VillafloresNo ratings yet
- All About Sti/Hiv/Aids: Some Signs & Symptoms of StiDocument6 pagesAll About Sti/Hiv/Aids: Some Signs & Symptoms of StiTang InaNo ratings yet
- Edwin Mwangi Zool 143 Assgn. 3Document4 pagesEdwin Mwangi Zool 143 Assgn. 3nattydreadfathelahNo ratings yet
- Group8 Sexually Transmitted InfectionDocument10 pagesGroup8 Sexually Transmitted InfectionSheika Briones GalletaNo ratings yet
- A Simple Guide To Sexually Transmitted Infections, Diagnosis, Treatment And Related ConditionsFrom EverandA Simple Guide To Sexually Transmitted Infections, Diagnosis, Treatment And Related ConditionsRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (3)
- A Simple Guide to Sexually Transmitted DiseasesFrom EverandA Simple Guide to Sexually Transmitted DiseasesRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (9)
- The Complete Guide To HIV / AIDs: Symptoms, Diagnosis, Risks, Treatments & SupportFrom EverandThe Complete Guide To HIV / AIDs: Symptoms, Diagnosis, Risks, Treatments & SupportNo ratings yet
- The Complete Guide to Syphilis: Symptoms, Risks, Diagnosis & TreatmentsFrom EverandThe Complete Guide to Syphilis: Symptoms, Risks, Diagnosis & TreatmentsNo ratings yet
- Alere Hiv ComboDocument1 pageAlere Hiv ComboJohn Mark PamittanNo ratings yet
- Answers: TEST - 9 (Code-A) All India Aakash Test Series For Medical-2016Document19 pagesAnswers: TEST - 9 (Code-A) All India Aakash Test Series For Medical-2016Miss Jasmine0% (1)
- HIV 12 Stat Pak Dipstick Product Packet EnglishDocument6 pagesHIV 12 Stat Pak Dipstick Product Packet EnglishSagkyNo ratings yet
- Diseases & Immunity 1 QPDocument7 pagesDiseases & Immunity 1 QPbdb6wxhyxfNo ratings yet
- The AIDS Fighters - Brighthope, Ian Fitzgerald, PeterDocument196 pagesThe AIDS Fighters - Brighthope, Ian Fitzgerald, Peterpdf ebook free download100% (1)
- Pathogenic Properties of VirusesDocument12 pagesPathogenic Properties of VirusesAnika Yasmin 2012965048No ratings yet
- Doctor Letterhead 6Document1 pageDoctor Letterhead 6ziya mehraNo ratings yet
- Scientific American 1993-2013 Article IndexDocument147 pagesScientific American 1993-2013 Article IndexamlferreiraNo ratings yet
- Chapter 12 - Congenital and Acquired ImmunodeficienciesDocument11 pagesChapter 12 - Congenital and Acquired ImmunodeficienciesFYMNo ratings yet
- Hiv/Aids Law: Harvey Mher M. RarangDocument2 pagesHiv/Aids Law: Harvey Mher M. RarangHarvey Mher RarangNo ratings yet
- Rates of Molecular Evolution in RNA Viruses: A Quantitative Phylogenetic AnalysisDocument10 pagesRates of Molecular Evolution in RNA Viruses: A Quantitative Phylogenetic AnalysisImperialAquillaNo ratings yet
- Immunoassay Quick Ref. GuideDocument25 pagesImmunoassay Quick Ref. GuideকাজীসামাদNo ratings yet
- DR Anil Dissertation 2014Document144 pagesDR Anil Dissertation 2014Syed FurqanNo ratings yet
- Cal Cont Enz Sub p400 enDocument30 pagesCal Cont Enz Sub p400 enLince WijoyoNo ratings yet
- Introduction of Rapid Syphilis Testing in Antenatal Care: A Systematic Review of The Impact On HIV and Syphilis Testing Uptake and CoverageDocument28 pagesIntroduction of Rapid Syphilis Testing in Antenatal Care: A Systematic Review of The Impact On HIV and Syphilis Testing Uptake and CoveragezahiraNo ratings yet
- Suppression of Human Immunodeficiency Virus Replication by Ascorbate in Chronically and Acutely Infected Cells.Document5 pagesSuppression of Human Immunodeficiency Virus Replication by Ascorbate in Chronically and Acutely Infected Cells.Hector Javier Chavez RamirezNo ratings yet
- Virology - Exam 2 - ZipgradeDocument4 pagesVirology - Exam 2 - ZipgradeFelix NepumocenoNo ratings yet
- Bhavya-Reflective EssayDocument10 pagesBhavya-Reflective EssayKumar Creative ContentsNo ratings yet
- Case StudyDocument10 pagesCase StudyAdelle SmithNo ratings yet
- Ketiga 1 3 EngDocument14 pagesKetiga 1 3 EngAulia putriNo ratings yet
- Autophagy and CancerDocument349 pagesAutophagy and CancerSohibun21No ratings yet
- 3 Murex HIV Ag Ab CombinationDocument7 pages3 Murex HIV Ag Ab CombinationElias Dii Rivas GarvanNo ratings yet
- Module 7 - Health-and-Promotion-and-EducationDocument7 pagesModule 7 - Health-and-Promotion-and-EducationPascua, Aliah M.No ratings yet
- Dr. Dalia El-Shafei: Assistant Professor, Community Medicine Department, Zagazig UniversityDocument51 pagesDr. Dalia El-Shafei: Assistant Professor, Community Medicine Department, Zagazig UniversityArpit MahoreNo ratings yet
- Covid Vaccine Risks PDFDocument16 pagesCovid Vaccine Risks PDFIrmgart Jedamski Mitchell100% (2)
- All DrugsDocument482 pagesAll DrugsJessica IbañezNo ratings yet
- Exam Quest Special 2023Document24 pagesExam Quest Special 2023Yalvant YadavNo ratings yet
- Questionsheet 1: Disease / Immunology A2.15Document6 pagesQuestionsheet 1: Disease / Immunology A2.15Nabindra RuwaliNo ratings yet
EG11_Heath
EG11_Heath
Uploaded by
bhanukafelixCopyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
EG11_Heath
EG11_Heath
Uploaded by
bhanukafelixCopyright:
Available Formats
Let us prevent sexually
17 transmitted diseases
A sexually transmitted disease (STD), is a disease that is contracted from a
sexual encounter with a person who is already infected with the disease. They can be
contracted from an unprotected sexual encounter, sharing needles and unscreened
blood transfusion. Sexually transmitted diseases are also spreading rapidly across
the world. Unfortunately, adolescents contract these diseases due to lack of proper
knowledge about them. Therefore it is important to know about STDs to prevent
from contracting and spreading STDs
In the previous grades you learnt about communicable and non-communicable
diseases and methods of preventing them by leading a healthy lifestyle.
In this lesson, you will learn about sexually transmitted diseases and preventive
measures.
Sexually transmitted diseases
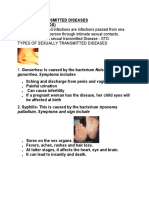
Gonorrhoea
Signs of disease
- A white discharge or secretion from a man’s penis or a burning sensation or pain
during urination.
- In females, occasionally a discharge or secretion from the vagina is seen, but
this is rare.
- Females do not show signs of infection in the early stages.
- A baby can get infected from an infected mother during birth. The baby’s eyes
can be affected leading to loss of sight.
Figure 17.1
186 For Free Distribution.
Genital Herpes
This can be transmitted during vaginal intercourse with an infected person as
well as from kissing, or having oral or anal intercourse with such a person.
Once the virus enters the body, it will be in your system for life and symptoms
will manifest on and off.
Signs of disease
- It starts with liquid filled bubbles and lead to painful wounds
- It takes between 10-14 days for the initial wounds to heal
- Pain or burning sensation when urinating
- Fever
- If a healthy person comes into contact with herpes bubbles that contain the virus,
he may get infected.
Figure 17.2
The disease may occur even after an initial cure due to the following:
• Stress and fatigue
• Fever and other severe infections
• Menstruation
• Certain medicines
• Pregnancy
• Any from of immune deficiency
Although can be controlled, a cure has not been discovered for genital herpes as
yet.
Syphilis
Symptoms appear between 9-90 days after being infected. Syphilis is contracted
chiefly by infection during sexual intercourse, but can pass on to a baby during
pregnancy.
This can be transmitted via unscreened blood transfusions too.
For Free Distribution. 187
Symptoms and signs
- Painless lesion around or in the genitalia
- Inflammation of inguinal lymph nodes
Figure 17.3
If proper treatment is not taken early, symptoms may manifest again after six
months.
Chlamydia
Chlamydia can be transmitted through vaginal, anal or oral intercourse.
There is a possibility of a child born to an infected mother becoming blind.
Symptoms and signs
- Discharge from vagina penise
- Pain or burning sensation during urination
- Cervix is affected, manifestation of symptoms is delayed in females
- Inflammation of area around the genitalia in males
Genital warts
Symptoms
- Warts that look like small pinkish scales are seen in groups of two or more or
individually in areas around the vagina and penis
- In case of anal intercourse, the warts may appear around the anus, and in case
of oral sex, they may appear around the mouth
- May be a cause for cervical cancer.
This condition can be managed, but it cannot be permanently cured.
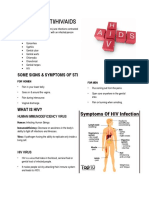
HIV/AIDS
HIV/AIDS is caused by the human immunodeficiency virus.
Let us concentrate more on HIV/AIDS that has become a major problem.
188 For Free Distribution.
HIV/AIDS
Methods of transmission
1. Due to unprotected sexual intercourse (among homosexual or heterosexual
persons)
2. Via unscreened blood transfusions
3. From an infected mother to children:
- during pregnancy
- during delivery of baby
- through breast milk
4. Using unsterilised needles (injection) by oneself or in a group
eg: using drugs, creating body tattoos.
Illnesses are prevented by the body’s own immune system by destroying germs.
When infected with HIV, the immune system gets weak and the body becomes
more susceptible to illnesses.
The symptoms of HIV manifest from 3-12 years after the virus enters the body.
It may take even 10 years to manifest symptoms. Gradually, the body’s immunity
decreases. Due to this weakened immunity, other illnesses are contracted which can
lead to death.
Any type of infection will make an AIDS patient very ill. Symptoms manifest
depending on the type of infection.
Symptoms
► Loss of weight in a short period
► Diarrhoea lasting a long time
► Fever lasting for more than a month
► Tuberculosis
► Pneumonia
In addition,
- breathlessness, fatigue and cough lasting a long time
- inflammation of neck and axillary glands
For Free Distribution. 189
- oral candidiasis
- night sweats
- loss of appetite
A large number of people are unaware that they are infected with HIV as it takes a
long time for symptoms to manifest
The HIV virus cannot survive in a normal environment. It can survive in living cells
only. The virus is predominantly present in the blood of an infected person.
Other secretions where on the virus can be found
- Semen
- Cervical and vaginal secretions
- Breast milk
Small quantities of the virus can be present in saliva, tears, sweat, urine and faeces,
but illness cannot be transmitted from these secretions.
AIDS is not transmitted by:
- shaking hands
- mosquitoes
- kissing and embracing
- playing group sports
- sharing the utensils such as cups, plates,towels etc
- sharing the same household, bed etc
- sputum, nasal secretion and saliva
- toilets
When HIV enters the body, it grows rapidly and produces antibodies.
When AIDS was first identified, it was found that three times more men than women
were infected. At present both males and females are equally infected.
Women are three to nine times more likely than men to get infected with AIDS
because the wall of the vagina is thin and also after intercourse, sperm remain in the
vagina for a relatively long period. Further, semen contains more virus than vaginal
190 For Free Distribution.
secretions thus women are more likely to get AIDS than males.
Inadequate support from sexual partner to prevent the spreading of AIDS makes it
a serious concern.
Women face many problems within the family and society when they get infected
with HIV.
A newborn of an infected mother is likely to be infected. If both parents are affected
they may die prematurely and their children become orphans. This is likely to
become a major social issue.
Detecting HIV infection
1' Blood tests to detect HIV antibodies
There are two tests available:
i' ELISA Test
ii' Rapid Test
If either of these tests is positive for HIV, a further confirmatory test has to
be performed as these are only screening tests. They cannot detect HIV during the
first three months which is called the window period.
2. -Confirmatory test
-Western Blot test
Importance of HIV testing
1. Once diagnosed as infected with HIV, ART (Anti Retroviral Therapy) can be
given
2. By taking ART, quality of life and life span can be increased
3. When proper treatment is taken, the concentration of the virus is reduced and
the chances of infecting another person is become minimal
4. By identifying infected people, the illness can be prevented from spreading
5. By taking ARV (antiretroviral drugs), maternal transmission of the virus during
pregnancy and breastfeeding can be reduced.
For Free Distribution. 191
If you have had unprotected sexual intercourse, it is important that you
get tested for HIV. Testing for HIV is done at all veneraeology clinics in
government hospitals island-wide free of charge and confidentiality is
maintained.
Prevention of HIV and other sexually transmitted diseases
1. Postpone sexual activities until marriage
2. Limit sexual activities only to your spouse
3. Refrain from unsafe sexual activities
4. Identify risky situations in society and protect yourself from them
5. Maintain a strong family unit
6. If you suspect you have a sexually transmitted disease discuss with a doctor
immediately
7. If you have a sexually transmitted disease take medication
8. Avoid sexual activity during an infected period
9. Avoid using illicit substances
People who have a higher likelihood of being infected with HIV
and other sexually transmitted diseases
- Commercial sex workers
- Those with multiple sexual partners
- People who engage in homosexual activities
- People who have warts or wounds on their genitalia
- People who share needles to inject illicit substances
- Offspring of HIV positive mothers
Activity
Write an essay on the effect of sexually transmitted diseases on biology,
economy and culture.
People who are HIV positive can have many psychological problems and emotions
such as shame, anger, suspicion, stress and fear.
192 For Free Distribution.
Summary
Sexually transmitted diseases are transmitted during sexual activity between an
infected person and a healthy person.
Common sexually transmitted diseases are syphilis, herpes, gonorrhoea, chlamydia,
genital warts and HIV/AIDS.
AIDS is a dangerous illness that weakens the immune system and makes people
more vulnerable to other illnesses.
Sexually transmitted diseases also give rise to physical, psychological and social
problems.
The best way to prevent contracting sexually transmitted diseases is to engage in
safe and healthy sexual practices.
Exercise
1. Name four common sexually transmitted diseases
2. Name four ways AIDS can be transmitted
3. Name the tests that identify and confirm HIV
4. Name four reasons why HIV testing is important
5. Name four ways of preventing sexually transmitted diseases.
For Free Distribution. 193
Glossary
abortion .íidj P¸a]øuÄ
acceleration ;ajrKh Bº•kPÀ
acquired immune deficiency k;= lr .;a m%;sYla;s W!kkd ÷|õ´ Gvº¨¦a \UvU
syndrom (AIDS) iy ,laIKh SøÓ£õkPÎß AÔSÔ
adolescence kj fhdjqka úh PmiÍø©¨ £¸Á®
aerobic iajdhq PõØÖa _Áõ\®
agility W,eÕs;dj x›u®
anaerobic ks¾jdhq _¯õwÚ GÔøP
angle of release uqodyeÍfï fldaKh ÂkøPU ÷Põn®
angle of take-off kslaófï fldaKh ªvzöuÊ® ÷Põn®
anti oxidant m%;s Tlaisldrh Jm] Gv›
antibody m%;sfoayh ÷|õ´ Gvº¨¦a \Uv
antiretroviral drugs (ARV) m%;sffjria T!IO øÁµ_ Gvº¨¦ ©¸¢x
approach run wj;S¾K Odjkh Ki AqSuÀ
athlete bib ;r. wxlh ÷£õmi C»UP[PÒ
attack wdl%uKh uõUSuÀ
balance iunr;dj \©{ø»
ball in play mkaÿj lS%vdfõ fhfok wjia:d £¢x ÂøͯõmiÀ
Dk£kzu¨£k® \¢uº¨£[PÒ
ball out of play mkaÿj lS%vdfõ fkdfhfok £¢x ÂøͯõmiÀ
wjia:d Dk£kzu¨£hõu \¢uº¨£[PÒ
bio diversity ffcj úúO;ajh E°›¯À £ÀÁøPø©
biological factor Ôj úoHd;aul idOlh E°›¯Ø Põµo
biomechanic principle Ôj hdka;% uQ,O¾uh EhØöÓõȼ¯À ÷Põm£õkPÒ
centre of gravity .=re;aj flakaøh ¦Â±º¨¦ ø©¯®
clearing the hurdle lvq,a, ;rKh uøhø¯z uõskuÀ
conditioned reflex ;;ajdfrdams; m%;Slh ©søh÷¯õmkz öu›ÂøÚ
controlling the ball mkaÿ md,kh £¢øuU Pmk¨£kzuÀ
coordination iudfhdackh Jzvø\
corner kick fldka myr ‰ø» Eøu
corner post fldka lKqj ‰ø»U P®£®
critical thinking úpdrYS,S Ñka;kh ]Ó¢u ]¢uøÚ BØÓÀ
cross-over yria md ;eîu £õu[PøÍU SÖUPõP øÁzuÀ
crouch start l=ÿ werUqu SÖ®¦Ó¨£õk
direct free kick Rcq ksoyia myr ÷|º _¯õwÚ Eøu
194 For Free Distribution.
driblling the ball mkaÿj mdofhka /f.k hdu £¢øu EøuzuÀ
dye j¾Kldrlh {Ó‰mi
early childhood fmr <ud úh •ß ¤Òøͨ £¸Á®
effector ldrlh PnzuõUP®
effort wdhdih _Ǽh®
empathy iylïmkh £›ÄnºÄ
fast twitch fibres (FTF) fõ.fhka l%shd lrk ;ka;= ÂøµÁõP C¯[S® uø\ |õº
field defending msáh /lSu ø©uõÚ® PõzuÀ
field event msáfha ;r.h ø©uõÚ {PÌa]
flavour rildrlh _øÁ³mi
flight .=jka .; ùu £ÓzuÀ {ø»
follower wkq.dñlhd ¤ß£ØÖ|º
food allergy wdydr wid;añl;dj EnÄ JÆÁõø©
food adulteration wdydr nd, lsÍu EnÄU |g\õuÀ
food safety wdydrj, fi!LHdrlaIs;nj EnÄU Põ¨¦
foot print md i,l=K £õuzuh¯[PÒ
foot work mdo yqrej £õu Aø\Ä
force n,h Á¾
free kick ksoyia myr ªvzuÀ
free pass ksoyia hejqu _¯õwÚ Eøu
fulcrum Orh GzuÚ®
goal úÿï lKqj ÷£Ö
goal kick f.da,a myr ÷£ØÖUS Eøu
goal post f.da,a lKqj ÷£ØÖU P®£®
heading the ball mkaÿjg ysiska myr §u £¢øua ö\õmia ö\À¾uÀ
health promotion fi!LH m%j¾Okh _Põuõµ ÷©®£õk
hight of release uqodyeÍfï Wi ÂkøP E¯µ®
hight of take-off kslaófï Wi ªvzöuÊ® E¯µ®
hop l=kaÿj öP¢xuÀ
human resourse udkj iïm;a ©Ûu ÁÍ®
indirect free kick wkshï ksoyia myr ÷|›À _¯õwÚ
inertia wjiaÓ;sh \hzxÁ®
ingredients wvx.= øjH £uõºzu®
instant food CI‚l wdydr Ehß EnÄ
jungle craft jk Ys,amh ÁÚ ~m£®
For Free Distribution. 195
jungle exploration le,E .fõIKh ÁÚ B´Ä
junk food ksire wdydr Ehß EnÄPÒ
kick off` md werUqu ÷£õmi Bµ®£®
kicking the ball mkaÿjg mdofhka myr §u £¢øu uø»¯õ»izuÀ
knockout tournament meros ms<su,qka msgq ±lSfï »PÀ •øÓ {µØ ÷£õmi
l%uh$bj; ,Efï l%uh
land mark u. i,l=K £¯n¨ £õøu Aøh¯õÍ[PÒ
landing m;s; ùu {»®£hÀ
late childhood miq <udúh £¢øu EøuzuÀ
league tournament idl,H l%uh _ÇØ] •øÓ {µØ ÷£õmi
lever ,Sjrh DµÀ
line of gravity .=re;aj f¾Ldj ¦Â±º¨¦U ÷Põk
load Ndrh _ø©
middle age ueÈ úh |kzuµ Á¯x
momentum .uH;dj E¢u®
mountaineering l÷ ;rKh ©ø»÷¯ÖuÀ
neonatal period kjc wjêh ]_¨£¸Á®
off side ksis fkdjk ia:dkh E›zuØÓ Ch®
old age jeäysá úh •xø©
opposing player ms<su,a l%Säldj Gvµo°Úº
penalty area o`vqjï m%foaYh ush¨ ¤µ÷u\®
penalty kick o`vqjï myr ush Eøu
penalty pass o~qjï hejqu ush GÔøP
penalty shot o`vqjï úÿu ush G´øP
physical fitness YdÍßl fhda.H;dj EhØÓøPø©PÒ
power cjh Á¾
power position cj bßhõj Á¾ {ø»
prenatal period mQ¾j m%ij wjêh •Ø¤µ\Á¨ £¸Á®
processed food msßhï lrk ,o wdydr £u¨£kzu¨£mh EnÄ
projectile m%laIsma;h E¢x Âø\
projection m%lafIamKh øP ÂkøP
public health inspector (PHI) uyck fi!LH mÍCIl ö£õxa _Põuõµ £›÷\õuPº
quality of life Ôú;fha .=Kd;aulNdjh ÁõÌUøPz uµ®
reaction speed m%;sl%shd fõ.h ©ÖuõUP ÷ÁP®
receptor m%;s.%dylh ysi
196 For Free Distribution.
recovery (follow through) mYapd;a bßhõj Ehßöuõhº {ø»
reflex m%;Sl l%shdj öuÔÂøÚ
reflex arc m%;Sl pdmh öu›ÂÀ
road map ud¾. is;shu Ãv Áøµ¦
road sign ud¾. ix{dj Ãva \ªgø\
running exersice Odjk wNHdi Kmh¨£°Ø]
running track Odjk m:h Kk £õøu
school sanitation survey mdi,a ikSmdrlaIl iólaIKh £õh\õø» _Põuõµ¨ £›÷\õuøÚ
self awarenss wd;audjfndaOh _¯ ÂȨ¦nº¦
service msßkeóu £ozuÀ
sexual harrassment ,sx.sl wmpdrh £õ¼¯À x褵÷¯õP®
slow twitch fibres (STF) fifuka l%shd lrk ;ka;= ö©xÁõP C¯[S® uø\ |õº
standing start ysá werUqu {ßÓ {ø»¨ ¦Ó¨£õk
starting block wdrïNl mqjrej öuõhUPU Pmøh
step mshjr ªvzuÀ
supporting base wdOdrl m;=, uõ[S® £õu®
take off kslaóu ªvzöuÇÀ
toss up fofofkl= w;r mkaÿj Wv ÷©ö»ÔøP
±óu
tournament ;r.dj,sh ÷£õmi
toxin OQ,l PÈÄPÒ
trajectory mrdjl%h £µÁøÍÄ
trow-in ;=<g úis lsÍu EÒ GÔøP
velocity of release uqodyeÍfï fõ.h ªvzöuÊ® ÷ÁP®
velocity of take-off kslaófï fõ.h ªvzöuÊ® ÷ÁP®
youth ;reK úh Áõ¼£¨ £¸Á®
For Free Distribution. 197
Lesson Sequence
Lesson in text book Competency No. of
level Periods
1st term
1. Let us build a healthy society 1.1 6
2. Let us identify stages after childhood 2.1 5
3. Let us identify principles of biomechanics to maintain correct postures 3.1 3
4. Let us play volleyball 4.1 4
5. Let us play netball 4.2 4
6. Let us play football 4.3 4
2nd term
7. Let us manipulate equipment adapting correct postures 3.2 2
8. Let us engage in outdoor activities 4.4 2
9. Let us learn about running events in athletics 5.1, 5.2, 5.3 8
10. Let us cooperate in management and organizing through sports 6.1, 6.2 6
11. Let us consume nutritious food for a healthy life 7.1, 7.2 10
3rd term
12. Let us learn about jumping and throwing events in athletics 5.4, 5.5 4
13. Let us understand the musculoskeletal system 8.1 8
14. Let us maintain fitness related to motor skills 9.1 2
15. Let us maintain good interpersonal relationships 9.2 5
16. Let us identify the challenges in adolescence 10.1 4
17. Let us prevent sexually transmitted diseases 10.2 4
198 For Free Distribution.
You might also like
- Rhivda-Rapid Hiv Diagnostic AlgorithmDocument12 pagesRhivda-Rapid Hiv Diagnostic Algorithmninafatima allam100% (2)
- Basic Immunology Functions and Disorders of Immune System PDFDocument3 pagesBasic Immunology Functions and Disorders of Immune System PDFMusa TadzNo ratings yet
- Bio Project - 1 InvestigatoryDocument12 pagesBio Project - 1 Investigatoryanonymous user 345No ratings yet
- Understanding The Self Part 2 The Sexual SelfDocument8 pagesUnderstanding The Self Part 2 The Sexual SelfRemart DejosNo ratings yet
- NSTPDocument2 pagesNSTPBernadette ArrojoNo ratings yet
- Exually Ransmitted IseasesDocument52 pagesExually Ransmitted Iseasesjanjan eresoNo ratings yet
- Bio ProjectDocument13 pagesBio ProjectKarishma TiwariNo ratings yet
- Sexual Trasmission DiseaseDocument9 pagesSexual Trasmission Diseasevivekanand100% (2)
- Sex Stories IndonesiaDocument3 pagesSex Stories IndonesiausahamerekaNo ratings yet
- Sexual Health STDs ppt1Document90 pagesSexual Health STDs ppt120154712No ratings yet
- Remulta ExamDocument3 pagesRemulta Examgerone remultaNo ratings yet
- Health 8: Issues and Problems Related To Human SexualityDocument14 pagesHealth 8: Issues and Problems Related To Human SexualityAizel Mae Consas /Amado HernandezNo ratings yet
- What Is SyphilisDocument12 pagesWhat Is SyphilisBheru LalNo ratings yet
- STD 101Document42 pagesSTD 101Clarice BedicoNo ratings yet
- Chapter 4 Communicable DiseaseDocument33 pagesChapter 4 Communicable DiseaseAyro Business CenterNo ratings yet
- Grade 8Document89 pagesGrade 8Regie Apilado Cayosa100% (1)
- Sexually Transmitted DiseaseDocument3 pagesSexually Transmitted DiseaseKim FresnilloNo ratings yet
- Report in HS - HIV and AIDSDocument29 pagesReport in HS - HIV and AIDSJolina Mae NatuelNo ratings yet
- STDs HIVsAIDsDocument26 pagesSTDs HIVsAIDsMarco AvenillaNo ratings yet
- Issues and Problems Related To Human SexualityDocument23 pagesIssues and Problems Related To Human SexualityGeeya Mariel AntonioNo ratings yet
- UTS-STDs-TOMAS SF. COLARINADocument15 pagesUTS-STDs-TOMAS SF. COLARINAAngela Kim T. DaragNo ratings yet
- Sexually Transmitted DiseasesDocument9 pagesSexually Transmitted DiseasespromiseNo ratings yet
- 3 Percent: Ivy Marie R. Maratas BSED Mathematics 1-2 Understanding The Self (GE 1)Document8 pages3 Percent: Ivy Marie R. Maratas BSED Mathematics 1-2 Understanding The Self (GE 1)Ivy Marie MaratasNo ratings yet
- Hiv Aids: Presented By: Chavez - Galang - Kaur - Noguera 2DcnDocument24 pagesHiv Aids: Presented By: Chavez - Galang - Kaur - Noguera 2DcnKate ChavezNo ratings yet
- Term PaperDocument11 pagesTerm PaperclarencecalignerNo ratings yet
- Sexually Transmitted DiseasesDocument4 pagesSexually Transmitted DiseasesTamilore WilliamsNo ratings yet
- Student WorkDocument12 pagesStudent Workapi-376705276No ratings yet
- Lesson 10: Sexually Transmitted Disease Types of StdsDocument19 pagesLesson 10: Sexually Transmitted Disease Types of StdsJeya Plays YTNo ratings yet
- Sexually Transmitted DiseasesDocument76 pagesSexually Transmitted Diseasessomaya abdulhakimNo ratings yet
- Sexually Transmitted Infections PowerpointDocument12 pagesSexually Transmitted Infections Powerpointkriss ellisNo ratings yet
- Quiz Answer Key: Personal Health SeriesDocument3 pagesQuiz Answer Key: Personal Health SeriesYehla marie ArnaizNo ratings yet
- Case Study On SyphillisDocument18 pagesCase Study On Syphillisdia_pee100% (1)
- Understanding Sexually Transmitted Diseases (STD) : A Guidebook To Better Sexual Health (Men) - Free EbookDocument22 pagesUnderstanding Sexually Transmitted Diseases (STD) : A Guidebook To Better Sexual Health (Men) - Free EbookDr Tan & PartnersNo ratings yet
- Human Immunodeficiency Virus (HIV)Document7 pagesHuman Immunodeficiency Virus (HIV)Ambar WulanNo ratings yet
- Health 9 Venereal Diseases: - Caused by A Bacteria Named Chlamydia TrachomatisDocument8 pagesHealth 9 Venereal Diseases: - Caused by A Bacteria Named Chlamydia TrachomatisClaire MedianaNo ratings yet
- Term PaperDocument13 pagesTerm PaperclarencecalignerNo ratings yet
- Aids:: (Acquired Immune Deficiency Syndrome)Document6 pagesAids:: (Acquired Immune Deficiency Syndrome)Farwa DarNo ratings yet
- 1 Summarization-Updated (AutoRecovered)Document6 pages1 Summarization-Updated (AutoRecovered)Joan SevillaNo ratings yet
- Gay Sex and Risk Booklet WebDocument36 pagesGay Sex and Risk Booklet WebryasakijilhaniNo ratings yet
- Being An HFLE Teacher Portfolio1Document23 pagesBeing An HFLE Teacher Portfolio1raianna rogersNo ratings yet
- STD OutlineDocument16 pagesSTD OutlineLory TangpusNo ratings yet
- UntitledDocument40 pagesUntitledHam FeliasNo ratings yet
- 7 Most Common Sexually Transmitted DiseasesDocument3 pages7 Most Common Sexually Transmitted DiseasesTrixon B. LapidNo ratings yet
- The Basics: Cervical Cancer PregnancyDocument9 pagesThe Basics: Cervical Cancer PregnancyOm DarnalNo ratings yet
- Sexually Transmitted Disease or STI Complete SymtomsDocument11 pagesSexually Transmitted Disease or STI Complete SymtomsPowerzNo ratings yet
- Hiv/AidsDocument5 pagesHiv/Aidspaulporras93No ratings yet
- Human Immunodeficiency Virus Infection / Acquired Immunodeficiency Syndrome (HIV/AIDS) IsDocument4 pagesHuman Immunodeficiency Virus Infection / Acquired Immunodeficiency Syndrome (HIV/AIDS) IsL.a.ZumárragaNo ratings yet
- Basic Facts On HIVDocument16 pagesBasic Facts On HIVTimon AgarNo ratings yet
- Sexually Transmitted DiseaseDocument38 pagesSexually Transmitted Diseaserana arslanNo ratings yet
- Expose AidsDocument7 pagesExpose AidsKouadio Bi RichardNo ratings yet
- Adapted From: Sexually Transmitted Infections Pamphlet. Public Health Agency of Canada, 2007Document25 pagesAdapted From: Sexually Transmitted Infections Pamphlet. Public Health Agency of Canada, 2007Mohamoud MohamedNo ratings yet
- The Difference Between HIV and AidsDocument14 pagesThe Difference Between HIV and AidsAnonymous bq4KY0mcWGNo ratings yet
- Group 6Document12 pagesGroup 6Joy VillafloresNo ratings yet
- All About Sti/Hiv/Aids: Some Signs & Symptoms of StiDocument6 pagesAll About Sti/Hiv/Aids: Some Signs & Symptoms of StiTang InaNo ratings yet
- Edwin Mwangi Zool 143 Assgn. 3Document4 pagesEdwin Mwangi Zool 143 Assgn. 3nattydreadfathelahNo ratings yet
- Group8 Sexually Transmitted InfectionDocument10 pagesGroup8 Sexually Transmitted InfectionSheika Briones GalletaNo ratings yet
- A Simple Guide To Sexually Transmitted Infections, Diagnosis, Treatment And Related ConditionsFrom EverandA Simple Guide To Sexually Transmitted Infections, Diagnosis, Treatment And Related ConditionsRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (3)
- A Simple Guide to Sexually Transmitted DiseasesFrom EverandA Simple Guide to Sexually Transmitted DiseasesRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (9)
- The Complete Guide To HIV / AIDs: Symptoms, Diagnosis, Risks, Treatments & SupportFrom EverandThe Complete Guide To HIV / AIDs: Symptoms, Diagnosis, Risks, Treatments & SupportNo ratings yet
- The Complete Guide to Syphilis: Symptoms, Risks, Diagnosis & TreatmentsFrom EverandThe Complete Guide to Syphilis: Symptoms, Risks, Diagnosis & TreatmentsNo ratings yet
- Alere Hiv ComboDocument1 pageAlere Hiv ComboJohn Mark PamittanNo ratings yet
- Answers: TEST - 9 (Code-A) All India Aakash Test Series For Medical-2016Document19 pagesAnswers: TEST - 9 (Code-A) All India Aakash Test Series For Medical-2016Miss Jasmine0% (1)
- HIV 12 Stat Pak Dipstick Product Packet EnglishDocument6 pagesHIV 12 Stat Pak Dipstick Product Packet EnglishSagkyNo ratings yet
- Diseases & Immunity 1 QPDocument7 pagesDiseases & Immunity 1 QPbdb6wxhyxfNo ratings yet
- The AIDS Fighters - Brighthope, Ian Fitzgerald, PeterDocument196 pagesThe AIDS Fighters - Brighthope, Ian Fitzgerald, Peterpdf ebook free download100% (1)
- Pathogenic Properties of VirusesDocument12 pagesPathogenic Properties of VirusesAnika Yasmin 2012965048No ratings yet
- Doctor Letterhead 6Document1 pageDoctor Letterhead 6ziya mehraNo ratings yet
- Scientific American 1993-2013 Article IndexDocument147 pagesScientific American 1993-2013 Article IndexamlferreiraNo ratings yet
- Chapter 12 - Congenital and Acquired ImmunodeficienciesDocument11 pagesChapter 12 - Congenital and Acquired ImmunodeficienciesFYMNo ratings yet
- Hiv/Aids Law: Harvey Mher M. RarangDocument2 pagesHiv/Aids Law: Harvey Mher M. RarangHarvey Mher RarangNo ratings yet
- Rates of Molecular Evolution in RNA Viruses: A Quantitative Phylogenetic AnalysisDocument10 pagesRates of Molecular Evolution in RNA Viruses: A Quantitative Phylogenetic AnalysisImperialAquillaNo ratings yet
- Immunoassay Quick Ref. GuideDocument25 pagesImmunoassay Quick Ref. GuideকাজীসামাদNo ratings yet
- DR Anil Dissertation 2014Document144 pagesDR Anil Dissertation 2014Syed FurqanNo ratings yet
- Cal Cont Enz Sub p400 enDocument30 pagesCal Cont Enz Sub p400 enLince WijoyoNo ratings yet
- Introduction of Rapid Syphilis Testing in Antenatal Care: A Systematic Review of The Impact On HIV and Syphilis Testing Uptake and CoverageDocument28 pagesIntroduction of Rapid Syphilis Testing in Antenatal Care: A Systematic Review of The Impact On HIV and Syphilis Testing Uptake and CoveragezahiraNo ratings yet
- Suppression of Human Immunodeficiency Virus Replication by Ascorbate in Chronically and Acutely Infected Cells.Document5 pagesSuppression of Human Immunodeficiency Virus Replication by Ascorbate in Chronically and Acutely Infected Cells.Hector Javier Chavez RamirezNo ratings yet
- Virology - Exam 2 - ZipgradeDocument4 pagesVirology - Exam 2 - ZipgradeFelix NepumocenoNo ratings yet
- Bhavya-Reflective EssayDocument10 pagesBhavya-Reflective EssayKumar Creative ContentsNo ratings yet
- Case StudyDocument10 pagesCase StudyAdelle SmithNo ratings yet
- Ketiga 1 3 EngDocument14 pagesKetiga 1 3 EngAulia putriNo ratings yet
- Autophagy and CancerDocument349 pagesAutophagy and CancerSohibun21No ratings yet
- 3 Murex HIV Ag Ab CombinationDocument7 pages3 Murex HIV Ag Ab CombinationElias Dii Rivas GarvanNo ratings yet
- Module 7 - Health-and-Promotion-and-EducationDocument7 pagesModule 7 - Health-and-Promotion-and-EducationPascua, Aliah M.No ratings yet
- Dr. Dalia El-Shafei: Assistant Professor, Community Medicine Department, Zagazig UniversityDocument51 pagesDr. Dalia El-Shafei: Assistant Professor, Community Medicine Department, Zagazig UniversityArpit MahoreNo ratings yet
- Covid Vaccine Risks PDFDocument16 pagesCovid Vaccine Risks PDFIrmgart Jedamski Mitchell100% (2)
- All DrugsDocument482 pagesAll DrugsJessica IbañezNo ratings yet
- Exam Quest Special 2023Document24 pagesExam Quest Special 2023Yalvant YadavNo ratings yet
- Questionsheet 1: Disease / Immunology A2.15Document6 pagesQuestionsheet 1: Disease / Immunology A2.15Nabindra RuwaliNo ratings yet