Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Drug-Study
Drug-Study
Uploaded by
Mhica Prestoza0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
5 views1 pageCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as docx, pdf, or txt
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
5 views1 pageDrug-Study
Drug-Study
Uploaded by
Mhica PrestozaCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as docx, pdf, or txt
You are on page 1of 1
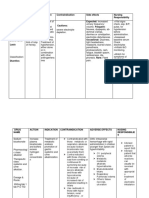
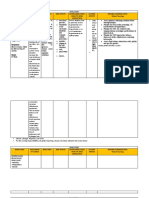
MECHANIS
DRUG INDICATION CONTRAINDICATI ADVERSE
M OF NURSING RESPONSIBILITIES
NAME S ONS EFFECTS
ACTION
Generic Supplemental For use as an Contraindicated with Dermatologic: Rash
Name: potassium in electrolyte allergy to tartrazine, GI: Nausea, vomiting, Assessment
Potassium the form of replenisher and aspirin (tartrazine is diarrhea, abdominal Assess for signs and symptoms of hypokalaemia (weakness,
chloride high in the treatment found in some discomfort, GI fatigue, U wave on ECG, arrhythmias, polyuria, polydipsia) and
potassium of hypokalemia. preparations marketed obstruction, GI hyperkalaemia (see Toxicity and Overdose).
Brand food or as Kaon-Cl, Klor- bleeding, GI Monitor pulse, blood pressure, and ECG periodically during IV
Name: potassium Con); severe renal ulceration or therapy.
Potassium chloride may impairment with perforation
Chloride , be able to oliguria, anuria, Hematologic: Lab Test Considerations:
Kaon, K-G restore normal azotemia; untreated Hyperkalemia— Monitor serum potassium before and periodically during therapy.
Elixir, potassium Addison’s disease; increased serum K+, Monitor renal function, serum bicarbonate, and ph.
Kolyum, Tri- levels. hyperkalemia; ECG changes (peaking Determine serum magnesium level if patient has refractory
K, Twin-K Treatment of adynamia episodica of T waves, loss of P hypokalaemia; hypomagnesaemia should be corrected to facilitate
cardiac hereditaria; acute waves, depression of effectiveness of potassium replacement.
Classificatio arrhythmias dehydration; heat ST segment, Monitor serum chloride because hypochloremia may occur if
n: due to cardiac cramps; GI disorders prolongation of QTc replacing potassium without con- current chloride.
Electrolytes glycosides that delay passage in interval)
the GI tract. Local: Tissue Toxicity and Overdose:
Route: Use cautiously with sloughing, local Symptoms of toxicity are those of hyperkalaemia (slow, irregular
IV, P.O cardiac disorders, necrosis, local heartbeat; fatigue; muscle weakness; paraesthesia; confusion;
especially if treated phlebitis, and dyspnoea; peaked T waves; de- pressed ST segments; prolonged
with digitalis, venospasm with QT segments; widened QRS complexes; loss of P waves; and
pregnancy, lactation. injection cardiac arrhythmias).
Treatment includes discontinuation of potassium, administration of
sodium bicarbonate to correct acidosis, dextrose and insulin to
facilitate passage of potassium into cells, calcium salts to reverse
ECG effects (in patients who are not receiving digoxin), sodium
polystyrene used as an exchange resin, and/or dialysis for patient
with impaired renal function.
You might also like
- Full Download Test Bank Medical Surgical Nursing Making Connections To Practice 2nd Edition Hoffman Sullivan PDF Full ChapterDocument36 pagesFull Download Test Bank Medical Surgical Nursing Making Connections To Practice 2nd Edition Hoffman Sullivan PDF Full Chapterlindahensondgfyiwsbzc100% (26)
- Calcium Gluconate Drug StudyDocument1 pageCalcium Gluconate Drug StudyChaepmunk Cy75% (4)
- DRUG STUDY - Furosemide (Lasix)Document1 pageDRUG STUDY - Furosemide (Lasix)julesubayubay542876% (25)
- Hypokalemia 180813073624Document26 pagesHypokalemia 180813073624korotkofNo ratings yet
- Kalium Durule Drug StudyDocument3 pagesKalium Durule Drug StudyJustine Garcia100% (1)
- KaliumDocument2 pagesKaliumJustine Kaye Iballa HarligaNo ratings yet
- Electrolytes TableDocument4 pagesElectrolytes TableMeg NoriegaNo ratings yet
- Drug Study: SaluronDocument4 pagesDrug Study: Saluronunkown userNo ratings yet
- Drug Study: SaluronDocument4 pagesDrug Study: Saluronunkown userNo ratings yet
- Drug Study Potassium ChlorideDocument5 pagesDrug Study Potassium ChlorideKenneth Mark B. TevesNo ratings yet
- Potassium ChlorideDocument2 pagesPotassium ChlorideAinaB ManaloNo ratings yet
- Drug Name Dosage, Route, Frequency Mechanism of Action Indication Contraindication Adverse Effect Nursing ResponsibilitiesDocument1 pageDrug Name Dosage, Route, Frequency Mechanism of Action Indication Contraindication Adverse Effect Nursing ResponsibilitiesJonna Mae TurquezaNo ratings yet
- Lizzie Heisler - Hypertension MedsDocument2 pagesLizzie Heisler - Hypertension MedsTricia Kaye IblanNo ratings yet
- Name of Drugs Kaligen 8Document2 pagesName of Drugs Kaligen 8mellany100% (1)
- Drugstudy PotassiumchlorideDocument3 pagesDrugstudy Potassiumchloridetrina412No ratings yet
- Harriet Lane Handbook of Pediatrics 22nd Edition ExportDocument1 pageHarriet Lane Handbook of Pediatrics 22nd Edition ExportKashaf ZuhaNo ratings yet
- MS1 DRUG CARDSDocument22 pagesMS1 DRUG CARDStheresefrancotuNo ratings yet
- Drug Name Action Indication Contraindicat Ions Side Effects Nursing Considerations GenericDocument3 pagesDrug Name Action Indication Contraindicat Ions Side Effects Nursing Considerations GenericGenevang SeaweedsNo ratings yet
- Sodium BicarbonateDocument2 pagesSodium Bicarbonaterayne07No ratings yet
- Calcium GluconateDocument2 pagesCalcium GluconateMae Ann Bueno Castillon100% (1)
- Drug Study of FurosemideDocument5 pagesDrug Study of FurosemideAntonette Lei100% (1)
- Furosemide Drug StudyDocument2 pagesFurosemide Drug StudyCrisha Ann Billones BacutaNo ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument2 pagesDrug StudyAUBREY GARATENo ratings yet
- Assignment 1ADocument9 pagesAssignment 1Amarvinsanantonio0612No ratings yet
- DRUG STUDY Furosemide LasixDocument1 pageDRUG STUDY Furosemide LasixG4 AMOYO ANGELICA NICOLENo ratings yet
- Fluid and Electrolyte Imbalances Part 2Document46 pagesFluid and Electrolyte Imbalances Part 2Gabrielle Frances FernandezNo ratings yet
- PriapismDocument4 pagesPriapismLuckyNo ratings yet
- Potassium Supplements ParenteralDocument3 pagesPotassium Supplements Parenteralcarl meiNo ratings yet
- Institute of Nursing BSN110-GROUP 39 S.Y. 2010-2011: Lab Test Considerations: MonitorDocument5 pagesInstitute of Nursing BSN110-GROUP 39 S.Y. 2010-2011: Lab Test Considerations: MonitorIvy Grace LimNo ratings yet
- Calcium Gluconate PDFDocument2 pagesCalcium Gluconate PDFDayan CabrigaNo ratings yet
- Calcium Gluconate Drug StudyDocument4 pagesCalcium Gluconate Drug StudyAngelou Joefred CongresoNo ratings yet
- Drug Study Vitamin DDocument1 pageDrug Study Vitamin DErica VelascoNo ratings yet
- Drug Study LanoxinDocument2 pagesDrug Study LanoxinRaidis PangilinanNo ratings yet
- Drug LordsDocument25 pagesDrug LordsGlen DaleNo ratings yet
- Rug Therapy For Heart Failure: Dr. Santhosh RamakrishnaDocument40 pagesRug Therapy For Heart Failure: Dr. Santhosh RamakrishnaNiteesh Kumar SharmaNo ratings yet
- Tapazole and Calcium GluconateDocument3 pagesTapazole and Calcium Gluconatekuro hanabusaNo ratings yet
- Kayexalate Drug StudyDocument3 pagesKayexalate Drug StudyAngelou Joefred Congreso100% (1)
- Renal PharmacologyDocument7 pagesRenal PharmacologywanichysonlyNo ratings yet
- Generic Name & Brand Name Mechanism of Action Indications and Drug Rationale Contraindications Common Side Effects Nursing ConsiderationsDocument2 pagesGeneric Name & Brand Name Mechanism of Action Indications and Drug Rationale Contraindications Common Side Effects Nursing ConsiderationsMary Shine GonidaNo ratings yet
- PHS CVSDocument25 pagesPHS CVStewogbadeomobuwajo005No ratings yet
- CalciumDocument2 pagesCalciumtuffie85No ratings yet
- Sodium Bicarbonate Drug StudyDocument3 pagesSodium Bicarbonate Drug StudyShaira Suzane SabidoNo ratings yet
- Print MeDocument4 pagesPrint MeDoneva Lyn MedinaNo ratings yet
- Drug Studies and Health Teaching PlanDocument28 pagesDrug Studies and Health Teaching PlansfkjalkhsafgNo ratings yet
- Pharmacological Sheet Patient Name: BALDESTOY, Benedict Age: 19 Years Old Sex: Male Diagnosis: Hepatoma CAP-MRDocument5 pagesPharmacological Sheet Patient Name: BALDESTOY, Benedict Age: 19 Years Old Sex: Male Diagnosis: Hepatoma CAP-MRIngrid NicolasNo ratings yet
- KCL (FSW)Document3 pagesKCL (FSW)khelxoNo ratings yet
- NCM 112 Fluid and Electrolytes: Hyperkalemia or Potassium ExcessDocument2 pagesNCM 112 Fluid and Electrolytes: Hyperkalemia or Potassium ExcessAngeline NavarroNo ratings yet
- Chronic Kidney DiseaseDocument4 pagesChronic Kidney DiseaseImnot YouNo ratings yet
- Drug Study FinalDocument8 pagesDrug Study FinalWendy EscalanteNo ratings yet
- Drug Name Mechanism of Action Indication Contraindication Side Effects Nursing Responsibility Expected: IncreasedDocument4 pagesDrug Name Mechanism of Action Indication Contraindication Side Effects Nursing Responsibility Expected: IncreasedMichaella MalimitNo ratings yet
- Diuretics MOA Notes Indications Side Effects DrugsDocument1 pageDiuretics MOA Notes Indications Side Effects Drugsmonica leeNo ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument8 pagesDrug StudySamson, SatomiNo ratings yet
- Normal Values Prelim Reviewer UpdateDocument14 pagesNormal Values Prelim Reviewer Updatesantinaerikalee.flores-20No ratings yet
- Diuretic Drugs For Nursing PharmacologyDocument1 pageDiuretic Drugs For Nursing Pharmacologylhayes1234100% (7)
- Wk8 - Electrolyte Imbalances & Acid-Base ImbalancesDocument65 pagesWk8 - Electrolyte Imbalances & Acid-Base ImbalancesPotato PceeNo ratings yet
- AGE DrugDocument5 pagesAGE DrugLA GomezNo ratings yet
- Drug Study 1Document3 pagesDrug Study 1G4 AMOYO ANGELICA NICOLENo ratings yet
- Critical Care Medications: Anti-Arrhythmics Study Guide: Critical Care EssentialsFrom EverandCritical Care Medications: Anti-Arrhythmics Study Guide: Critical Care EssentialsNo ratings yet
- motivationsDocument2 pagesmotivationsMhica PrestozaNo ratings yet
- Occupational therapyDocument1 pageOccupational therapyMhica PrestozaNo ratings yet
- TherapyDocument5 pagesTherapyMhica PrestozaNo ratings yet
- Week 1Document2 pagesWeek 1Mhica PrestozaNo ratings yet
- First Sem MidtermDocument27 pagesFirst Sem MidtermMhica PrestozaNo ratings yet
- PSYCHDocument2 pagesPSYCHMhica PrestozaNo ratings yet
- Parasitology-Lec 13 MalariaDocument6 pagesParasitology-Lec 13 Malariaapi-3743217No ratings yet
- OA 6 SeptDocument19 pagesOA 6 Septstella pangestikaNo ratings yet
- Functional Amino Acids in Fish Nutrition, Health and Welfare: Frontiers in Bioscience (Elite Edition) December 2015Document28 pagesFunctional Amino Acids in Fish Nutrition, Health and Welfare: Frontiers in Bioscience (Elite Edition) December 2015Satrio Yudha WisesaNo ratings yet
- Crystalloid Fluid Choice and Clinical Outcomes in Pediatric Sepsis J Peds 2017 PDFDocument17 pagesCrystalloid Fluid Choice and Clinical Outcomes in Pediatric Sepsis J Peds 2017 PDFYan Hein TanawaniNo ratings yet
- Iron Deficiency Anemia in Predominantly Breastfed Young ChildrenDocument4 pagesIron Deficiency Anemia in Predominantly Breastfed Young ChildrenHenpaCh ParedesNo ratings yet
- Ich GCP: HistoryDocument57 pagesIch GCP: HistoryChandrashekhar Singh100% (1)
- Hypovolemic ShockDocument13 pagesHypovolemic ShockJed ProwellNo ratings yet
- Diploma in Osteopathic MedicineDocument15 pagesDiploma in Osteopathic MedicineSachin GoyalNo ratings yet
- Herdin - NCR Olfu 14051317072941Document2 pagesHerdin - NCR Olfu 14051317072941jozaauraNo ratings yet
- Student Medical CertificateDocument1 pageStudent Medical Certificatecharles doctolero0% (1)
- Insight: DR Ashish Debsikdar Resident-PsychiatryDocument73 pagesInsight: DR Ashish Debsikdar Resident-PsychiatrysprimalNo ratings yet
- List Obat ApotekDocument5 pagesList Obat ApotekMuhammad RaisNo ratings yet
- CetakDocument96 pagesCetakIkayulianiNo ratings yet
- Doc-20220620-Wa0036 22.Document7 pagesDoc-20220620-Wa0036 22.pokja4 ivjuraiNo ratings yet
- CMH - 30 10 1Document667 pagesCMH - 30 10 1cateerpillarNo ratings yet
- (1160) Pharmaceutical Calculations in Pharmacy PracticeDocument25 pages(1160) Pharmaceutical Calculations in Pharmacy Practiceprissila prindaniNo ratings yet
- WJH 9 1001Document11 pagesWJH 9 1001titis dwi tantiNo ratings yet
- Pharma Computation Assignment PDFDocument2 pagesPharma Computation Assignment PDFKasnhaNo ratings yet
- The Evils of Big Pharma ExposedDocument5 pagesThe Evils of Big Pharma ExposedAmr Basha100% (1)
- Microbial Limit TestDocument33 pagesMicrobial Limit TestSurendar KesavanNo ratings yet
- ACC2024 Programme-Day 2Document27 pagesACC2024 Programme-Day 2Bosco WoodsNo ratings yet
- Tarasoff Case BriefDocument5 pagesTarasoff Case BriefJill Stuart100% (2)
- DAFTAR PUSTAKA SarkomaDocument2 pagesDAFTAR PUSTAKA SarkomaantaniaaaNo ratings yet
- Wheat Gluten and Health Powerpoint PresentationDocument22 pagesWheat Gluten and Health Powerpoint PresentationCeliaNo ratings yet
- Anatomical Variations of Renal Artery and Its Clinical CorrelationsDocument6 pagesAnatomical Variations of Renal Artery and Its Clinical CorrelationsClaudia HusinNo ratings yet
- Rudraprayag Social Sector Status ReportDocument64 pagesRudraprayag Social Sector Status Reportgoraksh2014No ratings yet
- 020 - Metabolism of Proteins 3Document12 pages020 - Metabolism of Proteins 3Sargonan RaviNo ratings yet
- Ankle&fEET Written Procedure-MagsombolDocument2 pagesAnkle&fEET Written Procedure-Magsombolhazell_aseronNo ratings yet
- Helping Students Cope With Loss:: Incorporating Art Into Group CounselingDocument13 pagesHelping Students Cope With Loss:: Incorporating Art Into Group Counselingapi-268625907100% (1)