Professional Documents
Culture Documents
PHONOLOGICAL PROCESSES for esl
PHONOLOGICAL PROCESSES for esl
Uploaded by
novaenglishinstituteCopyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
PHONOLOGICAL PROCESSES for esl
PHONOLOGICAL PROCESSES for esl
Uploaded by
novaenglishinstituteCopyright:
Available Formats
PHONOLOGICAL PROCESSES
HANDOUT
Phonemes:
ENGLISH VOWELS: They are speech sounds produced with vibrating vocal chords and a continuous
unrestricted flow of air coming from the mouth…
ɑ: / ˄ / æ / Ə / e / ɝ / I / i: / ɒ / : / Ʊ / u:
NAME PHONEME SOUND EXAMPLE
Long A ɑ: Aaa / f ɑ: ð ɝ /
Stressed schwa ˄ a (ae) /k˄p/
Unstressed schwa Ə a (ae) /ƏweI/
Happy A æ aaa /kæt/
R colored vowel ɝ ar + er + rr /tɝn/
(rothocized)
Short E e ee /bed/
Short I I I /sItIŋ/
Long I I: iii / b I: /
British O ɒ O(very alike to ɑ:) /rɒk/
Long O : Oo / k : l /
Short U Ʊ u /kƱd/
Long U u: Uuu / b l u: /
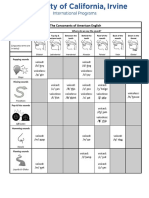
ENGLISH CONSONANTS (easy to feel): they are sounds made by blocking the flow of air coming out from the
lungs. The blockage must be accompanied by vibration of the vocal chords, in which case the consonant is
voiced; if there is no vibration, the consonant is voiceless.
b / p / m / w / v / f / ð / θ / d / t / z / s / n / l / r / Ʒ / ∫ / ʤ / t∫ / j / g / k / ŋ / h /
Phoneme Sound Manner of Point of Voicing Possible Spelling
Articulation Articulation
/b/ Ba Stop BILABIAL Voiced b (table) bb (robber)
/p/ Pa Stop Voiceless p (people) pp (shopping)
/m/ Mm Nasal Voiced m (family) mm (summer) “Last sounds
are silent mb (comb) mn (autumn)
/w/ Wa Approximant Voiceless w (woods) wh (what) u-after Q
(Glide) (question) u-after G (language) u-after S
(persuade) o (once) Silent on (write,
wrong, answer, two)
/v/ Va Fricative LABIO DENTAL Voiced v (river) unusual = (of)
/f/ Fff Fricative Voiceless f (funny) ff (office) ph (alphabet) gh
(laugh)
/ð/ Da Fricative DENTAL Voiced th (there) (together) (clothes)
/θ/ Da Fricative Voiceless th (think) (something)
(completely
labiodental)
/d/ Da Stop ALVEOLAR Voiced d (date) dd (address)
/t/ Ta Stop Voiceless t (try) tt (getting)
/z/ Zzz Fricative Voiced z (zoo) zz (buzz) ze (prize) s (easy) se
(please) ss (dessert) x-gz (example)
/s/ Ss Fricative Voiceless s (serious) ss (kiss) c-before (e-i-y)
(bicycle) se (horse) sc (scene) x-ks
(next) xc (exciting)
/n/ Nn Nasal Voiced n (name) nn (dinner) K/G silent (knife)
(foreign)
/l/ Lll Approximant Voiced l (early) ll (really) Sometimes silent (half)
(Liquid) (should) (palm)
/r/ Rr Approximant PALATAL Voiced r (repeat) rr (tomorrow) rh (rhythm) wr
(Alveolar) (wrong)
/Ʒ / Sh….. Fricative Voiced s (usually) ge (garage) z (seizure)
/∫/ Shsh Fricative Voiceless sh (show) ci (special) ssi (profession)
su (sure) ce (ocean)
unstressed endings ti (televition)
/ʤ / Ya/Ye/ Affricate Voiced j (enjoy) dge (judge) g-before e/i/y
Yi/Yo/ (agency) d-before U (graduate)
yu-Sh
(for J/Y)
/t∫/ Ch Affricate Voiceless ch (choose) tch (watch) t-before U
(picture) ti-before S (suggestion)
/j/ Ia Approximant Voiceless y (yesterday) u (use) ew (view) eu
(Glide) (europe) i-after n/l (opinión)
(familiar)
/g/ Ga Stop VELAR Voiced g (grass) gg (bigger) gu (guitar)
gh (ghost) x-gz (example)
/k/ Kk Stop Voiceless k (kitchen) c (call) ck (jacket) cc
(occasion) ch (chemistry) x (six) xc
(excellent) qu (quiet) silent before N
(know) ks-before E/I (success)
/ŋ/ Ngng Nasal Voiced ng (morning) before-K (bank)
before-G (english)
/ב/ {r} (Allophone for VELAR Voiced (city) (betty) (cutie)
T)
FLAP
/h/ Ja Fricative GLOTTAL Voiceless h (hope) wh (whose)
/wh/ Jua Combined GLOTTAL- Voiced (where) (when)
Sound BILABIAL
PHONOLOGICAL PROCESSES
They are changes in pronunciation that occur within or between words to their relation with neighboring
sounds.
- To simplify the production of complex words.
- To facilitate the articulation.
LINKING: It is made on the connection of final sounds to initial sounds.
1. Glide Linking:
Word or Syllable ends in a tense vowel or diphthong and the next word or syllable begins with a
vowel. (j or w sounds appear)
BE A SPORT // …the area… // …easy and…
HOW ARE YOU? // …no other… // …you are…
2. Consonant – Vowel Linking:
Word or Syllable ends in a single consonant and the next word or syllable begins with a vowel.
STOP IT // …can also… // … for only…
3. Consonant Cluster – Vowel Linking (Resyllabification):
Word or Syllable ends in a consonant cluster and the next word or syllable begins with a vowel.
FIND OUT // …hills of… // …largest and…
4. Consonant - Consonant Linking:
Word or Syllable ends in a consonant STOP sound and the next word or syllable begins with a
consonant STOP sound or consonant AFFRICATE sound. Also, it can happen when we find 2
identical consonant sounds together in both words.
Stop Sound – Stop Sound (/ b / p / d / t / g / k /) -- (/ b / p /d /t / g / k /)
BLACK DOOR // …and began… // …giant buildings…
Stop Sound – Affricate Sound (/ b / p /d /t / g / k /) – (/ ʤ / t∫ /)
SICK CHILD // …red jeans… // …up channel…
2 identical consonants come together.
HOT TEA // …in northern… // …and destroyed…
ASSIMILATION: It happens when a given sound (assimilating sound) takes the characteristics of a
neighboring sound (conditioning sound).
1) Progressive Assimilation (perseverative)
The Conditioning Sound precedes and affects the following sound; it happens with plurals and regular
past of 1 syllable words…
(Plurals: VOICED sounds = z // VOICELESS sounds = s)
(Regular Past: VOICED sounds = d // VOICELESS sounds = t)
BAG /b æ g z / // …jeans /ʤi:nz/… // …adults /æd˄lts/…
MOVE /m u: v d/ // …changed /t∫einʤd/… // …switched /swit∫t/…
2) Regressive Assimilation (anticipatory)
The Assimilating Sound precedes and it is affected by the Condition Sound, changing this way the
pronunciation…
(nasal sounds “m/n/ŋ/” - bilabial sounds “/b/p/m/w/”)
ONE MILLION // …began moving… // …moving west…
TEN BOATS // …clothing more…
3) Coalescent Assimilation (coalescence)
It is a reciprocal assimilation in which, the first sound in a near relationship with the second sound produces a
third sound with features of both. Normally, it occurs with final STOP – FRICATIVE / ALVEOLAR sounds
(/s/z/t/d/) combined with an APPROXIMANT PALATAL sound (/j/). They become into PALATAL / FRICATIVE
– AFFRICATE (/∫/Ʒ/t∫/ʤ/)
(/s/z/t/d/) + (/j/) = (/∫/Ʒ/t∫/ʤ/)
…this/s/ year (∫) … // …is/z/ your (Ʒ)…
…not/t/ young (t∫) … // …old /d/ yogurt (ʤ)…
DELETION… It is a radical form of adjustment in connected speech in which sounds disappear or are not
clearly articulated.
1) Loss of /t/ when there is nt between 2 vowels or before a syllabic l…
ENTER // …century…
WALTZ // …adults…
2) Loss of /t/ or /d/ when they occur second in sequence or cluster…
EXACTLY // …important… // …condor… // KINDNESS
3) Word Final on /t/ or /d/ in cluster or compound words starting in consonants…
EAST SIDE // …tent canvas… // BLIND MAN
4) Loss of unstressed vowel or syllable …
EVERY // TEMPERATURE
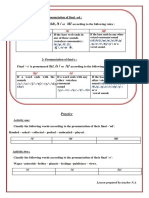
EPENTHESIS: It happens when it is necessary to insert a vowel or syllable to pronounce plurals and
regular past.
For nouns which finish in /s/.
(Plurals: (Əs) endings in s or z sounds)
For regular verbs which finish on /t/ or /d/…
(Regular Past: ID (Əd) for d or t sounds endings)
PLACE /pleisƏz/ // JUICE / ʤu:sƏz/
DECIDE /dIsƏIdId/ // RENT /rentId/
You might also like
- The Evolving Study of Philippine English by Tayao PDFDocument14 pagesThe Evolving Study of Philippine English by Tayao PDFJobelle Gallardo Agas100% (1)
- 1ST Term .JSS3 English LanguageDocument32 pages1ST Term .JSS3 English Languagesamuel joshuaNo ratings yet
- Somali PhonologyDocument7 pagesSomali PhonologyAbdiwaliNo ratings yet
- English Consonant Phonemes & AllophonesDocument2 pagesEnglish Consonant Phonemes & AllophonesJazmin Sanabria100% (1)
- Final Exam LinguisticsDocument5 pagesFinal Exam Linguisticsdomonique tameronNo ratings yet
- Exercises About ConsonantsDocument2 pagesExercises About Consonantsام اماني oum amaniNo ratings yet
- VariacionesDocument11 pagesVariacionesElena NavrotskayaNo ratings yet
- Sound Spelling ChartDocument4 pagesSound Spelling ChartDashaNo ratings yet
- Modul PRO MasterDocument34 pagesModul PRO MasterJohan Andi SaputraNo ratings yet
- Letters and Diacritics 4.3Document2 pagesLetters and Diacritics 4.3HantaoNo ratings yet
- What Are DigraphsDocument3 pagesWhat Are DigraphsMadelein Muñoz RoaNo ratings yet
- An Winaray - Guide To The Orthography and Grammar of The Waray LanguageDocument25 pagesAn Winaray - Guide To The Orthography and Grammar of The Waray LanguageROMEL A. ESPONILLANo ratings yet
- Diphtong and TriphtongDocument12 pagesDiphtong and TriphtongFahmiRizkyNo ratings yet
- Vowel Letter Vowel Sound (IPA Symbol) How To Pronounce It Example Word A I Ice O UDocument5 pagesVowel Letter Vowel Sound (IPA Symbol) How To Pronounce It Example Word A I Ice O UABHISHEK GOUTAMNo ratings yet
- Cool Phonics and Graphemes Guide v2020.12.15Document2 pagesCool Phonics and Graphemes Guide v2020.12.15Rami RamiNo ratings yet
- Silent SoundsDocument1 pageSilent SoundsTrung Tran VanNo ratings yet
- Pronunciation 2Document34 pagesPronunciation 2Adam PrabowoNo ratings yet
- Phonics and GraphemesDocument2 pagesPhonics and GraphemesAnglophile123No ratings yet
- Ling 103 Transcription of English Syllable Structure: General American English Consonants and GlidesDocument9 pagesLing 103 Transcription of English Syllable Structure: General American English Consonants and Glidessandra sNo ratings yet
- Pembelajaran 1Document8 pagesPembelajaran 1Hesti HestarikaNo ratings yet
- Czech Language PronunciationDocument3 pagesCzech Language PronunciationDan MagadiaNo ratings yet
- Contrastive Analysis: English Vs Bahasa Indonesia (Phonological Systems)Document43 pagesContrastive Analysis: English Vs Bahasa Indonesia (Phonological Systems)13.Naelis Tri BintariNo ratings yet
- English Sounds: A Sound of Two Different Vowel Sounds That Are Closely Joined Together and Treated As One VowelDocument8 pagesEnglish Sounds: A Sound of Two Different Vowel Sounds That Are Closely Joined Together and Treated As One Vowelmostafa mahmoud100% (1)
- Long and Short VowelsDocument17 pagesLong and Short VowelsAna Virginia Fernández100% (1)
- English Phonetics and PhonologyDocument13 pagesEnglish Phonetics and Phonologyanon_608348480No ratings yet
- Meeting 4-5 (ENGLISH CONSONANT (1) )Document31 pagesMeeting 4-5 (ENGLISH CONSONANT (1) )luna loudNo ratings yet
- Session 2Document68 pagesSession 2AlmaNo ratings yet
- PhoneticsDocument10 pagesPhoneticsvenkataveeranjaneyulNo ratings yet
- Word Advance Linguistic Group 1Document12 pagesWord Advance Linguistic Group 1Muhammad Yasin NugrohoNo ratings yet
- PronunciationGuide C1.2Document5 pagesPronunciationGuide C1.2Mihály Ale100% (1)
- Edital 01 Da Monitoria 2018.1Document8 pagesEdital 01 Da Monitoria 2018.1Anonymous 0uOPyTUwkNo ratings yet
- The Sound of Language - PhoneticsDocument12 pagesThe Sound of Language - PhoneticshaidarNo ratings yet
- A Vietnamese PhonologyDocument21 pagesA Vietnamese PhonologyBinh TranNo ratings yet
- Adjustments in Connected Speech - 2018 - IecDocument26 pagesAdjustments in Connected Speech - 2018 - IecValcarolNo ratings yet
- Pronouncing The "-Ed" Sound (Suffix) For: Regular VerbsDocument2 pagesPronouncing The "-Ed" Sound (Suffix) For: Regular VerbsledracNo ratings yet
- Ossetic Orth enDocument2 pagesOssetic Orth enconnororeily2012No ratings yet
- English Phonetic AlphabetDocument2 pagesEnglish Phonetic Alphabetahmad saleemNo ratings yet
- Table of English Consonant Place of Articulation: Ɪ (Sip) Ɪ (Date) Ɛ (Pet)Document1 pageTable of English Consonant Place of Articulation: Ɪ (Sip) Ɪ (Date) Ɛ (Pet)Myeshaena Ashryver GalathyniusNo ratings yet
- Tutor Pronunciation Workshop February 19 2022Document9 pagesTutor Pronunciation Workshop February 19 2022Roderick LeitchNo ratings yet
- Elvira - Assignment Lesson 1 2Document3 pagesElvira - Assignment Lesson 1 2Winford ElviraNo ratings yet
- INGLESE Cap II (Ripristinato)Document14 pagesINGLESE Cap II (Ripristinato)Daniela VivonaNo ratings yet
- Blend Phonics ChartsDocument8 pagesBlend Phonics ChartsKm Chun100% (1)
- Grapheme Phoneme Correspondence in RP English With KeyDocument2 pagesGrapheme Phoneme Correspondence in RP English With KeyJoaquin Toro MaturanaNo ratings yet
- International Phonetic AlphabetsDocument18 pagesInternational Phonetic AlphabetssyadormybeeNo ratings yet
- Names Orthography: Frafra People Ghana Upper East Region Dagbani MossiDocument3 pagesNames Orthography: Frafra People Ghana Upper East Region Dagbani MossiHBL MARCHNo ratings yet
- AN INTRODUCTION TO THE SOUNDS of ENGLISH AS SPOKEN IN ENGLANDDocument4 pagesAN INTRODUCTION TO THE SOUNDS of ENGLISH AS SPOKEN IN ENGLANDsupratimloveNo ratings yet
- The Consonants of American English: Where Do We Say The Sound?Document2 pagesThe Consonants of American English: Where Do We Say The Sound?Hien TaNo ratings yet
- Assignment 8 (Hanin Oransa)Document12 pagesAssignment 8 (Hanin Oransa)haninoransaNo ratings yet
- Danish Alphabet WorksheetDocument6 pagesDanish Alphabet WorksheetAndrianaNo ratings yet
- Pronunciation of Ed and SDocument20 pagesPronunciation of Ed and SwaxynhoNo ratings yet
- RevisionDocument3 pagesRevisionmnisa6701No ratings yet
- Phonological ProcessDocument21 pagesPhonological ProcessLeni SusianaNo ratings yet
- Unit 3: Consonants & Their Classification: English PhoneticsDocument16 pagesUnit 3: Consonants & Their Classification: English PhoneticsNguyễn Hữu NguyênNo ratings yet
- DISCUSSION PAPERinMAJOR 2 Multimodal CommunicationDocument4 pagesDISCUSSION PAPERinMAJOR 2 Multimodal CommunicationShiella Mae Olermo CardonaNo ratings yet
- Preliminaries 1.1 Stress in Polish and English: Po-Dło-Ga A-Le-Ja PƏ - Dło-Gə Ə-Le-JəDocument7 pagesPreliminaries 1.1 Stress in Polish and English: Po-Dło-Ga A-Le-Ja PƏ - Dło-Gə Ə-Le-JəEdawrd SmithNo ratings yet
- 44 SoundsDocument17 pages44 SoundsEhsanur Rahman JoyNo ratings yet
- NepaliDocument35 pagesNepaliastrolover119100% (1)
- Activity 4Document10 pagesActivity 4shixianNo ratings yet
- Am VI Hoc Tong Hop Ly Thuyet Chuyen Nganh Ngon Ngu AnhDocument23 pagesAm VI Hoc Tong Hop Ly Thuyet Chuyen Nganh Ngon Ngu Anhphanthuthao128abcNo ratings yet
- Phonetic Transcription First GroupDocument14 pagesPhonetic Transcription First GroupNanda ainul kholizaNo ratings yet
- Consonant Pairs EXAMPLEDocument3 pagesConsonant Pairs EXAMPLEKOREAN AIRNo ratings yet
- Yes (Southern & Central)Document2 pagesYes (Southern & Central)Nguyễn Xuân HoàngNo ratings yet
- English to French Dictionary: Words Without Borders: Bilingual Dictionary SeriesFrom EverandEnglish to French Dictionary: Words Without Borders: Bilingual Dictionary SeriesNo ratings yet
- Plural Nouns Verbs in Third Person Possessive CaseDocument2 pagesPlural Nouns Verbs in Third Person Possessive Casevanessa rodriguez minayaNo ratings yet
- Connected Speech: Assimilation: Source:onestopenglishDocument17 pagesConnected Speech: Assimilation: Source:onestopenglishتحریم اشرفNo ratings yet
- Phonetics For The ExamDocument2 pagesPhonetics For The ExamLarisa FlorentinaNo ratings yet
- Spanish American Dialect Zones - John LipskyDocument17 pagesSpanish American Dialect Zones - John Lipskymspanish100% (2)
- Finnish Sound Structure Phonological OverviewDocument153 pagesFinnish Sound Structure Phonological Overviewlobotomy, save meNo ratings yet
- Sofl Library Answers To PhoneticsDocument32 pagesSofl Library Answers To PhoneticsYermek RamazanovNo ratings yet
- Vowels and Consonants ChartDocument2 pagesVowels and Consonants ChartVianne Denine TipayNo ratings yet
- English Phonetic Course Assimilation & Elision: Related PapersDocument8 pagesEnglish Phonetic Course Assimilation & Elision: Related PapersẶňąÀšlňMặX-MợŞhklặNo ratings yet
- Bengali Consonants (: Bænjônbôrnô)Document3 pagesBengali Consonants (: Bænjônbôrnô)Aarajita ParinNo ratings yet
- Introduction To PhonologyDocument8 pagesIntroduction To PhonologyJunjet FamorcanNo ratings yet
- Sofl Library Answers To PhoneticsDocument32 pagesSofl Library Answers To Phoneticsnguyenhoaianhthu0% (1)
- PluralsDocument7 pagesPluralsDavid KMNo ratings yet
- Phonetics, Semester 3Document24 pagesPhonetics, Semester 3Cute_CharmiinG1210100% (5)
- 112015book PapersinArabic EnglishtranslationdocxDocument282 pages112015book PapersinArabic EnglishtranslationdocxAnilNo ratings yet
- (German Coloma) Illustration of The IPA - Argentine SpanishDocument8 pages(German Coloma) Illustration of The IPA - Argentine SpanishdecarvalhothiNo ratings yet
- id/ /T/ /D/: / T / /D/ /K/,/P/, /F/, /Ʃ /, (/D/,/B/,L/,/M/,/N/,/Z/,/Ð/,/ / ,/Ŋ/,/R/,/V/,/DƷ/ /Ʒ/)Document2 pagesid/ /T/ /D/: / T / /D/ /K/,/P/, /F/, /Ʃ /, (/D/,/B/,L/,/M/,/N/,/Z/,/Ð/,/ / ,/Ŋ/,/R/,/V/,/DƷ/ /Ʒ/)Øptímí ŠtãNo ratings yet
- Phonetics IIDocument9 pagesPhonetics IIAdriel Galdames MelladoNo ratings yet
- Phonetics and Phonology - Task 6 - Written ExercisesDocument9 pagesPhonetics and Phonology - Task 6 - Written ExercisesstefanyNo ratings yet
- Anh 6 Hkii (2018-2019)Document184 pagesAnh 6 Hkii (2018-2019)MillanPhanNo ratings yet
- English Consonants: Intelligibility, Credibility and IdentityDocument6 pagesEnglish Consonants: Intelligibility, Credibility and IdentityPerry AshleyNo ratings yet
- Corrected ExercisesDocument15 pagesCorrected ExercisesKhlifibrahimNo ratings yet
- Dialects English Indian Subcontinent Colonial Rule India Census of IndiaDocument13 pagesDialects English Indian Subcontinent Colonial Rule India Census of Indiaaditya18889100% (1)
- Adjustments in Connected Speech - 2018 - IecDocument26 pagesAdjustments in Connected Speech - 2018 - IecValcarolNo ratings yet
- Mini Project 2Document6 pagesMini Project 2Vy Hoàng HạNo ratings yet
- Inflectional Suffix FormationDocument2 pagesInflectional Suffix FormationLaury M VLNo ratings yet
- Les Cours AnglaisDocument32 pagesLes Cours AnglaisAya ZemaliNo ratings yet
- Phonetics Vs PhonologyDocument53 pagesPhonetics Vs PhonologyValquiria CarvalhoNo ratings yet