Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Musculoskeletal
Musculoskeletal
Uploaded by
Friday JaneCopyright:
Available Formats
You might also like
- Case File HuckabyDocument7 pagesCase File HuckabyAmrit SahotaNo ratings yet
- Avn On ScriptDocument13 pagesAvn On Scriptclaire.deveraNo ratings yet
- Hard Tissue Replacement-OrthopedicsDocument77 pagesHard Tissue Replacement-OrthopedicsbiomedyuvaNo ratings yet
- Orthopedic NursingDocument201 pagesOrthopedic NursingMitch Hellgirl Almonte100% (2)
- Fascial Fitness - SchleipDocument44 pagesFascial Fitness - SchleipIacopoMariaFilippoBarniNo ratings yet
- Movement System: By: Fadhilah HarmenDocument30 pagesMovement System: By: Fadhilah HarmenFadhilah HarmenNo ratings yet
- Musculos Descripcion Video 1Document4 pagesMusculos Descripcion Video 1fiorellaNo ratings yet
- Locomotion System: (Skeletal and Muscular Systems)Document36 pagesLocomotion System: (Skeletal and Muscular Systems)Cut Thirza TalithaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 6 Content Review Questions 1-8Document3 pagesChapter 6 Content Review Questions 1-8Rhonique MorganNo ratings yet
- Topic 5. Bone Microscopic Anatomy and Devt 1Document24 pagesTopic 5. Bone Microscopic Anatomy and Devt 1Janine Jerica JontilanoNo ratings yet
- A FractureDocument10 pagesA FractureFredimar CondeNo ratings yet
- Functions of The Musculoskeletal SystemDocument9 pagesFunctions of The Musculoskeletal SystemLinda XueNo ratings yet
- HSS AnatomyDocument5 pagesHSS AnatomyruguNo ratings yet
- Script Case PressDocument7 pagesScript Case PressMa. Gina DerlaNo ratings yet
- Skeletal - Break A LegDocument9 pagesSkeletal - Break A LegShannon SandersNo ratings yet
- Biology of OtmDocument19 pagesBiology of OtmNaveenNo ratings yet
- Total Hip Replacement - Educational PacketDocument19 pagesTotal Hip Replacement - Educational Packetapi-549337910No ratings yet
- Skeletal SystemDocument104 pagesSkeletal Systemsyafi zulNo ratings yet
- OrifDocument13 pagesOrifAhmabelle Mara D. AbellaNo ratings yet
- Case Study For CastDocument10 pagesCase Study For CastMaria JuvilisaNo ratings yet
- Anaphy Exercise 5 - SKELETAL AND ARTICULAR SYSTEMDocument12 pagesAnaphy Exercise 5 - SKELETAL AND ARTICULAR SYSTEMKenzoNo ratings yet
- Anatomy, Lecture 2, Joints (Lecture Notes)Document12 pagesAnatomy, Lecture 2, Joints (Lecture Notes)Ali Al-QudsiNo ratings yet
- Orthopaedic SlidesDocument163 pagesOrthopaedic SlidesVivian ChepkemeiNo ratings yet
- Musculoskeletal Assesment Medical Terminologies: Luyun, Erica Mae V. BSN 1 Set 01Document18 pagesMusculoskeletal Assesment Medical Terminologies: Luyun, Erica Mae V. BSN 1 Set 01Aldwin AyuyangNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Fracture: Parathyroid Hormone CalcitoninDocument6 pagesIntroduction To Fracture: Parathyroid Hormone CalcitoninJoem DagusanNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Fracture: Parathyroid Hormone CalcitoninDocument6 pagesIntroduction To Fracture: Parathyroid Hormone CalcitoninJoem DagusanNo ratings yet
- ArthroplastyDocument64 pagesArthroplastyAmit Kochhar75% (4)
- Proposedas A Task Subjects Basic Science NursingDocument20 pagesProposedas A Task Subjects Basic Science Nursingdwi adindaNo ratings yet
- Musculoskeletal Note1Document34 pagesMusculoskeletal Note1FreeNursingNotes100% (4)
- Pyogenic Discitis Power PointDocument121 pagesPyogenic Discitis Power Pointjav_luv37No ratings yet
- Chapter 45 CanvasDocument49 pagesChapter 45 CanvasSheNo ratings yet
- Module-5-The Skeletal SystemDocument13 pagesModule-5-The Skeletal SystemMARIA CORAZON CONTANTENo ratings yet
- 1the Functions of The Skeletal SystemDocument27 pages1the Functions of The Skeletal SystemRuffa May OlayaNo ratings yet
- Kacnkkle KC L CqlkecDocument25 pagesKacnkkle KC L CqlkecLing101No ratings yet
- Lec Activity6 Skeletal System CastroDocument8 pagesLec Activity6 Skeletal System CastropelielNo ratings yet
- Types of FractureDocument6 pagesTypes of FractureChristine Marie Barce MartinezNo ratings yet
- Ch07 - EOC - Skeletal SystemDocument4 pagesCh07 - EOC - Skeletal SystemGaveen CoatesNo ratings yet
- Musculoskeletal SystemDocument9 pagesMusculoskeletal SystemEduardson PHNo ratings yet
- Musculoskeletal and ENT (HERMOSISIMA)Document17 pagesMusculoskeletal and ENT (HERMOSISIMA)Jerom HermosisimaNo ratings yet
- Anatomy and PhysiologyDocument26 pagesAnatomy and Physiologymusondaaugustine07_4No ratings yet
- LommusculoDocument59 pagesLommusculoLibi FarrellNo ratings yet
- Document 5Document22 pagesDocument 5dawidkubiak222No ratings yet
- FIBROINTEGRATIONDocument11 pagesFIBROINTEGRATIONScribdTranslationsNo ratings yet
- Extended Project QualificationDocument15 pagesExtended Project Qualificationapi-215526022No ratings yet
- Lesson 3: Bone Growth, Remodeling, and Repair: Break A LegDocument8 pagesLesson 3: Bone Growth, Remodeling, and Repair: Break A LegEduardo SantosNo ratings yet
- Chronic OsteomyelitisDocument35 pagesChronic OsteomyelitisMelissa Gines100% (2)
- Knee ArthrosDocument13 pagesKnee ArthrosAna ĐikoliNo ratings yet
- 3 Bone Injury InflammationDocument24 pages3 Bone Injury InflammationGwyneth Koleen LopezNo ratings yet
- Fisiologi TulangDocument33 pagesFisiologi Tulangrizka dwi auliaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3Document12 pagesChapter 3Deolita BadiangNo ratings yet
- Skeletal System - mp4 - Google DriveDocument7 pagesSkeletal System - mp4 - Google Drivefaresalesa2005No ratings yet
- Musculoskeletal and ENDocument17 pagesMusculoskeletal and ENJerom HermosisimaNo ratings yet
- The Skeletal SystemDocument54 pagesThe Skeletal SystemsunepwalawallingwallingNo ratings yet
- 6.1 The Functions of The Skeletal System - Anatomy & PhysiologyDocument13 pages6.1 The Functions of The Skeletal System - Anatomy & PhysiologyA.No ratings yet
- NCM 104 Musculo Anaphy, DxticsDocument80 pagesNCM 104 Musculo Anaphy, DxticsJordz PlaciNo ratings yet
- SkeletAl SystemDocument18 pagesSkeletAl SystemYen BailadoNo ratings yet
- HANDOUTS Prelim CH 6Document40 pagesHANDOUTS Prelim CH 6Abia Annieson A. LorenzoNo ratings yet
- 02 Skeletal SystemDocument32 pages02 Skeletal SystemHarshika KDGNo ratings yet
- Case Study in GoutDocument17 pagesCase Study in GoutPaulette Olisco0% (1)
- Advanced farriery knowledge: A study guide and AWCF theory course companionFrom EverandAdvanced farriery knowledge: A study guide and AWCF theory course companionNo ratings yet
- FE Imbalances NotesDocument11 pagesFE Imbalances NotesFriday JaneNo ratings yet
- FE NOTESDocument3 pagesFE NOTESFriday JaneNo ratings yet
- Focus ChartingDocument31 pagesFocus ChartingFriday JaneNo ratings yet
- SCRUBBING With RationaleDocument3 pagesSCRUBBING With RationaleFriday JaneNo ratings yet
- Effects of Chewing On Cognitive Processing Speed PDFDocument6 pagesEffects of Chewing On Cognitive Processing Speed PDFValeria Alejandra Hilda Riquelme CárcamoNo ratings yet
- Atrial MyxomaDocument36 pagesAtrial MyxomaPrince Jevon YapNo ratings yet
- Krok 2014 Base All 2Document237 pagesKrok 2014 Base All 2Gaurav S Batra0% (1)
- Ehp 1206136Document7 pagesEhp 1206136SaiKai54No ratings yet
- SpermatogenesisDocument31 pagesSpermatogenesiselzenyNo ratings yet
- Nicom CompetencyDocument2 pagesNicom Competencyapi-258141893No ratings yet
- Organizing A High School Weight RoomDocument72 pagesOrganizing A High School Weight Roommalloryc100% (1)
- WorksheetDocument10 pagesWorksheetMomay RojalesNo ratings yet
- 4.nervous System of EarthwormDocument1 page4.nervous System of Earthwormarjab acharyaNo ratings yet
- Tri Strength TemplateDocument13 pagesTri Strength TemplateAmogh PanditNo ratings yet
- Lymphatic Research and BiologyDocument6 pagesLymphatic Research and BiologyJuhiJahan AmanullahNo ratings yet
- Behavioral NeuroscienceDocument40 pagesBehavioral Neurosciencebananita_2006533975% (4)
- Intro 70Document75 pagesIntro 70bockoneNo ratings yet
- Exercise 10 The Lymphatic System: ZOO 115 Animal Histology Laboratory Exercises 1Document4 pagesExercise 10 The Lymphatic System: ZOO 115 Animal Histology Laboratory Exercises 1Christi Lorraine LayogNo ratings yet
- GayaHidup August 2010Document32 pagesGayaHidup August 2010Elena Doina CristacheNo ratings yet
- Skenario IDocument12 pagesSkenario IRajasa FathahilllahNo ratings yet
- MALARIA Descriptive Epidemiology of MalariaDocument16 pagesMALARIA Descriptive Epidemiology of MalariaAms BeeNo ratings yet
- Characteristics of A NewbornDocument3 pagesCharacteristics of A NewbornNash EstoqueNo ratings yet
- The True Self 07Document12 pagesThe True Self 07Swaran J. Omcawr100% (2)
- Recent Advances in NGF and Related Molecules: Laura Calzà Luigi Aloe Luciana Giardino EditorsDocument302 pagesRecent Advances in NGF and Related Molecules: Laura Calzà Luigi Aloe Luciana Giardino EditorsPedro CastroNo ratings yet
- Nursing Practice 1Document4 pagesNursing Practice 1Nurul IzzahNo ratings yet
- Awesome ReviewDocument11 pagesAwesome Reviewapi-512337782No ratings yet
- Management of Diabetic Ketoacidosis in Children and AdolescentsDocument8 pagesManagement of Diabetic Ketoacidosis in Children and AdolescentsnurlatifahNo ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument6 pagesDrug Studyuntoned100% (1)
- Electricution ShockDocument4 pagesElectricution ShockQuinta HiiNo ratings yet
- JumpSTART Training Presentation Instructor Course 2016 FinalDocument109 pagesJumpSTART Training Presentation Instructor Course 2016 FinalvictorioNo ratings yet
- Interaction With PZ Myers' CommentersDocument36 pagesInteraction With PZ Myers' CommentersJustin VaculaNo ratings yet
- Soal Respi 2010Document41 pagesSoal Respi 2010Joseph ThanaNo ratings yet
- Physiology and Neurobiology of Stress and Adaptation - Central Role of The BrainDocument33 pagesPhysiology and Neurobiology of Stress and Adaptation - Central Role of The BrainJSGINo ratings yet
Musculoskeletal
Musculoskeletal
Uploaded by
Friday JaneCopyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Musculoskeletal
Musculoskeletal
Uploaded by
Friday JaneCopyright:
Available Formats
Key functions of the musculoskeletal system include Bone remodeling is a continuous process based on the
movement, structural support, protection of your internal activity of osteoblast, which are bone-forming cells, and
organs, blood cell production, and storage of minerals. osteoclast which are bone-destroying cells.
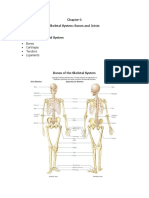
The components of the musculoskeletal system include So we have a little cool chicken hint here on the card.
bones as well as joints. So this is where two or more bones Osteoblast equals bone building. So when you see B for
come together to allow for movement. blast, think bone building.
So an example of a joint would be your shoulder or your There are a number of minerals and hormones to be
knee, which are examples of synovial joints, which we will familiar with that affect bone growth.
be talking more about here in a minute.
So calcium and phosphorus are essential minerals that are
Other components of the musculoskeletal system include needed for bone formation.
skeletal muscles, as well as tendons, which attach muscles
to bones, and ligaments, which attach bones to bones. So
if you could remember the phrase bones like bones, then
Vitamin D is needed for absorption of calcium. So if
that will help you remember that bones are attached to
someone's taking in enough calcium, if they don't have
other bones through ligaments because L for likes and L
enough vitamin D, then that calcium is not going to be
for ligaments. Here's an illustration of a long bone from
absorbed readily.
our medical-surgical nursing flashcard deck.
Parathyroid hormone or PTH is a hormone produced by
The outer layer of the bone is the cortex, which is made up
the parathyroid glands. And PTH will bring calcium out of
of dense, compact bone tissue.
the bones and into the bloodstream. So it will increase
blood calcium levels.
The inner layer of the bone is comprised of spongy bone
tissue, and it contains bone marrow, which is where
Calcitonin is a hormone that counteracts the activity of
hematopoiesis occurs, which is the formation of blood
PTH. So calcitonin will tone down those blood calcium
cells.
levels, and it does this by inhibiting the activity of
osteoclast, which are those bone destroying cells. It also
decreases reabsorption of calcium at the kidneys. So again,
So we have the red bone marrow here in the upper calcitonin is going to tone down blood calcium levels. And
epiphysis, and that contains stem cells that will become PTH is going to increase those blood calcium levels.
red blood cells, white blood cells, or platelets.
And then growth hormone will increase bone formation.
Then we have the yellow bone marrow here in the So it will stimulate the activity of osteoblast, which are
diaphysis, which contains stem cells that will become those bone-building cells.
cartilage, fat, or bone. So this line here that separates the
epiphysis from the diaphysis is the metaphysis, which
contains the epiphyseal plate or the growth plate.
All right. Let's now take a look at a joint and talk about the
different components of a synovial joint. Here's an
illustration of a synovial joint from our medical-surgical to visualize the internal structure of a joint, and it also
nursing flashcard deck. So a synovial joint is a freely allows for the collection of biopsies. If we are doing an
movable joint such as the elbow or the knee. arthroscopy on a knee, the patient needs to be able to
bend their knee at least 40 degrees and there cannot be
any active infection present in that knee.
And you can see that we have the joint capsule, which
surrounds that synovial joint and is comprised of fibrous
connective tissue. Then we have a DXA, which is a dual X-ray absorptiometry.
And this procedure uses low levels of X-rays to measure a
patient's bone mass.
Then we have the synovium here, which is a membrane
that lines the joint capsule and secretes synovial fluid,
which helps to provide lubrication and shock absorption at So it is used to diagnose osteoporosis, which we will
that joint. definitely be talking more about later in this playlist.
The joint cavity here is fluid filled, and it is where the Then we have nuclear scans, which are used to identify
articulating surfaces of the two bones come in contact fractures, bone cancer, as well as bone infections.
with each other.
So for this procedure, a radioactive substance or isotope is
And we have this articular cartilage, which lines the administered to the patient about four to six hours before
surface of each of the bones in the synovial joint. The the procedure. And this radioactive material will gather in
purpose of this articular cartilage is to allow the bones to places of chemical or physical changes in the bone. So if
glide smoothly against each other. We will be talking the patient has bone cancer, for example, that's going to
about osteoarthritis in another video in this playlist, which cause rapidly replicating cells in the area of the bone
is caused by the wear and tear of this articular cartilage. cancer. And this radioactive material will definitely be
attracted to that area and gather in the site of that bone
______ cancer. Then when we do the scan, the nuclear scan of the
patient, we will see this hot spot where this radioactive
First up, let's talk about an arthrocentesis, which is
material has gathered. So nuclear scans can be repeated at
aspiration of synovial fluid from the joint cavity. And we
24, 48, and 72 hours.
may be removing some of the synovial fluid in order to
assist with diagnosis of an infection.
And then finally, we have something called an
electromyography, which is used to evaluate muscle
So for example, we'll take some of that synovial fluid and
weakness.
run a culture on it to see if the patient has infection. We
may also be removing some synovial fluid to help with
pain control. So if a patient has severe swelling, removal of
some of that fluid can help to decrease their pain. We may For example, if we're trying to diagnose myasthenia gravis,
also do a arthrocentesis in preparation for the injection of which we will be talking about in this playlist, then an
medications into that joint cavity, such as corticosteroids. electromyography would definitely be helpful. So during
this procedure, we have needles that are inserted into the
muscles and the electrical activity of the muscle is
recorded. And my understanding is that this is not a
Another diagnostic procedure to know within the
comfortable procedure. It's not like super painful, but it is
musculoskeletal system is an arthroscopy. This is where
definitely not pleasant
we insert a narrow tube with a camera on the end in order
_____
improve his pain with the RA. So, hopefully that will help
you remember that with RA, we get swan neck deformities
and boutonniere deformities. So think about that swan
with the boutonniere going to dance. Other deformities
are present as well that we talked about, like that ulnar
drift, etc.
And then, finally, when we run labs, a patient with
osteoarthritis will have a negative rheumatoid factor, as
opposed to a patient with rheumatoid arthritis who have a
positive rheumatoid factor.
You might also like
- Case File HuckabyDocument7 pagesCase File HuckabyAmrit SahotaNo ratings yet
- Avn On ScriptDocument13 pagesAvn On Scriptclaire.deveraNo ratings yet
- Hard Tissue Replacement-OrthopedicsDocument77 pagesHard Tissue Replacement-OrthopedicsbiomedyuvaNo ratings yet
- Orthopedic NursingDocument201 pagesOrthopedic NursingMitch Hellgirl Almonte100% (2)
- Fascial Fitness - SchleipDocument44 pagesFascial Fitness - SchleipIacopoMariaFilippoBarniNo ratings yet
- Movement System: By: Fadhilah HarmenDocument30 pagesMovement System: By: Fadhilah HarmenFadhilah HarmenNo ratings yet
- Musculos Descripcion Video 1Document4 pagesMusculos Descripcion Video 1fiorellaNo ratings yet
- Locomotion System: (Skeletal and Muscular Systems)Document36 pagesLocomotion System: (Skeletal and Muscular Systems)Cut Thirza TalithaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 6 Content Review Questions 1-8Document3 pagesChapter 6 Content Review Questions 1-8Rhonique MorganNo ratings yet
- Topic 5. Bone Microscopic Anatomy and Devt 1Document24 pagesTopic 5. Bone Microscopic Anatomy and Devt 1Janine Jerica JontilanoNo ratings yet
- A FractureDocument10 pagesA FractureFredimar CondeNo ratings yet
- Functions of The Musculoskeletal SystemDocument9 pagesFunctions of The Musculoskeletal SystemLinda XueNo ratings yet
- HSS AnatomyDocument5 pagesHSS AnatomyruguNo ratings yet
- Script Case PressDocument7 pagesScript Case PressMa. Gina DerlaNo ratings yet
- Skeletal - Break A LegDocument9 pagesSkeletal - Break A LegShannon SandersNo ratings yet
- Biology of OtmDocument19 pagesBiology of OtmNaveenNo ratings yet
- Total Hip Replacement - Educational PacketDocument19 pagesTotal Hip Replacement - Educational Packetapi-549337910No ratings yet
- Skeletal SystemDocument104 pagesSkeletal Systemsyafi zulNo ratings yet
- OrifDocument13 pagesOrifAhmabelle Mara D. AbellaNo ratings yet
- Case Study For CastDocument10 pagesCase Study For CastMaria JuvilisaNo ratings yet
- Anaphy Exercise 5 - SKELETAL AND ARTICULAR SYSTEMDocument12 pagesAnaphy Exercise 5 - SKELETAL AND ARTICULAR SYSTEMKenzoNo ratings yet
- Anatomy, Lecture 2, Joints (Lecture Notes)Document12 pagesAnatomy, Lecture 2, Joints (Lecture Notes)Ali Al-QudsiNo ratings yet
- Orthopaedic SlidesDocument163 pagesOrthopaedic SlidesVivian ChepkemeiNo ratings yet
- Musculoskeletal Assesment Medical Terminologies: Luyun, Erica Mae V. BSN 1 Set 01Document18 pagesMusculoskeletal Assesment Medical Terminologies: Luyun, Erica Mae V. BSN 1 Set 01Aldwin AyuyangNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Fracture: Parathyroid Hormone CalcitoninDocument6 pagesIntroduction To Fracture: Parathyroid Hormone CalcitoninJoem DagusanNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Fracture: Parathyroid Hormone CalcitoninDocument6 pagesIntroduction To Fracture: Parathyroid Hormone CalcitoninJoem DagusanNo ratings yet
- ArthroplastyDocument64 pagesArthroplastyAmit Kochhar75% (4)
- Proposedas A Task Subjects Basic Science NursingDocument20 pagesProposedas A Task Subjects Basic Science Nursingdwi adindaNo ratings yet
- Musculoskeletal Note1Document34 pagesMusculoskeletal Note1FreeNursingNotes100% (4)
- Pyogenic Discitis Power PointDocument121 pagesPyogenic Discitis Power Pointjav_luv37No ratings yet
- Chapter 45 CanvasDocument49 pagesChapter 45 CanvasSheNo ratings yet
- Module-5-The Skeletal SystemDocument13 pagesModule-5-The Skeletal SystemMARIA CORAZON CONTANTENo ratings yet
- 1the Functions of The Skeletal SystemDocument27 pages1the Functions of The Skeletal SystemRuffa May OlayaNo ratings yet
- Kacnkkle KC L CqlkecDocument25 pagesKacnkkle KC L CqlkecLing101No ratings yet
- Lec Activity6 Skeletal System CastroDocument8 pagesLec Activity6 Skeletal System CastropelielNo ratings yet
- Types of FractureDocument6 pagesTypes of FractureChristine Marie Barce MartinezNo ratings yet
- Ch07 - EOC - Skeletal SystemDocument4 pagesCh07 - EOC - Skeletal SystemGaveen CoatesNo ratings yet
- Musculoskeletal SystemDocument9 pagesMusculoskeletal SystemEduardson PHNo ratings yet
- Musculoskeletal and ENT (HERMOSISIMA)Document17 pagesMusculoskeletal and ENT (HERMOSISIMA)Jerom HermosisimaNo ratings yet
- Anatomy and PhysiologyDocument26 pagesAnatomy and Physiologymusondaaugustine07_4No ratings yet
- LommusculoDocument59 pagesLommusculoLibi FarrellNo ratings yet
- Document 5Document22 pagesDocument 5dawidkubiak222No ratings yet
- FIBROINTEGRATIONDocument11 pagesFIBROINTEGRATIONScribdTranslationsNo ratings yet
- Extended Project QualificationDocument15 pagesExtended Project Qualificationapi-215526022No ratings yet
- Lesson 3: Bone Growth, Remodeling, and Repair: Break A LegDocument8 pagesLesson 3: Bone Growth, Remodeling, and Repair: Break A LegEduardo SantosNo ratings yet
- Chronic OsteomyelitisDocument35 pagesChronic OsteomyelitisMelissa Gines100% (2)
- Knee ArthrosDocument13 pagesKnee ArthrosAna ĐikoliNo ratings yet
- 3 Bone Injury InflammationDocument24 pages3 Bone Injury InflammationGwyneth Koleen LopezNo ratings yet
- Fisiologi TulangDocument33 pagesFisiologi Tulangrizka dwi auliaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3Document12 pagesChapter 3Deolita BadiangNo ratings yet
- Skeletal System - mp4 - Google DriveDocument7 pagesSkeletal System - mp4 - Google Drivefaresalesa2005No ratings yet
- Musculoskeletal and ENDocument17 pagesMusculoskeletal and ENJerom HermosisimaNo ratings yet
- The Skeletal SystemDocument54 pagesThe Skeletal SystemsunepwalawallingwallingNo ratings yet
- 6.1 The Functions of The Skeletal System - Anatomy & PhysiologyDocument13 pages6.1 The Functions of The Skeletal System - Anatomy & PhysiologyA.No ratings yet
- NCM 104 Musculo Anaphy, DxticsDocument80 pagesNCM 104 Musculo Anaphy, DxticsJordz PlaciNo ratings yet
- SkeletAl SystemDocument18 pagesSkeletAl SystemYen BailadoNo ratings yet
- HANDOUTS Prelim CH 6Document40 pagesHANDOUTS Prelim CH 6Abia Annieson A. LorenzoNo ratings yet
- 02 Skeletal SystemDocument32 pages02 Skeletal SystemHarshika KDGNo ratings yet
- Case Study in GoutDocument17 pagesCase Study in GoutPaulette Olisco0% (1)
- Advanced farriery knowledge: A study guide and AWCF theory course companionFrom EverandAdvanced farriery knowledge: A study guide and AWCF theory course companionNo ratings yet
- FE Imbalances NotesDocument11 pagesFE Imbalances NotesFriday JaneNo ratings yet
- FE NOTESDocument3 pagesFE NOTESFriday JaneNo ratings yet
- Focus ChartingDocument31 pagesFocus ChartingFriday JaneNo ratings yet
- SCRUBBING With RationaleDocument3 pagesSCRUBBING With RationaleFriday JaneNo ratings yet
- Effects of Chewing On Cognitive Processing Speed PDFDocument6 pagesEffects of Chewing On Cognitive Processing Speed PDFValeria Alejandra Hilda Riquelme CárcamoNo ratings yet
- Atrial MyxomaDocument36 pagesAtrial MyxomaPrince Jevon YapNo ratings yet
- Krok 2014 Base All 2Document237 pagesKrok 2014 Base All 2Gaurav S Batra0% (1)
- Ehp 1206136Document7 pagesEhp 1206136SaiKai54No ratings yet
- SpermatogenesisDocument31 pagesSpermatogenesiselzenyNo ratings yet
- Nicom CompetencyDocument2 pagesNicom Competencyapi-258141893No ratings yet
- Organizing A High School Weight RoomDocument72 pagesOrganizing A High School Weight Roommalloryc100% (1)
- WorksheetDocument10 pagesWorksheetMomay RojalesNo ratings yet
- 4.nervous System of EarthwormDocument1 page4.nervous System of Earthwormarjab acharyaNo ratings yet
- Tri Strength TemplateDocument13 pagesTri Strength TemplateAmogh PanditNo ratings yet
- Lymphatic Research and BiologyDocument6 pagesLymphatic Research and BiologyJuhiJahan AmanullahNo ratings yet
- Behavioral NeuroscienceDocument40 pagesBehavioral Neurosciencebananita_2006533975% (4)
- Intro 70Document75 pagesIntro 70bockoneNo ratings yet
- Exercise 10 The Lymphatic System: ZOO 115 Animal Histology Laboratory Exercises 1Document4 pagesExercise 10 The Lymphatic System: ZOO 115 Animal Histology Laboratory Exercises 1Christi Lorraine LayogNo ratings yet
- GayaHidup August 2010Document32 pagesGayaHidup August 2010Elena Doina CristacheNo ratings yet
- Skenario IDocument12 pagesSkenario IRajasa FathahilllahNo ratings yet
- MALARIA Descriptive Epidemiology of MalariaDocument16 pagesMALARIA Descriptive Epidemiology of MalariaAms BeeNo ratings yet
- Characteristics of A NewbornDocument3 pagesCharacteristics of A NewbornNash EstoqueNo ratings yet
- The True Self 07Document12 pagesThe True Self 07Swaran J. Omcawr100% (2)
- Recent Advances in NGF and Related Molecules: Laura Calzà Luigi Aloe Luciana Giardino EditorsDocument302 pagesRecent Advances in NGF and Related Molecules: Laura Calzà Luigi Aloe Luciana Giardino EditorsPedro CastroNo ratings yet
- Nursing Practice 1Document4 pagesNursing Practice 1Nurul IzzahNo ratings yet
- Awesome ReviewDocument11 pagesAwesome Reviewapi-512337782No ratings yet
- Management of Diabetic Ketoacidosis in Children and AdolescentsDocument8 pagesManagement of Diabetic Ketoacidosis in Children and AdolescentsnurlatifahNo ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument6 pagesDrug Studyuntoned100% (1)
- Electricution ShockDocument4 pagesElectricution ShockQuinta HiiNo ratings yet
- JumpSTART Training Presentation Instructor Course 2016 FinalDocument109 pagesJumpSTART Training Presentation Instructor Course 2016 FinalvictorioNo ratings yet
- Interaction With PZ Myers' CommentersDocument36 pagesInteraction With PZ Myers' CommentersJustin VaculaNo ratings yet
- Soal Respi 2010Document41 pagesSoal Respi 2010Joseph ThanaNo ratings yet
- Physiology and Neurobiology of Stress and Adaptation - Central Role of The BrainDocument33 pagesPhysiology and Neurobiology of Stress and Adaptation - Central Role of The BrainJSGINo ratings yet