Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Bios - Fungi
Bios - Fungi
Uploaded by
calebleu0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
2 views7 pagesCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pdf or txt
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
2 views7 pagesBios - Fungi
Bios - Fungi
Uploaded by
calebleuCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pdf or txt
You are on page 1of 7
Malassezia furfur Fungi Bio Clinical Presentation:
- Lipophilic yeast 1) Pityriasis – superficial infection
- Normal flora on most adults, not a - Hyper- or hypopigmented macular lesions on
dermatophyte trunk and limbs
- Spaghetti and meatballs appearance - Does not affect hair or nails
2) Invasive infection – in NICU when receiving
parenteral nutrition (high lipid content)
- risk of fungemia
Disease: Tinea versicolor, pityriasis
Carrierstate: normal flora Diagnosis:
- Direct microscopy
Treatment and resistance:
- Largely aesthetic issue, treatment not necessary
- Must treat infected infants, immunocompromised
Sporothrix schenckii Fungi Bio Clinical Presentation:
- Dimorphic fungus 1) Rose-handler’s disease
- Not an endemic - Deep ulcerated skin lesions with spread along
- Subcutaneous infection requiring trauma to lymphatic channels
enter (thorn, barb or pine needle injury) - Lesions are granulomas
- Present in soil and moss worldwide
- Rarely invades deeper tissues
- Rose handlers, tree farmers, hay bailers,
gardeners more likely to get infected
Disease: see clinical presentation
Carrierstate: N/A Diagnosis:
- Tissue biopsy of leading nodules (swabs of lesions
are low yield)
- Direct microscopy and culture
Treatment and resistance:
- Don’t need to know
Candida sp. Fungi Bio Clinical Presentation:
- yeast 1) Immunocompetent – frequently asymptomatic
- common species include C. albicans (50-60% - Thrush, vaginitis, diaper rash
of all infections), C. glabrata, C. tropicalis, C. - Candidemia ranges from asymptomatic to
parapsilosis, C. krusei sepsis (fever common)
- endogenous flora on skin, mouth, GI tract,
2) Immunocompromised
vagina
- budding yeast with pseudohyphae - severe thrush, esophagitis, endophthalmitis,
- risks: entry point for candida, endocarditis, meningitis, UTI, peritonitis,
immunosuppressed hepatosplenomegaly, abscess
Disease: see clinical presentation
Carrierstate: normal flora Diagnosis:
- Cellular morphology on agar
- Microscopic examination of blood/tissue
- Germ tube (C. albicans only)
Treatment and resistance:
- ALL positive blood cultures require treatment, do NOT
delay, remove all lines
- Fluconazole or Caspofungin then Ampho B (+/- resistance)
- Surgery for endocarditis, intravitreal injections for
endophthtalmitis,
- Topical treatment, nystatin useful for non-invasive infection
-
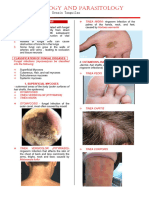
Superficial infections Fungi Bio Clinical Presentation:
1) Tinea capitis – head
- 3 genera: Trichophyton, Microsporum, - annular scaling patch with raised margin, +/-
Epidermophyton pustules and hair loss, dandruff
- moulds, tropism for keratinized tissue (skin, - M. Canis from dogs, common in kids
hair, nails) and chronic growth 2) Tinea corporis – body (ring worm)
- Do not invade deeper than skin due to tropism, - Trichophyton species, common in athletes
inability to grow at 37° C, and inability to - annular scaling patch with raised margin
withstand innate immunity
3) Tinea pedis – feet (athlete’s foot)
- Keratinases and binding factors allow
- Itching, erythema, scaling +/- pustules
germination
- E. floccosum, T. mentagrophytes in sports, wet,
- May be zoophilic, anthropophilic or geophilic
poor hygiene
4) Tinea cruris – groin (jock itch)
- scaling and irritation of groin and inner thigh, no
pustules
Disease: see clinical presentation - T. rubrum, E. floccosum, in military and
institutionalized
Carrierstate: N/A
5) Tinea unguium – nails
- onchomycosis, discoloration, thickening, scaling
- T. rubrum, Candida sp.
Diagnosis
- Skin/nail scraping or collection of hair stubs
- Direct microscopy or culture
Treatment and resistance
- Topical treatments
Coccidioides immitis Fungi Bio Clinical Presentation:
- Dimorphic fungus – hyphae and spherules 1) Primary infections
- Endemic to central USA, particularly Arizona - 60% asymptomatic, 40% flu-like illness
- “Snowbird” disease - usually resolves without treatment in 2-3
- Present in soil and arthroconidia may be kicked weeks
up by dust storms
2) Pulmonary disease
- chronic pneumonia, pulmonary nodules and
cavitation – quickly progresses, fatal
3) Extrapulmonary disease
- dissemination in blood, seeds to skin, joints,
bone and brain (meningitis)
Disease: see clinical presentation
Carrierstate: N/A Diagnosis:
- CXR with infiltrates and hilar lymphadenopathy
- Biopsy and culture
- Ab detection
Treatment and resistance:
- Amphotericin B, fluconazole or itraconazole
- Treat only serious infections or infections in
immunocompromised
Blastomycosis dermatitidis Fungi Bio Clinical Presentation:
- Dimorphic fungus – mould and yeast 1) Pulmonary disease – inhalation of conidia
- Endemic to south eastern USA, river basins - Highly variable disease, may be asympomatic
- Infection in pet dogs may be a sentinel event or flu-like
- No anthropophilic transmission
- Cough initially nonproductive, but later
becomes purulent
2) Extrapulmonary disease
- dissemination in blood, seeds to skin
(lesions), joints and bones, genitourinary tract
and brain (meningitis or abscess)
Disease: see clinical presentation
Carrierstate: N/A Diagnosis:
- CXR with lobular consolidation +/- cavitation, hilar
lymphadenopathy rare
- Smear from tissue or exudate
Treatment and resistance:
- All cases MUST be treated – mortality reaches 60%
otherwise
- Ketoconazole or itraconazole in most cases, Ampho B in
severe/immunocompromised
Histoplasmosis capsulatum Fungi Bio Clinical Presentation:
- Dimorphic fungus – mould and yeast 1) Pulmonary disease – inhalation of conidia
- Endemic to Mississippi and Ohio river valleys - May cause granulomas, calcification of
- Bird and bat feces aids growth (watch out for masses, fibrosis, cavitation, hemoptysis,
spelunkers, chicken coop cleaners, etc.) 2) Acute progressive disseminated disease
- Favors moderate climate and humidity
- Abrupt onset of fever, malaise, weight loss,
- Disease severity is related to the size of the
inoculum cough, diarrhea, rash, pancytopenia
- 100% fatal if untreated
- may be chronic if a slower onset
- complications include CNS involvement,
endocarditis
Disease: see clinical presentation
Carrierstate: N/A Diagnosis:
- CXR with patchy infiltrates and hilar
lymphadenopathy
- Fungal stain most useful, culture, serology and Ag
detection helpful
Treatment and resistance:
- Symptoms usually resolve in 10 days
- Itraconazole in most cases, Ampho B then itraconazole in
severe/immunocompromised
You might also like
- The MCAT Physics BookDocument445 pagesThe MCAT Physics Bookichephren75% (12)
- Maximillien de Lafayette PDFDocument43 pagesMaximillien de Lafayette PDFAmeli Apuy80% (10)
- Exam 3Document9 pagesExam 3karlNo ratings yet
- Chapter 4Document6 pagesChapter 4VikasNo ratings yet
- Bacterial Infection 2Document3 pagesBacterial Infection 2jihanNo ratings yet
- MicrofinalDocument7 pagesMicrofinaljwanaNo ratings yet
- Microbiology PinkDocument3 pagesMicrobiology PinkBenjamin GaliaNo ratings yet
- Mycology TransDocument11 pagesMycology TransKita kitaNo ratings yet
- Mycology SOM CJBDocument91 pagesMycology SOM CJBYlia MastarsNo ratings yet
- Med Org Topic 234Document9 pagesMed Org Topic 234barbadillojames419No ratings yet
- Lecture-2: Pustular Diseases of The Skin and Mucous Membranes. Mycotic Skin and Mucous Membranes. Viral DermatosesDocument31 pagesLecture-2: Pustular Diseases of The Skin and Mucous Membranes. Mycotic Skin and Mucous Membranes. Viral DermatosesLatika ChoudhuryNo ratings yet
- Bios - ParasitesDocument15 pagesBios - ParasitescalebleuNo ratings yet
- FUNGAL and PARASITIC INFECTIONSDocument3 pagesFUNGAL and PARASITIC INFECTIONSKathleen Hazel AndresNo ratings yet
- Lecture 2 Cutaneous and Subcutaneous MycosesDocument46 pagesLecture 2 Cutaneous and Subcutaneous MycoseschiyeoncherryNo ratings yet
- Clinical AND ADVANCE Pathology: TopicDocument7 pagesClinical AND ADVANCE Pathology: TopicNestley TiongsonNo ratings yet
- $RG8JJJ1Document82 pages$RG8JJJ1Rasha mohammadNo ratings yet
- Fungal InfectionDocument3 pagesFungal InfectionNicole TorralbaNo ratings yet
- Antifungal Agents General Introduction To Fungi: Medical Mycology Cutaneous Infections (Dermatophytoses)Document4 pagesAntifungal Agents General Introduction To Fungi: Medical Mycology Cutaneous Infections (Dermatophytoses)Ad Rianne DeniseNo ratings yet
- Fungal Infections Mycotic Infections MycosesDocument12 pagesFungal Infections Mycotic Infections MycosesHussein QasimNo ratings yet
- Opportunistic MycosesDocument6 pagesOpportunistic MycosesJullana Rondina EscondeNo ratings yet
- Reviewer in Micro para Lec FinalsDocument9 pagesReviewer in Micro para Lec FinalsJohn Carl CastilloNo ratings yet
- SDL - 5 Wound MicrobiologyDocument7 pagesSDL - 5 Wound MicrobiologyShift UallNo ratings yet
- InfestDocument26 pagesInfestIndraNo ratings yet
- PEDIA Bacterial Infections Part 2 Dr. E. Lim FinalDocument5 pagesPEDIA Bacterial Infections Part 2 Dr. E. Lim FinalClaire DuNo ratings yet
- Module#2-Student Activity Sheet SUPERFICIAL YCOSESDocument5 pagesModule#2-Student Activity Sheet SUPERFICIAL YCOSESYlia MastarsNo ratings yet
- Microbiology 19 PDFDocument6 pagesMicrobiology 19 PDFLyka Villagracia AsiloNo ratings yet
- Community in Tables AllTalabaDocument14 pagesCommunity in Tables AllTalabaAhmed MansourNo ratings yet
- Antifungal TheraphyDocument4 pagesAntifungal TheraphyOrhan AsdfghjklNo ratings yet
- Fungal Infections: Sri Winarsih - Pharmacy Study Program FmubDocument58 pagesFungal Infections: Sri Winarsih - Pharmacy Study Program FmubWidi Alya ZhafiraNo ratings yet
- DNA VIRUSES-handout PDFDocument11 pagesDNA VIRUSES-handout PDFROTHESSA MARY CARINGALNo ratings yet
- Pedia Bacte Table 08amDocument25 pagesPedia Bacte Table 08ampedia blue bookNo ratings yet
- Dermatomyositis: Dermatoses Morphology Etiology PathogenesisDocument3 pagesDermatomyositis: Dermatoses Morphology Etiology PathogenesisRiena Austine Leonor NarcillaNo ratings yet
- MycosesDocument7 pagesMycosesJazmine Rose DelrosarioNo ratings yet
- Dermatology RevisionDocument7 pagesDermatology RevisionAbdelrahman MohamedNo ratings yet
- CandidiasisDocument27 pagesCandidiasisfarmasi_hmNo ratings yet
- MICP Bacterial Infections s1Document12 pagesMICP Bacterial Infections s1Valerian VolkzkiNo ratings yet
- Overview of Skin InfectionsDocument53 pagesOverview of Skin Infectionsadamu mohammadNo ratings yet
- Opportunistic Mycoses - DR SantosDocument20 pagesOpportunistic Mycoses - DR SantosRonald BeasleyNo ratings yet
- Tinea Corporis, Caused by Microsporum Canis - A Case Report From KosovoDocument2 pagesTinea Corporis, Caused by Microsporum Canis - A Case Report From KosovoAsterlita RyaneNo ratings yet
- PapulosquamousDocument5 pagesPapulosquamousMinh ChâuNo ratings yet
- PREFINALS HandoutsDocument82 pagesPREFINALS HandoutskrstnkyslNo ratings yet
- General Pathology of Infectious DiseasesDocument47 pagesGeneral Pathology of Infectious DiseasesAbdullah EmadNo ratings yet
- Bacteria TableDocument4 pagesBacteria TableBrittany Lynn Myers100% (1)
- Enterococci: S. AureusDocument2 pagesEnterococci: S. AureusShift UallNo ratings yet
- Ssti 2021Document65 pagesSsti 2021Ausu OfficialNo ratings yet
- Med Surg (Midterm)Document9 pagesMed Surg (Midterm)Jennica BubanNo ratings yet
- SubcutaneousDocument2 pagesSubcutaneousMary ChristelleNo ratings yet
- Parasit IntegumenDocument43 pagesParasit Integumenandi mutiah armusNo ratings yet
- Macules Papules Plaques Nodules Bullae Pustules Urticaria (Wheals or HivesDocument10 pagesMacules Papules Plaques Nodules Bullae Pustules Urticaria (Wheals or HivesHERLIN HOBAYANNo ratings yet
- l7 Common Bacterial Infection in DermatologyDocument35 pagesl7 Common Bacterial Infection in DermatologyOmar HamwiNo ratings yet
- Pseudo, Burk, Histo, Glae, Avi, Actino, Fuso, Bacte, Dichelo DiseasesDocument14 pagesPseudo, Burk, Histo, Glae, Avi, Actino, Fuso, Bacte, Dichelo DiseasesTricia Mae JuanitasNo ratings yet
- FungiDocument3 pagesFungikrystal TortolaNo ratings yet
- Bacte Lec 1Document11 pagesBacte Lec 12234382No ratings yet
- DERM NotesDocument19 pagesDERM NoteszakyNo ratings yet
- FILARIASISDocument2 pagesFILARIASIShaoc0425No ratings yet
- W2 Antimicrobial DrugsDocument3 pagesW2 Antimicrobial Drugsseanne kskwkwkaNo ratings yet
- w2 Antimicrobial DrugsDocument3 pagesw2 Antimicrobial Drugsseanne kskwkwkaNo ratings yet
- Bacteriology Edited 1Document65 pagesBacteriology Edited 1Ali AhmedNo ratings yet
- Pathogens That Involve The SkinDocument57 pagesPathogens That Involve The SkinLeeShauran100% (2)
- Introduction To Fungi: Ex - Aspergillus, DermatophytesDocument4 pagesIntroduction To Fungi: Ex - Aspergillus, DermatophytesBanana CakeNo ratings yet
- Infection Control PDFDocument3 pagesInfection Control PDFLaura CerritelliNo ratings yet
- Derma PrintDocument82 pagesDerma PrintthackeryuktaNo ratings yet
- 3) Bacterial Skin Infections Semi NotesDocument2 pages3) Bacterial Skin Infections Semi NotesIssa MoodNo ratings yet
- Dermatology Notes for Medical StudentsFrom EverandDermatology Notes for Medical StudentsRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (5)
- PPT - Polymers-Final-3-161225131244Document37 pagesPPT - Polymers-Final-3-161225131244mahaNo ratings yet
- BOSCH 01 Family OriginsDocument7 pagesBOSCH 01 Family OriginsAntonela ElenaNo ratings yet
- Ultra: DSE3000 Series Control ModuleDocument45 pagesUltra: DSE3000 Series Control ModuleGabriel RochaNo ratings yet
- Angle MergesDocument1 pageAngle Mergesdesky nguyenNo ratings yet
- Trimble R8s GNSS Receiver: User GuideDocument71 pagesTrimble R8s GNSS Receiver: User GuideSilvio Vuolo NetoNo ratings yet
- Science Mentor Guide of HOTS 2022Document34 pagesScience Mentor Guide of HOTS 2022Ike LeeNo ratings yet
- Guide To Organic Farming in India, 2011.Document13 pagesGuide To Organic Farming in India, 2011.Amrit Sharma100% (3)
- Agricultural Cooperative Society ReportDocument44 pagesAgricultural Cooperative Society Reportckeerthana56No ratings yet
- IELTS Writing Task1 TableDocument16 pagesIELTS Writing Task1 TableRakesh Kumar Sharma100% (1)
- EPC Saur Energy InternationalDocument3 pagesEPC Saur Energy InternationalNarendra PatelNo ratings yet
- CIMAP Charges For AnalysisDocument11 pagesCIMAP Charges For AnalysisSaloman RaviNo ratings yet
- Lea 1 To Lea 6Document415 pagesLea 1 To Lea 6kimkimkouiNo ratings yet
- TechRef StationControllerDocument28 pagesTechRef StationControllerАлишер ГалиевNo ratings yet
- Quarter 3 - Module 1-W3: Computer Systems Servicing (CSS)Document3 pagesQuarter 3 - Module 1-W3: Computer Systems Servicing (CSS)AC BalioNo ratings yet
- Chemical Technicians 10-2021Document30 pagesChemical Technicians 10-2021PRC Baguio0% (1)
- ML-C and C Micro PDFDocument94 pagesML-C and C Micro PDFvulcanescuNo ratings yet
- Orientation Special... : Byu Indian Education Department SUMMER 1979Document4 pagesOrientation Special... : Byu Indian Education Department SUMMER 1979blopbookNo ratings yet
- FovizamDocument18 pagesFovizamMickey PierceNo ratings yet
- Engl 316 Resume FinalDocument1 pageEngl 316 Resume Finalapi-466382256No ratings yet
- Shri A.D.K.Mahila Polytechnic, Mathura: Summer Training ReportDocument46 pagesShri A.D.K.Mahila Polytechnic, Mathura: Summer Training Reportanand011No ratings yet
- Project of SecurityDocument9 pagesProject of SecurityBerehe GezuNo ratings yet
- Herodotus and The Emergence of The DemagDocument15 pagesHerodotus and The Emergence of The DemagKsenija BirmanacNo ratings yet
- Skills Needed For Discussion of Research PaperDocument21 pagesSkills Needed For Discussion of Research PaperPacha Khan Khogyani100% (1)
- 2nd Dispatch DLPD - IIT JEE - Class XI - English - PC (Physics) PDFDocument162 pages2nd Dispatch DLPD - IIT JEE - Class XI - English - PC (Physics) PDFRaja Bisht50% (8)
- Https Sis Cat Com Sisweb Sisweb Techdoc Techdoc Print Page 2Document4 pagesHttps Sis Cat Com Sisweb Sisweb Techdoc Techdoc Print Page 2Tshidiso LekalakalaNo ratings yet
- Lecture 2-Environmental Health HazardsDocument13 pagesLecture 2-Environmental Health HazardsAzizulHuqueNo ratings yet