Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Lesson 2.2_ Animal Cells
Lesson 2.2_ Animal Cells
Uploaded by
d5mzdt2khbCopyright:
Available Formats
You might also like
- Installation and Operating Instructions Weishaupt Gas Burners Sizes 1 To 11Document46 pagesInstallation and Operating Instructions Weishaupt Gas Burners Sizes 1 To 11abuMalak75% (4)
- Activity 2: Unifying Themes in The Study of Life: A. DAD (Decode, Arrange, Describe)Document12 pagesActivity 2: Unifying Themes in The Study of Life: A. DAD (Decode, Arrange, Describe)Kyla Renoballes92% (12)
- Toshiba Case 3Document4 pagesToshiba Case 3Deta Detade100% (1)
- Ic 01 Last Day Test 3Document30 pagesIc 01 Last Day Test 3Sohini0% (1)
- Presentation On Busbar Arrangement, 87B & 50BF ProtectionDocument55 pagesPresentation On Busbar Arrangement, 87B & 50BF Protectionabu sayedNo ratings yet
- SPLK-1001: Number: SPLK-1001 Passing Score: 800 Time Limit: 120 Min File Version: 1Document36 pagesSPLK-1001: Number: SPLK-1001 Passing Score: 800 Time Limit: 120 Min File Version: 1abhishek_singh10272No ratings yet
- LESSON 3 - CELL MODIFICATION (Sofia Talagon)Document5 pagesLESSON 3 - CELL MODIFICATION (Sofia Talagon)Rafael SalcedoNo ratings yet
- Grade 7 Science Worksheets For January 8-12-2024Document7 pagesGrade 7 Science Worksheets For January 8-12-2024mark john baltazarNo ratings yet
- CHAPTER 1. Anatomy and Physiology OverviewDocument11 pagesCHAPTER 1. Anatomy and Physiology Overviewwella wellaNo ratings yet
- The Biosphere: Living BeingsDocument44 pagesThe Biosphere: Living BeingsGuillermo ChavesNo ratings yet
- 001 - Science 2 ImageDocument1 page001 - Science 2 Imagesantiago Estrada VasquezNo ratings yet
- 1 Organization of Living ThingsDocument2 pages1 Organization of Living ThingscarlNo ratings yet
- St. Anthony's College San Jose, Antique High School Department SY 2020 - 2021 General Biology 1 Name: Grade/Section: Activity 1: ApplicationDocument3 pagesSt. Anthony's College San Jose, Antique High School Department SY 2020 - 2021 General Biology 1 Name: Grade/Section: Activity 1: ApplicationMichal Decena CastroNo ratings yet
- GEN BIO 2 Final ReviewerDocument12 pagesGEN BIO 2 Final ReviewerJemuel Luc JavierNo ratings yet
- Marielle Hoefnagels - Biology - First SessionDocument10 pagesMarielle Hoefnagels - Biology - First SessionNegar AslaniNo ratings yet
- Biology ModuleDocument8 pagesBiology Modulerian ririNo ratings yet
- Unifying Themes of LifeDocument33 pagesUnifying Themes of LifeRyan Dave MacariayNo ratings yet
- Foz Lec M2Document9 pagesFoz Lec M2jsbitsoflyfNo ratings yet
- Anatomy and PhysiologyDocument6 pagesAnatomy and PhysiologyCheese KekNo ratings yet
- Module 2 Summary BiologyDocument16 pagesModule 2 Summary BiologyzhvgbpsxdxNo ratings yet
- Salud - Lab Activity 3 - The Cell - Biochem - BSN 1-Coc A. PDFDocument5 pagesSalud - Lab Activity 3 - The Cell - Biochem - BSN 1-Coc A. PDFFaye SaludNo ratings yet
- Unifying Themes in The Study of LifeDocument2 pagesUnifying Themes in The Study of LifeLiya Mae SantiagoNo ratings yet
- Cell Types Animal Tissue ReviewerDocument6 pagesCell Types Animal Tissue ReviewerShane LaluNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1 Bio122Document34 pagesChapter 1 Bio122Leo PietroNo ratings yet
- Unifying Themes of LifeDocument2 pagesUnifying Themes of LifeBeyoung GamefightNo ratings yet
- Anaphy Lec - TransesDocument44 pagesAnaphy Lec - TransescarlolandichocabatoNo ratings yet
- 1.1 Cells (Theory, Types and Ultrastructure)Document6 pages1.1 Cells (Theory, Types and Ultrastructure)Ivan RamirezNo ratings yet
- CHAPTER 3. Tissue BiologyDocument26 pagesCHAPTER 3. Tissue Biologywella wellaNo ratings yet
- AnaphyDocument2 pagesAnaphynaomimarielleNo ratings yet
- Life Is Organized01 (1) 1Document3 pagesLife Is Organized01 (1) 1Arjen San antonioNo ratings yet
- UNIT 1. - The Organisation of The Human BodyDocument45 pagesUNIT 1. - The Organisation of The Human Bodysanaadehmej05No ratings yet
- Science Form 1 - Chapter 2Document20 pagesScience Form 1 - Chapter 2Beevy GB85% (39)
- M. Anatomy Lesson 1Document9 pagesM. Anatomy Lesson 1Lainie ZefiahNo ratings yet
- Branches of BiologyDocument11 pagesBranches of BiologyMyraSimoraNo ratings yet
- Structures and Functions of Animal Cells - 030031Document63 pagesStructures and Functions of Animal Cells - 030031Cine EurabaNo ratings yet
- Activity 2 TissuesDocument6 pagesActivity 2 TissuesMartina SilerioNo ratings yet
- Campbell Biology Chapter 1: Terms in This SetDocument3 pagesCampbell Biology Chapter 1: Terms in This SetAngelene PelayoNo ratings yet
- The Levels of Biological OrganizationDocument16 pagesThe Levels of Biological OrganizationEliana Maricela Hernandez100% (1)
- Class 9 TissueDocument10 pagesClass 9 Tissuekhatridheeraj657No ratings yet
- L1 - Characteristics of Living OrganismsDocument52 pagesL1 - Characteristics of Living OrganismsAditya MishraNo ratings yet
- Introduction To BiologyDocument46 pagesIntroduction To BiologyLawrence AnDrew FrondaNo ratings yet
- Elsci LT 2.2: Chapter 8: Animals' Need To SurviveDocument4 pagesElsci LT 2.2: Chapter 8: Animals' Need To SurvivelemonNo ratings yet
- Kebo 107Document23 pagesKebo 107Manu MittalNo ratings yet
- BioNOTES Midterm Study GuideDocument14 pagesBioNOTES Midterm Study Guidebro jo lolNo ratings yet
- 4 Levels of Biological OrganizationPPTDocument26 pages4 Levels of Biological OrganizationPPTEmerson GongoraNo ratings yet
- Anaphy Rev1Document6 pagesAnaphy Rev1antonettevegamia3No ratings yet
- Answer Sheet in General Biology Week 2 ACTIVITY 1: Prokaryotic Cell vs. Eukaryotic CellDocument6 pagesAnswer Sheet in General Biology Week 2 ACTIVITY 1: Prokaryotic Cell vs. Eukaryotic CellMark Joedel MendezNo ratings yet
- Epithelial Tissue: Absorption, Transport, Excretion, Protection, SecretionDocument7 pagesEpithelial Tissue: Absorption, Transport, Excretion, Protection, SecretionKenneth Rodriguez HerminadoNo ratings yet
- TissueDocument7 pagesTissueGodhuli SahooNo ratings yet
- Structural Organisation in Animals: Animal TissuesDocument34 pagesStructural Organisation in Animals: Animal Tissuesafsas rpNo ratings yet
- Animal Form and FunctionDocument18 pagesAnimal Form and FunctionJerome Formaran100% (4)
- Gen Bio Sem 1 NotesDocument12 pagesGen Bio Sem 1 NotesFrances Chynna KhoNo ratings yet
- The Principles of Modern Zoology Are Derived FromDocument1 pageThe Principles of Modern Zoology Are Derived FromJackelyn SalazarNo ratings yet
- Kebo107 PDFDocument23 pagesKebo107 PDFbashraaNo ratings yet
- Untitled 4Document11 pagesUntitled 4KAMALANo ratings yet
- Chapter 7 Structural Organisation in AnimalsDocument23 pagesChapter 7 Structural Organisation in AnimalsAanvi ThakurNo ratings yet
- 2.3 BiologyDocument12 pages2.3 BiologykaryanNo ratings yet
- Unit 1 - Cell Structure and Organisation Without Slide Prep BackupDocument9 pagesUnit 1 - Cell Structure and Organisation Without Slide Prep BackupWaseem AhmedNo ratings yet
- Levelsoforganizationlifefernandobiodeluna 110918164908 Phpapp02Document36 pagesLevelsoforganizationlifefernandobiodeluna 110918164908 Phpapp02Rocil ValdezNo ratings yet
- Exercise 3. The Cells That Surround UsDocument6 pagesExercise 3. The Cells That Surround Usjunso2771No ratings yet
- Reviewer: Animal CellDocument1 pageReviewer: Animal CellJosua GarciaNo ratings yet
- Short Notes Form 4 Biology Chapter 1 4 PDFDocument6 pagesShort Notes Form 4 Biology Chapter 1 4 PDFTanUeiHorngNo ratings yet
- Human Body A1Document15 pagesHuman Body A1Jhazumy Zharick Aguilar LoloyNo ratings yet
- Body SytemsDocument6 pagesBody SytemsJl LeeNo ratings yet
- BREAKDOWN TIMELINE - Rev1Document12 pagesBREAKDOWN TIMELINE - Rev1Dimas AndiNo ratings yet
- Math WD Solns PDFDocument13 pagesMath WD Solns PDFVinceNo ratings yet
- De Claro SinglesDocument96 pagesDe Claro Singlesapi-3701495No ratings yet
- NikeDocument3 pagesNikeAadnya UjagareNo ratings yet
- Multiple Choice Questions:: SAARC Head QuarterDocument35 pagesMultiple Choice Questions:: SAARC Head QuarterQazi Sajjad Ul HassanNo ratings yet
- Chapter 6 Project ManagementDocument54 pagesChapter 6 Project ManagementSHAWN TAKAONANo ratings yet
- WH2009 WaterHorseCatalogDocument132 pagesWH2009 WaterHorseCatalogAiko FeroNo ratings yet
- Sucker Rod Elevators (25-Ton)Document1 pageSucker Rod Elevators (25-Ton)CESAR SEGURANo ratings yet
- Chapter 18: Concurrency Control: Database System Concepts, 7 EdDocument91 pagesChapter 18: Concurrency Control: Database System Concepts, 7 Edzhazhiy newNo ratings yet
- 1390388459576-Own Request Transfer FormatDocument3 pages1390388459576-Own Request Transfer FormatAkhilesh BhuraNo ratings yet
- TTD Series Configurable Fault AnnunciatorDocument4 pagesTTD Series Configurable Fault AnnunciatorAlejandroMuñozNo ratings yet
- Home Assignment - JUNK BOND Subject: Corporate FinanceDocument3 pagesHome Assignment - JUNK BOND Subject: Corporate FinanceAsad Mazhar100% (1)
- Lean Six Sigma Black Belt - BrochureDocument3 pagesLean Six Sigma Black Belt - BrochureDevraj NagarajraoNo ratings yet
- BUMA 20053 BUSINESS RESEARCH ModuleDocument59 pagesBUMA 20053 BUSINESS RESEARCH ModuleJanell Aganan100% (1)
- Chemical Engineering Plant Economics Questions and AnswersDocument32 pagesChemical Engineering Plant Economics Questions and AnswersLily Antonette Agustin100% (1)
- Disinfection Cabinet and Insect KillersDocument4 pagesDisinfection Cabinet and Insect Killerssathya moorthy KamakottiNo ratings yet
- University of Michigan Dissertation ArchiveDocument6 pagesUniversity of Michigan Dissertation ArchiveBuyResumePaperUK100% (1)
- KX71 3 en - HDDocument8 pagesKX71 3 en - HDסטניסלב טלשבסקיNo ratings yet
- Achieving Success Through Effective Business CommunicationDocument36 pagesAchieving Success Through Effective Business Communicationfaizankhan23No ratings yet
- Degenerate Hyperbola.: Conic Sections Geometric Properties of CurvesDocument2 pagesDegenerate Hyperbola.: Conic Sections Geometric Properties of CurvesJohn Renzo ErfeloNo ratings yet
- (REVIEW) KENDALL, Stuart - The Philosophy of Design by Glenn ParsonsDocument5 pages(REVIEW) KENDALL, Stuart - The Philosophy of Design by Glenn ParsonsOmega ZeroNo ratings yet
- Lapczyk PDFDocument22 pagesLapczyk PDFFredy PicaulyNo ratings yet
- Ebiz Steps PDFDocument59 pagesEbiz Steps PDFBathina Srinivasa RaoNo ratings yet
- Botech. IDocument37 pagesBotech. IKevin Rose BarnuevoNo ratings yet
- Sonargaon University (SU) Dhaka, Bangladesh: Grade Sheet Date: 22.12.2020Document1 pageSonargaon University (SU) Dhaka, Bangladesh: Grade Sheet Date: 22.12.2020Shuvo Biswas TopuNo ratings yet
Lesson 2.2_ Animal Cells
Lesson 2.2_ Animal Cells
Uploaded by
d5mzdt2khbCopyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Lesson 2.2_ Animal Cells
Lesson 2.2_ Animal Cells
Uploaded by
d5mzdt2khbCopyright:
Available Formats
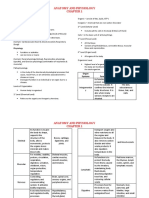
GENERAL BIOLOGY 1
S.Y. ‘23 - ‘24 | MS. FAITH LUMANOG LESSON 2.2: STRUCTURES AND FUNCTIONS OF
ANIMAL CELLS
Organ groups of skin, lungs, heart
tissues that muscle, brain
1.0 HEIRARCHY OF BIOLOGICAL
work together to
ORGANIZATION perform a
specialized
function
Level of Description Examples Organ groups of organs integumentary
Biological System that work system,
together to respiratory
Organizat
perform a system,
ion certain process circulatory
in the body system
Chemical atoms and types of
molecules that biomolecules or Organism formed by humans, grasses,
make up the molecules: different organ dogs, cats,
basic unit of life - carbohydrates systems that mushroom
- proteins create complex
- lipids or fats interactions with
- nucleic acids one another to
maintain
Organelle - distinct and mitochondria, balance or
specialized nucleus, Golgi homeostasis,
subcellular apparatus, and sustain life
structures that endoplasmic
contribute to the reticulum Population organisms that humans living in
cell’s belong to the the same house,
maintenance same species koalas living in an
and reproduction and live in the area of the forest
same area
-membrane-boun
d structures in Communit different humans, cats, and
eukaryotic cells y populations dogs living in the
living in the same house
Cell the smallest, skin cells, blood same area
basic, functional cells, muscle cells
unit of life or fibers, neurons Ecosystem includes all the humans, cats,
formed when communities dogs, and grasses
different atoms interacting with getting resources
and molecules one another and from nonliving
combine and with their things like soil,
function environment water, and
together sunlight
Tissue groups of cells types of animal Biosphere includes all the the entire surface
that work tissue: different kinds of of Earth where life
together to -epithelial tissue ecosystem thrives
perform a - connective
specialized tissue
function - muscle tissue
- nervous tissue
STEM 12 | SEMESTER 1 | QUARTER 1 | GENERAL BIOLOGY 1 PAGE 1
GENERAL BIOLOGY 1
S.Y. ‘23 - ‘24 | MS. FAITH LUMANOG LESSON 2.2: STRUCTURES AND FUNCTIONS OF
ANIMAL CELLS
PSEUDOSTRATIFIED COLUMNAR
2.0 TISSUES ● one layer
● elongated or column-shaped
● absorption and secretion; usually
2.1 EPITHELIAL TISSUES ciliated; cells have unequal length and
position of nucleus forming a false
layering of cells
● type of animal tissue that forms the ● ex. the lining of the respiratory tract
inner and outer lining of organs, the
covering in surfaces, and the primary
glandular tissue of the body
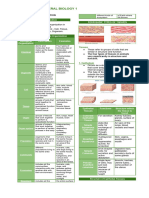
TYPES OF EPITHELIAL TISSUES
STRATIFIED SQUAMOUS
SIMPLE SQUAMOUS ● more than one layer
● one layer ● flat, scale-like
● flat, scale-like ● protection against abrasion or constant
● site of diffusion or exchange of exposure to friction
substances; secretion ● ex. the epidermis, lining of mouth,
● ex. air sacs or alveoli, capillary walls esophagus, and vagina
SIMPLE CUBOIDAL
● one layer
● cube-shaped STRATIFIED CUBOIDAL
● absorption and secretion ● more than one layer
● ex. glands and their ducts, ovaries, and ● cube- shaped
lining of kidney tubules ● protection and secretion
● ex. sweat glands, salivary glands, and
mammary glands
SIMPLE COLUMNAR
● one layer
● elongated or column-shaped STRATIFIED COLUMNAR
● absorption and secretion; contains ● more than one layer
goblet cells that secrete mucus ● elongated or column-shaped
● ex. walls of the gastro-intestinal tract ● protection and secretion
and body cavities ● ex. male urethra and ducts of some
glands
STEM 12 | SEMESTER 1 | QUARTER 1 | GENERAL BIOLOGY 1 PAGE 2
GENERAL BIOLOGY 1
S.Y. ‘23 - ‘24 | MS. FAITH LUMANOG LESSON 2.2: STRUCTURES AND FUNCTIONS OF
ANIMAL CELLS
● with fibers that are only visible during
clotting because they are made up of
2.2 CONNECTIVE TISSUES soluble proteins
● transport of substance, immune
response, and blood clotting
● basic components of connective tissues
● ex. Blood and blood cells
vary according to their type (left,
extracellular matrix; right, fibers and
fibroblast)
● connective tissues vary with the 2.3 MUSCLE TISSUES
composition of their extracellular
matrices and the types of cells they
consist of ● types of muscle tissues differ in their
general structure but more or less
perform the same function, i.e., to elicit
TYPES OF CONNECTIVE TISSUES movement.
BONE OR OSSEOUS TISSUE
● layers of a very hard matrix with calcium TYPES OF MUSCULAR TISSUES
salts and collagen fibers
● consists of bone cells called lacunae
● protection and support SKELETAL MUSCLE
● ex. skull and ribs ● attached to the skeleton or bones
● long, cylindrical, striated (with visible
CARTILAGE stripes), and multinucleated (with more
● more flexible matrix than bone than one nucleus)
● cartilage cells called chondrocytes ● Voluntary muscle control
● protection and support
● ex. hyaline cartilage, fibro cartilage, SMOOTH MUSCLE
elastic cartilage ● found in the walls of hollow organs such
as intestines, stomach, bladder, blood
DENSE CONNECTIVE TISSUE/ DENSE vessels, and uterus
FIBROUS TISSUE ● made up of nonstriated, uninucleated,
● Matrix is predominantly made up of and spindle-shaped (have pointed ends)
collagen fibers and has lesser cells cells
● a fibroblast or a fiber-forming cell ● Involuntary muscle control
● for support
● ex. tendon and ligament CARDIAC MUSCLE
● found in the heart
LOOSE CONNECTIVE TISSUE ● uninucleated (one nucleus) and has
● contains more cells and lesser fibers striations and intercalated disks
than dense connective tissue so it is ● involuntary muscle control
softer
● protection, insulation, storage, and
support
● ex. areolar tissue, adipose tissue or fat 2.4 NERVOUS TISSUES
tissue, reticular connective tissue
● Neuron, the basic unit of the nervous
BLOOD
system, consists of structures that can
● Plasma
conduct electrochemical signals as a
● Cellular components consist of blood
STEM 12 | SEMESTER 1 | QUARTER 1 | GENERAL BIOLOGY 1 PAGE 3
GENERAL BIOLOGY 1
S.Y. ‘23 - ‘24 | MS. FAITH LUMANOG LESSON 2.2: STRUCTURES AND FUNCTIONS OF
ANIMAL CELLS
form of information OLIGODENROCYTES
● may be classified based from their ● located in the central nervous system
number of cellular processes ● responsible for the production of the
myelin sheath
TYPES OF NERVOUS TISSUES
ASTROCYTES
● located in the central nervous system
● star-shaped cells that support and
control the chemical environment
around the neurons
● star-shaped cells that support and SATELLITE CELLS
control the chemical environment ● located in the peripheral nervous
around the neurons system
● they surround the cell body of a neuron
MICROGLIAL CELLS
● located in the central nervous system SCHWANN CELLS
● ovoid cells in the CNS that can ● located in the peripheral nervous
transform into a phagocytic macrophage system
to clean neuronal debris and wastes ● they surround all the nerve fibers and
produce myelin sheath similar to the
oligodendrocytes
EPENDYMAL CELLS
● located in the central nervous system
● these are ciliated cells that line the
central cavities of the brain and the
spinal cord and form a fairly permeable
membrane between the cavities with
cerebrospinal fluid and the tissues of
CNS
STEM 12 | SEMESTER 1 | QUARTER 1 | GENERAL BIOLOGY 1 PAGE 4
You might also like
- Installation and Operating Instructions Weishaupt Gas Burners Sizes 1 To 11Document46 pagesInstallation and Operating Instructions Weishaupt Gas Burners Sizes 1 To 11abuMalak75% (4)
- Activity 2: Unifying Themes in The Study of Life: A. DAD (Decode, Arrange, Describe)Document12 pagesActivity 2: Unifying Themes in The Study of Life: A. DAD (Decode, Arrange, Describe)Kyla Renoballes92% (12)
- Toshiba Case 3Document4 pagesToshiba Case 3Deta Detade100% (1)
- Ic 01 Last Day Test 3Document30 pagesIc 01 Last Day Test 3Sohini0% (1)
- Presentation On Busbar Arrangement, 87B & 50BF ProtectionDocument55 pagesPresentation On Busbar Arrangement, 87B & 50BF Protectionabu sayedNo ratings yet
- SPLK-1001: Number: SPLK-1001 Passing Score: 800 Time Limit: 120 Min File Version: 1Document36 pagesSPLK-1001: Number: SPLK-1001 Passing Score: 800 Time Limit: 120 Min File Version: 1abhishek_singh10272No ratings yet
- LESSON 3 - CELL MODIFICATION (Sofia Talagon)Document5 pagesLESSON 3 - CELL MODIFICATION (Sofia Talagon)Rafael SalcedoNo ratings yet
- Grade 7 Science Worksheets For January 8-12-2024Document7 pagesGrade 7 Science Worksheets For January 8-12-2024mark john baltazarNo ratings yet
- CHAPTER 1. Anatomy and Physiology OverviewDocument11 pagesCHAPTER 1. Anatomy and Physiology Overviewwella wellaNo ratings yet
- The Biosphere: Living BeingsDocument44 pagesThe Biosphere: Living BeingsGuillermo ChavesNo ratings yet
- 001 - Science 2 ImageDocument1 page001 - Science 2 Imagesantiago Estrada VasquezNo ratings yet
- 1 Organization of Living ThingsDocument2 pages1 Organization of Living ThingscarlNo ratings yet
- St. Anthony's College San Jose, Antique High School Department SY 2020 - 2021 General Biology 1 Name: Grade/Section: Activity 1: ApplicationDocument3 pagesSt. Anthony's College San Jose, Antique High School Department SY 2020 - 2021 General Biology 1 Name: Grade/Section: Activity 1: ApplicationMichal Decena CastroNo ratings yet
- GEN BIO 2 Final ReviewerDocument12 pagesGEN BIO 2 Final ReviewerJemuel Luc JavierNo ratings yet
- Marielle Hoefnagels - Biology - First SessionDocument10 pagesMarielle Hoefnagels - Biology - First SessionNegar AslaniNo ratings yet
- Biology ModuleDocument8 pagesBiology Modulerian ririNo ratings yet
- Unifying Themes of LifeDocument33 pagesUnifying Themes of LifeRyan Dave MacariayNo ratings yet
- Foz Lec M2Document9 pagesFoz Lec M2jsbitsoflyfNo ratings yet
- Anatomy and PhysiologyDocument6 pagesAnatomy and PhysiologyCheese KekNo ratings yet
- Module 2 Summary BiologyDocument16 pagesModule 2 Summary BiologyzhvgbpsxdxNo ratings yet
- Salud - Lab Activity 3 - The Cell - Biochem - BSN 1-Coc A. PDFDocument5 pagesSalud - Lab Activity 3 - The Cell - Biochem - BSN 1-Coc A. PDFFaye SaludNo ratings yet
- Unifying Themes in The Study of LifeDocument2 pagesUnifying Themes in The Study of LifeLiya Mae SantiagoNo ratings yet
- Cell Types Animal Tissue ReviewerDocument6 pagesCell Types Animal Tissue ReviewerShane LaluNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1 Bio122Document34 pagesChapter 1 Bio122Leo PietroNo ratings yet
- Unifying Themes of LifeDocument2 pagesUnifying Themes of LifeBeyoung GamefightNo ratings yet
- Anaphy Lec - TransesDocument44 pagesAnaphy Lec - TransescarlolandichocabatoNo ratings yet
- 1.1 Cells (Theory, Types and Ultrastructure)Document6 pages1.1 Cells (Theory, Types and Ultrastructure)Ivan RamirezNo ratings yet
- CHAPTER 3. Tissue BiologyDocument26 pagesCHAPTER 3. Tissue Biologywella wellaNo ratings yet
- AnaphyDocument2 pagesAnaphynaomimarielleNo ratings yet
- Life Is Organized01 (1) 1Document3 pagesLife Is Organized01 (1) 1Arjen San antonioNo ratings yet
- UNIT 1. - The Organisation of The Human BodyDocument45 pagesUNIT 1. - The Organisation of The Human Bodysanaadehmej05No ratings yet
- Science Form 1 - Chapter 2Document20 pagesScience Form 1 - Chapter 2Beevy GB85% (39)
- M. Anatomy Lesson 1Document9 pagesM. Anatomy Lesson 1Lainie ZefiahNo ratings yet
- Branches of BiologyDocument11 pagesBranches of BiologyMyraSimoraNo ratings yet
- Structures and Functions of Animal Cells - 030031Document63 pagesStructures and Functions of Animal Cells - 030031Cine EurabaNo ratings yet
- Activity 2 TissuesDocument6 pagesActivity 2 TissuesMartina SilerioNo ratings yet
- Campbell Biology Chapter 1: Terms in This SetDocument3 pagesCampbell Biology Chapter 1: Terms in This SetAngelene PelayoNo ratings yet
- The Levels of Biological OrganizationDocument16 pagesThe Levels of Biological OrganizationEliana Maricela Hernandez100% (1)
- Class 9 TissueDocument10 pagesClass 9 Tissuekhatridheeraj657No ratings yet
- L1 - Characteristics of Living OrganismsDocument52 pagesL1 - Characteristics of Living OrganismsAditya MishraNo ratings yet
- Introduction To BiologyDocument46 pagesIntroduction To BiologyLawrence AnDrew FrondaNo ratings yet
- Elsci LT 2.2: Chapter 8: Animals' Need To SurviveDocument4 pagesElsci LT 2.2: Chapter 8: Animals' Need To SurvivelemonNo ratings yet
- Kebo 107Document23 pagesKebo 107Manu MittalNo ratings yet
- BioNOTES Midterm Study GuideDocument14 pagesBioNOTES Midterm Study Guidebro jo lolNo ratings yet
- 4 Levels of Biological OrganizationPPTDocument26 pages4 Levels of Biological OrganizationPPTEmerson GongoraNo ratings yet
- Anaphy Rev1Document6 pagesAnaphy Rev1antonettevegamia3No ratings yet
- Answer Sheet in General Biology Week 2 ACTIVITY 1: Prokaryotic Cell vs. Eukaryotic CellDocument6 pagesAnswer Sheet in General Biology Week 2 ACTIVITY 1: Prokaryotic Cell vs. Eukaryotic CellMark Joedel MendezNo ratings yet
- Epithelial Tissue: Absorption, Transport, Excretion, Protection, SecretionDocument7 pagesEpithelial Tissue: Absorption, Transport, Excretion, Protection, SecretionKenneth Rodriguez HerminadoNo ratings yet
- TissueDocument7 pagesTissueGodhuli SahooNo ratings yet
- Structural Organisation in Animals: Animal TissuesDocument34 pagesStructural Organisation in Animals: Animal Tissuesafsas rpNo ratings yet
- Animal Form and FunctionDocument18 pagesAnimal Form and FunctionJerome Formaran100% (4)
- Gen Bio Sem 1 NotesDocument12 pagesGen Bio Sem 1 NotesFrances Chynna KhoNo ratings yet
- The Principles of Modern Zoology Are Derived FromDocument1 pageThe Principles of Modern Zoology Are Derived FromJackelyn SalazarNo ratings yet
- Kebo107 PDFDocument23 pagesKebo107 PDFbashraaNo ratings yet
- Untitled 4Document11 pagesUntitled 4KAMALANo ratings yet
- Chapter 7 Structural Organisation in AnimalsDocument23 pagesChapter 7 Structural Organisation in AnimalsAanvi ThakurNo ratings yet
- 2.3 BiologyDocument12 pages2.3 BiologykaryanNo ratings yet
- Unit 1 - Cell Structure and Organisation Without Slide Prep BackupDocument9 pagesUnit 1 - Cell Structure and Organisation Without Slide Prep BackupWaseem AhmedNo ratings yet
- Levelsoforganizationlifefernandobiodeluna 110918164908 Phpapp02Document36 pagesLevelsoforganizationlifefernandobiodeluna 110918164908 Phpapp02Rocil ValdezNo ratings yet
- Exercise 3. The Cells That Surround UsDocument6 pagesExercise 3. The Cells That Surround Usjunso2771No ratings yet
- Reviewer: Animal CellDocument1 pageReviewer: Animal CellJosua GarciaNo ratings yet
- Short Notes Form 4 Biology Chapter 1 4 PDFDocument6 pagesShort Notes Form 4 Biology Chapter 1 4 PDFTanUeiHorngNo ratings yet
- Human Body A1Document15 pagesHuman Body A1Jhazumy Zharick Aguilar LoloyNo ratings yet
- Body SytemsDocument6 pagesBody SytemsJl LeeNo ratings yet
- BREAKDOWN TIMELINE - Rev1Document12 pagesBREAKDOWN TIMELINE - Rev1Dimas AndiNo ratings yet
- Math WD Solns PDFDocument13 pagesMath WD Solns PDFVinceNo ratings yet
- De Claro SinglesDocument96 pagesDe Claro Singlesapi-3701495No ratings yet
- NikeDocument3 pagesNikeAadnya UjagareNo ratings yet
- Multiple Choice Questions:: SAARC Head QuarterDocument35 pagesMultiple Choice Questions:: SAARC Head QuarterQazi Sajjad Ul HassanNo ratings yet
- Chapter 6 Project ManagementDocument54 pagesChapter 6 Project ManagementSHAWN TAKAONANo ratings yet
- WH2009 WaterHorseCatalogDocument132 pagesWH2009 WaterHorseCatalogAiko FeroNo ratings yet
- Sucker Rod Elevators (25-Ton)Document1 pageSucker Rod Elevators (25-Ton)CESAR SEGURANo ratings yet
- Chapter 18: Concurrency Control: Database System Concepts, 7 EdDocument91 pagesChapter 18: Concurrency Control: Database System Concepts, 7 Edzhazhiy newNo ratings yet
- 1390388459576-Own Request Transfer FormatDocument3 pages1390388459576-Own Request Transfer FormatAkhilesh BhuraNo ratings yet
- TTD Series Configurable Fault AnnunciatorDocument4 pagesTTD Series Configurable Fault AnnunciatorAlejandroMuñozNo ratings yet
- Home Assignment - JUNK BOND Subject: Corporate FinanceDocument3 pagesHome Assignment - JUNK BOND Subject: Corporate FinanceAsad Mazhar100% (1)
- Lean Six Sigma Black Belt - BrochureDocument3 pagesLean Six Sigma Black Belt - BrochureDevraj NagarajraoNo ratings yet
- BUMA 20053 BUSINESS RESEARCH ModuleDocument59 pagesBUMA 20053 BUSINESS RESEARCH ModuleJanell Aganan100% (1)
- Chemical Engineering Plant Economics Questions and AnswersDocument32 pagesChemical Engineering Plant Economics Questions and AnswersLily Antonette Agustin100% (1)
- Disinfection Cabinet and Insect KillersDocument4 pagesDisinfection Cabinet and Insect Killerssathya moorthy KamakottiNo ratings yet
- University of Michigan Dissertation ArchiveDocument6 pagesUniversity of Michigan Dissertation ArchiveBuyResumePaperUK100% (1)
- KX71 3 en - HDDocument8 pagesKX71 3 en - HDסטניסלב טלשבסקיNo ratings yet
- Achieving Success Through Effective Business CommunicationDocument36 pagesAchieving Success Through Effective Business Communicationfaizankhan23No ratings yet
- Degenerate Hyperbola.: Conic Sections Geometric Properties of CurvesDocument2 pagesDegenerate Hyperbola.: Conic Sections Geometric Properties of CurvesJohn Renzo ErfeloNo ratings yet
- (REVIEW) KENDALL, Stuart - The Philosophy of Design by Glenn ParsonsDocument5 pages(REVIEW) KENDALL, Stuart - The Philosophy of Design by Glenn ParsonsOmega ZeroNo ratings yet
- Lapczyk PDFDocument22 pagesLapczyk PDFFredy PicaulyNo ratings yet
- Ebiz Steps PDFDocument59 pagesEbiz Steps PDFBathina Srinivasa RaoNo ratings yet
- Botech. IDocument37 pagesBotech. IKevin Rose BarnuevoNo ratings yet
- Sonargaon University (SU) Dhaka, Bangladesh: Grade Sheet Date: 22.12.2020Document1 pageSonargaon University (SU) Dhaka, Bangladesh: Grade Sheet Date: 22.12.2020Shuvo Biswas TopuNo ratings yet