Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Nursing_CS_Pharmacokinetics_02
Nursing_CS_Pharmacokinetics_02
Uploaded by
olenvahvempiCopyright:
Available Formats
You might also like
- List of Pharmaceutical Companies in Ahmedabad WithDocument22 pagesList of Pharmaceutical Companies in Ahmedabad Withsandipsc88% (8)
- The Rule of Ethics: Organizations in EquilibriumDocument11 pagesThe Rule of Ethics: Organizations in EquilibriumAlzan ZanderNo ratings yet
- Comprehensive - Pharmacy Review For NAPLEX Practice Exams Cases and Test Prep.8thDocument63 pagesComprehensive - Pharmacy Review For NAPLEX Practice Exams Cases and Test Prep.8thRabie YahfoufiNo ratings yet
- Manual Skoda Octavia 1,4 55kWDocument120 pagesManual Skoda Octavia 1,4 55kWCornea Horatiu Sebastian50% (2)
- IntroductionDocument56 pagesIntroductionsamrawitmekonnen16No ratings yet
- Pharmacokinetics: Sun Yi Department of PharmacologyDocument53 pagesPharmacokinetics: Sun Yi Department of PharmacologyMOHAMMAD NAZMUL ISLAMNo ratings yet
- PharmacokineticsDocument34 pagesPharmacokineticsAbdelrahman GalalNo ratings yet
- Pharmababy Reviewer-1Document6 pagesPharmababy Reviewer-1Erika Mae Deleña MarcoNo ratings yet
- Pharmacokinetics: Biological MembraneDocument18 pagesPharmacokinetics: Biological MembraneRahul PalsNo ratings yet
- Pharma Lecture 2 2024Document26 pagesPharma Lecture 2 2024Ahmed SalahNo ratings yet
- PHARMACOLOGYDocument9 pagesPHARMACOLOGYaliyahalexie6No ratings yet
- Pharmacology in Nursing and Medication AdministrationDocument170 pagesPharmacology in Nursing and Medication AdministrationskuladilzNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1 Drug EliminationDocument116 pagesChapter 1 Drug Elimination221123No ratings yet
- Lecture 2 Pharmacokinetics Absorption DistributionDocument19 pagesLecture 2 Pharmacokinetics Absorption Distributionbeneficialboxer9237No ratings yet
- 1M PharmaDocument13 pages1M PharmaJohn Dave V. VillarmenteNo ratings yet
- NCM 106 - Pharmacology Midterms 1M-4M Edited PDFDocument43 pagesNCM 106 - Pharmacology Midterms 1M-4M Edited PDFKisha Bethel100% (3)
- Mechanism of Drug Action-1Document46 pagesMechanism of Drug Action-1Sameer HussainNo ratings yet
- Pharmacokinetics: "What The Body Does To The Drug"Document41 pagesPharmacokinetics: "What The Body Does To The Drug"Virgo Eri SendiNo ratings yet
- Pharmaco KineticsDocument42 pagesPharmaco KineticsNaghman ZuberiNo ratings yet
- Pharmaceutics I: Unit 2 Route of Drug AdministrationDocument24 pagesPharmaceutics I: Unit 2 Route of Drug AdministrationPujiana ashariNo ratings yet
- Pharmacology Transes - Unit 1Document13 pagesPharmacology Transes - Unit 1venturaphoenixNo ratings yet
- بيDocument48 pagesبيMojied AmeerNo ratings yet
- 2 Areas of PharmacologyDocument3 pages2 Areas of PharmacologyAdiel CalsaNo ratings yet
- TDM MergedDocument136 pagesTDM Mergedlaila kunjayatiNo ratings yet
- PHARMACOKINETICSDocument74 pagesPHARMACOKINETICSAndrew SilungweNo ratings yet
- Ilovepdf Merged (7)Document438 pagesIlovepdf Merged (7)maisammtair878No ratings yet
- PharmacokineticsDocument38 pagesPharmacokineticsAkshay NirwalNo ratings yet
- Pharmaco 2Document83 pagesPharmaco 2marydenu101No ratings yet
- Adme 1: Absorption and DistributionDocument48 pagesAdme 1: Absorption and DistributionAlex LesNo ratings yet
- PharmacokineticsDocument47 pagesPharmacokineticsْNo ratings yet
- Chapter 4 Pharmacotherapeutics, Dynamics & KineticsDocument47 pagesChapter 4 Pharmacotherapeutics, Dynamics & KineticsAshaNo ratings yet
- How The Body Affects The Drugs: College of Health SciencesDocument42 pagesHow The Body Affects The Drugs: College of Health SciencesNat Lynne Distor TrondilloNo ratings yet
- Pertemuan 10-11 Farmakologi 2023Document46 pagesPertemuan 10-11 Farmakologi 2023hrkmlia19No ratings yet
- Transport MembranDocument40 pagesTransport MembranFitri Nurussani AuliaNo ratings yet
- Pharmacokinetics: "What The Body Does To The Drug"Document54 pagesPharmacokinetics: "What The Body Does To The Drug"Nur FadhilahNo ratings yet
- Lecture 5 HND 603Document23 pagesLecture 5 HND 603MARIA TARIQNo ratings yet
- Drug AbsorptionDocument36 pagesDrug AbsorptionLawal AbidatNo ratings yet
- Drug Distribution & MetabolismDocument23 pagesDrug Distribution & MetabolismBareera NudratNo ratings yet
- Author(s) : License: Unless Otherwise Noted, This Material Is Made Available Under The Terms of TheDocument74 pagesAuthor(s) : License: Unless Otherwise Noted, This Material Is Made Available Under The Terms of ThePh OmarNo ratings yet
- Module 01Document60 pagesModule 01SAKSHINo ratings yet
- Pharmacokinetics Ii: (An Idea On Drug Distribution, Metabolism and Excretion With Traditional Views.)Document49 pagesPharmacokinetics Ii: (An Idea On Drug Distribution, Metabolism and Excretion With Traditional Views.)Karthika JayanNo ratings yet
- Drug Induced Liver Diseases HamidDocument57 pagesDrug Induced Liver Diseases HamidKhadija KamranNo ratings yet
- BARRIER and Cannot Reach The CNSDocument4 pagesBARRIER and Cannot Reach The CNSJan Federick BantayNo ratings yet
- Pharmacokinetics Part 1Document18 pagesPharmacokinetics Part 1Mahfuja khatun UrmeNo ratings yet
- Drug Absorption: Dr. Chandane R. DDocument54 pagesDrug Absorption: Dr. Chandane R. DBandameedi RamuNo ratings yet
- Module 1: Part A: Pharmacological Principles and Safe Medication AdministrationDocument56 pagesModule 1: Part A: Pharmacological Principles and Safe Medication AdministrationKamil MominNo ratings yet
- Pharmacotherapeutics, Pharmacokinetics, and PharmacodynamicsDocument40 pagesPharmacotherapeutics, Pharmacokinetics, and PharmacodynamicsPerry BearNo ratings yet
- Pharmacology Block 1.4 - PharmacokineticsDocument9 pagesPharmacology Block 1.4 - Pharmacokineticsdaleng subNo ratings yet
- Absorption and Distribution - 2023Document34 pagesAbsorption and Distribution - 2023Rhythm BhardwajNo ratings yet
- Basic Principles General PharmacologyDocument47 pagesBasic Principles General Pharmacologysapiah raman100% (2)
- LECT 2 Pharmakinetics FVDocument45 pagesLECT 2 Pharmakinetics FVnonaNo ratings yet
- w1 PharmacologyDocument81 pagesw1 PharmacologyGrazzie BearbitchNo ratings yet
- Annotated-CHIU, CHERYL S. - exeRCISE 2 - Transport ProcessesDocument4 pagesAnnotated-CHIU, CHERYL S. - exeRCISE 2 - Transport ProcessesCheryl ChiuNo ratings yet
- ADMEDocument15 pagesADMEsachin kumarNo ratings yet
- T1 BasicPrinciplesinPharmacologyPharmacokineticsDocument69 pagesT1 BasicPrinciplesinPharmacologyPharmacokineticsTRISHA MAE BATAUSANo ratings yet
- BIOPH@RDocument233 pagesBIOPH@RGIZACHEW ABEBENo ratings yet
- Lecture 3Document37 pagesLecture 3Shafqat UllahNo ratings yet
- Principle of PharmacologyDocument40 pagesPrinciple of PharmacologySolaNo ratings yet
- Basics of Pharmacology: Speaker - DR - SantoshDocument76 pagesBasics of Pharmacology: Speaker - DR - SantoshRamya ChallaNo ratings yet
- PharmacokineticsDocument35 pagesPharmacokineticsBandita DattaNo ratings yet
- KineticsDocument35 pagesKineticsMary Loise VillegasNo ratings yet
- 2 PktsDocument111 pages2 Pktsamanaba3993No ratings yet
- Handbook of Drug Interaction and the Mechanism of InteractionFrom EverandHandbook of Drug Interaction and the Mechanism of InteractionRating: 1 out of 5 stars1/5 (1)
- Nursing_CS_How-to-Calculate-an-IV-Drip-Rate_new_01Document1 pageNursing_CS_How-to-Calculate-an-IV-Drip-Rate_new_01olenvahvempiNo ratings yet
- Nursing_CS_Rh-Incompatibility_02Document1 pageNursing_CS_Rh-Incompatibility_02olenvahvempiNo ratings yet
- Nursing CS How to Describe Dermatologic Lesions 02Document1 pageNursing CS How to Describe Dermatologic Lesions 02olenvahvempiNo ratings yet
- Nursing CS Glasgow-Coma-Scale 08Document1 pageNursing CS Glasgow-Coma-Scale 08olenvahvempiNo ratings yet
- cs-fund-004-head_to_toe_assessment_updatedDocument2 pagescs-fund-004-head_to_toe_assessment_updatedolenvahvempiNo ratings yet
- Nursing_CS_Neonatal_Abstinence_Syndrome_02Document1 pageNursing_CS_Neonatal_Abstinence_Syndrome_02olenvahvempiNo ratings yet
- Nursing_CS_OpioidsDocument1 pageNursing_CS_OpioidsolenvahvempiNo ratings yet
- Nursing CS Basic Overview of Pharmacology 02Document1 pageNursing CS Basic Overview of Pharmacology 02olenvahvempiNo ratings yet
- Nursing_CS_Oral-Contraceptive-Management_02Document1 pageNursing_CS_Oral-Contraceptive-Management_02olenvahvempiNo ratings yet
- Mass SongsDocument20 pagesMass SongsJason LayaNo ratings yet
- Sample LangDocument10 pagesSample LangDivina Aguilar-Dela CruzNo ratings yet
- Cab MakerDocument131 pagesCab MakerMar Revant100% (1)
- Trimble R8s GNSS Receiver: User GuideDocument71 pagesTrimble R8s GNSS Receiver: User GuideSilvio Vuolo NetoNo ratings yet
- Chapter 7-User Defined PrimitivesDocument19 pagesChapter 7-User Defined PrimitivesDanh ZEUS49No ratings yet
- The Seventh Day: Resting With The LORD, by E.J.WaggonerDocument4 pagesThe Seventh Day: Resting With The LORD, by E.J.WaggonerKunedog1No ratings yet
- Behavioral Finance AssignmentDocument8 pagesBehavioral Finance Assignmentthulli06No ratings yet
- Gestetner MP C3001/4501 Gestetner MP C3002/ 3502: High PerformanceDocument2 pagesGestetner MP C3001/4501 Gestetner MP C3002/ 3502: High PerformanceDipa Nusantara ArthaNo ratings yet
- Educatio P I AND TDocument19 pagesEducatio P I AND TSadam IrshadNo ratings yet
- Design of Hot Air Drying For Better Foods: ReviewDocument11 pagesDesign of Hot Air Drying For Better Foods: ReviewRosio SandovalNo ratings yet
- Answers To 10 Most Common Job Interview QuestionsDocument3 pagesAnswers To 10 Most Common Job Interview QuestionsCorina Rotaru100% (1)
- Briefcase On Company Law Briefcase Series Michael Ottley Z LibraryDocument181 pagesBriefcase On Company Law Briefcase Series Michael Ottley Z Libraryhillaryambrose030No ratings yet
- The Plant Journal - 2023 - Selma Garc A - Engineering The Plant Metabolic System by Exploiting Metabolic RegulationDocument28 pagesThe Plant Journal - 2023 - Selma Garc A - Engineering The Plant Metabolic System by Exploiting Metabolic RegulationRodrigo ParolaNo ratings yet
- 4Document6 pages4nikko candaNo ratings yet
- 4 - Web Enabled Business Processes AssignmentDocument16 pages4 - Web Enabled Business Processes Assignmentrahulsanas0% (1)
- Yazykovoy Material Po TemamDocument83 pagesYazykovoy Material Po TemamNelly NelNo ratings yet
- Jungle Clear Compilation S14Document15 pagesJungle Clear Compilation S14Caio AnjosNo ratings yet
- Final Exam Intro To LgesticsDocument3 pagesFinal Exam Intro To LgesticsRiyan ArdNo ratings yet
- Today1 AchievementTestUnits3 4extensionDocument2 pagesToday1 AchievementTestUnits3 4extensionEmii GarcíaNo ratings yet
- Eng1 Q3 Mod20 Asking-Permission V4Document21 pagesEng1 Q3 Mod20 Asking-Permission V4Silverangel Gayo100% (1)
- Multi Touch TrademarkDocument18 pagesMulti Touch TrademarkJordan GolsonNo ratings yet
- City PumpsDocument2 pagesCity PumpsJohan ConradieNo ratings yet
- ML-C and C Micro PDFDocument94 pagesML-C and C Micro PDFvulcanescuNo ratings yet
- National Rural Health MissionDocument418 pagesNational Rural Health MissionRoy GoldenNo ratings yet
- Borchers Rheological Additives: For Waterborne Coating SystemsDocument6 pagesBorchers Rheological Additives: For Waterborne Coating Systemsrogerkid17No ratings yet
- Sub Zero Service Manual - IW-30CIDocument65 pagesSub Zero Service Manual - IW-30CIMarco ThrushNo ratings yet
- 2Z140002 SV enDocument21 pages2Z140002 SV enBob AndreiNo ratings yet
Nursing_CS_Pharmacokinetics_02
Nursing_CS_Pharmacokinetics_02
Uploaded by
olenvahvempiCopyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Nursing_CS_Pharmacokinetics_02
Nursing_CS_Pharmacokinetics_02
Uploaded by
olenvahvempiCopyright:
Available Formats
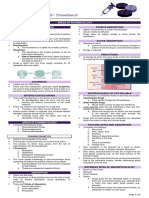
PHARMACOKINETICS
Pharmacokinetics is the movement of a drug through the body, from entrance to exit.
1. Absorption Common routes Bioavailability is the extent
of administration: and rate at which the drug
1 Movement from site • Oral enters the systemic
of administration to • Intravenous (IV) circulation.
bloodstream • Intramuscular (IM) Bioavailability is 100% in IV
• Subcutaneous (SubQ) administration, but varies
• Transdermal widely in all other routes.
• Pulmonary/nasal
2 2. Distribution Influenced by: Factors that may limit
• Adequate blood flow distribution:
Transport through • Ability of drug to exit • Vascular damage due to chronic
systemic circulation vascular system disease, such as diabetes
to target tissues or • Ability of drug to enter • Limited blood supply to
organs target cell abscesses or tumors
• Tight junctions of the
3 blood-brain barrier
3. Metabolism Primarily occurs in the liver:
Effects of metabolism vary by drug, may include:
Chemical alteration, • Conversion from lipid-soluble to water-soluble compound
or biotransformation,
of a drug to make it • Inactivation of drug
pharmacologically • Bioactivation of ‘prodrug’
active or to facilitate • Increased or decreased toxicity
elimination
4. Excretion Most drugs are filtered Other routes of excretion:
by the kidneys and • Bile → feces
Removal of drug eliminated in the urine. • Lungs (primarily anesthetics)
from the body Special care must be
• Sweat and saliva
4 taken in clients with
renal disease or kidney • Breast milk (caution during
failure. lactation)
1 2 First pass 3 4 Cytochrome P450 system
effect Absorption • A group of 12 closely related enzyme families
Drugs absorbed responsible for metabolism of most drugs
through the GI tract Absorption • Genetic variability in CYP450 enzyme function
pass through the liver contributes to differences in individuals’ ability
before entering the to metabolize drugs.
systemic circulation. • Many foods and medications can inhibit or induce
Hepatic metabolism the CYP450 enzyme system.
decreases
Gut wall Hepatic • It is important to counsel clients regarding the potential
bioavailability.
metabolism metabolism food and drug interactions of their specific medications.
NOTES
www.lecturio.com/nursing Watch Video
You might also like
- List of Pharmaceutical Companies in Ahmedabad WithDocument22 pagesList of Pharmaceutical Companies in Ahmedabad Withsandipsc88% (8)
- The Rule of Ethics: Organizations in EquilibriumDocument11 pagesThe Rule of Ethics: Organizations in EquilibriumAlzan ZanderNo ratings yet
- Comprehensive - Pharmacy Review For NAPLEX Practice Exams Cases and Test Prep.8thDocument63 pagesComprehensive - Pharmacy Review For NAPLEX Practice Exams Cases and Test Prep.8thRabie YahfoufiNo ratings yet
- Manual Skoda Octavia 1,4 55kWDocument120 pagesManual Skoda Octavia 1,4 55kWCornea Horatiu Sebastian50% (2)
- IntroductionDocument56 pagesIntroductionsamrawitmekonnen16No ratings yet
- Pharmacokinetics: Sun Yi Department of PharmacologyDocument53 pagesPharmacokinetics: Sun Yi Department of PharmacologyMOHAMMAD NAZMUL ISLAMNo ratings yet
- PharmacokineticsDocument34 pagesPharmacokineticsAbdelrahman GalalNo ratings yet
- Pharmababy Reviewer-1Document6 pagesPharmababy Reviewer-1Erika Mae Deleña MarcoNo ratings yet
- Pharmacokinetics: Biological MembraneDocument18 pagesPharmacokinetics: Biological MembraneRahul PalsNo ratings yet
- Pharma Lecture 2 2024Document26 pagesPharma Lecture 2 2024Ahmed SalahNo ratings yet
- PHARMACOLOGYDocument9 pagesPHARMACOLOGYaliyahalexie6No ratings yet
- Pharmacology in Nursing and Medication AdministrationDocument170 pagesPharmacology in Nursing and Medication AdministrationskuladilzNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1 Drug EliminationDocument116 pagesChapter 1 Drug Elimination221123No ratings yet
- Lecture 2 Pharmacokinetics Absorption DistributionDocument19 pagesLecture 2 Pharmacokinetics Absorption Distributionbeneficialboxer9237No ratings yet
- 1M PharmaDocument13 pages1M PharmaJohn Dave V. VillarmenteNo ratings yet
- NCM 106 - Pharmacology Midterms 1M-4M Edited PDFDocument43 pagesNCM 106 - Pharmacology Midterms 1M-4M Edited PDFKisha Bethel100% (3)
- Mechanism of Drug Action-1Document46 pagesMechanism of Drug Action-1Sameer HussainNo ratings yet
- Pharmacokinetics: "What The Body Does To The Drug"Document41 pagesPharmacokinetics: "What The Body Does To The Drug"Virgo Eri SendiNo ratings yet
- Pharmaco KineticsDocument42 pagesPharmaco KineticsNaghman ZuberiNo ratings yet
- Pharmaceutics I: Unit 2 Route of Drug AdministrationDocument24 pagesPharmaceutics I: Unit 2 Route of Drug AdministrationPujiana ashariNo ratings yet
- Pharmacology Transes - Unit 1Document13 pagesPharmacology Transes - Unit 1venturaphoenixNo ratings yet
- بيDocument48 pagesبيMojied AmeerNo ratings yet
- 2 Areas of PharmacologyDocument3 pages2 Areas of PharmacologyAdiel CalsaNo ratings yet
- TDM MergedDocument136 pagesTDM Mergedlaila kunjayatiNo ratings yet
- PHARMACOKINETICSDocument74 pagesPHARMACOKINETICSAndrew SilungweNo ratings yet
- Ilovepdf Merged (7)Document438 pagesIlovepdf Merged (7)maisammtair878No ratings yet
- PharmacokineticsDocument38 pagesPharmacokineticsAkshay NirwalNo ratings yet
- Pharmaco 2Document83 pagesPharmaco 2marydenu101No ratings yet
- Adme 1: Absorption and DistributionDocument48 pagesAdme 1: Absorption and DistributionAlex LesNo ratings yet
- PharmacokineticsDocument47 pagesPharmacokineticsْNo ratings yet
- Chapter 4 Pharmacotherapeutics, Dynamics & KineticsDocument47 pagesChapter 4 Pharmacotherapeutics, Dynamics & KineticsAshaNo ratings yet
- How The Body Affects The Drugs: College of Health SciencesDocument42 pagesHow The Body Affects The Drugs: College of Health SciencesNat Lynne Distor TrondilloNo ratings yet
- Pertemuan 10-11 Farmakologi 2023Document46 pagesPertemuan 10-11 Farmakologi 2023hrkmlia19No ratings yet
- Transport MembranDocument40 pagesTransport MembranFitri Nurussani AuliaNo ratings yet
- Pharmacokinetics: "What The Body Does To The Drug"Document54 pagesPharmacokinetics: "What The Body Does To The Drug"Nur FadhilahNo ratings yet
- Lecture 5 HND 603Document23 pagesLecture 5 HND 603MARIA TARIQNo ratings yet
- Drug AbsorptionDocument36 pagesDrug AbsorptionLawal AbidatNo ratings yet
- Drug Distribution & MetabolismDocument23 pagesDrug Distribution & MetabolismBareera NudratNo ratings yet
- Author(s) : License: Unless Otherwise Noted, This Material Is Made Available Under The Terms of TheDocument74 pagesAuthor(s) : License: Unless Otherwise Noted, This Material Is Made Available Under The Terms of ThePh OmarNo ratings yet
- Module 01Document60 pagesModule 01SAKSHINo ratings yet
- Pharmacokinetics Ii: (An Idea On Drug Distribution, Metabolism and Excretion With Traditional Views.)Document49 pagesPharmacokinetics Ii: (An Idea On Drug Distribution, Metabolism and Excretion With Traditional Views.)Karthika JayanNo ratings yet
- Drug Induced Liver Diseases HamidDocument57 pagesDrug Induced Liver Diseases HamidKhadija KamranNo ratings yet
- BARRIER and Cannot Reach The CNSDocument4 pagesBARRIER and Cannot Reach The CNSJan Federick BantayNo ratings yet
- Pharmacokinetics Part 1Document18 pagesPharmacokinetics Part 1Mahfuja khatun UrmeNo ratings yet
- Drug Absorption: Dr. Chandane R. DDocument54 pagesDrug Absorption: Dr. Chandane R. DBandameedi RamuNo ratings yet
- Module 1: Part A: Pharmacological Principles and Safe Medication AdministrationDocument56 pagesModule 1: Part A: Pharmacological Principles and Safe Medication AdministrationKamil MominNo ratings yet
- Pharmacotherapeutics, Pharmacokinetics, and PharmacodynamicsDocument40 pagesPharmacotherapeutics, Pharmacokinetics, and PharmacodynamicsPerry BearNo ratings yet
- Pharmacology Block 1.4 - PharmacokineticsDocument9 pagesPharmacology Block 1.4 - Pharmacokineticsdaleng subNo ratings yet
- Absorption and Distribution - 2023Document34 pagesAbsorption and Distribution - 2023Rhythm BhardwajNo ratings yet
- Basic Principles General PharmacologyDocument47 pagesBasic Principles General Pharmacologysapiah raman100% (2)
- LECT 2 Pharmakinetics FVDocument45 pagesLECT 2 Pharmakinetics FVnonaNo ratings yet
- w1 PharmacologyDocument81 pagesw1 PharmacologyGrazzie BearbitchNo ratings yet
- Annotated-CHIU, CHERYL S. - exeRCISE 2 - Transport ProcessesDocument4 pagesAnnotated-CHIU, CHERYL S. - exeRCISE 2 - Transport ProcessesCheryl ChiuNo ratings yet
- ADMEDocument15 pagesADMEsachin kumarNo ratings yet
- T1 BasicPrinciplesinPharmacologyPharmacokineticsDocument69 pagesT1 BasicPrinciplesinPharmacologyPharmacokineticsTRISHA MAE BATAUSANo ratings yet
- BIOPH@RDocument233 pagesBIOPH@RGIZACHEW ABEBENo ratings yet
- Lecture 3Document37 pagesLecture 3Shafqat UllahNo ratings yet
- Principle of PharmacologyDocument40 pagesPrinciple of PharmacologySolaNo ratings yet
- Basics of Pharmacology: Speaker - DR - SantoshDocument76 pagesBasics of Pharmacology: Speaker - DR - SantoshRamya ChallaNo ratings yet
- PharmacokineticsDocument35 pagesPharmacokineticsBandita DattaNo ratings yet
- KineticsDocument35 pagesKineticsMary Loise VillegasNo ratings yet
- 2 PktsDocument111 pages2 Pktsamanaba3993No ratings yet
- Handbook of Drug Interaction and the Mechanism of InteractionFrom EverandHandbook of Drug Interaction and the Mechanism of InteractionRating: 1 out of 5 stars1/5 (1)
- Nursing_CS_How-to-Calculate-an-IV-Drip-Rate_new_01Document1 pageNursing_CS_How-to-Calculate-an-IV-Drip-Rate_new_01olenvahvempiNo ratings yet
- Nursing_CS_Rh-Incompatibility_02Document1 pageNursing_CS_Rh-Incompatibility_02olenvahvempiNo ratings yet
- Nursing CS How to Describe Dermatologic Lesions 02Document1 pageNursing CS How to Describe Dermatologic Lesions 02olenvahvempiNo ratings yet
- Nursing CS Glasgow-Coma-Scale 08Document1 pageNursing CS Glasgow-Coma-Scale 08olenvahvempiNo ratings yet
- cs-fund-004-head_to_toe_assessment_updatedDocument2 pagescs-fund-004-head_to_toe_assessment_updatedolenvahvempiNo ratings yet
- Nursing_CS_Neonatal_Abstinence_Syndrome_02Document1 pageNursing_CS_Neonatal_Abstinence_Syndrome_02olenvahvempiNo ratings yet
- Nursing_CS_OpioidsDocument1 pageNursing_CS_OpioidsolenvahvempiNo ratings yet
- Nursing CS Basic Overview of Pharmacology 02Document1 pageNursing CS Basic Overview of Pharmacology 02olenvahvempiNo ratings yet
- Nursing_CS_Oral-Contraceptive-Management_02Document1 pageNursing_CS_Oral-Contraceptive-Management_02olenvahvempiNo ratings yet
- Mass SongsDocument20 pagesMass SongsJason LayaNo ratings yet
- Sample LangDocument10 pagesSample LangDivina Aguilar-Dela CruzNo ratings yet
- Cab MakerDocument131 pagesCab MakerMar Revant100% (1)
- Trimble R8s GNSS Receiver: User GuideDocument71 pagesTrimble R8s GNSS Receiver: User GuideSilvio Vuolo NetoNo ratings yet
- Chapter 7-User Defined PrimitivesDocument19 pagesChapter 7-User Defined PrimitivesDanh ZEUS49No ratings yet
- The Seventh Day: Resting With The LORD, by E.J.WaggonerDocument4 pagesThe Seventh Day: Resting With The LORD, by E.J.WaggonerKunedog1No ratings yet
- Behavioral Finance AssignmentDocument8 pagesBehavioral Finance Assignmentthulli06No ratings yet
- Gestetner MP C3001/4501 Gestetner MP C3002/ 3502: High PerformanceDocument2 pagesGestetner MP C3001/4501 Gestetner MP C3002/ 3502: High PerformanceDipa Nusantara ArthaNo ratings yet
- Educatio P I AND TDocument19 pagesEducatio P I AND TSadam IrshadNo ratings yet
- Design of Hot Air Drying For Better Foods: ReviewDocument11 pagesDesign of Hot Air Drying For Better Foods: ReviewRosio SandovalNo ratings yet
- Answers To 10 Most Common Job Interview QuestionsDocument3 pagesAnswers To 10 Most Common Job Interview QuestionsCorina Rotaru100% (1)
- Briefcase On Company Law Briefcase Series Michael Ottley Z LibraryDocument181 pagesBriefcase On Company Law Briefcase Series Michael Ottley Z Libraryhillaryambrose030No ratings yet
- The Plant Journal - 2023 - Selma Garc A - Engineering The Plant Metabolic System by Exploiting Metabolic RegulationDocument28 pagesThe Plant Journal - 2023 - Selma Garc A - Engineering The Plant Metabolic System by Exploiting Metabolic RegulationRodrigo ParolaNo ratings yet
- 4Document6 pages4nikko candaNo ratings yet
- 4 - Web Enabled Business Processes AssignmentDocument16 pages4 - Web Enabled Business Processes Assignmentrahulsanas0% (1)
- Yazykovoy Material Po TemamDocument83 pagesYazykovoy Material Po TemamNelly NelNo ratings yet
- Jungle Clear Compilation S14Document15 pagesJungle Clear Compilation S14Caio AnjosNo ratings yet
- Final Exam Intro To LgesticsDocument3 pagesFinal Exam Intro To LgesticsRiyan ArdNo ratings yet
- Today1 AchievementTestUnits3 4extensionDocument2 pagesToday1 AchievementTestUnits3 4extensionEmii GarcíaNo ratings yet
- Eng1 Q3 Mod20 Asking-Permission V4Document21 pagesEng1 Q3 Mod20 Asking-Permission V4Silverangel Gayo100% (1)
- Multi Touch TrademarkDocument18 pagesMulti Touch TrademarkJordan GolsonNo ratings yet
- City PumpsDocument2 pagesCity PumpsJohan ConradieNo ratings yet
- ML-C and C Micro PDFDocument94 pagesML-C and C Micro PDFvulcanescuNo ratings yet
- National Rural Health MissionDocument418 pagesNational Rural Health MissionRoy GoldenNo ratings yet
- Borchers Rheological Additives: For Waterborne Coating SystemsDocument6 pagesBorchers Rheological Additives: For Waterborne Coating Systemsrogerkid17No ratings yet
- Sub Zero Service Manual - IW-30CIDocument65 pagesSub Zero Service Manual - IW-30CIMarco ThrushNo ratings yet
- 2Z140002 SV enDocument21 pages2Z140002 SV enBob AndreiNo ratings yet