Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Hero in metallurgical
Hero in metallurgical
Uploaded by
boss.of.king030 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
2 views9 pagesThank you
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentThank you
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pdf or txt
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
2 views9 pagesHero in metallurgical
Hero in metallurgical
Uploaded by
boss.of.king03Thank you
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pdf or txt
You are on page 1of 9
Sameepa Banerjee
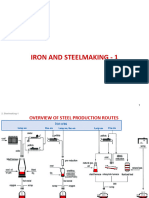
FLOW CHART OF SILICO MANGANESE PRODUCTION
Use of PLC Telfar
Vehicle BIN HOUSE WH-1,2&3 CHUT-1 TO 8
RM YRD Skip
BIN-1-12
Belt
SUB STATION
Gas & Smoke
PC UNIT FURNACE
TRANSFORMER
FINISH YARD
Metal Size &
Packing PUMP HOUSE
METAL SLAG
Ready for CI Pans Sand Bed
Despatch
1. Slag use of ground feeling
2. Separate metal & slag by
MIX using gravitational force
MRP MELT
RAW MATERIALS
Manganese Ores: Commonly used ores include pyrolusite (MnO₂),
rhodochrosite (MnCO₃), and other manganese oxides.
Silicon Ores: Typically quartz (SiO₂) or sand.Carbonaceous Reducing Agent:
Coke, coal, or charcoal are used to facilitate the reduction reactions.
PRODUCTION PROCESS
Preparation and Sizing of Raw Materials : Manganese ores are crushed and screened to
obtain the desired particle size.Silicon ores are similarly processed to achieve the required
size.The carbonaceous reducing agent is also prepared by crushing and screening.
Mixing and Batching: The raw materials are weighed and mixed in specific
proportions. The typical charge for the furnace consists of manganese ore, silicon
ore (quartz), and a carbonaceous reducing agent.
Smelting in Electric Arc Furnace (EAF) : The mixed charge is fed into an electric arc
furnace.An electric arc is struck between electrodes, generating high temperatures
(approximately 1600–1700°C).Under these conditions, the manganese oxides and
silicon dioxide are reduced by the carbonaceous material.
Reduction Reactions : Manganese oxide reacts with carbon to form manganese metal
and carbon monoxide:
𝑀𝑛𝑂2 + 2𝐶 → 𝑀𝑛 + 2𝐶𝑂𝑀𝑛𝑂2 + 2𝐶 → 𝑆𝑖 + 2𝐶𝑂𝑆𝑖𝑂2 + 2𝐶 → Si+2CO
Silicon dioxide reacts with carbon to form silicon metal and carbon monoxide:
𝑆𝑖𝑂2 + 2𝐶 → 𝑆𝑖 + 2𝐶𝑂𝑆𝑖𝑂2 + 2𝐶 → 𝑆𝑖 + 2𝐶𝑂
Iron, present in the ores, is also reduced and combines with manganese and silicon to
form the silicon manganese alloy.
Tapping and Casting : The molten silicon manganese alloy is tapped from the furnace into
molds. The slag, which is a by-product of the smelting process, is also tapped off
separately.
Cooling and Solidification: The alloy cools and solidifies in the molds. The ingots or lumps
are then broken down into smaller sizes suitable for transportation and use in
steelmaking.
Quality Control and Storage : Samples of the silicon manganese alloy are analyzed
for their composition to ensure they meet the required specifications.The final
product is stored and shipped to customers, primarily for use in steelmaking.
CHEMICAL REACTION
The main chemical reaction involved in the production of silicomanganese are :
1. Reduction of Manganese Oxide:
𝑀𝑛𝑂2 + 2𝐶 ⟶ 𝑀𝑛 + 2𝐶𝑂
2. Reduction of Silicon Dioxide:
𝑆𝑖𝑂2 + 2𝐶 → 𝑆𝑖 + 2𝐶𝑂
3. Formation of Alloy:
𝑀𝑛 + 𝑆𝑖 + 𝐹𝑒 → (𝐹𝑒𝑀𝑛𝑆𝑖)𝑎𝑙𝑙𝑜𝑦
IMPORTANT CONSIDERATIONS
Energy Consumption: The EAF consumes significant amounts of electricity, making
energy efficiency crucial in the production process. Environmental Impact: The
process generates carbon monoxide and other emissions. Implementing proper
environmental controls and emission treatment systems is essential to minimize the
environmental impact. Material Handling: High temperatures and reactive
materials require specialized handling and safety measures to protect
workers and equipment.
APPLICATIONS
Steelmaking: Manganese is a critical component in steel production, where it
acts as a deoxidizer and an alloying element to improve the strength, toughness,
and hardness of steel.
You might also like
- Molding Training PresentationDocument30 pagesMolding Training PresentationVinesh RJ100% (1)
- There is howDocument10 pagesThere is howboss.of.king03No ratings yet
- DSP Overview 10-07-2017Document46 pagesDSP Overview 10-07-2017Binod Kumar Padhi0% (1)
- MCR 321Document11 pagesMCR 321Rishu DeyNo ratings yet
- Chemistry of Portland CementDocument8 pagesChemistry of Portland CementTahmidtuhinNo ratings yet
- Composite RefractoriesDocument35 pagesComposite RefractoriesAjay SolankiNo ratings yet
- Heat Treatable of Magnisium AollyDocument33 pagesHeat Treatable of Magnisium Aolly19M647 - SRIRAM ANo ratings yet
- Nickel ProcessesDocument30 pagesNickel ProcessesArmank Man100% (2)
- Durgapur Steel Plant PDFDocument49 pagesDurgapur Steel Plant PDFApper kumariNo ratings yet
- Classification Wirsing 2011Document50 pagesClassification Wirsing 2011naikNo ratings yet
- Steel Plant Report FinalDocument54 pagesSteel Plant Report Finalkranthi chaitanyaNo ratings yet
- Tribological Studies of Fly Ash Based Carbon Ceramic Composites Synthesized at Different TemperaturesDocument22 pagesTribological Studies of Fly Ash Based Carbon Ceramic Composites Synthesized at Different TemperaturesDr. Dipen ShahNo ratings yet
- Production Characteristics and Uses of Ferrochrome SlagDocument9 pagesProduction Characteristics and Uses of Ferrochrome Slagpriya maranNo ratings yet
- Ferrite Processing: Powder Preparation-Raw Materials SelectionDocument66 pagesFerrite Processing: Powder Preparation-Raw Materials Selection吳尚謙No ratings yet
- Metal Mining Field TripDocument20 pagesMetal Mining Field Tripvictory shahbazNo ratings yet
- Classification Wirsing 2015 PDFDocument49 pagesClassification Wirsing 2015 PDFvũ minh tâmNo ratings yet
- Classification Wirsing 2015Document49 pagesClassification Wirsing 2015Moud Sakly100% (1)
- Blast Furnace Processing and It's OperationsDocument20 pagesBlast Furnace Processing and It's OperationsRaghava Chari Koilkonda100% (1)
- The Production of Ferromanganese: Rex HooperDocument2 pagesThe Production of Ferromanganese: Rex HooperNathali QuinteroNo ratings yet
- Material Product Data Sheet Copper & Copper Alloy (Brass, Bronze) Thermal Spray WiresDocument4 pagesMaterial Product Data Sheet Copper & Copper Alloy (Brass, Bronze) Thermal Spray WiresSerkan ÖzcanNo ratings yet
- The Primary Production of Platinum Group Metals (PGMS)Document7 pagesThe Primary Production of Platinum Group Metals (PGMS)Erdi Sofyandra AdikriNo ratings yet
- 30-Surface Hardening of Steel-II-26-10-2023Document36 pages30-Surface Hardening of Steel-II-26-10-2023NandiniNo ratings yet
- GR Chapter - 19 Cement 78, 12Document14 pagesGR Chapter - 19 Cement 78, 12Chemistry have a solutionNo ratings yet
- EAF Stainless Steel Dust ProcessingDocument13 pagesEAF Stainless Steel Dust Processingmd 80No ratings yet
- Magnesia-Spinel Composite Refractories For Cement Rotary KilnsDocument8 pagesMagnesia-Spinel Composite Refractories For Cement Rotary Kilnsakbar davoodiNo ratings yet
- Ankesh Training ReportDocument41 pagesAnkesh Training ReportANKESHNo ratings yet
- Mahakal Institute of Technology, Ujjain: TH THDocument35 pagesMahakal Institute of Technology, Ujjain: TH THashlay evans100% (1)
- Aglomerasi Bijih BesiDocument44 pagesAglomerasi Bijih BesiAlfiansyah DarmawanNo ratings yet
- Course 4 - Pengolahan Besi Dan BajaDocument41 pagesCourse 4 - Pengolahan Besi Dan BajaAditiya RamadhanNo ratings yet
- Applications and Processing of CeramicsDocument13 pagesApplications and Processing of CeramicsGonzalo CamposNo ratings yet
- An Overview On Designing An Environmental Friendly Electrode Manufacturing Process (EFEMP)Document7 pagesAn Overview On Designing An Environmental Friendly Electrode Manufacturing Process (EFEMP)jai2009No ratings yet
- Iwcc Cu-Vortrag AldDocument16 pagesIwcc Cu-Vortrag Aldhadjlarbi-h100% (1)
- Methods of Melting: Anil Kumar. GarikapatiDocument16 pagesMethods of Melting: Anil Kumar. GarikapatiAnil Kumar GarikapatiNo ratings yet
- Case Hardening of Mild Steel Using Animal Bone, Charcoal and Sea Shells As CarburizersDocument7 pagesCase Hardening of Mild Steel Using Animal Bone, Charcoal and Sea Shells As CarburizersAgbolade OluwaseyiNo ratings yet
- Ceramics NotesDocument35 pagesCeramics NotesAditya MahajanNo ratings yet
- 02 - MetE 414-Steelmaking 1 - Fall 2023Document29 pages02 - MetE 414-Steelmaking 1 - Fall 2023egesenturk2000No ratings yet
- CMI Chemline Production of High Purity Magnesia IM May 2013Document2 pagesCMI Chemline Production of High Purity Magnesia IM May 20137kkqg42m6cNo ratings yet
- BLAST FURNACE OPERATIONS-TATA STEEL - Dipika Sinha - 5.6.20 PDFDocument22 pagesBLAST FURNACE OPERATIONS-TATA STEEL - Dipika Sinha - 5.6.20 PDFGAGAN SOLANKINo ratings yet
- Monshi 1999 - RMDocument5 pagesMonshi 1999 - RMghada ghoudiNo ratings yet
- Wear Characteristics of Heat Treated Hadfield Austenitic Manganese Steel For Engineering ApplicationDocument15 pagesWear Characteristics of Heat Treated Hadfield Austenitic Manganese Steel For Engineering Applicationshrikant mishraNo ratings yet
- Steel Slag. Conversion of An Industrial Waste Material Into A Value Adding Asphalt IngredientDocument8 pagesSteel Slag. Conversion of An Industrial Waste Material Into A Value Adding Asphalt IngredientMehdi FarrokhiNo ratings yet
- Kalinga Nagar - Part3Document10 pagesKalinga Nagar - Part3cet.ranchi7024No ratings yet
- 113resuelto Procesamiento-Ceramicos ch13Document26 pages113resuelto Procesamiento-Ceramicos ch13Isac NumNo ratings yet
- Mechanical Engineering: KCT College of Engg and Tech. Village Fatehgarh Distt - SangrurDocument32 pagesMechanical Engineering: KCT College of Engg and Tech. Village Fatehgarh Distt - SangrurNaga KiranNo ratings yet
- Optimization of Machining Parameters in Milling Operation of Hybrid Metal Matrix Composites (Al7075/Sic+B C)Document17 pagesOptimization of Machining Parameters in Milling Operation of Hybrid Metal Matrix Composites (Al7075/Sic+B C)Kirubhakaran KathiresanNo ratings yet
- Gas Holders Risk AssessmentDocument48 pagesGas Holders Risk AssessmentRonak MotaNo ratings yet
- CERAMICSDocument27 pagesCERAMICSErika RamosNo ratings yet
- Powder Metallurgy PDFDocument9 pagesPowder Metallurgy PDFhavalNo ratings yet
- SMS Steel-Making-Practices PDFDocument32 pagesSMS Steel-Making-Practices PDFkalai0% (1)
- Prasanth LeeDocument46 pagesPrasanth LeePRASANTHNo ratings yet
- Construction Materials - SCMDocument40 pagesConstruction Materials - SCMWelday TsegayNo ratings yet
- Cement 12Document24 pagesCement 12prashannapandit832No ratings yet
- SP Brief Description1Document12 pagesSP Brief Description1Creative MindsNo ratings yet
- Debere Berhan University: Collage of EngineeringDocument15 pagesDebere Berhan University: Collage of EngineeringDagmawi MenweyeletNo ratings yet
- 2 YDK 669.1:622.267 O. P Baidin, V. I. Rostovsky, D.E EsezoborDocument11 pages2 YDK 669.1:622.267 O. P Baidin, V. I. Rostovsky, D.E EsezoborROWHEITNo ratings yet
- CLM Bref 0510Document495 pagesCLM Bref 0510Hamada Shoukry MohammedNo ratings yet
- Day 2 Part 1Document90 pagesDay 2 Part 1Edukondalu PentapatiNo ratings yet
- Induction Furnaces LiningDocument20 pagesInduction Furnaces LiningAkash Sharma100% (1)
- A Review of The Production of Ferromanganese in Blast FurnaceDocument13 pagesA Review of The Production of Ferromanganese in Blast FurnaceSofhia ChairunnisyaNo ratings yet
- Physic Study Plan - 2294 - 1708797511048Document1 pagePhysic Study Plan - 2294 - 1708797511048anshu mishraNo ratings yet
- Assembly Numbers Ovenpak 400 Burners: For These Products, Please Order Per The Following Product NumbersDocument14 pagesAssembly Numbers Ovenpak 400 Burners: For These Products, Please Order Per The Following Product NumbersJuan ShevchenkoNo ratings yet
- Well Performance SoftwaresDocument3 pagesWell Performance SoftwaresMotaz IbrahimNo ratings yet
- Injection Cream: Technical Information Sheet Article No. 0709Document2 pagesInjection Cream: Technical Information Sheet Article No. 0709wassimmahfouzNo ratings yet
- Lesson 1.2 The Formation of Heavier Elements During Star Formation and EvolutionDocument7 pagesLesson 1.2 The Formation of Heavier Elements During Star Formation and EvolutionMALOU ELEVERANo ratings yet
- ISO 6743-10 - 1989 - Part. 10 - Family Y - MiscellaneousDocument8 pagesISO 6743-10 - 1989 - Part. 10 - Family Y - MiscellaneousMassimiliano VolaNo ratings yet
- Cosan: The Holding ConundrumDocument10 pagesCosan: The Holding ConundrumJorge EchanizNo ratings yet
- Sharp Runtka395wjqz Dac38m011 Power-Inverter SCHDocument7 pagesSharp Runtka395wjqz Dac38m011 Power-Inverter SCHchathush.mihirangaNo ratings yet
- BUKH Lifeboat Engine - Instruction Manual - OcrDocument117 pagesBUKH Lifeboat Engine - Instruction Manual - OcrStanislava BerdnykNo ratings yet
- LM 27313Document20 pagesLM 27313Ali HussienNo ratings yet
- Oriented Strand Board: Product GuideDocument12 pagesOriented Strand Board: Product GuideDillonNo ratings yet
- Pdf24 MergedDocument22 pagesPdf24 MergedThu NguyenNo ratings yet
- Disassembly-Assembly - Engine - ARRIEL Engine Installation On Helicopter-71-10-00-402Document13 pagesDisassembly-Assembly - Engine - ARRIEL Engine Installation On Helicopter-71-10-00-402SiswadiNo ratings yet
- ChaptergtolDocument168 pagesChaptergtolIra Jane LosañezNo ratings yet
- 9.0 Pneumatic Conveying Preface: Bechtel ConfidentialDocument14 pages9.0 Pneumatic Conveying Preface: Bechtel ConfidentialCristhianNo ratings yet
- Project ThesisDocument12 pagesProject Thesismuhammd umerNo ratings yet
- SPIR STAR® - Your Specialists in High-Pressure Hose - High-Pressure Hose - Thermoplastic Hose - Thermoplastic High PDFDocument3 pagesSPIR STAR® - Your Specialists in High-Pressure Hose - High-Pressure Hose - Thermoplastic Hose - Thermoplastic High PDFmarcosNo ratings yet
- OL32S LED Low Intensity Single Obstruction Light - Datasheet - v202008Document2 pagesOL32S LED Low Intensity Single Obstruction Light - Datasheet - v202008REDDOT SIGNALNo ratings yet
- Hi Crush FB Silo To Blender Conveyor TechSheetDocument2 pagesHi Crush FB Silo To Blender Conveyor TechSheetsmithyry2014No ratings yet
- Challenging Assumptions On Remote WorkDocument189 pagesChallenging Assumptions On Remote WorkHadi SumartonoNo ratings yet
- 2015-TPC-0930 Reel-Lay Method To Allow For Direct Tie-In of Pipelines - DRAFTLDocument11 pages2015-TPC-0930 Reel-Lay Method To Allow For Direct Tie-In of Pipelines - DRAFTLnicholas_j_vaughanNo ratings yet
- Assignment On Bata India LTD: Presented by A.Ch - Kalyani (M.B.A)Document20 pagesAssignment On Bata India LTD: Presented by A.Ch - Kalyani (M.B.A)sanafatemaNo ratings yet
- Ocv Aerio N SwiftDocument6 pagesOcv Aerio N SwiftagusNo ratings yet
- B A Set - SpecificationDocument3 pagesB A Set - SpecificationVinit PeterNo ratings yet
- Mid TermDocument11 pagesMid TermMaha TharwatNo ratings yet
- 38-Hydraulic Design of Reservoir Outlet WorksDocument201 pages38-Hydraulic Design of Reservoir Outlet WorksAbdi RahimianNo ratings yet
- Internal Combustion Engines: MET 101 Basic Mechanical EngineeringDocument30 pagesInternal Combustion Engines: MET 101 Basic Mechanical EngineeringAnish RulesNo ratings yet
- Power Transformer Fundamentals: Design and ManufacturingDocument52 pagesPower Transformer Fundamentals: Design and Manufacturingjuliancansen100% (3)
- FM Unit I Two MarksDocument5 pagesFM Unit I Two MarksKomalaselvan VNo ratings yet
- Chemical Reactions and EquationsDocument48 pagesChemical Reactions and EquationsAnimesh AnshNo ratings yet