Professional Documents
Culture Documents
1
1
Uploaded by
bipexe2160Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
1
1
Uploaded by
bipexe2160Copyright:
Available Formats
It plays a crucial role in the biological signaling pathway.
The precursor of
potent signaling mediators is lipid peroxidation.
The metabolism of fatty acids acts as a cellular fuel source.
Fatty acids store energy as fat droplets- composed of hydrophobic triacylglycerol
molecules within adipocytes (specialized fat cells that store and metabolize
lipids).
It helps to form a cell membrane, also called a plasma membrane, which encloses all
cells and the other related intracellular organelles. The cell membrane is composed
of a phospholipid bilayer ( lipid molecules) comprised of two fatty acid chains
bound to glycerol and a hydrophilic (head) phosphate group joined to a smaller
hydrophilic (tail) compound (e.g., choline).
It helps in protein modification: fatty acids interact with various proteins.
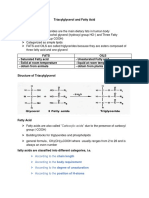
Types of Fatty Acids
There are three types of fatty acids:
Saturated fatty acids
Unsaturated fatty acids
Trans fats
Saturated Fatty Acids
Saturated fatty acids are saturated with hydrogen and contain 12–22 carbon atoms.
It is also known as bad or unhealthy fats because they are pernicious to our
health, such as increased risk of heart disease and stroke.
It remains solid at room temperature.
Saturated fatty acids have a higher melting point than unsaturated fatty acids.
Examples are lauric acid (CH3(CH2)10COOH), palmitic acid (CH3(CH2)14COOH), and
stearic acid (CH3(CH2)16COOH).
Saturated fats containing foods include cheese, butter, milk, Coconut, Palm and
palm kernel oils, Beef, Lamb, Pork, Skin of chicken and turkey, Lard, Full-fat
dairy, Ice cream, Cream, and Some baked and fried foods.
Trans Fatty Acids
There are two sources of trans fatty acids: natural and artificial (liquid oils).
In industrial processes, artificial trans fats are converted into solids.
Trans fatty acids are bad/ artificial fatty acids present in all processed foods.
The primary dietary source is partially hydrogenated oils.
It can cause the risk of heart disease, stroke, and type-2 diabetes.
Unsaturated Fatty Acids
Unsaturated fatty acids are fatty acids that have one or more double bonds between
carbons, such as alkenes.
It tends to be liquid at room temperature.
They are good or healthy fats because they are innocuous to our health.
Examples are Oleic (CH3(CH2)7CH=CH(CH2)7COOH), Linoleic
(CH3(CH2)4(CH=CHCH2)2(CH2)6COOH), Linolenic (CH3CH2(CH=CHCH2)3(CH2)6COOH), and
Arachidonic (CH3(CH2)4(CH=CHCH2)4(CH2)2COOH).
Unsaturated fat breaks down into two types:
Monounsaturated fatty acids
They are fatty acids containing one carbon-carbon double bond; most fatty acids are
present in positions between 16 and 22 carbons in length containing a cis double
bond.
The sources of monounsaturated fatty acids are Olive oil, Peanut oil, Canola oil,
Safflower oil, Sesame oil, Avocado, Peanut butter, and many nuts and seeds.
Polyunsaturated fatty acids (PUFAs)
Polyunsaturated fatty acids are fatty acids that comprise long chains of carbon
atoms with a carboxyl group at one end and a methyl group at the other.
These fatty acids contain more than one double bond produced by plants and
phytoplankton.
The two classes of polyunsaturated fatty acids (PUFAs) are: Omega-3 fatty acids
(Tuna, Salmon, Trout, Herring, Sardines, Flaxseeds and flaxseed oil, Walnuts, and
chia seeds ) and Omega-6 fatty acids (Safflower oil, Sunflower oil, Corn oil,
Soybean oil, Sunflower seeds, pumpkin seeds).
The carbon-carbon double bond located between the third and fourth carbon atoms
from the methyl end of the chain is called Omega-3 fatty acids (ω-3 fatty acids).
Omega-6 fatty acids (ω-6 fatty acids) are fatty acids in which the carbon-carbon
double bond is present between the sixth and seventh carbon atoms from the methyl
end of the chain. The Omega-6 fatty acid examples are Linoleic acid (C18:2n-6) and
arachidonic acid (C20:4n-6).
Omega-3 Fatty Acids (ω-3 Fatty Acids)
Omega-3 fatty acids, also known as n-3s, mean the carbon-carbon double bond is
present between the third and fourth end carbon atoms.
There are two ends in fatty acids: carboxylic acid (COOH) alpha end-initial of the
chain and methyl (CH3) omega end-tail of the chain.
C60H92O6 is the molecular formula of omega-3 fatty acids, and the molecular weight
is 909.39 g/mol.
Omega-3 fatty acids found in fish are long-chain, whereas Omega-3 fatty acids
present in plants are shorter chains. Long-chain omega-3 enters more rapidly in the
blood, and cells show fast effects. Short-chain omega-3 fatty acids convert into
long-chain fatty acids.
Examples are Linoleic acid, Gamma linoleic, Arachidonic Acid, Conjugated linoleic
acid, Alpha-linolenic acid, and Ocosahexaenoic acid.
In addition, Omega-3 supplements, such as Omega-3-acid ethyl esters, Boldfit
Flaxseed omega-3 Supplement, Boldfit omega-3 Fish Oil, Lovaza, Vascazen, Omtryg can
be ingested by those who do not eat omega-3-rich foods.
You might also like
- Prescription - 217923 - 27 07 2020 - Dr. Prof. Sanjay Sinha - Apollo 247Document3 pagesPrescription - 217923 - 27 07 2020 - Dr. Prof. Sanjay Sinha - Apollo 247badenaga75% (4)
- A View of The Cell Review PacketDocument7 pagesA View of The Cell Review Packetapi-259727482No ratings yet
- Validation of The Work-Life Balance Culture Scale (WLBCS)Document10 pagesValidation of The Work-Life Balance Culture Scale (WLBCS)Gunel JamaladdinovaNo ratings yet
- Ethics Chapter 5Document7 pagesEthics Chapter 5mine2515100% (1)
- PMDC Indexed JournalsDocument2 pagesPMDC Indexed JournalsOmair Riaz100% (1)
- Fatty AcidsDocument2 pagesFatty Acidsbipexe2160No ratings yet
- Lipid ChemistryDocument93 pagesLipid ChemistrySanreet RandhawaNo ratings yet
- BSE102 - Lecture 10 - LipidsDocument11 pagesBSE102 - Lecture 10 - LipidsAnonymous 001No ratings yet
- BCH 202 LipidsDocument17 pagesBCH 202 LipidskolawoleodewusiNo ratings yet
- Biochemistry (Ichem.3052) Chapter Five: Lipids: Department of Industrial ChemistryDocument18 pagesBiochemistry (Ichem.3052) Chapter Five: Lipids: Department of Industrial ChemistryBizuayehu Ze GeorgeNo ratings yet
- Chemistry of Lipids-LECTUREDocument88 pagesChemistry of Lipids-LECTUREKesha Marie TalloNo ratings yet
- Chapter Three The Process Technology of Oil and Fat Industries Fat and OilDocument21 pagesChapter Three The Process Technology of Oil and Fat Industries Fat and Oilabdisahurisa24No ratings yet
- Dr. Hewaida Fadel Dr. Tarek El Sewedy: Department of Medical Laboratory Technology Faculty of Allied Medical SciencesDocument45 pagesDr. Hewaida Fadel Dr. Tarek El Sewedy: Department of Medical Laboratory Technology Faculty of Allied Medical Sciencesraanja2No ratings yet
- Chemistry of Lipids: Preethi S Department of BiochemistryDocument37 pagesChemistry of Lipids: Preethi S Department of BiochemistryRamakrishnanNo ratings yet
- LIPIDSDocument9 pagesLIPIDSAkanksha SharmaNo ratings yet
- Hormone Like, Help Regulate Blood Pressure, Clotting, and Produce Pain and FeverDocument87 pagesHormone Like, Help Regulate Blood Pressure, Clotting, and Produce Pain and FeverReyana BaderNo ratings yet
- Diet For Bodybuilder by Guru MannDocument58 pagesDiet For Bodybuilder by Guru MannDhanjayNo ratings yet
- Lipids MLT and DPTDocument89 pagesLipids MLT and DPTZille HummaNo ratings yet
- c3 - LipidsDocument86 pagesc3 - LipidsAddis PeterNo ratings yet
- Structure of LipidDocument11 pagesStructure of LipidAfrah Alatas100% (1)
- LipidsDocument45 pagesLipidsDhaya VNo ratings yet
- LipidsDocument6 pagesLipidsMUHAMMAD SHOAIB MUNAWARNo ratings yet
- Lipids Classification: Presented By: Group 7Document28 pagesLipids Classification: Presented By: Group 7X x A7md x XNo ratings yet
- FatsDocument45 pagesFatsManshad AbbasNo ratings yet
- LIPIDS ReportDocument38 pagesLIPIDS ReportcharmsterNo ratings yet
- LipidDocument80 pagesLipidMirza Salman BaigNo ratings yet
- Screenshot 2024-05-29 at 7.15.33 PMDocument66 pagesScreenshot 2024-05-29 at 7.15.33 PMshreyamakkar1974No ratings yet
- Lipid ChemistryDocument40 pagesLipid Chemistryatfbdalmsyh672No ratings yet
- 003lipid ChemisteryDocument20 pages003lipid ChemisteryHiba HasanNo ratings yet
- Chemistry of LipidsDocument7 pagesChemistry of Lipidsbossbaby18105No ratings yet
- Fat PTC8Document52 pagesFat PTC8vNo ratings yet
- Chemistry of LipidsDocument88 pagesChemistry of LipidsNovia EkaNo ratings yet
- Lecture 10Document20 pagesLecture 10ishugoyalnktNo ratings yet
- Nutritional Biochemistry 1 - LIPIDSDocument62 pagesNutritional Biochemistry 1 - LIPIDSAdnan AhmedNo ratings yet
- Fat - WikipediaDocument29 pagesFat - WikipediaWaqar AhmadNo ratings yet
- Chemistry of LipidsDocument70 pagesChemistry of LipidsArpit JainNo ratings yet
- Chapter 4 Biochemistry and Clinical Pathology Complete Notes by Noteskarts Acc To ER20Document8 pagesChapter 4 Biochemistry and Clinical Pathology Complete Notes by Noteskarts Acc To ER20yplsinghNo ratings yet
- Introduction To LipidsDocument29 pagesIntroduction To LipidsBharaniDeepan50% (2)
- Functions of LipidsDocument4 pagesFunctions of Lipidsprashant kumarNo ratings yet
- Fats and LipidsDocument31 pagesFats and LipidsKaye Danielle HilomenNo ratings yet
- Nutritional Biochemistry 1 - LIPIDSDocument62 pagesNutritional Biochemistry 1 - LIPIDSSalah AlsafiNo ratings yet
- Lipid Structure and FunctionDocument47 pagesLipid Structure and FunctionMariam ShalabyNo ratings yet
- Structure and Classification of Lipids: PresentDocument4 pagesStructure and Classification of Lipids: Presentsamantha laurenthNo ratings yet
- Lipids BiochemistryDocument188 pagesLipids BiochemistryfayanNo ratings yet
- Triacylglycerol and Fatty AcidDocument6 pagesTriacylglycerol and Fatty AcidGil Angelo VillaluzNo ratings yet
- What Is FatDocument2 pagesWhat Is FatKarthi100% (1)
- Lipid ChemistryDocument53 pagesLipid Chemistryasrarulhaq4008No ratings yet
- Chapter 7chemistry of LipidDocument31 pagesChapter 7chemistry of Lipidbayan.grNo ratings yet
- LipidsDocument17 pagesLipidsathulkumardqNo ratings yet
- Biochemistry V. LiipidsDocument50 pagesBiochemistry V. LiipidsAlthea De TorresNo ratings yet
- Fats and Oils: Naemaa Mohamad Faculty of Applied Sciences Universiti Teknologi MARADocument65 pagesFats and Oils: Naemaa Mohamad Faculty of Applied Sciences Universiti Teknologi MARANaveenNo ratings yet
- Lipidi MastiDocument20 pagesLipidi MastiljubodragNo ratings yet
- LIPIDS BiochemistryDocument52 pagesLIPIDS BiochemistryMark BagamaspadNo ratings yet
- CH. 3 Lipid ChemistryDocument51 pagesCH. 3 Lipid Chemistryanushkappatil20No ratings yet
- Biological Chemistry 1B: Week 6 & Week 7 LipidsDocument37 pagesBiological Chemistry 1B: Week 6 & Week 7 Lipidsglenn johnstonNo ratings yet
- Medical Definition of Fatty Acids: DescriptionDocument1 pageMedical Definition of Fatty Acids: DescriptionJohn ValenzuelaNo ratings yet
- Lipids Revised 02-10-2021-1Document42 pagesLipids Revised 02-10-2021-1Niruta NepaliNo ratings yet
- BPD02181028 (Introduction To Lipids)Document8 pagesBPD02181028 (Introduction To Lipids)ChaudryNomiNo ratings yet
- Oleo Chemistry: Badrla SandeepDocument93 pagesOleo Chemistry: Badrla Sandeepsab_franc5286No ratings yet
- Lecture 3 Lipid Biochemistry and NutritionDocument43 pagesLecture 3 Lipid Biochemistry and NutritionWycliffe AsmanNo ratings yet
- Chemistry of LipidsDocument30 pagesChemistry of Lipidszahid mahmoodNo ratings yet
- BP301T Poc Unit IiiDocument15 pagesBP301T Poc Unit IiiSUBHASISH DASHNo ratings yet
- NURS 1012: Basic Biochemistry: Lecture #4: Lipid Structure and FunctionDocument26 pagesNURS 1012: Basic Biochemistry: Lecture #4: Lipid Structure and FunctionqpidjmNo ratings yet
- Sekolah Pelita Harapan Year 10 MYP ScienceDocument3 pagesSekolah Pelita Harapan Year 10 MYP ScienceherrisenNo ratings yet
- Anatomy of The Mediastinum CXRDocument26 pagesAnatomy of The Mediastinum CXRHassan AliNo ratings yet
- SRS Medical ManagementDocument7 pagesSRS Medical ManagementAtharv KatkarNo ratings yet
- Ijims 2017 105Document7 pagesIjims 2017 105Marcos HoilNo ratings yet
- Flame Scanner Developed by ITS: Reliability Is A Matter of QualityDocument16 pagesFlame Scanner Developed by ITS: Reliability Is A Matter of QualityMauricio GuanellaNo ratings yet
- The Rice Tariffication LawDocument2 pagesThe Rice Tariffication LawDusty 1245No ratings yet
- Kast o Lite20 Vsl35Document2 pagesKast o Lite20 Vsl35Señor123456789No ratings yet
- Final Genetics Syllabus ReferenceDocument8 pagesFinal Genetics Syllabus ReferenceLady EmeterioNo ratings yet
- Malawi - November 2018 Country Fact SheetDocument2 pagesMalawi - November 2018 Country Fact Sheetनिपुण कुमारNo ratings yet
- Case Study HaldiramDocument8 pagesCase Study Haldiramitsnaveds100% (1)
- Working at HeightsDocument1 pageWorking at HeightsVictor Quijano JrNo ratings yet
- Procedure Text Latihan Soal 2023 StudentDocument11 pagesProcedure Text Latihan Soal 2023 StudentShalahuddien Al AyyubiNo ratings yet
- Vacuum and Pressure Gauges For Fire Proteccion System 2311Document24 pagesVacuum and Pressure Gauges For Fire Proteccion System 2311Anonymous 8RFzObvNo ratings yet
- Heating, Air ConditioningDocument64 pagesHeating, Air ConditioningCésar Arturo Pajuelo EspinozaNo ratings yet
- Biofarmasetika - Kelompok IiDocument41 pagesBiofarmasetika - Kelompok IiWiwit Zuriati UnoNo ratings yet
- Control of Hospital Acquired Infection PDFDocument36 pagesControl of Hospital Acquired Infection PDFPrakashNo ratings yet
- Comparison of Simple Potential Functions For Simulating Liquid WaterDocument11 pagesComparison of Simple Potential Functions For Simulating Liquid WaterAdarsh PNo ratings yet
- Idiomatic ExpressionDocument27 pagesIdiomatic ExpressionJess Jess100% (1)
- Neet BiologyDocument9 pagesNeet Biologyjaseelanu2No ratings yet
- Xenon 21-22 Sheet Without Answer (EUDIOMETRY)Document3 pagesXenon 21-22 Sheet Without Answer (EUDIOMETRY)Krishna GoyalNo ratings yet
- Validation and Qualification of Heating, Ventilation, Air ConDocument18 pagesValidation and Qualification of Heating, Ventilation, Air ConJai MurugeshNo ratings yet
- Physics MidtermDocument14 pagesPhysics MidtermPrecious015100% (1)
- The Right To Sexual Orientation, CG ProjectDocument9 pagesThe Right To Sexual Orientation, CG ProjecttanayaNo ratings yet
- Eyewash & Safety ShowerDocument5 pagesEyewash & Safety Showershiekh faizNo ratings yet
- Filter MiliporeDocument8 pagesFilter Miliporemotasa mojosarilabNo ratings yet
- Minority Elite Continuity and Identity PDocument121 pagesMinority Elite Continuity and Identity PEvandro MonteiroNo ratings yet