Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Unit 1.4 Problem Solving answers
Unit 1.4 Problem Solving answers
Uploaded by
Kalesware MuniandyCopyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Unit 1.4 Problem Solving answers
Unit 1.4 Problem Solving answers
Uploaded by
Kalesware MuniandyCopyright:
Available Formats
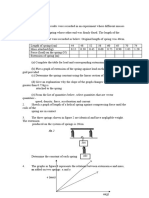
Solving Problems Involving Force and Extension of a Spring
Solutions:
1. 80 g – 20 g = 60 g
40 cm – 25 cm = 15 cm
An increase of mass of 60 g produces an increase in length of 15 cm
An increase of mass of 20 g produces an increase in length of 5 cm
Therefore, a decrease in mass of 20 g produces a decrease in length of 5 cm.
Scale reading = 40 cm – 5 cm
= 35 cm
2. For the four parallel springs:
tension in each spring = 100 g
extension of each spring = 2 cm
extension of the arrangement of four springs in parallel = 2 cm
For the two parallel springs:
tension in each spring = 200 g
extension of each spring = 4 cm
extension of the arrangement of two springs in parallel = 4 cm
Total extension = 2 + 4
= 6 cm
3. (a) Comparing springs P and Q:
load on spring Q = 150 g
= 0.150 kg
force applied, F = 0.150 × 10
= 1.5 N
extension, x = 14.0 – 12.0
= 2.0 cm
F
Spring constant, k = x
1.5
= 2
= 0.75 N cm–1
(b) R and S are in series
Load applied on R and S = 300 g
Extension of spring R = 4.0 cm
Extension of spring S = 4.0 cm
Total extension = 4.0 + 4.0
= 8.0 cm
(c) T and U are parallel
Load applied on T and U = 150 g
Extension of spring T = 2.0 cm
Extension of spring U = 2.0 cm
Total extension = 2.0 cm
4. Stretching force of 1.8 N is equivalent to 0.6 N + 0.6 N + 0.6 N
Stretching force of 1.8 N produces an extension of 3.0 cm
Stretching force of 0.9 N produces an extension of 1.5 cm
Stretching force of 0.6 N produces an extension of 1.0 cm
Tension = 0.6 N
Extension = 1.0 cm
Tension = 0.9 N
Extension = 1.5 cm
Tension = 1.8 N
Extension = 3.0 cm
1.8 N
Total extension = 1.0 + 1.5 + 3.0
= 5.5 cm
You might also like
- Uncertainty: Problems & Answers: CM CM CM CMDocument10 pagesUncertainty: Problems & Answers: CM CM CM CMarrowayNo ratings yet
- Activity 4 - Correction For TemperatureDocument11 pagesActivity 4 - Correction For TemperatureJohn Angelo CompetenteNo ratings yet
- Spring Extension Lab ReportDocument6 pagesSpring Extension Lab Report9름No ratings yet
- Lab 1 - PendulumDocument7 pagesLab 1 - PendulumirfanNo ratings yet
- JJ309 Fluid Mechanics Unit 5Document21 pagesJJ309 Fluid Mechanics Unit 5Adib AzharNo ratings yet
- Bernoulli ReportDocument4 pagesBernoulli ReportGabriel VaughnNo ratings yet
- Standing Waves LabDocument17 pagesStanding Waves LabOmarZinAbidineNo ratings yet
- Physics Lab SpringDocument3 pagesPhysics Lab SpringJackie ManNo ratings yet
- Hookes Law WorksheetDocument2 pagesHookes Law WorksheetKnofixNo ratings yet
- Physics Lab ReportDocument2 pagesPhysics Lab ReportFelix SonsunNo ratings yet
- CHP 1 Force NumericalsDocument11 pagesCHP 1 Force Numericals28 9D Raghav GargNo ratings yet
- Perla Espinosa Professor Dr. Ricci Physics 101 14 of November, 2021 Lab#9Document8 pagesPerla Espinosa Professor Dr. Ricci Physics 101 14 of November, 2021 Lab#9perla espinosaNo ratings yet
- Pptg101213 Rotations GallegoDocument39 pagesPptg101213 Rotations GallegoRed GallegoNo ratings yet
- Experiment No 02Document5 pagesExperiment No 02Farhan AliNo ratings yet
- HookeDocument6 pagesHookeTitus KaselaNo ratings yet
- Chapter5pp043 051 PDFDocument9 pagesChapter5pp043 051 PDFInderMaheshNo ratings yet
- Tut 1 SolDocument2 pagesTut 1 SolAlpha GamingNo ratings yet
- FORCES.pure (1)Document16 pagesFORCES.pure (1)thobegakutlo54No ratings yet
- Solution of ch8Document2 pagesSolution of ch8,冰果No ratings yet
- Hooke S LawDocument5 pagesHooke S Lawخلود البطاحNo ratings yet
- Spring: Muh - Fajrin, Sariwahyuni, Sulvita Dewi, Syamhijrah )Document16 pagesSpring: Muh - Fajrin, Sariwahyuni, Sulvita Dewi, Syamhijrah )Anonymous o2togP0p0No ratings yet
- STRainDocument10 pagesSTRainDioscura Cañedo ParanNo ratings yet
- Tutorial 1 SolnDocument2 pagesTutorial 1 Solnkaeshav manivannanNo ratings yet
- Contents : Measuring SystemDocument13 pagesContents : Measuring Systemanon-419501No ratings yet
- Chapter 09Document41 pagesChapter 09Syed Ahmed SakibNo ratings yet
- Perhitungan TCDocument3 pagesPerhitungan TCManda PutraNo ratings yet
- Diseño de ColumnasDocument1 pageDiseño de ColumnasRoberto CarlosNo ratings yet
- Uniform Circular MotionDocument14 pagesUniform Circular MotionKenneth NyuNo ratings yet
- Class 9 Project No. 2 2021 2022Document34 pagesClass 9 Project No. 2 2021 2022priyanshuprasad27150No ratings yet
- 1 Fundamentals, StaticsDocument14 pages1 Fundamentals, StaticsTom ManNo ratings yet
- Experiment No.4 Center of Gravity and Equilibrium I. AbstractDocument2 pagesExperiment No.4 Center of Gravity and Equilibrium I. AbstractJoyce CZ0% (2)
- Lab 8 (Spring Stiffness Constant)Document8 pagesLab 8 (Spring Stiffness Constant)Joud Alotaibi.No ratings yet
- Base PlateDocument5 pagesBase PlateYaserNo ratings yet
- Circular Motion LabDocument10 pagesCircular Motion LabVijay VishalNo ratings yet
- Workshop CalculationDocument64 pagesWorkshop Calculationbentapada100% (1)
- Yoyo 9.1 Lab Report On Hooke S Law 1Document7 pagesYoyo 9.1 Lab Report On Hooke S Law 1Linda LiNo ratings yet
- Lab Physics Hook's LawDocument7 pagesLab Physics Hook's LawSouvik GhoshNo ratings yet
- Workshop CalculationDocument61 pagesWorkshop CalculationAshwani Dogra80% (5)
- Ucm Ap Physic 1labDocument9 pagesUcm Ap Physic 1labapi-327824216No ratings yet
- Centre of Foundation Studies: Foundation Physics I Laboratory ReportDocument17 pagesCentre of Foundation Studies: Foundation Physics I Laboratory ReportMUHAMMAD YUS SHAFIQ MOHD HAFIZNo ratings yet
- V F T F: Dentify ET P XecuteDocument6 pagesV F T F: Dentify ET P XecuteAndrea YipNo ratings yet
- Zapata Aislada y CombinadaDocument1 pageZapata Aislada y CombinadaMega01No ratings yet
- General Chem. Answer Sheet Module 11Document7 pagesGeneral Chem. Answer Sheet Module 11Jayar GultianoNo ratings yet
- Question 197: (Forces Moments) : (At The 50cm Mark)Document8 pagesQuestion 197: (Forces Moments) : (At The 50cm Mark)ekjon1No ratings yet
- Lab Report Physics Hooke's LawDocument11 pagesLab Report Physics Hooke's LawAbu Huzaifah100% (1)
- Beam Balance & Principle of Moments 1Document4 pagesBeam Balance & Principle of Moments 1Laksh RameshNo ratings yet
- Assessment Lesson 3 Unit 2 Thermodynamic Measurements and QuantitiesDocument4 pagesAssessment Lesson 3 Unit 2 Thermodynamic Measurements and Quantitiesjcdnicolas12No ratings yet
- Unit 3 Forces and EnergyDocument47 pagesUnit 3 Forces and Energy4w7b9kkyp8No ratings yet
- Ejercicio 1 U2Document1 pageEjercicio 1 U2David Valverde BurneoNo ratings yet
- Tramo 1 DescansoDocument25 pagesTramo 1 DescansoRaymundo A ExebioNo ratings yet
- Physics p3 MsDocument8 pagesPhysics p3 MsElijah KirigaNo ratings yet
- Surveying: Linear MeasurementsDocument19 pagesSurveying: Linear MeasurementsRahul KumarNo ratings yet
- Flexo CompresionDocument2 pagesFlexo CompresionJoel ZapataNo ratings yet
- PHYS 1100 Collision & Momentum SolutionsDocument12 pagesPHYS 1100 Collision & Momentum Solutionsoreoluwaoshodi16No ratings yet
- Zapatas - Ed Depos. RecepcDocument56 pagesZapatas - Ed Depos. RecepcJuan André VásquezNo ratings yet
- Exercise 4A & 4BDocument9 pagesExercise 4A & 4BSrijita SinhaNo ratings yet
- Full Report (Simple Pendulum)Document7 pagesFull Report (Simple Pendulum)zulaikha100% (1)
- Design of BandharaDocument21 pagesDesign of BandharaNeil Agshikar100% (1)
- UNIT 1.1 Activity 1.2Document2 pagesUNIT 1.1 Activity 1.2Kalesware MuniandyNo ratings yet
- Acid and Alkali: 6.1 Properties of Acids and AlkalisDocument2 pagesAcid and Alkali: 6.1 Properties of Acids and AlkalisKalesware MuniandyNo ratings yet
- Tg3 - Praktis (b1-5) .Ms - enDocument34 pagesTg3 - Praktis (b1-5) .Ms - enKalesware MuniandyNo ratings yet
- Projects and Project-Based Learning - What's The DifferenceDocument5 pagesProjects and Project-Based Learning - What's The DifferenceKalesware MuniandyNo ratings yet
- Ecosystem: 2.1 Energy Flow in An EcosystemDocument3 pagesEcosystem: 2.1 Energy Flow in An EcosystemKalesware MuniandyNo ratings yet
- Skin Fold ThicknessDocument8 pagesSkin Fold ThicknessKalesware MuniandyNo ratings yet
- Biodiversity: 1.1 Diversity of OrganismsDocument2 pagesBiodiversity: 1.1 Diversity of OrganismsKalesware MuniandyNo ratings yet
- Boyle's Law SimulationDocument2 pagesBoyle's Law SimulationKalesware MuniandyNo ratings yet
- 8226 18984 1 PBDocument9 pages8226 18984 1 PBKalesware MuniandyNo ratings yet
- Overview of Curriculum Change: A Brief Discussion: Nilay Mondal Dr. Arjun Chandra DasDocument6 pagesOverview of Curriculum Change: A Brief Discussion: Nilay Mondal Dr. Arjun Chandra DasKalesware MuniandyNo ratings yet
- 5E Instructional Model OnlineDocument13 pages5E Instructional Model OnlineKalesware MuniandyNo ratings yet