Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Anatomy 23f 23s
Anatomy 23f 23s
Uploaded by
harshamanikandan050 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
0 views13 pagesCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pdf or txt
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
0 views13 pagesAnatomy 23f 23s
Anatomy 23f 23s
Uploaded by
harshamanikandan05Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pdf or txt
You are on page 1of 13
Вопросы по тесту: Anatomy 23f 23s
Вариант: 1
1. The Glisson capsule covers:
Esophagus
Stomach
Spleen
Liver
2. What separates the liver's right and left anatomical lobes?
The falciform ligament
The middle hepatic vein
The right sagittal fissure
The left sagittal fissure
3. How long is the bile duct typically?
2-4 cm
5-15 cm
16-20 cm
21-25 cm
4. What is the primary role of the cystic duct?
To produce bile
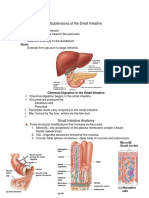
To store bile
To convey bile from the gallbladder to the bile duct
To absorb nutrients from bile
5. What characteristic shape does the neck of the gallbladder typically make?
A circular loop
A straight line
An S-shaped bend
A U-shaped bend
6. Into which part of the digestive system does pancreatic juice enter?
Ileum
Jejunum
Duodenum
Stomach
7. What hormone is NOT secreted by the pancreatic islets?
Insulin
Glucagon
Somatostatin
Adrenaline
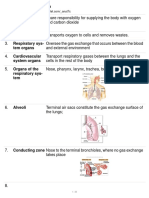
8. What lines the nasal cavity, excluding the nasal vestibule?
Skin
Mucosa
Perichondrium
Periosteum
9. The alae of the nose are located:
Medially, as part of the septum
At the root
Laterally, binding the nares
At the apex
10. The choanae connect the nasal cavity to the:
Oral cavity
Nasopharynx
Oropharynx
Laryngopharynx
11. The laryngeal vestibule is located between:
The laryngeal inlet and the vestibular folds
The laryngeal inlet and the vocal folds
The vestibular and vocal folds
The vocal folds and the infraglottic cavity
12. Anular ligaments connect:
The tracheal cartilaginous semi-rings
The lobes of the lungs
The bronchi to the trachea
The pleural layers
13. The visceral pleura of the lung:
Contains the pleural cavity
Adheres tightly to the lung
Is the outer layer of the pleura
Lines the thoracic cavity
14. The pleura that tightly adheres to the lung is called:
Diaphragmatic pleura
Mediastinal pleura
Visceral pleura
Parietal pleura
15. The lung surfaces include all EXCEPT:
Medial surface
Costal surface
Lateral surface
Diaphragmatic surface
16. The structural and functional unit of the liver is:
the hepatic rods
the hepatic acinus
the hepatic lobe
the hepatic lobule
17. What forms the roof of the oral cavity?
The palate
The buccinator muscle
The dental arches
The tongue
18. How many deciduous teeth do children have?
32
20
28
24
19. Where is the stomach located?
In the pelvic cavity
In the thoracic cavity
In the epigastric, umbilical, and left hypochondrium regions
Only in the left hypochondrium region
20. How is the duodenum divided?
Into two parts
Into three parts
Into four parts
Into five parts
21. Where does the jejunum begin?
At the pyloric orifice
At the ileocecal junction
At the midline of the L2 vertebra
At the duodenojejunal flexure
22. The anal valves are located:
At the inferior ends of the anal columns
Outside the anal canal
Along the entire length of the anal columns
At the superior ends of the anal columns
23. What type of muscle is found in the lower third of the esophagus?
Striated muscle
Smooth muscle
Cardiac muscle
Elastic muscle
24. Where is the liver primarily located?
Right upper quadrant
Left lower quadrant
Right lower quadrant
Left upper quadrant
25. How many hepatic segments?
Ten
Eight
Six
Four
26. The hepatopancreatic ampulla is formed by the union of which ducts?
The bile duct and the duct of Wirsung
The cystic duct and the common hepatic duct
The main pancreatic duct and the bile duct
The main pancreatic duct and the cystic duct
27. What structure is found at the neck of the gallbladder?
The pancreatic duct
The common bile duct
The hepatic duct
The spiral fold
28. Where is the pancreas located relative to the peritoneum?
Retroperitoneal
In the peritoneal cavity
Subperitoneal
Intraperitoneal
29. The pancreatic duct unites with which duct to form the hepatopancreatic
ampulla?
The duodenal duct
The common bile duct
The accessory pancreatic duct
The cystic duct
30. The nasal cavity is divided into right and left cavities by what?
The maxillary bone
The palatine bone
The nasal septum
The ethmoid bone
31. Which sinuses are located between the outer and inner tables of the frontal
bone?
Ethmoidal sinuses
Sphenoidal sinuses
Maxillary sinuses
Frontal sinuses
32. The nasal conchae are primarily responsible for:
Producing tears
Smelling
Filtering and warming inhaled air
Producing mucus
33. The pharyngeal tonsil is located in the:
Larynx
Nasopharynx
Laryngopharynx
Oropharynx
34. The tubal tonsil is found near the orifice of:
The pharyngotympanic tube (The Eustachian tube)
The esophagus
The laryngeal ventricle
The laryngeal saccule
35. The choanae are paired openings that connect the:
Laryngopharynx to the esophagus
Nasal cavity to the nasopharynx
Nasal cavity to the oropharynx
Oropharynx to the nasopharynx
36. The right lung is divided into how many lobes?
One
Two
Three
Four
37. The pleural cavity contains:
Air for lung expansion
Lymph nodes
Blood vessels
A small amount of pleural fluid
38. The pleural cavity is located:
Inside the lung parenchyma
Outside the thoracic cavity
Between the visceral and parietal pleura
Between the lungs and the mediastinum
39. The shortest part of the colon is:
Sigmoid
Descending
Transverse
Ascending
40. What is the largest cartilage in the larynx?
Hyoid bone
Arytenoid cartilages
Thyroid cartilage
Cricoid cartilage
41. What lies between the mucous membrane and the buccinators in the cheeks?
The labial frenula
Numerous small buccal glands
Superior and inferior labial muscles
Encapsulated collections of fat
42. How many permanent teeth do adults have?
32
24
28
20
43. How many constrictions does the esophagus normally have?
Three
Two
One
Four
44. What is the first part of the large intestine?
Appendix
Cecum
Ascending colon
Transverse colon
45. Which part of the stomach surrounds the opening of the esophagus?
The body
The fundus
The cardia
The pyloric part
46. What are teniae coli?
Types of intestinal villi
Folds of the peritoneum
Layers of fat around the colon
Thickened bands of smooth muscle in the colon
47. What is the length of the small intestine?
8-9 m
1-2 m
5-7 m
2-3 m
48. The liver has how many anatomical lobes?
One
Two
Four
Eight
49. What is the main function of bile?
To increase stomach acidity
To emulsify fats for absorption
To digest proteins
To absorb vitamins
50. The arterial supply to the gallbladder is primarily from which artery?
The cystic artery
The right hepatic artery
The left hepatic artery
The posterior superior pancreaticoduodenal artery
51. Which part of the gallbladder typically contacts the visceral surface of the liver?
Cystic duct
Body
Neck
Fundus
52. What type of secretions does the pancreas produce?
Both exocrine and endocrine
Neither exocrine nor endocrine
Only endocrine
Only exocrine
53. Where does the accessory pancreatic duct open?
Into the duodenum at the summit of the minor duodenal papilla
Into the stomach
Into the spleen
Directly into the liver
54. How many main cartilages are part of the cartilaginous part of the nose?
Six
Four
Three
Five
55. The superior part of the nasal septum is formed by:
The nasal spine of the frontal bone
The perpendicular plate of the ethmoid
The vomer
The septal cartilage
56. How many cartilages make up the laryngeal skeleton?
Twelve
Nine
Six
Three
57. Which part of the pharynx is posterior to the mouth?
None of the above
Laryngopharynx
Oropharynx
Nasopharynx
58. The vocal apparatus of the larynx is known as the:
Laryngeal saccule
Glottis
Vestibular fold
Laryngeal inlet
59. Which tonsils are located near the orifice of the pharyngotympanic tube?
Tubal tonsils
Pharyngeal tonsils
Palatine tonsils
Lingual tonsils
60. The left lung is divided into how many lobes?
Four
Three
Two
One
61. How many cartilaginous semi-rings does the trachea typically have?
26-30
21-25
10-15
16-20
62. The lung's base is oriented towards the:
Diaphragm
Head
Mediastinum
Rib cage
63. Which part of the duodenum does the pancreatic duct open in?
inferior part
superior part
descending part
ascending part
64. What is the labial frenula?
Free-edged folds of mucous membrane
Muscles controlling lip movement
Arteries supplying the lips
Glands within the lips
65. The cecum is found in which part of the abdomen?
Left lower quadrant
Right lower quadrant
Right upper quadrant
Left upper quadrant
66. The ileum ends at:
The sigmoid colon
The duodenojejunal flexure
The pyloric orifice
The ileocecal junction
67. Which part of the small intestine is the first and shortest?
Cecum
Ileum
Duodenum
Jejunum
68. How long is the appendix approximately?
2-4 cm
6-10 cm
14-15 cm
20-25 cm
69. Where are the thyroid and parathyroid glands located?
At the base of the brain
At the base of the neck
In the pelvic cavity
In the thoracic cavity
70. What structure joins the lobes of the thyroid gland?
Isthmus
Cricoid cartilage
Thyroid cartilage
Hyoid bone
71. What type of tissue encloses the adrenal glands and the kidneys?
Connective tissue capsule
Renal fascia
Peritoneum
Chromaffin cells
72. How many parathyroid glands do most individuals have?
Six
Two
Four
Eight
73. What is the main function of chromaffin cells in the adrenal medulla?
Secrete mineralocorticoids
Secrete androgens
Secrete corticosteroids
Secrete catecholamines
74. Which layer of the adrenal cortex produces cortisol?
Medulla
Zona reticularis
Zona glomerulosa
Zona fasciculata
75. What layer of the uterus is the innermost?
Endometrium
Myometrium
Perimetrium
Stratum basalis
76. Which layer of the uterus is a double-layered membrane continuous with the
abdominal peritoneum?
Myometrium
Endometrium
Perimetrium
Stratum basalis
77. Which ligament joins the ovaries to the uterus?
Ovarian ligament
Round ligament
Broad ligament
Cardinal ligament
78. What is the blood supply to the uterus?
Iliac artery
Uterine artery
Ovarian artery
Vaginal artery
79. Which ligament contains the uterine artery and vein?
Ovarian ligament
Round ligament
Cardinal ligament
Broad ligament
80. The glans penis contains the opening of which structure?
Vas deferens
External urethral orifice
Seminal vesicles
Ejaculatory duct
81. What structure forms an individual capsule around each cavernous body?
Scarpa's fascia
External fascia of Colles
Deep fascia of the penis (Buck’s fascia)
Tunica albuginea
82. Which part of the nephron is responsible for filtering blood?
Bowman's capsule
Proximal convoluted tubule
Distal convoluted tubule
Loop of Henle
83. What type of muscle is the urinary bladder primarily composed of?
Striated muscle
Smooth muscle
Skeletal muscle
Cardiac muscle
84. What structure drains urine from the kidney to the bladder?
Nephron
Loop of Henle
Ureter
Urethra
85. The female urethra lies anterior to which structure?
Uterus
Pubic symphysis
Bladder
Vagina
86. What is the length of the female urethra?
2 cm
4 cm
6 cm
8 cm
87. What marks the medial margin of each kidney?
Renal papilla
Renal hilum
Renal cortex
Renal pelvis
88. What are the three layers of the fallopian tube wall?
Submucosa, serosa, and muscularis
Mucosa, muscularis, and serosa
Adventitia, submucosa, and serosa
Mucosa, submucosa, and serosa
89. Which part of the ovary contains the developing ovarian follicles?
Cortex
Stroma
Hilum
Medulla
90. The vagina extends from the cervix to which external structure?
Vulva
Hymen
Clitoris
Labia minora
91. What are the finger-like projections at the end of the fallopian tubes called?
Microvilli
Fimbriae
Cilia
Villi
92. What is the main function of the fallopian tubes?
Transport urine
Produce hormones
Transport eggs from the ovaries to the uterus
Store sperm
93. Which part of the penis contains the urethra?
Corpus spongiosum
Corpora cavernosa
Glans
Root
94. What is the most distal part of the penis called?
Body
Glans
Shaft
Root
95. The scrotum is a sac that contains which structures?
Bulbourethral glands
Seminal vesicles
Testes
Prostate gland
96. What is the function of the cremaster muscle?
Contract the prostate gland
Maintain erection
Compress the urethra
Elevate the testes
97. Which part of the prostate gland surrounds the urethra?
Transitional zone
Peripheral zone
Anterior fibromuscular zone
Central zone
98. The bulbospongiosus muscle is associated with which part of the penis?
Crura
Bulb
Shaft
Glans
99. What structure divides the scrotum into two compartments?
Cremaster muscle
Raphe
Septum
Dartos muscle
100. Which artery supplies blood to the penis?
Femoral artery
Renal artery
Internal pudendal artery
External iliac artery
101. The pituitary gland is divided into which two main parts?
Superior and inferior lobes
Medial and lateral lobes
Central and peripheral lobes
Anterior and posterior lobes
102. Which part of the pituitary gland is derived from neural tissue?
Posterior pituitary
Anterior pituitary
Both anterior and posterior
Neither anterior nor posterior
You might also like
- Man of Steel Pre Phase HORIZONTALDocument6 pagesMan of Steel Pre Phase HORIZONTALJavi Martinez100% (1)
- The Nervous System MCQ'sDocument6 pagesThe Nervous System MCQ'sTahir Aziz100% (5)
- Urinary Tract Infection Anatomy and PhysiologyDocument12 pagesUrinary Tract Infection Anatomy and PhysiologyPaul Anthony Centeno PimentelNo ratings yet
- Histo FinalDocument298 pagesHisto Finalsanullah123khan.13No ratings yet
- Digestive SystemDocument64 pagesDigestive SystemAyro Business CenterNo ratings yet
- Respiratory AnatomyDocument50 pagesRespiratory Anatomynimonayoseph27No ratings yet
- Sistem RespirasiDocument154 pagesSistem RespirasiStephanie Ming FunNo ratings yet
- NursingBulletin Respiratory SystemDocument35 pagesNursingBulletin Respiratory Systemseigelystic100% (3)
- Apa Itu RESPIRASI??: Semua Organisma Menjalankan Proses Respirasi Untuk Mendapatkan TenagaDocument146 pagesApa Itu RESPIRASI??: Semua Organisma Menjalankan Proses Respirasi Untuk Mendapatkan TenagaAryati AiNo ratings yet
- Respiratory SystemDocument54 pagesRespiratory SystemEndin Nokik StujannaNo ratings yet
- LEC. 4&5. Digestive SystemDocument65 pagesLEC. 4&5. Digestive Systemmay498550No ratings yet
- Flashcards Surgical Recall Chapter 17Document2 pagesFlashcards Surgical Recall Chapter 17Wade Bullock0% (1)
- LAB EXERCISE 9 - 10 MM Pig Embryo - Endodermal DerivativesDocument5 pagesLAB EXERCISE 9 - 10 MM Pig Embryo - Endodermal DerivativesGerald Angelo DeguinioNo ratings yet
- 6 Digestive System 2Document11 pages6 Digestive System 2Hajar ObeidatNo ratings yet
- Digestive System QuizletDocument7 pagesDigestive System QuizletJewel ChukwunenyeNo ratings yet
- Anatomy Quiz 1Document4 pagesAnatomy Quiz 1Jacob BorongNo ratings yet
- 7th-The Alimentary SystemDocument25 pages7th-The Alimentary Systemprasun_v100% (1)
- Anatomy Respiratory Muscles& DiaphragmDocument6 pagesAnatomy Respiratory Muscles& DiaphragmEbraheem NegmNo ratings yet
- OesophagusDocument14 pagesOesophagusNyakie MotlalaneNo ratings yet
- PlenaryDocument31 pagesPlenaryIsmail AbdullahNo ratings yet
- Respiratory SystemDocument26 pagesRespiratory SystemCHESKA LYKA ASILONo ratings yet
- Respiratory System Anatomy and Physiology: Marianne Belleza, RNDocument18 pagesRespiratory System Anatomy and Physiology: Marianne Belleza, RNTiara GustiwiyanaNo ratings yet
- Digestive SystemDocument106 pagesDigestive Systemshahzaibzafargondal11786No ratings yet
- Erbil Polythecnic University Soran Technical Insititute Midwifery Dipartment First Stage (M)Document13 pagesErbil Polythecnic University Soran Technical Insititute Midwifery Dipartment First Stage (M)Kubra ĖdrisNo ratings yet
- 16 Respiratory System 2022Document67 pages16 Respiratory System 2022Yiannis AlatsathianosNo ratings yet
- Anatomy and Physiology of The Pharynx-Larynx-TracheaDocument22 pagesAnatomy and Physiology of The Pharynx-Larynx-TracheaZacky Abdoel AzamNo ratings yet
- Remember Question MDSDocument26 pagesRemember Question MDSBinayak UpadhyayaNo ratings yet
- Digestive SystemDocument52 pagesDigestive Systemdead yrroehNo ratings yet
- Ear, Nose and ThroatDocument23 pagesEar, Nose and ThroatWizz Háķìm ĻêşòwNo ratings yet
- Digestive 2022Document88 pagesDigestive 2022Nhelia Santos BañagaNo ratings yet
- Anatomy and Physiology 2nd Semester BSN Notes, Educational PlatformDocument367 pagesAnatomy and Physiology 2nd Semester BSN Notes, Educational PlatformMuhammad KashifNo ratings yet
- Hap Final TermDocument3 pagesHap Final TermNitz MainitNo ratings yet
- UNIT 3.2 The Respiratory System and Digestive and Respiratory Related IllnessesDocument21 pagesUNIT 3.2 The Respiratory System and Digestive and Respiratory Related IllnessesCarlos FloresNo ratings yet
- Digestive Sys Lab WorksheetDocument12 pagesDigestive Sys Lab WorksheetedwardNo ratings yet
- Topic 6 ReviewDocument11 pagesTopic 6 ReviewWahyu PradivaNo ratings yet
- All Human Body 4Document2,401 pagesAll Human Body 4Top MusicNo ratings yet
- Anatomy of The Pharynx and Esophagus 2012Document44 pagesAnatomy of The Pharynx and Esophagus 2012Syahmi IeskandarNo ratings yet
- Var 29 - 30Document4 pagesVar 29 - 30Honey BabaNo ratings yet
- Broncho PneumoniaDocument23 pagesBroncho Pneumoniaanon-84769398% (43)
- 2- الجاهزة20.02.2022 lower Respiratory system physiologyDocument32 pages2- الجاهزة20.02.2022 lower Respiratory system physiologybessan alfqeatNo ratings yet
- 72 Hours Chick EmbryoDocument18 pages72 Hours Chick EmbryoZhairra Marie DionsonNo ratings yet
- Final Anatomy Exam Questions PRE MED: Yara AdeebDocument3 pagesFinal Anatomy Exam Questions PRE MED: Yara AdeebMadani TawfeeqNo ratings yet
- Abdomen Study Guide QuestionsDocument6 pagesAbdomen Study Guide QuestionsGuarina MolinaNo ratings yet
- Digestive System Anatomy 1 1Document17 pagesDigestive System Anatomy 1 1jsrz9vmj5jNo ratings yet
- Self Test 3Document6 pagesSelf Test 3202310446No ratings yet
- Ac 2Document104 pagesAc 2saide limNo ratings yet
- Digestive SystemDocument32 pagesDigestive SystemHashley CastellyNo ratings yet
- Respiratory System Anatomy and PhysiologyDocument19 pagesRespiratory System Anatomy and PhysiologyKBDNo ratings yet
- Anatomi Fisiologi Dada AbdomenDocument16 pagesAnatomi Fisiologi Dada AbdomenemiliatamaraNo ratings yet
- Anatomy 2nd-U-3 Respiratory SystemDocument113 pagesAnatomy 2nd-U-3 Respiratory Systemsinte beyuNo ratings yet
- Hard Word: - Keyword 1. A Man 70 Years OldDocument20 pagesHard Word: - Keyword 1. A Man 70 Years OldkasmaNo ratings yet
- USMLE Anatomy ReviewDocument19 pagesUSMLE Anatomy ReviewAmber Merritt50% (2)
- Body Cavities and MembranesDocument31 pagesBody Cavities and MembranesMary AkellaNo ratings yet
- Unit 3Document6 pagesUnit 3Sushil AcharyaNo ratings yet
- Respiratory System: by Mekdes.sDocument56 pagesRespiratory System: by Mekdes.sAbas AhmedNo ratings yet
- Modul 2 Tests ListDocument29 pagesModul 2 Tests ListНваневу СильванусNo ratings yet
- 13 - Respiratory SystemDocument68 pages13 - Respiratory SystemNur Shahirah Nasir Faculty of Social Science and FoundationNo ratings yet
- Respiration Grade 10 Biology - StudentDocument65 pagesRespiration Grade 10 Biology - StudentAsawni McDowellNo ratings yet
- Human Body Book | Introduction to the Respiratory System | Children's Anatomy & Physiology EditionFrom EverandHuman Body Book | Introduction to the Respiratory System | Children's Anatomy & Physiology EditionNo ratings yet
- Atlas of Regional ANATOMY of The Brain Using MRIDocument100 pagesAtlas of Regional ANATOMY of The Brain Using MRIhoangNo ratings yet
- Acupoint NotesDocument4 pagesAcupoint Notesunbelievable686100% (1)
- Pectoral Region and AxillaDocument25 pagesPectoral Region and AxillaSelva pandi100% (1)
- Written Report NeuroDocument7 pagesWritten Report NeuroHoney Bee S. PlatolonNo ratings yet
- Increased Intracranial Pressure and Other Neurological TraumaDocument14 pagesIncreased Intracranial Pressure and Other Neurological TraumaMhoy CostesNo ratings yet
- อจท.Upstream 4 Unit 1bDocument16 pagesอจท.Upstream 4 Unit 1bNt WnVNo ratings yet
- Stretching Exercises For MenDocument24 pagesStretching Exercises For Menfarooq hayat100% (1)
- Single Choice Questions in ORTHOPAEDICS Mahmood A Sulaiman: January 2019Document186 pagesSingle Choice Questions in ORTHOPAEDICS Mahmood A Sulaiman: January 2019Kiran Kumar100% (1)
- Chapter 12Document5 pagesChapter 12sprinkle50100% (1)
- The Loss of Deep Reflexes Puts Athletes at A Greater Risk of InjuryDocument13 pagesThe Loss of Deep Reflexes Puts Athletes at A Greater Risk of Injuryapi-621599790No ratings yet
- Body Beast Huge Workout SheetsDocument11 pagesBody Beast Huge Workout SheetsDenis OsmenajNo ratings yet
- Perfusion Technology SyllabusDocument56 pagesPerfusion Technology SyllabusVysakh PRNo ratings yet
- Book FEMALE REPRODUCTIVE SYSTEM OF CHICKENDocument6 pagesBook FEMALE REPRODUCTIVE SYSTEM OF CHICKENBriones Paula MaeNo ratings yet
- The Central Nervous SystemDocument606 pagesThe Central Nervous SystemViorel BudeNo ratings yet
- Anatomy Quiz 2Document45 pagesAnatomy Quiz 2Upscaled100% (1)
- PDF Soal Bahasa Inggris Kelas 3 SD Bab 1 Parts of The Body Dan Kunci Jawaban - CompressDocument6 pagesPDF Soal Bahasa Inggris Kelas 3 SD Bab 1 Parts of The Body Dan Kunci Jawaban - CompressPutu Dian PratamawatiNo ratings yet
- Cerebellum (Section 3, Chapter 5) Neuroscience Online - An Electronic Textbook For The Neurosciences - Department of Neurobiology and Anatomy - The University of Texas Medical School at HoustonDocument9 pagesCerebellum (Section 3, Chapter 5) Neuroscience Online - An Electronic Textbook For The Neurosciences - Department of Neurobiology and Anatomy - The University of Texas Medical School at HoustonNaveen KumarNo ratings yet
- Divine Intervention Episode 44 Usmle Anatomy Series Part 1Document11 pagesDivine Intervention Episode 44 Usmle Anatomy Series Part 1Swisskelly1No ratings yet
- Chapter 9 - Circulatory Responses To ExerciseDocument3 pagesChapter 9 - Circulatory Responses To Exercisearvinp89No ratings yet
- Aospine-Spine Trauma Classification System: The Value of Modifiers: A Narrative Review With Commentary On Evolving Descriptive PrinciplesDocument12 pagesAospine-Spine Trauma Classification System: The Value of Modifiers: A Narrative Review With Commentary On Evolving Descriptive PrinciplesDonate 049No ratings yet
- Cable Arm Exercise GuideDocument2 pagesCable Arm Exercise GuideTóth LászlóNo ratings yet
- Serial ExtractionDocument38 pagesSerial Extractionmanishpankaj123No ratings yet
- Unit 1Document10 pagesUnit 1aseel algamdiNo ratings yet
- Hap PDFDocument17 pagesHap PDFRishu Rishma100% (1)
- ID 7851 Стомат Англ Задачі 1540 English Sem 2Document237 pagesID 7851 Стомат Англ Задачі 1540 English Sem 2acerNo ratings yet
- Digestive SystemDocument5 pagesDigestive SystemFrances Anne OrbinoNo ratings yet
- ELS Q2 M6 Organ Systems of Representative Animals 1 RDocument22 pagesELS Q2 M6 Organ Systems of Representative Animals 1 RtjeremyalleneNo ratings yet
- Drugs Affecting The Endocrine SystemDocument43 pagesDrugs Affecting The Endocrine SystemJustine Vens G. AgustinNo ratings yet