Professional Documents
Culture Documents
PEDIGREE CHARTS
PEDIGREE CHARTS
Uploaded by
pavanwagh111213Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
PEDIGREE CHARTS
PEDIGREE CHARTS
Uploaded by
pavanwagh111213Copyright:
Available Formats
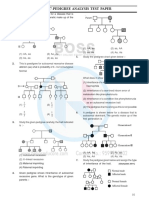
Q.
4 -‘I’
To study the prepared pedigree charts of genetic traits such as
rolling of tongue, widow’s peak, blood group and colour blindness.
FOR INABILITY TO ROLL THE TONGUE
1 2
II 1 2 3 4
III
1 2 3 4 5
Aa aa
Aa aa aa Aa AA Aa
Aa aa AA Aa AA
COMMENTS on the pedigree chart with respect to:
1. Inheritance of traits-
It is a dominant autosomal inheritance. Person having ability to roll the tongue is may be
homozygous (AA) or heterozygous (Aa) dominant. Non-roller is recessive (aa)
2. Number of normal, carriers and affected progeny-
Normal or Rollers (AA)-3, Carriers (Aa)- 6, Affected or non-rollers (aa)-4
3. Linkage- sex linked or autosomal
Autosomal (autosome linked inheritance),
SOLUTION
Comment on the given pedigree chart with respect to :
1. Inheritance of trait- Dominant autosomal trait. i.e. person showing widow’s peak is either
homozygous (WW) or heterozygous (Ww). While person with straight hairline is recessive (ww)
2. Number of traits- Normal i.e. Widow’s peak ( WW) = 1
Carrier (Ww)= 5
Straight hair line = 6
3. Linkage- Autosomal i.e. gene for widow’s peak is located on autosome.
HUMAN BLOOD GROUPS
I
AB 1 2 A O 3 4B
II
B 1 A 2 A 3 A 4 B 5 O 6 O 7
III
O 1 AB 2
SOLUTION: I
IAIB IAi ii IBi
II IBi IAIA IAi IAi IBi ii ii
III ii IAIB
COMMENTS on the pedigree chart and give the genotypes of the blood groups of individuals
marked in blank box numbers-
Generation Phenotype Genotype
& Box no
I-2 Blood group A IAi
I-4 Blood group B IBi
II-4 Blood group A IAi
II-5 Blood group B IBi
III-1 Blood group O ii
III-2 Blood group AB IAIB
This is an example of autosomal inheritance. It shows co-dominance as blood group AB is due to the genotype
IAIB. Both these alleles are equally dominant; therefore, both are expressed. Hence such person’s RBCs have
both the types of antigens viz. Antigen A and Antigen B.
COLORBLINDNESS
I
1 2
II
1 2 3 4 5 6
III
1 2 3 4 5
I X cY XCXC
II XCXc XCY XCXc XCY XCXc XCY
III XCXC XCXc XcY XCXC XCY
This is a pedigree chart of colorblindness.
COMMENTS on the pedigree chart with respect to:
1. Inheritance of trait-
It is an X-linked recessive trait. Even if there is only one Xc, the male ( XcY) is colorblind. But the
colorblind female has genotype XcXc.
Generally, the males are sufferers of the X-linked traits because of the presence of only one X-
chromosome and the Y-chromosome has no allele of the concerned gene.
Carrier man does not exist although carrier woman may exist.
2. Number of normal, carriers and affected progeny- Normal ♂-
4 ; Normal ♀-3
Carrier ♀ - 4
Colorblind ♂- 2 ; Colorblind ♀- nil
3. Linkage- sex linked or autosomal-
It shows sex-linked inheritance. It is due to the recessive X-linked gene (Xc).
Questions
1. What is pedigree?
Ans: Pedigree charts are diagrams that show the phenotypes and/or genotypes for a particular organism and
its ancestors. While commonly used in human families to track genetic diseases, they can be used for
any species and any inherited trait. These diagrams are used to determine the mode of inheritance of a
particular disease or trait, and to predict the probability of its appearance among offspring. It appears
like a family tree.
2. Why X-linked disorders are more common in male than in female?
Ans: In female two X chromosomes are present if out of two X chromosomes one is recessive, female is
just carrier for that trait. But in male has only one X-chromosome. If such a chromosome has the
recessive gene, the male definitely suffers from the disorder. Because on Y chromosome allele or
that trait is absent.
So in female if both the X-chromosomes have the defective (recessive) genes, then only she
suffers. Such a possibility is rare.
3. What are holandric traits?
Ans: The traits which are controlled by genes located on Y chromosome are called holandric traits. The
genes responsible for such characters are found only on the non-homologous portions of Y-
chromosome. therefore, it has no allele on X-chromosome.
e.g. Hypertrichosis or hairy pinna is found in male human beings only.
4. Give an example of autosomal recessive disorder in humans.
Ans: Sickle cell anemia, Phenyl Ketonuria, Cystic fibrosis, Thalassemia, etc.
5. Explain the concept of co-dominance with respect to ABO system in humans. Ans: The ABO
blood grouping system is controlled by 3 alleles viz. IA, IB andi.
Of these, the allele i is recessive to both IA and IB.
If both IA and IB are present in an individual, then both the Antigens i.e. Antigen A and Antigen B
are formed and present on the RBCs.
It means that IA and IB are co-dominant. The genotype
IAIB indicates Blood group AB.
You might also like
- 4b Oral Exam Practice - Mock Exam FOUR - ANSWER Guide PDFDocument8 pages4b Oral Exam Practice - Mock Exam FOUR - ANSWER Guide PDFJyothsna SridharNo ratings yet
- Pedigree Analysis WorksheetDocument6 pagesPedigree Analysis WorksheetLloaana 12No ratings yet
- O Level Biology Practice Questions And Answers: Heredity And Molecular GeneticsFrom EverandO Level Biology Practice Questions And Answers: Heredity And Molecular GeneticsNo ratings yet
- Happy Birthday in 100+ LanguagesDocument5 pagesHappy Birthday in 100+ LanguagesRustam Ali0% (1)
- Biology 10 Formative 04 18 Mayis-KeyDocument7 pagesBiology 10 Formative 04 18 Mayis-KeyANIT SARP CAYMAZNo ratings yet
- Experiment 9Document3 pagesExperiment 9F4DEDNo ratings yet
- Provisional Key Biol221 Exam 1 v3 2017Document13 pagesProvisional Key Biol221 Exam 1 v3 2017Gizem OsmanogluNo ratings yet
- Week 4 Non - Mendelian InheritanceDocument7 pagesWeek 4 Non - Mendelian InheritanceCarl Brian L. MonteverdeNo ratings yet
- LQB182 Pedigree 2008Document3 pagesLQB182 Pedigree 2008NathanNo ratings yet
- Cyto TalentoDocument6 pagesCyto TalentoJethro TalentoNo ratings yet
- Pedigree QuestionsDocument4 pagesPedigree QuestionsSaumya SelvarajiNo ratings yet
- Grade 10 - Unit 2 - Booklet - Genetics - 2 - SonDocument32 pagesGrade 10 - Unit 2 - Booklet - Genetics - 2 - SonBenanNo ratings yet
- Homework 2 AnswersDocument10 pagesHomework 2 AnswersButterlesstoastNo ratings yet
- Non-Mendelian Patterns of Heredity: Prepared by Imelda A. YganDocument38 pagesNon-Mendelian Patterns of Heredity: Prepared by Imelda A. YganJeestin Kent GabineraNo ratings yet
- Day-17-Pedigree Analysis Answer Key: Generation-IDocument2 pagesDay-17-Pedigree Analysis Answer Key: Generation-IalishNo ratings yet
- Genetic5 & 6Document39 pagesGenetic5 & 6Shaker MahmoodNo ratings yet
- PDF Document 2Document7 pagesPDF Document 2ANIT SARP CAYMAZNo ratings yet
- Dominant and Recessive AllelesDocument3 pagesDominant and Recessive AllelesDanny Siloka100% (1)
- Pedigree Analysis in Humans: Background InformationDocument6 pagesPedigree Analysis in Humans: Background InformationDaniel SutterNo ratings yet
- حل اسئلة هيكل الاحياء فصل اول 2022Document132 pagesحل اسئلة هيكل الاحياء فصل اول 2022ッفوكسي-FoxyNo ratings yet
- Pedigree AnalysisDocument30 pagesPedigree AnalysisJolly RiveraNo ratings yet
- Multiple Alleles CompleteDocument39 pagesMultiple Alleles Completegnana08No ratings yet
- Day-17 - Pedigree Analysis Test Paper - FinalDocument2 pagesDay-17 - Pedigree Analysis Test Paper - FinalalishNo ratings yet
- Midterm GeneticsDocument12 pagesMidterm GeneticsĐức Huy NguyễnNo ratings yet
- Solutions To Genetics Unit ExamDocument8 pagesSolutions To Genetics Unit ExamEUNAH LimNo ratings yet
- Nes With Multiple AllelesDocument3 pagesNes With Multiple AllelessanNo ratings yet
- Heredity and Variation Part IIDocument3 pagesHeredity and Variation Part IIPatient SaintNo ratings yet
- Genetics 3: Bedford School 1Document4 pagesGenetics 3: Bedford School 1George AshcroftNo ratings yet
- GeneticsDocument49 pagesGeneticsKenia AvilaNo ratings yet
- Science 9 Week 3 and 4Document7 pagesScience 9 Week 3 and 4Cherry Beth PagenteNo ratings yet
- Nicolas Osborn - Genetics WKSTDocument3 pagesNicolas Osborn - Genetics WKSTNicolas OsbornNo ratings yet
- Lesson 5 Extra Exam Questions For Practice 5Document15 pagesLesson 5 Extra Exam Questions For Practice 5serenappiperscorner.co.ukNo ratings yet
- I. Multiple Alleles: Extensions and Modifications of Basic PrinciplesDocument11 pagesI. Multiple Alleles: Extensions and Modifications of Basic PrinciplesArthe RajarajanNo ratings yet
- BABS2213 TutorialDocument12 pagesBABS2213 TutorialAnusia ThevendaranNo ratings yet
- FINAL Non-Mendelian GeneticsDocument52 pagesFINAL Non-Mendelian Geneticsdr.alkreissNo ratings yet
- 06 Notes Non-Mendelian Genetics StudentDocument20 pages06 Notes Non-Mendelian Genetics StudentDeliadina QuintoNo ratings yet
- 06 Notes Non-Mendelian Genetics StudentDocument20 pages06 Notes Non-Mendelian Genetics StudentVicky GuzmánNo ratings yet
- Non-Mendelian GeneticsDocument20 pagesNon-Mendelian GeneticsKarl Christian YuNo ratings yet
- 06 Notes Non-Mendelian Genetics StudentDocument20 pages06 Notes Non-Mendelian Genetics StudentJillian jan HamoyNo ratings yet
- Genetics 603: Bamhi G A C Bglii T ADocument8 pagesGenetics 603: Bamhi G A C Bglii T AZenPhiNo ratings yet
- Multiple AllelesDocument12 pagesMultiple AllelesAmy LalringhluaniNo ratings yet
- 1exercises InheritanceDocument8 pages1exercises InheritancebebaNo ratings yet
- Recall GeneticsDocument55 pagesRecall GeneticsJemson VictorioNo ratings yet
- Non-Mendelian Practice KeyDocument4 pagesNon-Mendelian Practice KeyJopit O. RiveraNo ratings yet
- 2.2 Non-Mendelian InheritanceDocument26 pages2.2 Non-Mendelian InheritanceJayas Maria De PeraltaNo ratings yet
- Non-Mendelian Patterns of Inheritance 1Document23 pagesNon-Mendelian Patterns of Inheritance 1Jolly RiveraNo ratings yet
- Non-Mendelian GeneticsDocument39 pagesNon-Mendelian GeneticsKing TagabuenNo ratings yet
- Incomplete and CodominanceDocument28 pagesIncomplete and CodominanceIrvin EcalnirNo ratings yet
- Multiple AllelesDocument5 pagesMultiple AllelesWinndell DupresNo ratings yet
- Non-Mendelian GeneticsDocument21 pagesNon-Mendelian Geneticshengst librandoNo ratings yet
- PedigreesDocument5 pagesPedigreestpn72hjg88No ratings yet
- NAME: Brian CapraroDocument5 pagesNAME: Brian CapraroBrian CapraroNo ratings yet
- 8 Inheritance & SelectionDocument177 pages8 Inheritance & SelectionKassyKasNo ratings yet
- Practical 7 Class 12 (23-24)Document5 pagesPractical 7 Class 12 (23-24)kumarimehak2006No ratings yet
- The Genetic Basis of White TigersDocument5 pagesThe Genetic Basis of White TigersDiana GonzalezNo ratings yet
- L08 - Fillable Inheritance IIDocument2 pagesL08 - Fillable Inheritance IIjesselyn.tubayasNo ratings yet
- Pedigree AnalysisDocument18 pagesPedigree AnalysisAndreea Maria ManoleNo ratings yet
- IB Biology: Topic 10 Genetics TestDocument8 pagesIB Biology: Topic 10 Genetics TestJune ChowNo ratings yet
- Non-Mendelian GeneticsDocument18 pagesNon-Mendelian GeneticskhadijaNo ratings yet
- Question 1043842Document19 pagesQuestion 1043842A.B.Karthick kumar PGT BOTANYNo ratings yet
- List of Dragons in Literature - WikipediaDocument10 pagesList of Dragons in Literature - Wikipediajorge solieseNo ratings yet
- Teaching Japanese Tea Ceremony To Chinese University Students: Developing English Learning MaterialsDocument17 pagesTeaching Japanese Tea Ceremony To Chinese University Students: Developing English Learning MaterialsGlobal Research and Development ServicesNo ratings yet
- Rank List Test 43 03-04-2022Document153 pagesRank List Test 43 03-04-2022VIVEKANANDAN JVNo ratings yet
- Example of Group Work RubricDocument2 pagesExample of Group Work RubricKryzzx LapuzNo ratings yet
- Research Proposal Toxic Leadership and Its ConsequencesDocument19 pagesResearch Proposal Toxic Leadership and Its Consequencesبشير حيدرNo ratings yet
- Proven Music Teaching MethodsDocument6 pagesProven Music Teaching MethodsDipo BankoleNo ratings yet
- DISTRIBUTION STATEMENT A: Approved For Public Release Distribution Is UnlimitedDocument189 pagesDISTRIBUTION STATEMENT A: Approved For Public Release Distribution Is UnlimitedStein Hjalmar Hansen100% (1)
- 0-1 Knapsack ProblemDocument57 pages0-1 Knapsack ProblemMITALBAHEN DHOLAKIYANo ratings yet
- PG 1 To 41 PagesDocument26 pagesPG 1 To 41 Pagessatish malikNo ratings yet
- GET Landing Page Templates With Copy Prompts That You Can Have in Just One Click!Document3 pagesGET Landing Page Templates With Copy Prompts That You Can Have in Just One Click!dadadadaadaNo ratings yet
- Biresin G33 EngDocument2 pagesBiresin G33 Engleonardo gregorioNo ratings yet
- Change LogDocument22 pagesChange LogRavinderRaviNo ratings yet
- Daily English Language Lesson Plan: MissashDocument5 pagesDaily English Language Lesson Plan: MissashAsyraf DeenNo ratings yet
- Lesson 11: Stakeholder Theory: A Comprehensive Approach To Corporate Social ResponsibilityDocument17 pagesLesson 11: Stakeholder Theory: A Comprehensive Approach To Corporate Social ResponsibilityMerlanie MaganaNo ratings yet
- Stanislavski ExercisesDocument8 pagesStanislavski ExercisesEshan PurohitNo ratings yet
- Modeling of Ablation Phenomena in Space Applications: Ph.D. ThesisDocument228 pagesModeling of Ablation Phenomena in Space Applications: Ph.D. ThesisIbraheem AlQadiNo ratings yet
- ReferencesDocument2 pagesReferencesFakhira ShehzadiNo ratings yet
- Passivation On Chemical TankerDocument15 pagesPassivation On Chemical TankerRonald MesinaNo ratings yet
- "Can I Touch It?" Playbill, Company One TheatreDocument15 pages"Can I Touch It?" Playbill, Company One TheatretylerprendergastNo ratings yet
- Department of Computer Science & Engineering Cs6502-Object Oriented Analysis and Design Unit Iii Case StudyDocument4 pagesDepartment of Computer Science & Engineering Cs6502-Object Oriented Analysis and Design Unit Iii Case StudyvijiNo ratings yet
- 2020 Passion Project Student PacketDocument12 pages2020 Passion Project Student PacketDavid ReyesNo ratings yet
- Group Assignment - Research MethodologyDocument6 pagesGroup Assignment - Research MethodologyAMAMNo ratings yet
- CASE DIGEST: Roque vs. IACDocument3 pagesCASE DIGEST: Roque vs. IACMichael Joseph NogoyNo ratings yet
- RPP Teaching of WritingDocument10 pagesRPP Teaching of WritingRizqa RahimiNo ratings yet
- Prist University: Question BankDocument4 pagesPrist University: Question BankGanesan NkNo ratings yet
- Adultery On The Part of The Wife - Desertion On The Part of The Husband - Loss of Affection - Cruelty - Insanity - ChildlessnessDocument2 pagesAdultery On The Part of The Wife - Desertion On The Part of The Husband - Loss of Affection - Cruelty - Insanity - ChildlessnesschiaocoNo ratings yet
- Nakshatras Pushya 150410Document3 pagesNakshatras Pushya 150410Anthony WriterNo ratings yet
- Summative Test 2nd QuarterDocument3 pagesSummative Test 2nd QuarterHenry Canon LumangtadNo ratings yet