Professional Documents
Culture Documents
EE3402-LIC MODEL EXAM QUESTION
EE3402-LIC MODEL EXAM QUESTION
Uploaded by
Surya Natarajan0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
2 views7 pageslic
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this Documentlic
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as docx, pdf, or txt
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
2 views7 pagesEE3402-LIC MODEL EXAM QUESTION
EE3402-LIC MODEL EXAM QUESTION
Uploaded by
Surya Natarajanlic
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as docx, pdf, or txt
You are on page 1of 7
OXFORD ENGINEERING COLLEGE b) Explain the working principle of emitter coupled differential
DEPARTMENT OF ELECTRICAL AND ELECTRONICS amplifier?
ENGINEERING 15. a) Write a CMOS fabrication with neat sketches.
MODEL EXAM or
EE3402-LINEAR INTEGRATED CIRCUITS b) Explain the various methods of fabricating diodes in monolithic
DATE: 25.6.24 YEAR&SEM: II/IV integrated circuits.
TIME: 1 pm to 4 pm Total marks: 100
PART A 10*2=20
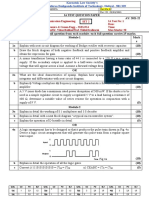
1. Define an integrated circuit.
2. What is meant by dielectric isolation in I.C. fabrication. Mention
its applications and limitations
3. List out the ideal characteristics of OP-OMP.
4. Define slew rate. What causes it?
5. List the various applications of a comparator.
6. What is zero crossing detector?
7. Draw the functional block diagram of a PLL.
8. Define lock in range.
9. Define line regulation.
10. What is an Opto-coupler IC?
PART B 5*16=80
11. a) Explain the function of SMPS with neat waveforms and
schema.
or
b) Discuss in detail about switching regulator.
12. a) Explain the working of an analog multiplier using emitter
coupler transistor pair
OR
b) Mention breify the application of PLL.
13. a) Explain the working of instrumentation amplifier.
or
b) Explain the operation of Schmitt trigger.
14. a) Explain in detail about various methods of frequency
compensation used in operational amplifiers.
or
OXFORD ENGINEERING COLLEGE or
DEPARTMENT OF ELECTRICAL AND ELECTRONICS b) what are the different types of testing of insulators? Explain any
ENGINEERING one method.
MODEL EXAM 14. a) with neat diagram, explain the various methods of grading of
EE3401-TRANSMISSION AND DISTRIBUTION underground cables.
DATE: 22.6.24 YEAR&SEM: II/IV or
TIME: 1 pm to 4 pm Total marks: 100 b) describe the general construction of an underground cable with
a neat sketch.
PART A 10*2=20
15. a) discuss the method of voltage control in transmission line.
1. what are the various types of HVDC transmission system? or
2. List out the main components of a HVDC system b) what are the different types of bus bar arrangements used in
3. Give an expression for the flux linkages due to a single current substations? Illustrate your answer with suitable diagrams.
carrying capacitor?
4. Write an expression for electrical potential at a charged single
conductor?
5. What is corona?
6. Define Ferranti effect?
7. Why cables are not used for long distance transmission?
8. State the advantages of polythene insulators.
9. Define resonant frequency
10. Name the various types of grounding.
PART B 5*16=80
11. a) derive the expression for capacitance of symmetrical and
unsymmetrical double circuit three phase line.
or
b) derive the expression for inductance of three phase line with
unsymmetrical spacing.
12. a) derive the expression power flow through transmission line and
explain various steps involved in sending end power circle
diagram with neat sketch
OR
b) using rigorous method, derive expression for sending end
voltage and current for a long transmission line.
13. a) derive the expression for the insulation resistance, capacitance
and electrostatic stress of single core cable.
OXFORD ENGINEERING COLLEGE 13. a) derive the expression for unknown inductance using Maxwell’s
DEPARTMENT OF ELECTRICAL AND ELECTRONICS bridge.
ENGINEERING or
MODEL EXAM b) State the conditions for a ac bridge to be balanced. Draw the
EE3403-MEASUREMENTS AND INSTRUMENTATION circuit diagram of a schering’s bridge and derive the expressions
DATE: 27.6.24 YEAR&SEM: II/IV for the unknown quantities.
TIME: 1 pm to 4 pm Total marks: 100 14. a) Explain why the ac tachometer deviates from linearity
characteristics at high speeds.
PART A 10*2=20
or
1. what is calibrations? b) With a circuit explain the working of a thermistor and explain
2. Define static error. why it is not suited at high temperatures.
3. Define gravity control 15. a) Explain four important features of virtual instrumentation and
4. What are the types of instruments? Its consist of two types draw the block diagram of a DSO and explain the working,
5. Mention some applications of AC potentiometers. compare between ASO and DSO performance.
6. What is kelvin’s bridge? or
7. Differentiate between LED and LCD. b) Design a R-2R converter circuit by assuming suitable
8. Define data logger? specifications.
9. What is piezoelectric effect?
10. Mention the applications of LVDT.
PART B 5*16=80
11. a) Explain in detail about instrumental errors, their classification
and remedial step taken in the case of occurrence of such errors.
or
b) Draw the block diagram of a measurement system and explain
about each functional element in it.
12. a) With neat diagrams, explain the working of dynamometer
wattmeter and write the expression for average deflecting torque
while measuring AC power.
OR
b) Explain the construction and principle of working of induction
type wattmeter.
13. a) With neat diagram, explain the architecture and interfacing of
8255 PPI.
or
OXFORD ENGINEERING COLLEGE b) Draw the internal block diagram of 8279 keyboard display
DEPARTMENT OF ELECTRICAL AND ELECTRONICS controller and explain its features.
ENGINEERING 14. a) Explain the various operating modes of 8051 timer and special
MODEL EXAM function registers associated with timer/counter.
EE3404-MICROPROCESSOR AND MICROCONTROLLER or
DATE: 29.6.24 YEAR&SEM: II/IV b) Explain the structure of port 0 and port 3 of 8051
TIME: 1 pm to 4 pm Total marks: 100 microcontroller.
15. a) Draw the architecture and list the major functional elements of
PART A 10*2=20
PIC microcontroller.
1. What is stack and what is the use of stack pointer? or
2. What is interrupt? b) Mention the instructions of PIC microcontroller and their
3. Explain the difference between a JMP instruction and CALL functions.
instruction.
4. What are the different types of addressing modes?
5. Distinguish between synchronous and asynchronous transmission.
6. What are the functions of USART?
7. Define IDE.
8. Mention the role of stack pointer in using stack.
9. Compare CISC with RISC.
10. List any four special features of PIC controller.
PART B 5*16=80
11. a) Explain the software and hardware interrupts available in 8085
along with their vector addresses.
or
b) Draw and explain the timing diagram of I memory red machine
cycle and ii memory write cycle of 8085
12. a) List and define the addressing modes supported by 8085
microprocessor with examples.
or
b) State the data manipulation instructions in 8051 microprocessor
and mention their functions.
or
b) explain the torque slip characteristic of 3 phase induction motor.
14. a) with neat diagram explain the slip power recovery scheme.
OXFORD ENGINEERING COLLEGE or
DEPARTMENT OF ELECTRICAL AND ELECTRONICS b) explain the cascaded operation of three phase induction motor.
ENGINEERING 15. a) explain the operation os single phase induction motor using
MODEL EXAM double field revolving theory.
EE3405-ELECTRICAL MACHINES-II or
DATE: 2.7.24 YEAR&SEM: II/IV b) explain the constructional features and principle of operation of
TIME: 1 pm to 4 pm Total marks: 100 AC series motor.
PART A 10*2=20
1. Write down the equation for frequency of emf induced in an
alternator.
2. Define the term voltage regulation of alternator.
3. What is meant by torque angle.
4. What are the main parts of synchronous motor?
5. Why the rotor slots are slightle skewed in squirrel cage IM?
6. Define slip of induction motor?
7. What are the various methods of speed control of 3 phase
induction motor?
8. Define dynamic braking.
9. Why single phase induction motor is not a self starting?
10. State the applications of shaded pole single phase induction motor.
PART B 5*16=80
11. a) describe with neat sketches the constructional details of a salient
pole type alternator.
or
b) derive the emf equation of an alternator.
12. a) explain what is meant by V cruves. Draw the V curves of a
sysnchronous motor.
or
b) draw the equivalent circuit and phasor diagram of a
synchronous motor.
13. a) explain the equivalent circuit of double cage induction motor.
12. a) With neat diagrams explain the construction and working
OXFORD ENGINEERING COLLEGE principle of DC generator.
DEPARTMENT OF ELECTRICAL AND ELECTRONICS or
ENGINEERING b) Describe about the construction of core type and shell type
MODEL EXAM single phase transformers.
BE3251-BASIC ELECTRICAL AND ELECTRONICS 13. a) Explain the operation of BJT in common emitter mode with its
ENGINEERING characteristics.
DATE: 27.6.24 YEAR&SEM: I/II or
TIME: 1 pm to 4 pm Total marks: 100 b) Explain the constructional details and different modes of
operation of MOSFET.
PART A 10*2=20
14. a) Explain about the error detection and correction codes.
1. Write down the expression for active power and apparent power or
2. Parallel combination of three 3 ohm resistors, connected in series
with parallel combination of two 2 ohm resistors. Find the b) Simplifiy the Boolean function,
equivalent resistance of the circuit. f(W,X,Y,Z)=WX’Y’+WY+W’YZ’ using k-map.
3. Differentiate step up transformer and step down transformer. 15. a) Describe the construction, working principle of PMMC
4. List out the application of transformers. instruments. Also derive the torque equations.
5. Draw the circuit for Zener voltage regulator. or
6. Differentiate the operation of rectifiers and inverters. b) Explain the measurement of power in three phase circuits using
7. Convert the giver expression in canonical SOP form
two-wattmeter method.
Y=AC+AB+BC.
8. What is meant by combinational logic circuits? Give examples. PART-C 1*15=15
9. Mention the functional element of a measuring system.
16. a) Draw the functional block diagram of data acquisition system
10. Name the constructional parts of induction type energy meter.
and explain the role of each component.
PART B 5*13=65 or
11. a) Discuss about the working of RLC series circuit and derive the b) Describe the working of bridge rectifier. Derive its ripple factor.
relationships. Give the necessary phasor diagrams.
or
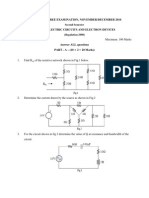
b) Using mesh analysis, determine the current and potential
difference across each resistor in the given circuit. The battery has
90V in first loop and the current source 5A in second loop and the
resistor are (R1=9ohm, R2=6ohm, R3=8ohm) R1 & R3 connected
in series and R2 common in loop 1 and loop 2.
OXFORD ENGINEERING COLLEGE 12. a) With neat diagrams explain the construction and working
DEPARTMENT OF ELECTRICAL AND ELECTRONICS principle of DC generator.
ENGINEERING or
MODEL EXAM b) Describe about the construction of core type and shell type
BE3251-BASIC ELECTRICAL ELECTRONICS AND single phase transformers.
INSTRUMENTATION ENGINEERING 13. a) Explain the operation of BJT in common emitter mode with its
(CIVIL) characteristics.
DATE: 27.6.24 YEAR&SEM: I/II or
TIME: 1 pm to 4 pm Total marks: 100 b) Explain the constructional details and different modes of
operation of MOSFET.
PART A 10*2=20
14. a) Explain the working principle of magnetic circuit?
1. Write down the expression for active power and apparent power or
2. Parallel combination of three 3 ohm resistors, connected in series
with parallel combination of two 2 ohm resistors. Find the b) Write a short notes on
equivalent resistance of the circuit. i) MMF ii) Flux density iii) Wire and cables
3. Differentiate step up transformer and step down transformer. 15. a) Discuss the classification of transducers based on different
4. List out the application of transformers. characteristics.
5. Draw the circuit for Zener voltage regulator. or
6. Differentiate the operation of rectifiers and inverters. b) Explain the electro pneumatic system? And the principle and
7. Convert the giver expression in canonical SOP form
operation to explain in it?
Y=AC+AB+BC.
8. What is meant by combinational logic circuits? Give examples. PART-C 1*15=15
9. Mention the functional element of a measuring system.
16. a) Explain the construction operation and working on LVDT
10. Name the constructional parts of induction type energy meter.
or
PART B 5*13=65 b) Explain the working principle of domestic wiring?
11. a) Discuss about the working of RLC series circuit and derive the
relationships. Give the necessary phasor diagrams.
or
b) Using mesh analysis, determine the current and potential
difference across each resistor in the given circuit. The battery has
90V in first loop and the current source 5A in second loop and the
resistor are (R1=9ohm, R2=6ohm, R3=8ohm) R1 & R3 connected
in series and R2 common in loop 1 and loop 2.
You might also like
- Profit at RiskDocument2 pagesProfit at Risktimothy454No ratings yet
- Question PapersDocument6 pagesQuestion Papersgunasekar3538No ratings yet
- EE8701 High Voltage EngineeringDocument3 pagesEE8701 High Voltage EngineeringRishi KaranNo ratings yet
- Hve - Dec 12 - 8Document2 pagesHve - Dec 12 - 8C454 Rathika. PNo ratings yet
- R17 EMI Model QP Set 2Document2 pagesR17 EMI Model QP Set 2kisnamohanNo ratings yet
- 15A04602 Electronic Measurements & InstrumentationDocument1 page15A04602 Electronic Measurements & Instrumentation17BF1A04L7 kalyanNo ratings yet
- Regulation - 2010: K.S.Rangasamy College of Technology, Tiruchengode - 637 215Document3 pagesRegulation - 2010: K.S.Rangasamy College of Technology, Tiruchengode - 637 215Latta SakthyyNo ratings yet
- 17 Ec 322Document2 pages17 Ec 322KomalNo ratings yet
- B.E. / B.Tech. Degree Examination, November/ December 2007Document2 pagesB.E. / B.Tech. Degree Examination, November/ December 2007tamilmaranNo ratings yet
- Pdf&rendition 1Document43 pagesPdf&rendition 1kajal aggarwalNo ratings yet
- Ec8252ed Set2 PDFDocument2 pagesEc8252ed Set2 PDFRajkumar PerumalNo ratings yet
- EE301 Power Generation, Transmission and Protection, December 2017 PDFDocument2 pagesEE301 Power Generation, Transmission and Protection, December 2017 PDFAfsal Abdul KarimNo ratings yet
- Model QuestionDocument2 pagesModel QuestionkrishnandrkNo ratings yet
- IES 1988 Question PaperpdfDocument8 pagesIES 1988 Question Paperpdfh9emanth4No ratings yet
- Basic Eln-2021-IA-1-Set 2 - ModifiedDocument2 pagesBasic Eln-2021-IA-1-Set 2 - ModifiedProf. Nikhil KulkarniNo ratings yet
- Advanced Power Electronics: M.Tech. (Integrated Power System) First SemesterDocument1 pageAdvanced Power Electronics: M.Tech. (Integrated Power System) First SemesterMahesh ShendeNo ratings yet
- Beem Uni Que PDFDocument14 pagesBeem Uni Que PDFPragna SidhireddyNo ratings yet
- RF&MW Apr-May 17Document2 pagesRF&MW Apr-May 17JayapalNo ratings yet
- 9A04301 Electronic Devices & CircuitsDocument1 page9A04301 Electronic Devices & CircuitssivabharathamurthyNo ratings yet
- Ese 88Document8 pagesEse 88Prasanna KumarNo ratings yet
- X10401 (Ee8552)Document3 pagesX10401 (Ee8552)Sujesh ChittarikkalNo ratings yet
- Microwave EnggDocument2 pagesMicrowave Enggdeepuj20No ratings yet
- Elective II - EHVAC & HVDC Transmission System PDFDocument2 pagesElective II - EHVAC & HVDC Transmission System PDFanon_328698868No ratings yet
- 2022 Summer Question Paper (Msbte Study Resources)Document4 pages2022 Summer Question Paper (Msbte Study Resources)first kingNo ratings yet
- 3 Hours / 100 Marks: Seat NoDocument4 pages3 Hours / 100 Marks: Seat Nosahil satputeNo ratings yet
- Question Paper Code:: Reg. No.Document3 pagesQuestion Paper Code:: Reg. No.Samraj JebasinghNo ratings yet
- Candidates Are Required To Give Their Answers in Their Own Words As Far As Practicable. The Figures in The Margin Indicate Full MarksDocument2 pagesCandidates Are Required To Give Their Answers in Their Own Words As Far As Practicable. The Figures in The Margin Indicate Full MarkssushilNo ratings yet
- Question Paper Code:: Reg. No.Document2 pagesQuestion Paper Code:: Reg. No.senthil periakaruppanNo ratings yet
- Electronic Devices Circuits2Document1 pageElectronic Devices Circuits2Shaik BawajanNo ratings yet
- R7410402 Electronic Measurements & InstrumentationDocument4 pagesR7410402 Electronic Measurements & InstrumentationsivabharathamurthyNo ratings yet
- Ee 3 Sem Electronic Devices and Circuits 2016Document3 pagesEe 3 Sem Electronic Devices and Circuits 2016Priyanshu AgaseNo ratings yet
- High Voltage Engineering Kamaraju and NaiduDocument2 pagesHigh Voltage Engineering Kamaraju and NaiduAnbalagan GuruNo ratings yet
- EC8351 EC I ModelDocument2 pagesEC8351 EC I ModelDeepak RameshNo ratings yet
- Anna University Microwave Question PapersDocument9 pagesAnna University Microwave Question PapersDeepak100% (2)
- EDC Model PapersDocument12 pagesEDC Model PapersanithaNo ratings yet
- ELECTRONICS-ENGINEERING-NEC201 (1)Document2 pagesELECTRONICS-ENGINEERING-NEC201 (1)nikhildev516No ratings yet
- WWW - Manaresults.co - In: Part-B (50 Marks)Document2 pagesWWW - Manaresults.co - In: Part-B (50 Marks)Manish KushwahaNo ratings yet
- 19A02303T DC Machines & TransformersDocument1 page19A02303T DC Machines & Transformerschaithanya kumarNo ratings yet
- Fundamental of HVDC FACTS DevicesDocument4 pagesFundamental of HVDC FACTS DevicesgauthamNo ratings yet
- BT I/d 20Document4 pagesBT I/d 20Aditya BhukkarNo ratings yet
- USN 18EEEE62: High Voltage EngineeringDocument2 pagesUSN 18EEEE62: High Voltage Engineering1DA18EE013Gagana B.RNo ratings yet
- EDC Question-Papers Complete SetDocument13 pagesEDC Question-Papers Complete Setselvi04120% (1)
- PTEE7304 April-2014Document2 pagesPTEE7304 April-2014imman46920No ratings yet
- Set No: 1 R10Document4 pagesSet No: 1 R10Viswa ChaitanyaNo ratings yet
- Total Pages: 2: Answer All Questions, Each Carries5 MarksDocument2 pagesTotal Pages: 2: Answer All Questions, Each Carries5 MarksHaripriya k aNo ratings yet
- BMS College of Engineering, Bangalore-560019: December 2015 Semester End Main ExaminationsDocument3 pagesBMS College of Engineering, Bangalore-560019: December 2015 Semester End Main ExaminationsrameshNo ratings yet
- Code: 20A02101TDocument2 pagesCode: 20A02101Tkurubamailagani ravaliNo ratings yet
- BEEE Important Questions 16 MarksDocument6 pagesBEEE Important Questions 16 MarkskrishnandrkNo ratings yet
- QP Ec8701Document6 pagesQP Ec8701sruthiga kNo ratings yet
- Seventh Semester B.Tech Degree Examination 13.701 Nanoelectronics (At)Document3 pagesSeventh Semester B.Tech Degree Examination 13.701 Nanoelectronics (At)AjuuNo ratings yet
- Kings: Question BankDocument6 pagesKings: Question BankRameez FaroukNo ratings yet
- Estelar: Faculty of EngineeringDocument2 pagesEstelar: Faculty of Engineeringsrinureddy2014No ratings yet
- Basic Electronics EngineeringDocument2 pagesBasic Electronics EngineeringsushilNo ratings yet
- 123 Au 032017Document2 pages123 Au 032017pittalasureshNo ratings yet
- Stucor QP Ec8701Document6 pagesStucor QP Ec8701diamond puppyNo ratings yet
- BEE-UG11T2104-1104-DEC 2015Document2 pagesBEE-UG11T2104-1104-DEC 2015Anshuman SharmaNo ratings yet
- 13A99101 Basic Electrical & Electronics EngineeringDocument2 pages13A99101 Basic Electrical & Electronics Engineeringjagadeesh0% (1)
- Organic Light-Emitting Transistors: Towards the Next Generation Display TechnologyFrom EverandOrganic Light-Emitting Transistors: Towards the Next Generation Display TechnologyNo ratings yet
- Impedance Spectroscopy: Theory, Experiment, and ApplicationsFrom EverandImpedance Spectroscopy: Theory, Experiment, and ApplicationsEvgenij BarsoukovNo ratings yet
- Electrochemical Processes in Biological SystemsFrom EverandElectrochemical Processes in Biological SystemsAndrzej LewenstamNo ratings yet
- Physics and Technology of Crystalline Oxide Semiconductor CAAC-IGZO: Application to DisplaysFrom EverandPhysics and Technology of Crystalline Oxide Semiconductor CAAC-IGZO: Application to DisplaysNo ratings yet
- Model Based Control Design: Alf IsakssonDocument17 pagesModel Based Control Design: Alf IsakssonSertug BaşarNo ratings yet
- Mode Choice Modelling For Work Trips in Calicut City: Tushara T, Rajalakshmi P, Bino I KoshyDocument8 pagesMode Choice Modelling For Work Trips in Calicut City: Tushara T, Rajalakshmi P, Bino I KoshyjoemarNo ratings yet
- Explicit Dynamics Chapter 6 Explicit MeshingDocument50 pagesExplicit Dynamics Chapter 6 Explicit Meshingivillen001No ratings yet
- Mass Lynx SoftwareDocument94 pagesMass Lynx SoftwareKansy HaikalNo ratings yet
- FM and TMDocument445 pagesFM and TMKrishna Singh100% (1)
- PDF Automatic Transmissions and Transaxles 7Th Edition James D Halderman Ebook Full ChapterDocument53 pagesPDF Automatic Transmissions and Transaxles 7Th Edition James D Halderman Ebook Full Chapterevon.gaskins482100% (3)
- Hot Rolling Mill IndustryDocument12 pagesHot Rolling Mill IndustryJanuar Kurniawan KurniawanNo ratings yet
- ProjectDocument76 pagesProjectMohammed GaberNo ratings yet
- MDRDocument3 pagesMDRjeffreymacasero100% (1)
- Jagdtiger: Panzerjäger Tiger Ausf. BDocument11 pagesJagdtiger: Panzerjäger Tiger Ausf. Bjason maiNo ratings yet
- Scottie Emmert Honors Self-Designed Proposal Biomedical RampDocument6 pagesScottie Emmert Honors Self-Designed Proposal Biomedical Rampapi-299660206No ratings yet
- IAAC Final Round 2020Document9 pagesIAAC Final Round 2020Dennil JobyNo ratings yet
- Traumatic Diaphragmatic Hernia: Case Series and Topic ReviewDocument12 pagesTraumatic Diaphragmatic Hernia: Case Series and Topic ReviewMohammad SyahrezkiNo ratings yet
- Warning: No Smoking! No Open Flame! While Installing Your Jet KitDocument2 pagesWarning: No Smoking! No Open Flame! While Installing Your Jet KitBrad MonkNo ratings yet
- Homeopathy in Reflexive PerspectiveDocument398 pagesHomeopathy in Reflexive Perspectivealex100% (1)
- Title: PDX RX Block - Pi Pico Based DIGITAL MODES HF TransceiverDocument1 pageTitle: PDX RX Block - Pi Pico Based DIGITAL MODES HF TransceiverDhiru Kholia100% (2)
- Intravenous Fluid Therapy in Adults and ChildrenDocument16 pagesIntravenous Fluid Therapy in Adults and Childrenannisa hayati100% (1)
- Ba SyllabusDocument5 pagesBa SyllabusKamlesh Kumar MandalNo ratings yet
- Application of UV Spectrophotometric Method For Estimation of Iron in Tablet Dosage FormDocument2 pagesApplication of UV Spectrophotometric Method For Estimation of Iron in Tablet Dosage Formahmed ismailNo ratings yet
- KSP Solutibilty Practice ProblemsDocument22 pagesKSP Solutibilty Practice ProblemsRohan BhatiaNo ratings yet
- Welder and Procedure QualificationDocument25 pagesWelder and Procedure QualificationRamón G. Pacheco100% (3)
- TAC640 Service ManualDocument15 pagesTAC640 Service ManualCARMAIN100% (1)
- Proyek PT Asiana Technologies PDFDocument49 pagesProyek PT Asiana Technologies PDFAlexandro AndooNo ratings yet
- Canon BJC-3000 Printer: Error CodesDocument1 pageCanon BJC-3000 Printer: Error Codeseu mibNo ratings yet
- GMW8 2019 03 (Hot Dip Zinc Coating Sheet Steel)Document8 pagesGMW8 2019 03 (Hot Dip Zinc Coating Sheet Steel)dpfloresNo ratings yet
- Eye Bolt StandardsDocument5 pagesEye Bolt Standardsnilesh tadhaNo ratings yet
- Remarks On T1 (2015)Document8 pagesRemarks On T1 (2015)Wong JiayangNo ratings yet
- The Wedding Dance 2Document16 pagesThe Wedding Dance 2JojhelNo ratings yet
- ALTITUDE Presentation DeckDocument35 pagesALTITUDE Presentation DeckVikas ChaudharyNo ratings yet