Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Ccm in Punjab Case
Ccm in Punjab Case
Uploaded by
kjaspreet1510Copyright:
Available Formats
You might also like
- The Essentials of Material Science and Technology for EngineersFrom EverandThe Essentials of Material Science and Technology for EngineersRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- LESSON PLAN Math 7Document4 pagesLESSON PLAN Math 7izai vitorNo ratings yet
- Experiment No. 5 Centrifugal Casting ProcessDocument6 pagesExperiment No. 5 Centrifugal Casting ProcessDhananjay ShimpiNo ratings yet
- Research Paper Optimization To Improve The Quality of Centrifugal Casting by Grey Fuzzy MethodDocument3 pagesResearch Paper Optimization To Improve The Quality of Centrifugal Casting by Grey Fuzzy Methodavnishchauhan8_46499No ratings yet
- Centrifugal CastingDocument21 pagesCentrifugal Castingadwankarparag50% (2)
- Centrifugal Casting: Sufei Wei, The Centrifugal Casting Machine Company, and Steve Lampman, ASM InternationalDocument7 pagesCentrifugal Casting: Sufei Wei, The Centrifugal Casting Machine Company, and Steve Lampman, ASM InternationalmuseNo ratings yet
- Impulse Forming by Vaporizing Foil ActuatorDocument35 pagesImpulse Forming by Vaporizing Foil ActuatorAnjithNo ratings yet
- Journal of Harmonized Research in EngineeringDocument4 pagesJournal of Harmonized Research in EngineeringBravianNo ratings yet
- Semi-Centrifugal Casting: An Extensive Analysis: Technical ReportDocument10 pagesSemi-Centrifugal Casting: An Extensive Analysis: Technical ReportS. R. OvhalNo ratings yet
- Horizontal Centrigugal CastingDocument17 pagesHorizontal Centrigugal CastingpurusharthNo ratings yet
- Centrifugal CastingDocument18 pagesCentrifugal CastingArijit PatraNo ratings yet
- Al-Si Centrifugalni Lijev LMMDocument8 pagesAl-Si Centrifugalni Lijev LMMMarija MusaNo ratings yet
- Amp ReportDocument21 pagesAmp ReportAadip KushwahaNo ratings yet
- MODULE 1 - Other Casting ProcessesDocument78 pagesMODULE 1 - Other Casting ProcessesrishavrajbabaNo ratings yet
- Products Used in Steel Manufacturing (ZAM)Document31 pagesProducts Used in Steel Manufacturing (ZAM)osama raufNo ratings yet
- Casting DefectsDocument7 pagesCasting DefectsCarlos SolerNo ratings yet
- Irjet V6i2220Document4 pagesIrjet V6i2220sonuNo ratings yet
- Project PPT Spot WeldingDocument19 pagesProject PPT Spot WeldingMehul BariyaNo ratings yet
- 1506329872Document4 pages1506329872Jeevan Landge PatilNo ratings yet
- 2nd ProjectDocument72 pages2nd ProjectrohanNo ratings yet
- Flow Forming of Tubes A Review PDFDocument11 pagesFlow Forming of Tubes A Review PDFRanga SriNo ratings yet
- What Exactly Is Rolling?Document39 pagesWhat Exactly Is Rolling?Ashish12312No ratings yet
- 03 - Rolling of MetalsDocument61 pages03 - Rolling of MetalsAbhishek SinhaNo ratings yet
- A Case Study of The Effectiveness of Rolling Process To Manufacture The Strip of Leaf Spring P. S. ChauhanDocument5 pagesA Case Study of The Effectiveness of Rolling Process To Manufacture The Strip of Leaf Spring P. S. ChauhanSamir BoseNo ratings yet
- Project Presentation 3.0Document35 pagesProject Presentation 3.0CH.SUMANTHNo ratings yet
- MP-I-Lecture No. 12-13-14Document50 pagesMP-I-Lecture No. 12-13-14Osaid AhmadNo ratings yet
- #Conclave of Rolling Processes#: Malaviya National Institute of Technology JaipurDocument57 pages#Conclave of Rolling Processes#: Malaviya National Institute of Technology JaipurAnup MauryaNo ratings yet
- 1 s2.0 S0924013605006011 Main - FlowformingDocument10 pages1 s2.0 S0924013605006011 Main - FlowformingAnil JainNo ratings yet
- 12 GinzelDocument15 pages12 GinzelTHIRU.SNo ratings yet
- Forming Processes MaterialDocument34 pagesForming Processes MaterialBALA GANESHNo ratings yet
- Alimentacion de Hierro y AceroDocument22 pagesAlimentacion de Hierro y Acerojose.figueroa@foseco.comNo ratings yet
- 8 12 01 2023Document22 pages8 12 01 2023keshavkoolwalNo ratings yet
- To Study About The Behaviour of Mechanical Properties of The Material in Cryo-Rolling Process: A Review ApproachDocument6 pagesTo Study About The Behaviour of Mechanical Properties of The Material in Cryo-Rolling Process: A Review ApproachEditor IJIRMFNo ratings yet
- Tutorial Last AnswerDocument9 pagesTutorial Last AnswerEswaran ManakorNo ratings yet
- Chapter 13 Teams 2 and Team 3Document6 pagesChapter 13 Teams 2 and Team 3miguel martínezNo ratings yet
- Assignment Advance Manufacturing Processes: by Vaibhav M. Enroll No. 171E021 May 8, 2020Document11 pagesAssignment Advance Manufacturing Processes: by Vaibhav M. Enroll No. 171E021 May 8, 2020Vaibhav MishraNo ratings yet
- of Centrifugal Casting ProcessDocument14 pagesof Centrifugal Casting Processakshay sawansukha100% (1)
- 2.14. Multiple-Use-Mould Casting ProcessesDocument3 pages2.14. Multiple-Use-Mould Casting Processesaman chaudharyNo ratings yet
- WRM Proceses - Copy (Autosaved)Document41 pagesWRM Proceses - Copy (Autosaved)Vikrant HanwatNo ratings yet
- ME Test 2 ConvDocument7 pagesME Test 2 ConvrajivkumarbalagaNo ratings yet
- (23005319 - Acta Mechanica Et Automatica) Crossing Axes of Workpiece and Tool at Grinding of The Circular Trough With Variable ProfileDocument5 pages(23005319 - Acta Mechanica Et Automatica) Crossing Axes of Workpiece and Tool at Grinding of The Circular Trough With Variable ProfilesumanthNo ratings yet
- X Ray Tubes New Advances: Surg LT CDR TC BhattDocument21 pagesX Ray Tubes New Advances: Surg LT CDR TC BhattSachin BalutkarNo ratings yet
- Workshop ManualDocument26 pagesWorkshop ManualHarender KumarNo ratings yet
- Materials 15 02249Document17 pagesMaterials 15 02249Nut AssanaiNo ratings yet
- Metal Forming ProcessesDocument40 pagesMetal Forming ProcessesRyat AtmadjaNo ratings yet
- Experiment 1Document16 pagesExperiment 1samayNo ratings yet
- Cylinder Liners & Piston RingsDocument16 pagesCylinder Liners & Piston RingsMr.Babu TNo ratings yet
- Microstructure Simulation of Copper Tube and Its Application in Three Roll Planetary RollingDocument9 pagesMicrostructure Simulation of Copper Tube and Its Application in Three Roll Planetary RollingandrreaskinzNo ratings yet
- Lecture 2 Continuous CastingDocument41 pagesLecture 2 Continuous Castingnoahshredx13No ratings yet
- Sheet MetalDocument5 pagesSheet MetalDilhan RajasekaraNo ratings yet
- MP-I-Lecture No. 15-16Document27 pagesMP-I-Lecture No. 15-16Osaid AhmadNo ratings yet
- Pipelines Welding HandbookDocument64 pagesPipelines Welding HandbookSixto GerardoNo ratings yet
- Design of Castelleated Beam by British CodeDocument8 pagesDesign of Castelleated Beam by British Codemsn sastryNo ratings yet
- Powder Metallurgy ProjectDocument54 pagesPowder Metallurgy ProjectDhruv Raj33% (3)
- 6127-The Kavery Engineering College Mechanical Engineering B5-Final Year ProjectDocument16 pages6127-The Kavery Engineering College Mechanical Engineering B5-Final Year ProjectSathya prakashNo ratings yet
- CRITICAL REVIEW ON DESIGN OF ROLLING PROCESS Kondapalli Siva Prasad1Document16 pagesCRITICAL REVIEW ON DESIGN OF ROLLING PROCESS Kondapalli Siva Prasad1Samir BoseNo ratings yet
- Drilling Parameter Analysis in Solving Pipe Sticking in a Total Loss CirculationDocument21 pagesDrilling Parameter Analysis in Solving Pipe Sticking in a Total Loss CirculationSntno papotNo ratings yet
- Design and Development of A Centrifugal Casting Machine For Pistons ProductionDocument21 pagesDesign and Development of A Centrifugal Casting Machine For Pistons ProductionThankgodIsraelNo ratings yet
- A Practical Workshop Companion for Tin, Sheet Iron, and Copper Plate Workers: Containing Rules for Describing Various Kinds of Patterns used by Tin, Sheet Iron, and Copper Plate Workers, Practical Geometry, Mensuration of Surfaces and Solids, Tables of the Weights of Metals, Lead Pipe, Tables of Areas and CircumferencesFrom EverandA Practical Workshop Companion for Tin, Sheet Iron, and Copper Plate Workers: Containing Rules for Describing Various Kinds of Patterns used by Tin, Sheet Iron, and Copper Plate Workers, Practical Geometry, Mensuration of Surfaces and Solids, Tables of the Weights of Metals, Lead Pipe, Tables of Areas and CircumferencesNo ratings yet
- Rock Blasting: A Practical Treatise on the Means Employed in Blasting Rocks for Industrial PurposesFrom EverandRock Blasting: A Practical Treatise on the Means Employed in Blasting Rocks for Industrial PurposesNo ratings yet
- File System - Node - Js v12.10.0 DocumentationDocument82 pagesFile System - Node - Js v12.10.0 DocumentationMarcos GarciaNo ratings yet
- Right To Information Vs Right To Privacy: BY-Kanhaiya SinghalDocument5 pagesRight To Information Vs Right To Privacy: BY-Kanhaiya SinghalKanhaiya SinghalNo ratings yet
- Flow Chart Example For ThesisDocument4 pagesFlow Chart Example For Thesisjuliasolembellevue100% (2)
- Protocol Germ CellDocument82 pagesProtocol Germ CellTanh NguyenNo ratings yet
- Icse Timetable For 2008Document6 pagesIcse Timetable For 2008ReshmabsrNo ratings yet
- C16 - Lec 07 - Chemical ReactionsDocument62 pagesC16 - Lec 07 - Chemical ReactionsJohn Lloyd GildoNo ratings yet
- Model by Brandon Build by LuisDocument16 pagesModel by Brandon Build by LuisixosotocNo ratings yet
- WA-LD-45 PPP For New Direction PAC (March 2017)Document2 pagesWA-LD-45 PPP For New Direction PAC (March 2017)Daily Kos ElectionsNo ratings yet
- Safety Plan 2023Document4 pagesSafety Plan 2023Raphy BrionesNo ratings yet
- 2 Span PSC Composite Girder Bridge PDFDocument51 pages2 Span PSC Composite Girder Bridge PDFAnkitKeshriNo ratings yet
- Darkeden Legend - The Rare Skills ListDocument6 pagesDarkeden Legend - The Rare Skills ListGM Badr100% (4)
- Keldysh PDFDocument8 pagesKeldysh PDFElektronika PMFNo ratings yet
- K80000 Technical Datasheet PDFDocument1 pageK80000 Technical Datasheet PDFKhalid ZghearNo ratings yet
- RDBMS SeminarDocument70 pagesRDBMS SeminarSohoo Abdul QayoomNo ratings yet
- Eco MCQ 1 Multiple Choice Questions MCQ For Economics 1 BallbbballbDocument10 pagesEco MCQ 1 Multiple Choice Questions MCQ For Economics 1 BallbbballbsanchiNo ratings yet
- Gaming Industry E Mail Id OnlyDocument4 pagesGaming Industry E Mail Id OnlySundararajan SrinivasanNo ratings yet
- Collaborative Journalling As A Professional Development ToolDocument13 pagesCollaborative Journalling As A Professional Development ToolBurcu SenerNo ratings yet
- T REC G.984.4 200911 I!Amd2!PDF EDocument164 pagesT REC G.984.4 200911 I!Amd2!PDF ERoberto CardosoNo ratings yet
- Manufacturing Process For A PenDocument7 pagesManufacturing Process For A PenFeIipe MunozNo ratings yet
- Label Non 3T v1Document9 pagesLabel Non 3T v1Febry Hisbullah NurmanNo ratings yet
- Elements of Aeroelastic Design: Xie ChangchuanDocument21 pagesElements of Aeroelastic Design: Xie ChangchuanAbaziz Mousa OutlawZzNo ratings yet
- 1 L.M. College of Pharmacy Gujarat (Government of Gujarat) Assistant Professor Recruitment Examination Question Paper 2016Document9 pages1 L.M. College of Pharmacy Gujarat (Government of Gujarat) Assistant Professor Recruitment Examination Question Paper 2016pratyush swarnkarNo ratings yet
- Ch. 9 - Basic Router TroubleshootingDocument15 pagesCh. 9 - Basic Router TroubleshootingArad RezaNo ratings yet
- Service Experience (OCSE) Using The Emerging Consensus Technique (ECT)Document41 pagesService Experience (OCSE) Using The Emerging Consensus Technique (ECT)Naveen KNo ratings yet
- Ufc 3 301 01 2013Document168 pagesUfc 3 301 01 2013praveen0907No ratings yet
- China in A Changing Global Environment enDocument97 pagesChina in A Changing Global Environment enEskindirGirmaNo ratings yet
- Ge1000 Guitar Complex Effect ManualDocument3 pagesGe1000 Guitar Complex Effect Manualpaolo.sinistroNo ratings yet
Ccm in Punjab Case
Ccm in Punjab Case
Uploaded by
kjaspreet1510Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Ccm in Punjab Case
Ccm in Punjab Case
Uploaded by
kjaspreet1510Copyright:
Available Formats
Research Paper Engineering Volume : 4 | Issue : 6 | June 2014 | ISSN - 2249-555X
Study of Centrifugal Casting of Cast Iron Rolls and
its Problem Formulation at India Factory, Malerkotla,
Punjab (India)
Keywords Centrifugal casting, Spectroscopy, India factory, Cast Iron Rolls
Charanjeet Singh Yunis Ahmad Dar
HJ-472, Housing Board Colony, B. R. S. Nagar, House #128, Lane # 3, Shivpora -A, Srinagar, 190004,
Ludhiana, 141012, Punjab. J&K.
Dikshant Malhotra Depanshu Sharma
169-C, Rishi Nagar, chotti haibowal, Ludhiana,
Kachi chawni, Jammu, 180001, J&K.
141001,Punjab.
ABSTRACT India Factory was established in 1970 and was the first company to introduce Chilled Rolls manufactured by
centrifugal casting in India for Roller Flour Mills. Now the plant is manufacturing Chill Rolls for Roller Flour
Mills, Solvent Extraction Plants, Vegetable Oil Mills, Feed Mills, Crushing, Grinding, Milling, Roller Mills, etc.
A brief study is conducted about the present methodology, techniques and practices being adopted at the site and the
problem formulation is suggested as per the rejection rates of products. The plant procedures and processes are carefully
examined to check for any deviations from the standard principles and modifications/alterations for the present adopted
methods are accordingly suggested to minimize rejections as far as possible.
Most of the rolled castings are produced by centrifugal casting; however some sand moulds with cores are also used for
large and solid/hollow cylindrical profile castings. The chemical composition of the material is constantly examined via
atomic spectroscopic techniques to assure the quality of the products as per the requirements and a simple 2D layout of
the plant is shown to predict an efficient and effective process flow paths and material handling.
Introduction of Centrifugal Casting tion of Alfred Krupp, who used it to manufacture cast steel
Centrifugal casting or rotocasting is a casting technique that tyres for railway wheels in 1852.
is typically used to cast thin-walled cylinders. It is noted for
the high quality of the results attainable, particularly for pre- Centrifugal force acting on a rotating body is, C.F = mv2 /r
cise control of their metallurgy and crystal structure. Unlike
most other casting techniques, centrifugal casting is chiefly Where m is mass, v is peripheral speed, r is radius.
used to manufacture stock materials in standard sizes for fur-
ther machining, rather than shaped parts tailored to a par- Gravitational force, G.F = mg
ticular end-use.
Where g is acceleration due to gravity.
G factor = CF/GF =mv2/r.mg =v2/r.g
Solving further, we get, N = 4
Thornton suggested 50 – 100 G speed range for die cast
(metal mould) and 25 – 50 G for sand cast pots and shaped
castings. Too high speed results in excessive stresses and hot
tears in outside surfaces.
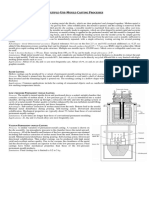
Characteristics and Features of centrifugal casting
• Castings can be made in almost any length, thickness
Process and diameter.
In centrifugal casting, a permanent mold is rotated continu- • Different wall thicknesses can be produced from the
ously about its axis at high speeds (300 to 3000 rpm) as the same size mold.
molten metal is poured. The molten metal is centrifugally • Eliminates the need for cores and castings are relatively
thrown towards the inside mold wall, where it solidifies after free from defects.
cooling. The casting is usually a fine-grained casting with a • Resistant to atmospheric corrosion, a typical situation
very fine-grained outer diameter, owing to chilling against with pipes.
the mould surface. Impurities and inclusions are thrown to • Only cylindrical shapes can be produced with this pro-
the surface of the inside diameter, which can be machined cess.
away. Casting machines may be either horizontal or vertical- • Size limits are up to 3 m (10 feet) diameter and 15 m (50
axis. Horizontal axis machines are preferred for long, thin cyl- feet) length.
inders, vertical machines for rings. • Wall thickness range from 2.5 mm to 125 mm (0.1 - 5.0
in).
Most castings are solidified from the outside first. This may • Non metallic impurities which segregate toward the bore
be used to encourage directional solidification of the casting, can be machined off.
and thus give useful metallurgical properties to it. Often the • Less loss of metal in tundish compared to that in gating
inner and outer layers are discarded and only the intermedi- and risering in conventional sand casting.
ary columnar zone is used. Centrifugal casting was the inven- • Production rate is high.
188 X INDIAN JOURNAL OF APPLIED RESEARCH
Research Paper Volume : 4 | Issue : 6 | June 2014 | ISSN - 2249-555X
• Can be employed to manufacture bimetallic pipes. argon gas is ionized in the intense electromagnetic field and
• Centrifugal casting process can be used for fabricating flows in a particular rotationally symmetrical pattern towards
functionally gradient metal matrix composite material. the magnetic field of the RF coil. Stable, high temperature
plasma of about 7000 K is then generated as the result of
Benefits the inelastic collisions created between the neutral argon
Cylinders and shapes with rotational symmetry are most atoms and the charged particles. A peristaltic pump deliv-
commonly cast by this technique. “Tall” castings (in the di- ers an aqueous or organic sample into an analytical nebulizer
rection of the settling force acting, usually gravity) are always where it is changed into mist and introduced directly inside
more difficult than short castings. In the centrifugal casting the plasma flame. The sample immediately collides with the
technique the radius of the rotation, along which the centrifu- electrons and charged ions in the plasma and is itself bro-
gal force acts, replaces the vertical axis. The casting machine ken down into charged ions. The various molecules break
may be rotated to place this in any convenient orientation, up into their respective atoms which then lose electrons and
relative to gravity’s vertical. Thin-walled cylinders are difficult recombine repeatedly in the plasma, giving off radiation
to cast by other means, but centrifugal casting is particularly at the characteristic wavelengths of the elements involved.
suited to them. To the rotation radius, these are effectively One or two transfer lenses are then used to focus the emit-
shallow flat castings and are thus simple. Centrifugal casting ted light on a diffraction grating where it is separated into
is also applied to the casting of disk and cylindrical shaped its component wavelengths in the optical spectrometer. In
objects such as railway carriage wheels or machine fittings other designs, the plasma impinges directly upon an optical
where the grain, flow, and balance are important to the du- interface which consists of an orifice from which a constant
rability and utility of the finished product. Providing that the flow of argon emerges, deflecting the plasma and provid-
shape is relatively constant in radius, noncircular shapes may ing cooling while allowing the emitted light from the plasma
also be cast. to enter the optical chamber. Still other designs use optical
fibers to convey some of the light to separate optical cham-
Materials and Applications bers. Within the optical chamber(s), after the light is sepa-
Typical materials that can be cast with this process are iron, rated into its different wavelengths (colors), the light intensity
steel, stainless steels, glass, and alloys of aluminum, copper is measured with a photomultiplier tube or tubes physically
and nickel. Two materials can be cast together by introducing positioned to “view” the specific wavelength(s) for each ele-
a second material during the process. ment line involved, or, in more modern units, the separated
colors fall upon an array of semiconductor photo detectors
Typical parts made by this process are pipes, boilers, pres- such as charge coupled devices (CCDs). In units using these
sure vessels, flywheels, cylinder liners and other parts that detector arrays, the intensities of all wavelengths (within the
are axi-symmetric. It is notably used to cast cylinder liners system’s range) can be measured simultaneously, allowing
and sleeve valves for piston engines, parts which could not the instrument to analyze for every element to which the unit
be reliably manufactured otherwise. is sensitive all at once. Thus, samples can be analyzed very
quickly. The intensity of each line is then compared to previ-
Theory of Atomic Emission Spectroscopy ously measured intensities of known concentrations of the
Atomic emission spectroscopy (AES) is a method of chemical elements, and their concentrations are then computed by
analysis that uses the intensity of light emitted from a flame, interpolation along the calibration lines. In addition, special
plasma, arc, or spark at a particular wavelength to determine software generally corrects for interferences caused by the
the quantity of an element in a sample. The wavelength of presence of different elements within a given sample matrix.
the atomic spectral line gives the identity of the element
while the intensity of the emitted light is proportional to the Procedure of Centrifugal Casting of Cast Iron Rolls at India
number of atoms of the element. In spark and arc atomic Factory
emission spectroscopy Spark or arc atomic emission spec- • First of all scrap is melted in induction furnaces. The fur-
troscopy is used for the analysis of metallic elements in solid naces were two in number and of 800 kg capacity each.
samples. Both qualitative and quantitative spark analysis are This molten metal can be taken to the moulds with the
widely used for production quality control in foundries and help of laddles which are carried away by a heavy duty
steel mill EOT crane as shown below
Technique Used
Inductively coupled plasma atomic emission spectroscopy
(ICP-AES), also referred to as inductively coupled plasma
optical emission spectrometry (ICP-OES), is an analytical
technique used for the detection of trace metals. It is a type
of emission spectroscopy that uses the inductively coupled
plasma to produce excited atoms and ions that emit electro-
magnetic radiation at wavelengths characteristic of a particu-
lar element. The intensity of this emission is indicative of the
concentration of the element within the sample.
Mechanism • Time to time samples are taken from furnace and
The ICP-AES is composed of two parts: the ICP and the op- checked in atomic emission spectrometer used with ar-
tical spectrometer. The ICP torch consists of 3 concentric gon gas at about 5 bar pressure to produce the required
quartz glass tubes. The output or “work” coil of the radio spark to determine the contents in the sample as well as
frequency (RF) generator surrounds part of this quartz torch. their concentration.
Argon gas is typically used to create the plasma. When the • The roller dies of various diameters are available. Thus
torch is turned on, an intense electromagnetic field is created castings of various diameters can be obtained as per the
within the coil by the high power radio frequency signal flow- desired size.
ing in the coil. This RF signal is created by the RF generator • First of all roller die is placed over the set of rolls. The
which is, effectively, a high power radio transmitter driving rolls are driven by a set of belts being driven by a diesel
the “work coil” the same way a typical radio transmitter drives engine. The variation in speeds is obtained by the provi-
a transmitting antenna. The argon gas flowing through the sion of gears. A centrifugal mould on belt driven rollers
torch is ignited with a Tesla unit that creates a brief discharge is shown below
arc through the argon flow to initiate the ionization process.
Once the plasma is “ignited”, the Tesla unit is turned off. The
INDIAN JOURNAL OF APPLIED RESEARCH X 189
Research Paper Volume : 4 | Issue : 6 | June 2014 | ISSN - 2249-555X
Results And Problem Formulation
The rejection rate of rolls at India factory was near about 4
to 5 percent. The main causes of rejection were presence of
cracks, scales over the surface of rolls. Other causes of rejec-
tion were hot tears, segregation and banding.
Hot tears: Hot tears are developed in centrifugal castings
for which the highest rotation speeds are used. Longitudinal
tears occur when contraction of casting combined with the
expansion of the mould, generates hoop stresses exceed-
ing the cohesive strength of the metal at temperatures in the
• Roller dies are placed over the set of rolls. If the molten solidus region.
material is directly poured into the metallic mould, it
would likely to weld itself with the mould and would be- Segregation: Centrifugal castings are under various forms of
come impossible to remove the solidified ingot. In or- segregation thus pushing less dense constituents at centre.
der to prevent it, the metallic die is coated with ceramic
material that can use colloidal silica as a bonding agent. Various types of Non destructive techniques such as dye pen-
The water must vaporize rapidly, leaving behind a coher- etrant testing are used to detect cracks.
ent refractory layer which can withstand erosive effects of
molten material and act as release agent for the finished Conclusion
ingot. The defects such as hot tears and segregation were devel-
• The rollers which are produced are made up of dual cast oped because no required data was available with the in-
iron. Dual cast iron consists of two layers, the outer layer dustry about revolution per minute required for casting of
is harder one and inner layer is comparatively softer. particular diameter of rolls in the roller die. Without any prior
• The outer layer of casting is made hard and tough by knowledge about RPM required for particular diameter rolls,
adding chromium and manganese with brinell hardness only past experience was used for casting rolls.
number BHN 550.
• For inner layer which is softer, silicon, which acts as a Presence of cracks and scales were observed due to manual
softening agent is added and brinell hardness number errors. Pouring time of molten material may be inadequate
obtained of softer inner layer is BHN 300. due to which scales and cracks were formed since there were
• After mixing the required agents in melted material. no provisions for constant pouring of material and manual
Firstly outer layer which is harder one is poured from one approaches were used for pouring.
side of roller die with the help of hopper like structure as
shown below The contents for the dual cast iron rolls during casting may
not be of required amount.
Future Expansions
Certain suggestions regarding these defects were given to
the industry. It was suggested that the rejections will be mini-
mized to the least value by using appropriate rpm of cen-
trifugal moulds. Some mathematical model may be used to
get the optimal rpm of the moulds in order to have defect
free castings. Arrangement for pouring should be precised to
facilitate uniform and constant mass flow rate which will aid
in the prevention of inclusions and scales. Further, advanced
• After pouring the harder layer in the roller die from one refractory ceramic material layers that can withstand high
side, its allowed to rotate for some time and then next temperatures without melting and decomposing and with
layer of molten material containing silicon is poured from high thermal insulation should be applied to metallic moulds
other side of roller die. instead of simple clay products which ultimately cause unde-
• It takes about 20 to 25 minutes to cast one roll. sirable properties in castings.
• After the roll is prepared, its allowed to cool down to
harden and then the casting is sent to turning shop with Acknowledgement
the help of EOT crane for the required turning operation. We acknowledge our sincere thanks to Mr. Puneet Dhingra,
• The roller dies are cooled to 90 degree centigrade be- CEO, INDIA FACTORY for explaining us the overall proce-
fore the next run of casting another roll. dure of centrifugal casting of iron rolls and other machinery
• Engines instead of electric motors are preferred for driv- available. We are also thankful to our research guide Dr.
ing the set of rolls for centrifugal casting to get the re- Jatinder Kapoor (A.P.,GNDEC, Punjab) for guiding us to ac-
quired high power and speeds. complish our study successfully.
Simple Plant Layout of India Factory
REFERENCE Hajra Choudhary S.K. and A.K., Workshop Technology, Vol. I, II, Media Promoters and Publishers Pvt. Ltd., Mumbai. | Moeed K.M.,
Manufacturing Processes, Umesh Publication Delhi. | Centrifugal Casting by Nathan Janco, Amer Foundrymens Society (June 1, 1988). | The
complete Handbook of centrifugal casting by Philip Romanoff, Tab Books (November 1980). | http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Atomic_emission_spectroscopy. | http://
en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Inductively_coupled_plasma_atomic_emission_spectroscopy. |
190 X INDIAN JOURNAL OF APPLIED RESEARCH
You might also like
- The Essentials of Material Science and Technology for EngineersFrom EverandThe Essentials of Material Science and Technology for EngineersRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- LESSON PLAN Math 7Document4 pagesLESSON PLAN Math 7izai vitorNo ratings yet
- Experiment No. 5 Centrifugal Casting ProcessDocument6 pagesExperiment No. 5 Centrifugal Casting ProcessDhananjay ShimpiNo ratings yet
- Research Paper Optimization To Improve The Quality of Centrifugal Casting by Grey Fuzzy MethodDocument3 pagesResearch Paper Optimization To Improve The Quality of Centrifugal Casting by Grey Fuzzy Methodavnishchauhan8_46499No ratings yet
- Centrifugal CastingDocument21 pagesCentrifugal Castingadwankarparag50% (2)
- Centrifugal Casting: Sufei Wei, The Centrifugal Casting Machine Company, and Steve Lampman, ASM InternationalDocument7 pagesCentrifugal Casting: Sufei Wei, The Centrifugal Casting Machine Company, and Steve Lampman, ASM InternationalmuseNo ratings yet
- Impulse Forming by Vaporizing Foil ActuatorDocument35 pagesImpulse Forming by Vaporizing Foil ActuatorAnjithNo ratings yet
- Journal of Harmonized Research in EngineeringDocument4 pagesJournal of Harmonized Research in EngineeringBravianNo ratings yet
- Semi-Centrifugal Casting: An Extensive Analysis: Technical ReportDocument10 pagesSemi-Centrifugal Casting: An Extensive Analysis: Technical ReportS. R. OvhalNo ratings yet
- Horizontal Centrigugal CastingDocument17 pagesHorizontal Centrigugal CastingpurusharthNo ratings yet
- Centrifugal CastingDocument18 pagesCentrifugal CastingArijit PatraNo ratings yet
- Al-Si Centrifugalni Lijev LMMDocument8 pagesAl-Si Centrifugalni Lijev LMMMarija MusaNo ratings yet
- Amp ReportDocument21 pagesAmp ReportAadip KushwahaNo ratings yet
- MODULE 1 - Other Casting ProcessesDocument78 pagesMODULE 1 - Other Casting ProcessesrishavrajbabaNo ratings yet
- Products Used in Steel Manufacturing (ZAM)Document31 pagesProducts Used in Steel Manufacturing (ZAM)osama raufNo ratings yet
- Casting DefectsDocument7 pagesCasting DefectsCarlos SolerNo ratings yet
- Irjet V6i2220Document4 pagesIrjet V6i2220sonuNo ratings yet
- Project PPT Spot WeldingDocument19 pagesProject PPT Spot WeldingMehul BariyaNo ratings yet
- 1506329872Document4 pages1506329872Jeevan Landge PatilNo ratings yet
- 2nd ProjectDocument72 pages2nd ProjectrohanNo ratings yet
- Flow Forming of Tubes A Review PDFDocument11 pagesFlow Forming of Tubes A Review PDFRanga SriNo ratings yet
- What Exactly Is Rolling?Document39 pagesWhat Exactly Is Rolling?Ashish12312No ratings yet
- 03 - Rolling of MetalsDocument61 pages03 - Rolling of MetalsAbhishek SinhaNo ratings yet
- A Case Study of The Effectiveness of Rolling Process To Manufacture The Strip of Leaf Spring P. S. ChauhanDocument5 pagesA Case Study of The Effectiveness of Rolling Process To Manufacture The Strip of Leaf Spring P. S. ChauhanSamir BoseNo ratings yet
- Project Presentation 3.0Document35 pagesProject Presentation 3.0CH.SUMANTHNo ratings yet
- MP-I-Lecture No. 12-13-14Document50 pagesMP-I-Lecture No. 12-13-14Osaid AhmadNo ratings yet
- #Conclave of Rolling Processes#: Malaviya National Institute of Technology JaipurDocument57 pages#Conclave of Rolling Processes#: Malaviya National Institute of Technology JaipurAnup MauryaNo ratings yet
- 1 s2.0 S0924013605006011 Main - FlowformingDocument10 pages1 s2.0 S0924013605006011 Main - FlowformingAnil JainNo ratings yet
- 12 GinzelDocument15 pages12 GinzelTHIRU.SNo ratings yet
- Forming Processes MaterialDocument34 pagesForming Processes MaterialBALA GANESHNo ratings yet
- Alimentacion de Hierro y AceroDocument22 pagesAlimentacion de Hierro y Acerojose.figueroa@foseco.comNo ratings yet
- 8 12 01 2023Document22 pages8 12 01 2023keshavkoolwalNo ratings yet
- To Study About The Behaviour of Mechanical Properties of The Material in Cryo-Rolling Process: A Review ApproachDocument6 pagesTo Study About The Behaviour of Mechanical Properties of The Material in Cryo-Rolling Process: A Review ApproachEditor IJIRMFNo ratings yet
- Tutorial Last AnswerDocument9 pagesTutorial Last AnswerEswaran ManakorNo ratings yet
- Chapter 13 Teams 2 and Team 3Document6 pagesChapter 13 Teams 2 and Team 3miguel martínezNo ratings yet
- Assignment Advance Manufacturing Processes: by Vaibhav M. Enroll No. 171E021 May 8, 2020Document11 pagesAssignment Advance Manufacturing Processes: by Vaibhav M. Enroll No. 171E021 May 8, 2020Vaibhav MishraNo ratings yet
- of Centrifugal Casting ProcessDocument14 pagesof Centrifugal Casting Processakshay sawansukha100% (1)
- 2.14. Multiple-Use-Mould Casting ProcessesDocument3 pages2.14. Multiple-Use-Mould Casting Processesaman chaudharyNo ratings yet
- WRM Proceses - Copy (Autosaved)Document41 pagesWRM Proceses - Copy (Autosaved)Vikrant HanwatNo ratings yet
- ME Test 2 ConvDocument7 pagesME Test 2 ConvrajivkumarbalagaNo ratings yet
- (23005319 - Acta Mechanica Et Automatica) Crossing Axes of Workpiece and Tool at Grinding of The Circular Trough With Variable ProfileDocument5 pages(23005319 - Acta Mechanica Et Automatica) Crossing Axes of Workpiece and Tool at Grinding of The Circular Trough With Variable ProfilesumanthNo ratings yet
- X Ray Tubes New Advances: Surg LT CDR TC BhattDocument21 pagesX Ray Tubes New Advances: Surg LT CDR TC BhattSachin BalutkarNo ratings yet
- Workshop ManualDocument26 pagesWorkshop ManualHarender KumarNo ratings yet
- Materials 15 02249Document17 pagesMaterials 15 02249Nut AssanaiNo ratings yet
- Metal Forming ProcessesDocument40 pagesMetal Forming ProcessesRyat AtmadjaNo ratings yet
- Experiment 1Document16 pagesExperiment 1samayNo ratings yet
- Cylinder Liners & Piston RingsDocument16 pagesCylinder Liners & Piston RingsMr.Babu TNo ratings yet
- Microstructure Simulation of Copper Tube and Its Application in Three Roll Planetary RollingDocument9 pagesMicrostructure Simulation of Copper Tube and Its Application in Three Roll Planetary RollingandrreaskinzNo ratings yet
- Lecture 2 Continuous CastingDocument41 pagesLecture 2 Continuous Castingnoahshredx13No ratings yet
- Sheet MetalDocument5 pagesSheet MetalDilhan RajasekaraNo ratings yet
- MP-I-Lecture No. 15-16Document27 pagesMP-I-Lecture No. 15-16Osaid AhmadNo ratings yet
- Pipelines Welding HandbookDocument64 pagesPipelines Welding HandbookSixto GerardoNo ratings yet
- Design of Castelleated Beam by British CodeDocument8 pagesDesign of Castelleated Beam by British Codemsn sastryNo ratings yet
- Powder Metallurgy ProjectDocument54 pagesPowder Metallurgy ProjectDhruv Raj33% (3)
- 6127-The Kavery Engineering College Mechanical Engineering B5-Final Year ProjectDocument16 pages6127-The Kavery Engineering College Mechanical Engineering B5-Final Year ProjectSathya prakashNo ratings yet
- CRITICAL REVIEW ON DESIGN OF ROLLING PROCESS Kondapalli Siva Prasad1Document16 pagesCRITICAL REVIEW ON DESIGN OF ROLLING PROCESS Kondapalli Siva Prasad1Samir BoseNo ratings yet
- Drilling Parameter Analysis in Solving Pipe Sticking in a Total Loss CirculationDocument21 pagesDrilling Parameter Analysis in Solving Pipe Sticking in a Total Loss CirculationSntno papotNo ratings yet
- Design and Development of A Centrifugal Casting Machine For Pistons ProductionDocument21 pagesDesign and Development of A Centrifugal Casting Machine For Pistons ProductionThankgodIsraelNo ratings yet
- A Practical Workshop Companion for Tin, Sheet Iron, and Copper Plate Workers: Containing Rules for Describing Various Kinds of Patterns used by Tin, Sheet Iron, and Copper Plate Workers, Practical Geometry, Mensuration of Surfaces and Solids, Tables of the Weights of Metals, Lead Pipe, Tables of Areas and CircumferencesFrom EverandA Practical Workshop Companion for Tin, Sheet Iron, and Copper Plate Workers: Containing Rules for Describing Various Kinds of Patterns used by Tin, Sheet Iron, and Copper Plate Workers, Practical Geometry, Mensuration of Surfaces and Solids, Tables of the Weights of Metals, Lead Pipe, Tables of Areas and CircumferencesNo ratings yet
- Rock Blasting: A Practical Treatise on the Means Employed in Blasting Rocks for Industrial PurposesFrom EverandRock Blasting: A Practical Treatise on the Means Employed in Blasting Rocks for Industrial PurposesNo ratings yet
- File System - Node - Js v12.10.0 DocumentationDocument82 pagesFile System - Node - Js v12.10.0 DocumentationMarcos GarciaNo ratings yet
- Right To Information Vs Right To Privacy: BY-Kanhaiya SinghalDocument5 pagesRight To Information Vs Right To Privacy: BY-Kanhaiya SinghalKanhaiya SinghalNo ratings yet
- Flow Chart Example For ThesisDocument4 pagesFlow Chart Example For Thesisjuliasolembellevue100% (2)
- Protocol Germ CellDocument82 pagesProtocol Germ CellTanh NguyenNo ratings yet
- Icse Timetable For 2008Document6 pagesIcse Timetable For 2008ReshmabsrNo ratings yet
- C16 - Lec 07 - Chemical ReactionsDocument62 pagesC16 - Lec 07 - Chemical ReactionsJohn Lloyd GildoNo ratings yet
- Model by Brandon Build by LuisDocument16 pagesModel by Brandon Build by LuisixosotocNo ratings yet
- WA-LD-45 PPP For New Direction PAC (March 2017)Document2 pagesWA-LD-45 PPP For New Direction PAC (March 2017)Daily Kos ElectionsNo ratings yet
- Safety Plan 2023Document4 pagesSafety Plan 2023Raphy BrionesNo ratings yet
- 2 Span PSC Composite Girder Bridge PDFDocument51 pages2 Span PSC Composite Girder Bridge PDFAnkitKeshriNo ratings yet
- Darkeden Legend - The Rare Skills ListDocument6 pagesDarkeden Legend - The Rare Skills ListGM Badr100% (4)
- Keldysh PDFDocument8 pagesKeldysh PDFElektronika PMFNo ratings yet
- K80000 Technical Datasheet PDFDocument1 pageK80000 Technical Datasheet PDFKhalid ZghearNo ratings yet
- RDBMS SeminarDocument70 pagesRDBMS SeminarSohoo Abdul QayoomNo ratings yet
- Eco MCQ 1 Multiple Choice Questions MCQ For Economics 1 BallbbballbDocument10 pagesEco MCQ 1 Multiple Choice Questions MCQ For Economics 1 BallbbballbsanchiNo ratings yet
- Gaming Industry E Mail Id OnlyDocument4 pagesGaming Industry E Mail Id OnlySundararajan SrinivasanNo ratings yet
- Collaborative Journalling As A Professional Development ToolDocument13 pagesCollaborative Journalling As A Professional Development ToolBurcu SenerNo ratings yet
- T REC G.984.4 200911 I!Amd2!PDF EDocument164 pagesT REC G.984.4 200911 I!Amd2!PDF ERoberto CardosoNo ratings yet
- Manufacturing Process For A PenDocument7 pagesManufacturing Process For A PenFeIipe MunozNo ratings yet
- Label Non 3T v1Document9 pagesLabel Non 3T v1Febry Hisbullah NurmanNo ratings yet
- Elements of Aeroelastic Design: Xie ChangchuanDocument21 pagesElements of Aeroelastic Design: Xie ChangchuanAbaziz Mousa OutlawZzNo ratings yet
- 1 L.M. College of Pharmacy Gujarat (Government of Gujarat) Assistant Professor Recruitment Examination Question Paper 2016Document9 pages1 L.M. College of Pharmacy Gujarat (Government of Gujarat) Assistant Professor Recruitment Examination Question Paper 2016pratyush swarnkarNo ratings yet
- Ch. 9 - Basic Router TroubleshootingDocument15 pagesCh. 9 - Basic Router TroubleshootingArad RezaNo ratings yet
- Service Experience (OCSE) Using The Emerging Consensus Technique (ECT)Document41 pagesService Experience (OCSE) Using The Emerging Consensus Technique (ECT)Naveen KNo ratings yet
- Ufc 3 301 01 2013Document168 pagesUfc 3 301 01 2013praveen0907No ratings yet
- China in A Changing Global Environment enDocument97 pagesChina in A Changing Global Environment enEskindirGirmaNo ratings yet
- Ge1000 Guitar Complex Effect ManualDocument3 pagesGe1000 Guitar Complex Effect Manualpaolo.sinistroNo ratings yet