Professional Documents
Culture Documents
06-Fulid Mechanics-SC
06-Fulid Mechanics-SC
Uploaded by
banerjeesamriddha889Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
06-Fulid Mechanics-SC
06-Fulid Mechanics-SC
Uploaded by
banerjeesamriddha889Copyright:
Available Formats
FLUID MECHANICS (NSEP Questions Bank)
SECTION-I
• This section contains TWENTY (20) questions.
• Each question has Four options (A), (B), (C) and (D). ONLY ONE of these four options is correct.
• For each question, choose the option corresponding to the correct answer.
• Answer to each question will be evaluated according to the following marking scheme:
Full Marks : +3 If ONLY the correct option is chosen.
Zero Marks : 0 If none of the options is chosen (i.e. the question is unanswered)
Negative Marks : –1 In all other cases.
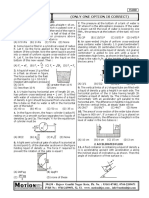
1. Two vessels A and B of different shapes have the same base area and are filled with water up to
the same height h (see figure). The force exerted by water on the base is FA for vessel A and FB for
vessel B. The respective weights of the water filled in vessels are WA and WB. Then
(A) FA > FB ; WA > WB (B) FA = FB ; WA > WB
(C) FA = FB ; WA < WB (D) FA > FB ; WA = WB
2. Figure here shows the vertical cross-section of a vessel filled with a liquid of density . The normal
thrust per unit area on the walls of the vessel at point. P, as shown, will be
(A) h g (B) H g
(C) (H – h) g (D) (H – h) g cos
3. Two bodies are in equilibrium when suspended in water from the arms of a balance. The mass of
one body is 36 g and its density is 9 g/cc. If the mass of the other is 48 g, its density in
g/cc is:
(A) 4/3 (B) 3/2
(C) 3 (D) 5
Space for Rough Work
For more study material visit - https://unacademy.com/content/jee2024/ 1
FLUID MECHANICS (NSEP Questions Bank)
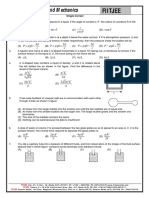
4. A cubical block of wood 10 cm on a side, floats at the interface of oil and water as shown in figure.
The density of oil is 0.6 g cm–3 and density of water is 1 g cm–3. The mass of the block is
(A) 706 g (B) 607 g (C) 760 g (D) 670 g
5. A tank is filled with water up to height H. Water is allowed to come out of a hole P in one of the
walls at a depth D below the surface of water as shown in the figure. Express the horizontal
distance x in terms of H and D:
D(H − D)
(A) x = D(H − D) (B) x = (C) x = 2 D(H − D) (D) x = 4 D(H − D)
2
6. An incompressible liquid flows through a horizontal tube as shown in the figure. Then the velocity
' v ' of the fluid is :
(A) 3.0 m/s (B) 1.5 m/s (C) 1.0 m/s (D) 2.25 m/s
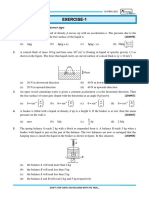
7. A cylindrical tank of height 0.4 m is open at the top and has a diameter 0.16 m. Water is filled in
it up to a height of 0.16 m. How long it will take to empty the tank through a hole of radius
5×10–3 m at its bottom?
(A) 46.26 sec. (B) 4.6 sec. (C) 462.6 sec. (D) 0.46 sec.
Space for Rough Work
For more study material visit - https://unacademy.com/content/jee2024/ 2
FLUID MECHANICS (NSEP Questions Bank)
8. A large cylindrical vessel contains water to a height of 10m. It is found that the thrust acting on
the curved surface is equal to that at the bottom. If atmospheric pressure can support a water
column of 10m, the radius of the vessel is:
(A) 10 m (B) 15m (C) 5m (D) 25m
9. A jet of water of cross-sectional area A hits a plate normally with velocity v. the plate is moving
in the direction of the jet with velocity V. therefore, the force exerted on the plate is proportional to
(A) v (B) v2 (C) (v-V) (D) (v-V)2
10. A fire hydrant (as shown in the figure) delivers water of density at a volume
rate L. The water travels vertically upward through the hydrant and then does
900 turn to emerge horizontally at speed V. The pipe and nozzle have uniform
cross-section throughout. The force exerted by the water on the corner of
the hydrant is:
(A) VL (B) zero (C) 2VL (D) 2VL
11. A tube in vertical plane is shown in figure. It is filled with a liquid of density and its end B is
closed Then the force exerted by the fluid on the tube at end B will be:
[Neglect atmospheric pressure and assume the radius of the tube to be negligible in comparison to ]
g A 0
(A) 0 (B) g A0 (C) 2g A0 (D)
2
12. A U-tube of base length “” filled with same volume of two liquids of densities and 2 is moving
with an acceleration “a” on the horizontal plane as shown in the figure. If the height difference
between the two surfaces (open to atmosphere) becomes zero, then the height h is given by:
a 3a a 2a
(A) (B) (C) (D)
2g 2g g 3g
Space for Rough Work
For more study material visit - https://unacademy.com/content/jee2024/ 3
FLUID MECHANICS (NSEP Questions Bank)
13. In the figure shown water is filled in a symmetrical container. Four pistons of equal area A are
used at the four opening to keep the water in equilibrium. Now an additional force F is applied at
each piston. The increase in the pressure at the centre of the container due to this addition is:
F 2F 4F
(A) (B) (C) (D) 0
A A A
14. A non uniform cylinder of mass m, length and radius r is having its centre of mass at a distance
/4 from the centre and lying on the axis of the cylinder as shown in the figure. The cylinder is
kept in a liquid of uniform density The moment of inertia of the rod about the centre of mass
is . The angular acceleration of point A relative to point B just after the rod is released from the
position shown in figure is
g 2r 2 g 2r 2 g 2r 2 3 g 2r 2
(A) (B) (C) (D)
4 2 4
15. A block of iron is kept at the bottom of a bucket full of water at 2°C. The water exerts buoyant
force on the block. If the temperature of water is increased by 1°C the temperature of iron block
also increases by 1°C. The buoyant force on the block by water
(A) will increase
(B) will decrease
(C) will not change
(D) may decrease or increase depending on the values of their coefficient of expansion
16. A liquid is kept in a cylindrical vessel which is rotated about its axis. The liquid rises at the sides.
If the radius of the vessel is 0.05 m and the speed of rotation is 2 rev/s, The difference in the
height of the liquid at the centre of the vessel and its sides will be (2 = 10):
(A) 3 cm (B) 2 cm (C) 3/2 cm (D) 2/3 cm
Space for Rough Work
For more study material visit - https://unacademy.com/content/jee2024/ 4
FLUID MECHANICS (NSEP Questions Bank)
17. The velocity of the liquid coming out of a small hole of a large vessel containing two different
liquids of densities 2 and as shown in figure is
(A) 6gh (B) 2 gh (C) 2 2gh (D) gh
18. A large open tank has two holes in the wall. One is a square hole of side L at a depth y from the
top and the other is a circular hole of radius R at a depth 4y from the top. When the tank is
completely filled with water, the quantities of water flowing out per second from both holes are
the same. Then radius R, is equal to:
L L
(A) (B) 2 L (C) L (D)
2 2
19. A cup of water is placed in a car moving at a constant acceleration a to the left. Inside the water
is a small air bubble. The figure that correctly shows the shape of the water surface and the
direction of motion of the air bubble is.
a
a
(A) (B)
a a
(C) (D)
(A) A (B) B (C) C (D) D
Space for Rough Work
For more study material visit - https://unacademy.com/content/jee2024/ 5
FLUID MECHANICS (NSEP Questions Bank)
20. A spherical ball is dropped in a long column of viscous liquid. Which of the following graphs
represent the variation of
F
P
Q
R
O t
(i) gravitational force with time
(ii) viscous force with time
(iii) net force acting on the ball with time
(A) Q, R, P (B) R, Q, P (C) P, Q, R (D) R, P, Q
Space for Rough Work
For more study material visit - https://unacademy.com/content/jee2024/ 6
FLUID MECHANICS (NSEP Questions Bank)
SECTION-II
• This section contains TEN (10) questions.
• Each question has FOUR options. ONE OR MORE THAN ONE of these four option(s) is (are) correct
answer(s).
• For each question, choose the option(s) corresponding to (all) the correct answer(s)
• Answer to each question will be evaluated according to the following marking scheme:
Full Marks : +4 If only (all) the correct option(s) is (are) chosen.
Partial Marks : +3 If all the four options are correct but ONLY three options are chosen.
Partial Marks : +2 If three or more options are correct but ONLY two options are chosen
and both of which are correct.
Partial Marks : +1 If two or more options are correct but ONLY one option is chosen and it
is a correct option.
Zero Marks : 0 If none of the options is chosen (i.e. the question is unanswered).
Negative Marks : –2 In all other cases.
For Example: If first, third and fourth are the ONLY three correct options for a question with second
option being an incorrect option; selecting only all the three correct options will result in +4 marks.
Selecting only two of the three correct options (e.g. the first and fourth options), without selecting any
incorrect option (second option in this case), will result in +2 marks. Selecting only one of the three
correct options (either first or third or fourth option), without selecting any incorrect option (second
option in this case), will result in +1 marks. Selecting any incorrect option(s) (second option in this case),
with or without selection of any correct option(s) will result in –2 marks.
21. An air bubble in a water tank rises from the bottom to the top. Which of the following statements
are true ?
(A) Bubble rises upwards because pressure at the bottom is less than that at the top.
(B) Bubble rises upwards because pressure at the bottom is greater than that at the top.
(C) As the bubble rises, its size increases.
(D) As the bubble rises, its size decreases.
22. Pressure gradient in a static fluid is represented by (z–direction is vertically upwards, and x-axis
is along horizontal,d is density of fluid) :
p p p p
(A) = – dg (B) = dg (C) =0 (D) =0
z x x z
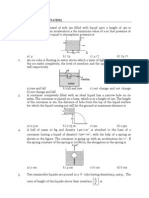
A1
h
23. The vessel shown in Figure has two sections of area of cross-section A1 and
A2. A liquid of density fills both the sections, up to height h in each.
x
Neglecting atmospheric pressure,
(A) the pressure at the base of the vesel is 2 h g A2
h
(B) the weight of the liquid in vessel is equal to 2 h gA2
(C) the force exerted by the liquid on the base of vessel is 2 h g A2
(D) the walls of the vessel at the level X exert a force h g (A2 – A1) downwards on the liquid.
Space for Rough Work
For more study material visit - https://unacademy.com/content/jee2024/ 7
FLUID MECHANICS (NSEP Questions Bank)
24. A cubical block of wood of edge 10cm and mass 0.92kg floats on a tank of water with oil of rel.
density 0.6. Thickness of oil is 4cm above water. When the block attains equilibrium with four of
its sides edges vertical:
(A) 1 cm of it will be above the free surface of oil.
(B) 5 cm of it will be under water.
(C) 2 cm of it will be above the common surface of oil and water.
(D) 8 cm of it will be under water.
25. Following are some statements about buoyant force, select incorrect statement/statements
(Liquid is of uniform density)
(A) Buoyant force depends upon orientation of the concerned body inside the liquid.
(B) Buoyant force depends upon the density of the body immersed.
(C) Buoyant force depends on the fact whether the system is on moon or on the earth.
(D) Buoyant force depends upon the depth at which the body (fully immersed in the liquid) is
placed inside the liquid.
26. A wooden block with a coin placed on its top, floats in water as shown in figure. The distance
and h are shown here. After some time the coin falls into the water. Then:
(A) decreases and h increase (B) increases and h decreases
(C) both and h increases (D) both and h decrease
27. A block of density 2000 kg/m3 and mass 10 kg is suspended by a spring stiffness 100 N/m. The
other end of the spring is attached to a fixed support. The block is completely submerged in a
liquid of density 1000 kg/m3 If the block is in equilibrium position then,
(A) the elongation of the spring is 1 cm.
(B) the magnitude of buoyant force acting on the block is 50 N.
(C) the spring potential energy is 12.5 J.
(D) magnitude of spring force on the block is greater than the weight of the block.
Space for Rough Work
For more study material visit - https://unacademy.com/content/jee2024/ 8
FLUID MECHANICS (NSEP Questions Bank)
28. A cylindrical vessel of 90 cm height is kept filled upto the brim as shown in the figure. It has four
holes 1, 2, 3, 4 which are respectively at heights of 20cm, 30 cm, 40 cm and 50 cm from the
horizontal floor PQ. The water falling at the maximum horizontal distance from the vessel comes
from
4
3
2
P Q
(A) hole number 4 (B) hole number 3
(C) hole number 2 (D) hole number 1
29. A fine rubber band which in its unstretched condition forms a circle of radius r is dropped on a
soap film formed over a wire frame. When the film inside the band is broken, it stretches into a
circle of radius nr. If the band is cut and used as a single strand to suspend a mass m, equilibrium
elongation is equal to unstretched length. Surface tension of soap film is:
mg(n − 1) mg(n − 1)
(A) S= (B) S=
2 nr 2nr
mg(n − 1) mg (n − 1)
(C) S = (D) S =
2r 2nr
30. A small ball bearing is released at the top of a long vertical column of glycerine of height 2h. The
ball bearing falls through a height h in a time t1 and then the remaining height with the terminal
velocity in time t2. Let W1 and W2 be the work done against viscous drag over these height.
Therefore,
(A) t1 < t2 (B) t1 > t2 (C) W1 = W2 (D) W1 < W2
Space for Rough Work
For more study material visit - https://unacademy.com/content/jee2024/ 9
FLUID MECHANICS (NSEP Questions Bank)
ANSWER KEY
1. (B) 2. (C) 3. (C) 4. (C) 5. (C) 6. (C) 7. (A)
8. (B) 9. (D) 10. (D) 11. (B) 12. (B) 13. (A) 14. (B)
15. (A) 16. (B) 17. (B) 18. (A) 19. (D) 20. (C) 21. (B, C)
22. (A, C) 3. (A, C, D) 24. (C, D) 25. (A, B, D) 26. (D) 27. (B, C) 28. (A, B)
29. (B) 30. (BD)
Space for Rough Work
For more study material visit - https://unacademy.com/content/jee2024/ 10
You might also like
- Gagne's Conditions of LearningDocument3 pagesGagne's Conditions of LearningCza Mae ArsenalNo ratings yet
- Mg623 - Project Management PlanDocument79 pagesMg623 - Project Management PlanIBRAHIM NYIRENDANo ratings yet
- 06 Fluid Mechanics QuestionsDocument6 pages06 Fluid Mechanics Questionsakshitwalia209No ratings yet
- Fluid Mechanics_Revision SheetDocument7 pagesFluid Mechanics_Revision Sheetkanwar.navdeep26No ratings yet
- Fluid Mechanics (QB) 13thDocument16 pagesFluid Mechanics (QB) 13thRaju SinghNo ratings yet
- Fluid Mechanics-1 (11A04)Document4 pagesFluid Mechanics-1 (11A04)Sagar paulNo ratings yet
- DPP 2 18TH April 2020Document10 pagesDPP 2 18TH April 2020gauravNo ratings yet
- Assignment 4 - HydrodynamicsDocument10 pagesAssignment 4 - HydrodynamicsluluNo ratings yet
- Assignment IIT JEE2013 Physics Fluid Statics PDFDocument6 pagesAssignment IIT JEE2013 Physics Fluid Statics PDFAnkit Singh100% (1)
- Assignment 2 - Hydrostatic Pressure and Pascal - S LawDocument8 pagesAssignment 2 - Hydrostatic Pressure and Pascal - S LawluluNo ratings yet
- Fluid Mechanics Exercises FINAL 1676700516410Document51 pagesFluid Mechanics Exercises FINAL 1676700516410Shahroz NomaniNo ratings yet
- Exer. 1Document7 pagesExer. 1SureshNo ratings yet
- Physics Topic: Fluid Statics: Class Assignment (For IIT JEE 2013 Batch)Document6 pagesPhysics Topic: Fluid Statics: Class Assignment (For IIT JEE 2013 Batch)Vikrant VatsalNo ratings yet
- Supplement Questions of FLUID MECHANICS: Paragraph For Question Nos. 1 To 3Document7 pagesSupplement Questions of FLUID MECHANICS: Paragraph For Question Nos. 1 To 3Tanuj Gupta0% (2)
- Fluid Mechanics (Supplement) 12th (An) WADocument6 pagesFluid Mechanics (Supplement) 12th (An) WAPrashantcool1999No ratings yet
- QUIZ(FLUID)PDB SIRDocument6 pagesQUIZ(FLUID)PDB SIRAryan SinghNo ratings yet
- Hydrostatics PDFDocument13 pagesHydrostatics PDFNsBhasinNo ratings yet
- Adobe Scan 06 Dec 2023-2Document4 pagesAdobe Scan 06 Dec 2023-2GenNo ratings yet
- Fluid Mechanics QuestionsDocument11 pagesFluid Mechanics QuestionsabcdNo ratings yet
- Physics BY NKC Sir Crash Course Topic: Fluid Statics and DynamicsDocument6 pagesPhysics BY NKC Sir Crash Course Topic: Fluid Statics and Dynamicssureshserious7226No ratings yet
- Fluids Practice Problems: Multiple Choice QuestionsDocument11 pagesFluids Practice Problems: Multiple Choice QuestionsHey Zac100% (1)
- NK C SI R: Fluid Mechanics, Home Work Sheet-2Document2 pagesNK C SI R: Fluid Mechanics, Home Work Sheet-2Anup kumar PathakNo ratings yet
- 10 Fluid Mechanics Practice ProblemDocument11 pages10 Fluid Mechanics Practice ProblemanirudhNo ratings yet
- Range of Water Streams From A Container Qno. 15 Similar To 1.376 (B)Document11 pagesRange of Water Streams From A Container Qno. 15 Similar To 1.376 (B)abhayNo ratings yet
- Fluid Mechanics - LPP-3Document5 pagesFluid Mechanics - LPP-3Lester LewisNo ratings yet
- Fluids Test 1 - PS & Baner - ALP Sir PDFDocument3 pagesFluids Test 1 - PS & Baner - ALP Sir PDFlalani aakashNo ratings yet
- NK C SI R: Fluid Mechanics, Home Work Sheet-3Document2 pagesNK C SI R: Fluid Mechanics, Home Work Sheet-3Anup kumar PathakNo ratings yet
- Fluid Mechanics - LPP-5Document4 pagesFluid Mechanics - LPP-5Lester LewisNo ratings yet
- Fluid DynamicsDocument4 pagesFluid DynamicsRamo Apu100% (1)
- Fluid Mechanics Practice ProblemDocument10 pagesFluid Mechanics Practice ProblemTahreem iqraNo ratings yet
- Properties of Liquids MCQ TestDocument7 pagesProperties of Liquids MCQ Testeka123No ratings yet
- Exercise - 1 To 3 STDocument11 pagesExercise - 1 To 3 STSky SirNo ratings yet
- DPP - 01 _ Fluid NJ_247Document4 pagesDPP - 01 _ Fluid NJ_247Shivek agrawalNo ratings yet
- Fluid Mechanics - LPP-4Document4 pagesFluid Mechanics - LPP-4Lester LewisNo ratings yet
- Fluid Mechanism PDFDocument30 pagesFluid Mechanism PDFEs ENo ratings yet
- DPP - Solids & FluidsDocument6 pagesDPP - Solids & FluidsMohammed Aftab AhmedNo ratings yet
- Fluid Mechanics - LPP-1Document6 pagesFluid Mechanics - LPP-1Lester LewisNo ratings yet
- Fluids Practice Problems 2009-05-13Document10 pagesFluids Practice Problems 2009-05-13Liam James Payne100% (1)
- Chapter 7 ProblemsDocument3 pagesChapter 7 ProblemsLương Thị Quỳnh PhượngNo ratings yet
- CPP FiitjeeDocument18 pagesCPP FiitjeeAmey Kale0% (1)
- Worksheet-1 (Fluid Mechanics) : Concept Coaching ClassesDocument6 pagesWorksheet-1 (Fluid Mechanics) : Concept Coaching ClassesSachin GargNo ratings yet
- Exercise-1: Mcqs With One Correct Answer TypeDocument21 pagesExercise-1: Mcqs With One Correct Answer TypeVanshdip RawatNo ratings yet
- Fluid Mechanics Ed1e6196 E62f 4e0d 9f9f 9a16ecf4b27cDocument22 pagesFluid Mechanics Ed1e6196 E62f 4e0d 9f9f 9a16ecf4b27cveereshgajwelNo ratings yet
- MORSEL 20 (Fluid Statics)Document4 pagesMORSEL 20 (Fluid Statics)Lalitha RamakrishnanNo ratings yet
- Chapter 10-1Document8 pagesChapter 10-1Naman AgarwalNo ratings yet
- Chapter 10-1Document8 pagesChapter 10-1Naman AgarwalNo ratings yet
- RAP 07 Fluids HW KeyDocument7 pagesRAP 07 Fluids HW KeyChandrea WillardNo ratings yet
- Fluid ND ElasticityDocument54 pagesFluid ND ElasticityChhaya Sharma ce18b028No ratings yet
- Course: Surface Tension: Presented by Kailash SharmaDocument22 pagesCourse: Surface Tension: Presented by Kailash SharmaShreyash ShekharNo ratings yet
- 08 FluidsDocument7 pages08 Fluidsananya.jannareddiNo ratings yet
- 6 NSEP-TEST-6 Fluidsoundwave PCDocument11 pages6 NSEP-TEST-6 Fluidsoundwave PCShohom DeNo ratings yet
- Fluid MDocument3 pagesFluid Msaheb.alromiamNo ratings yet
- 43403125mech 2102Document5 pages43403125mech 2102080Zaid MallickNo ratings yet
- Wa0003.Document54 pagesWa0003.subhrojyoti balaNo ratings yet
- Ut2 XiDocument4 pagesUt2 Xivineet guptaNo ratings yet
- 62BDocument2 pages62BJamie SchultzNo ratings yet
- 03 - Hydrostatics Ex. Module-2Document7 pages03 - Hydrostatics Ex. Module-2Raju SinghNo ratings yet
- fluid ١٢٥٧٥٦ 010006Document3 pagesfluid ١٢٥٧٥٦ 010006saheb.alromiamNo ratings yet
- 06 GR Fluid Mechanics Eng Watermark PDFDocument6 pages06 GR Fluid Mechanics Eng Watermark PDFHappy SinghNo ratings yet
- Phy 1231 SolutionDocument73 pagesPhy 1231 Solutionhusnerh musaNo ratings yet
- Detailed Lesson Plan in MathematicsDocument6 pagesDetailed Lesson Plan in MathematicsRodel CaliniahanNo ratings yet
- Toray TM810 Sea Water RO Element LDocument2 pagesToray TM810 Sea Water RO Element LMohamad JammalNo ratings yet
- G9 Quarter 1 Week 2 WLPDocument5 pagesG9 Quarter 1 Week 2 WLPAiselle Jane GasohNo ratings yet
- Training and Development: 06/30/2022 HRM Chapter 5 - Truong Nu To Giang 1Document54 pagesTraining and Development: 06/30/2022 HRM Chapter 5 - Truong Nu To Giang 1Trần LuânNo ratings yet
- Rencana Pelaksanaan Pembelajaran (RPP) : School Identity Course Name Class/Semester Topic Discussion Skill Time AllocationDocument6 pagesRencana Pelaksanaan Pembelajaran (RPP) : School Identity Course Name Class/Semester Topic Discussion Skill Time AllocationNadya Septiani RahmanNo ratings yet
- Wade-Kidd (2019) PDFDocument11 pagesWade-Kidd (2019) PDFJ. David Rodríguez MarinNo ratings yet
- Round Cassette Catalogue - A4Document4 pagesRound Cassette Catalogue - A4Pongalfest byaravNo ratings yet
- Dwnload Full Fundamentals of Cost Accounting 3rd Edition Lanen Solutions Manual PDFDocument35 pagesDwnload Full Fundamentals of Cost Accounting 3rd Edition Lanen Solutions Manual PDFmatte.caudalebvf100% (13)
- Hedlin Novian Napitupulu Tugas3Document7 pagesHedlin Novian Napitupulu Tugas3hedlinbarcelona10 hedlinNo ratings yet
- MSC Thesis Defense Presentation - TufailDocument38 pagesMSC Thesis Defense Presentation - TufailNeerajNo ratings yet
- Automated Object Oriented Door BellDocument3 pagesAutomated Object Oriented Door Bellcarl eliot100% (1)
- Chapter1 Microchip FabricationDocument39 pagesChapter1 Microchip Fabrication吳文嘉100% (1)
- RA - Trays InstallationDocument11 pagesRA - Trays InstallationIbrahim EsmatNo ratings yet
- Aesop Sustainability Report 2021 1670404443Document33 pagesAesop Sustainability Report 2021 1670404443eNo ratings yet
- Introduction To LinguisticsDocument14 pagesIntroduction To LinguisticsasdfadsNo ratings yet
- Excel Skills For Data Analytics and Visualization: InstructionsDocument6 pagesExcel Skills For Data Analytics and Visualization: InstructionsKAPIL MBA 2021-23 (Delhi)No ratings yet
- Lorus Watch Manual PDFDocument2 pagesLorus Watch Manual PDFDave Long100% (1)
- Mental Health TalkDocument78 pagesMental Health Talkram100% (2)
- GREENE AaronDocument56 pagesGREENE AaronVisnja DjordjicNo ratings yet
- Jenitri 3Document7 pagesJenitri 3Zaenal MubaroqNo ratings yet
- 2000 Words EssayDocument6 pages2000 Words Essaylwfdwwwhd100% (2)
- Challenges Faced by An Economics TeacherDocument8 pagesChallenges Faced by An Economics TeacherSanjay mehta100% (4)
- Bahasa Inggris I: (Teknik Informatika/Sistem Komputer)Document13 pagesBahasa Inggris I: (Teknik Informatika/Sistem Komputer)Kadek DitoNo ratings yet
- Deepgaze Iii: Modeling Free-Viewing Human Scanpaths With Deep LearningDocument27 pagesDeepgaze Iii: Modeling Free-Viewing Human Scanpaths With Deep Learningbronson.harryNo ratings yet
- Homework 2 IENG584Document3 pagesHomework 2 IENG584Frida YoungNo ratings yet
- Unit-1 Chemistry (Matter) Lesson 1-A Properties of Matter-Solid, Liquid, and Gas (Grade 3) ObjectivesDocument16 pagesUnit-1 Chemistry (Matter) Lesson 1-A Properties of Matter-Solid, Liquid, and Gas (Grade 3) Objectiveshaizelle resmaNo ratings yet
- Assignment 4 - Techno - MauricioDocument4 pagesAssignment 4 - Techno - Mauricioairu mauricioNo ratings yet
- Leviton AppNote RetentionForceTechnologyDocument5 pagesLeviton AppNote RetentionForceTechnologySajeda M. Al-TalafhaNo ratings yet