Professional Documents
Culture Documents
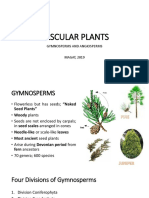
1. Maize
1. Maize
Uploaded by
Soumili Bera0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
2 views10 pagesCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pdf or txt
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
2 views10 pages1. Maize
1. Maize
Uploaded by
Soumili BeraCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pdf or txt
You are on page 1of 10
Maize and its Breeding
• Botanical Name: Zea mays L.
• Family: Poaceae
• Chromosome No.: 2n = 20
• Center of Origin: Central America (Mexico)
•Distribution: USA, China, Russia, Canada and many south Asian
countries
• Progenitors: Zea tunicata , Z. teosinte
• Mode of pollination : Cross pollination
• Out crossing percentage: 95%
•India is the sixth largest producer of maize in the world contributing 2%
of the global production.
•In India maize is the third most important crop after rice and wheat
and accounts for 9% of the total food grain production in country.
•The important maize growing states are Karnataka, Andhra Pradesh,
Bihar, Punjab and Himachal Pradesh
“The last two decades saw the revolution in rice and wheat, the next few
decades will be maize era” – Dr N. E. Borlaug
Zea mays, 2n =20
Leaves Morphology of Maize
• Leaves are broad and a single leaf.
• Leaves are arranged in two vertical rows on the opposite sides of an axis.
(distichous)
• Long, large, alternate, parallel veins
Root Morphology of Maize
• Fibrous root
• Brace root
~ form at the bottom of the stalk.
~ support the plant and scavenge top levels of soil for moisture and nutrients.
• Seminal root
~ nodal roots originate from scutellar node.
~ sustain seedling development by virtue water intake.
Reproductive Morphology of Maize
• Male & female inflorescence located at different part.
• Male inflorescence called tassel.
• Female inflorescence called ear.
• Maize pollen dispersion by wind.
• Annual plant.
The ear is the female reproductive part of a corn plant.
• Ears develop from "shanks," which are stalk like structures that grow from the plant's leaf
nodes.
• A corn plant may produce many ears, but the uppermost ear will grow to be the largest.
• The ear consists of a cob, eggs that eventually develop into kernels and silks.
• Pollination occurs when pollen from the male tassel falls on the female silks.
You might also like
- Palak SinghDocument19 pagesPalak SinghPalak Singh0% (1)
- Describing The Reproduction in Non-Flowerign PlantsDocument45 pagesDescribing The Reproduction in Non-Flowerign PlantsEim NellaNo ratings yet
- Food Crops: Tanaman MakananDocument66 pagesFood Crops: Tanaman MakananSleeping BeautyNo ratings yet
- Evolution of Zea Mays L EditedDocument34 pagesEvolution of Zea Mays L EditedJaclyn UyNo ratings yet
- 8 Plant ReproductionDocument8 pages8 Plant Reproductionsrijansingha10No ratings yet
- 2nd Quarter Lessons 2.0Document97 pages2nd Quarter Lessons 2.0Jean Zyrelle AuronNo ratings yet
- Plant BiodiversityDocument27 pagesPlant Biodiversityjuniorbolokang65No ratings yet
- Angiosperms and GynospermsDocument20 pagesAngiosperms and GynospermsMicaszen MendozaNo ratings yet
- Evolution of Oryza SativaDocument11 pagesEvolution of Oryza Sativaangelotagupa12345100% (1)
- Asexual Reproduction Grade 12 Yellow Biology Education For The Real WorldDocument34 pagesAsexual Reproduction Grade 12 Yellow Biology Education For The Real WorldChoolwe CheeloNo ratings yet
- Year 10 Term 3 Notes 2024Document18 pagesYear 10 Term 3 Notes 2024raghavmathur639No ratings yet
- Plant Parts (Modified)Document24 pagesPlant Parts (Modified)Riddhi TyagiNo ratings yet
- Tagupa - Evolution of Crops - CropScie 3Document11 pagesTagupa - Evolution of Crops - CropScie 3Marjorie TacordaNo ratings yet
- Crop ScienceDocument28 pagesCrop ScienceNovah Mae AmbosNo ratings yet
- Lecture 12 - Flowering Plants and Civilization - FA22Document14 pagesLecture 12 - Flowering Plants and Civilization - FA22Kaitlyn RosasNo ratings yet
- Pinophyta Conifers)Document15 pagesPinophyta Conifers)Jared Chong Tze MengNo ratings yet
- Plant DiversityDocument87 pagesPlant DiversityMeenakshi SinghNo ratings yet
- Asexual Multiplication of Horticultural PlantsDocument7 pagesAsexual Multiplication of Horticultural PlantsDr.Eswara Reddy SiddareddyNo ratings yet
- Reproduction PLANTDocument48 pagesReproduction PLANTmonamoikoNo ratings yet
- Makalah Padi Bahasa InggrisDocument13 pagesMakalah Padi Bahasa InggrisAndrea Rootz OnlyskyproNo ratings yet
- CHAPTER 5 Plant ReproductionDocument48 pagesCHAPTER 5 Plant ReproductionNealieNo ratings yet
- Asexual Multiplication of Horticultural PlantsDocument5 pagesAsexual Multiplication of Horticultural PlantsDr.Eswara Reddy SiddareddyNo ratings yet
- Castor Floral BiologyDocument16 pagesCastor Floral BiologyVishal KuntalNo ratings yet
- IGCSE ReproductionDocument77 pagesIGCSE ReproductionTonkaaw KatayouwongchareonNo ratings yet
- Sexual Reproduction in Flowering Plants Gr.11Document23 pagesSexual Reproduction in Flowering Plants Gr.11Heba AliNo ratings yet
- Plant PhysiologyDocument21 pagesPlant PhysiologyPANSARILI KONo ratings yet
- Dr. Abhinandan R Patil Research ScientistDocument59 pagesDr. Abhinandan R Patil Research ScientistAbhinandan PatilNo ratings yet
- Ppt.x.reproduction 10 23Document83 pagesPpt.x.reproduction 10 23ammara hyderNo ratings yet
- Lecture 9 Plant DiversityDocument100 pagesLecture 9 Plant DiversityDon TevesNo ratings yet
- Presentation 2Document21 pagesPresentation 2Maro Ridhwan RidhiwaniNo ratings yet
- Plant ReproductionDocument62 pagesPlant ReproductionAdonis BesaNo ratings yet
- Agricultural Biology Anatomy and Physiology SPU 2024 Notes 1Document44 pagesAgricultural Biology Anatomy and Physiology SPU 2024 Notes 1Gift ThobaneNo ratings yet
- A. Objective Type QuestionsDocument5 pagesA. Objective Type QuestionsPOONAM SHARMANo ratings yet
- Roots: Members: Albert Escober Ervin Joseph Flores Aldrin ErminoDocument16 pagesRoots: Members: Albert Escober Ervin Joseph Flores Aldrin ErminoJnll JstnNo ratings yet
- Sexual Reproduction in Flowering PlantsDocument36 pagesSexual Reproduction in Flowering PlantsTishonna DouglasNo ratings yet
- Structure and Development of Root, Stem and LeafDocument83 pagesStructure and Development of Root, Stem and LeafSNo ratings yet
- Carrotandradish 170110142422Document41 pagesCarrotandradish 170110142422narayananNo ratings yet
- Crop MorphologyDocument108 pagesCrop MorphologyRyan Calderon0% (1)
- PLANTAEDocument25 pagesPLANTAELyrra Jorramie Rull GragedaNo ratings yet
- Plants 21-24Document30 pagesPlants 21-24Brandi Hughes CaldwellNo ratings yet
- በቆቆሎሎDocument49 pagesበቆቆሎሎJemalNo ratings yet
- PP3.Biodiversity of PlantsDocument30 pagesPP3.Biodiversity of Plantssamsonvaphi8No ratings yet
- Sunflower: Muhammad AnasDocument7 pagesSunflower: Muhammad AnasMuhammad AnasNo ratings yet
- Plant Diversity Part Two 2021Document6 pagesPlant Diversity Part Two 2021sulimansmart22No ratings yet
- Modern PlantsDocument3 pagesModern PlantshomamunfatNo ratings yet
- Evelyn Hone College Lecture 6 2022 Kingdom PlantaeDocument21 pagesEvelyn Hone College Lecture 6 2022 Kingdom PlantaeJoyce KapembwaNo ratings yet
- PR Manual Agron 111Document47 pagesPR Manual Agron 111Ganpat Lal SharmaNo ratings yet
- Examining Fruits and FlowersDocument45 pagesExamining Fruits and Flowerscarlos monteaNo ratings yet
- LECTURE 2 Tanaman Kelapa SawitDocument127 pagesLECTURE 2 Tanaman Kelapa SawitZulhelmi MustafaNo ratings yet
- SoybeanDocument52 pagesSoybeanammadkundi3222No ratings yet
- Chapter 5 Plant ReproductionDocument50 pagesChapter 5 Plant ReproductionRina Abigail CarterNo ratings yet
- Sexual Reproduction in Flowering PlantsDocument7 pagesSexual Reproduction in Flowering Plantsrichie2885No ratings yet
- Hybrid Seed Production MaizeDocument15 pagesHybrid Seed Production MaizeVinaBellaLestariNo ratings yet
- Sexual Reproduction in Flowering Plants Complete NotesDocument133 pagesSexual Reproduction in Flowering Plants Complete NotesMathews K ManiNo ratings yet
- #2 AngiospermDocument65 pages#2 AngiospermrandelNo ratings yet
- CoconutDocument62 pagesCoconutddhcoimbatoreNo ratings yet
- Reproduction PPT 3 ANGIOSPERMSDocument76 pagesReproduction PPT 3 ANGIOSPERMSlisanames.23No ratings yet
- Wheat: From Seed To SustenanceDocument17 pagesWheat: From Seed To Sustenancenimrakhalid574No ratings yet
- Reproduction in PlantsDocument24 pagesReproduction in PlantsgebrilomarNo ratings yet
- Broom-Corn and Brooms - A Treatise on Raising Broom-Corn and Making Brooms, on a Small or Large Scale, Written and Compiled by the Editors of The American AgriculturistFrom EverandBroom-Corn and Brooms - A Treatise on Raising Broom-Corn and Making Brooms, on a Small or Large Scale, Written and Compiled by the Editors of The American AgriculturistRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)